Metformin Hydrochloride
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS, USP 40-8987 Revised – October 2008 Rx only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- BOXED WARNING
- PRECAUTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, USP are an oral antihyperglycemic drug used in the management of type 2 diabetes. Metformin hydrochloride (N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride) is not chemically or pharmacologically related to any other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. The structural formula is as shown:

Metformin hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline compound with a molecular formula of C4H11N5 • HCl and a molecular weight of 165.63. Metformin hydrochloride is freely soluble in water and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether, and chloroform. The pKa of metformin is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin hydrochloride is 6.68.
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, USP contain 750 mg of metformin hydrochloride as the active ingredient. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism Of Action
Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Its pharmacologic mechanisms of action are different from other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Unlike sulfonylureas, metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in either patients with type 2 diabetes or normal subjects (except in special circumstances, see PRECAUTIONS) and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption And Bioavailability:
Following a single oral dose of metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, Cmax is achieved with a median value of 7 hours and a range of 4 hours to 8 hours. Peak plasma levels are approximately 20% lower compared to the same dose of metformin hydrochloride tablets, however, the extent of absorption (as measured by AUC) is similar to metformin hydrochloride tablets.
At steady state, the AUC and Cmax are less than dose proportional for metformin hydrochloride extended-release within the range of 500 mg to 2000 mg administered once daily. Peak plasma levels are approximately 0.6, 1.1, 1.4, and 1.8 µg/mL for 500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 mg once-daily doses, respectively. The extent of metformin absorption (as measured by AUC) from metformin hydrochloride extended-release at a 2000 mg once-daily dose is similar to the same total daily dose administered as metformin hydrochloride tablets 1000 mg twice daily. After repeated administration of metformin hydrochloride extended-release, metformin did not accumulate in plasma.
Within-subject variability in Cmax and AUC of metformin from metformin hydrochloride extended-release is comparable to that with metformin hydrochloride tablets.
Although the extent of metformin absorption (as measured by AUC) from the metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablet increased by approximately 50% when given with food, there was no effect of food on Cmax and Tmax of metformin. Both high and low fat meals had the same effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin hydrochloride extended-release.
Distribution:
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of metformin following single oral doses of metformin hydrochloride 850 mg averaged 654 ± 358 L. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins, in contrast to sulfonylureas, which are more than 90% protein bound. Metformin partitions into erythrocytes, most likely as a function of time. At usual clinical doses and dosing schedules of metformin hydrochloride tablets, steady state plasma concentrations of metformin are reached within 24-48 hours and are generally <1 µg/mL. During controlled clinical trials of metformin hydrochloride tablets, maximum metformin plasma levels did not exceed 5 µg/mL, even at maximum doses.
Metabolism And Elimination: Intravenous single-dose studies in normal subjects demonstrate that metformin is excreted unchanged in the urine and does not undergo hepatic metabolism (no metabolites have been identified in humans) nor biliary excretion. Renal clearance (see Table 1) is approximately 3.5 times greater than creatinine clearance, which indicates that tubular secretion is the major route of metformin elimination. Following oral administration, approximately 90% of the absorbed drug is eliminated via the renal route within the first 24 hours, with a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 6.2 hours. In blood, the elimination half-life is approximately 17.6 hours, suggesting that the erythrocyte mass may be a compartment of distribution.
Special Populations: Patients with type 2 diabetes: In the presence of normal renal function, there are no differences between single- or multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of metformin between patients with type 2 diabetes and normal subjects (see Table 1), nor is there any accumulation of metformin in either group at usual clinical doses.
The pharmacokinetics of metformin hydrochloride extended-release in patients with type 2 diabetes are comparable to those in healthy normal adults.
Renal Insufficiency:In patients with decreased renal function (based on measured creatinine clearance), the plasma and blood half-life of metformin s prolonged and the renal clearance is decreased in proportion to the decrease in creatinine clearance (see Table 1; also see WARNINGS).
Hepatic Insufficiency:No pharmacokinetic studies of metformin have been conducted in patients with hepatic insufficiency.
Geriatrics:Limited data from controlled pharmacokinetic studies of metformin in healthy elderly subjects suggest that total plasma clearance of metformin is decreased, the half-life is prolonged, and Cmax is increased, compared to healthy young subjects. From these data, it appears that the change in metformin pharmacokinetics with aging is primarily accounted for by a change in renal function (see Table 1). Metformin treatment should not be initiated in patients ≥80 years of age unless measurement of creatinine clearance demonstrates that renal function is not reduced (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
| Subject Groups: Metformin HCl Dosea (number of subjects) |
Cmaxb (µg/mL) |
Tmaxc (hrs) |
Renal Clearance (mL/min) |
| a All doses given fasting except the first 18 doses of the multiple dose studies | |||
| b Peak plasma concentration | |||
| c Time to peak plasma concentration | |||
| d Combined results (average means) of five studies: mean age 32 years (range 23-59 yrs) | |||
| e Kinetic study done following dose 19, given fasting | |||
| f Elderly subjects, mean age 71 years (range 65-81 years) | |||
| g CLcr = creatinine clearance normalized to body surface area of 1.73 m2 | |||
| Healthy, nondiabetic adults: 500 mg single dose (24) 850 mg single dose (74)d 850 mg three times daily for 19 dosese (9) |
1.03 (±0.33) 1.60 (±0.38) 2.01 (±0.42) |
2.75 (±0.81) 2.64 (±0.82) 1.79 (±0.94) |
600 (±132) 552 (±139) 642 (±173) |
| Adults with type 2 diabetes: 850 mg single dose (23) 850 mg three times daily for 19 dosese (9) |
1.48 (±0.5) 1.90 (±0.62) |
3.32 (±1.08) 2.01 (±1.22) |
491 (±138) 550 (±160) |
| Elderlyf, healthy nondiabetic adults: 850 mg single dose (12) |
2.45 (±0.70) |
2.71 (±1.05) |
412 (±98) |
| Renal-impaired adults: 850 mg single dose Mild(CLcrg 61-90 mL/min) (5) Moderate(CLcr 31-60 mL/min) (4) Severe(CLcr 10-30 mL/min) (6) |
1.86 (±0.52) 4.12 (±1.83) 3.93 (±0.92) |
3.20 (±0.45) 3.75 (±0.50) 4.01 (±1.10) |
384 (±122) 108 (±57) 130 (±90) |
Pediatrics:After administration of a single oral metformin hydrochloride 500 mg tablet with food, geometric mean metformin Cmax and AUC differed less than 5% between pediatric type 2 diabetic patients (12 to 16 years of age) and gender- and weight- matched healthy adults (20 to 45 years of age), all with normal renal function.
Gender: Metformin pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ significantly between normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes when analyzed according to gender (males = 19, females = 16). Similarly, in controlled clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes, the antihyperglycemic effect of metformin hydrochloride tablets was comparable in males and females.
Race:No studies of metformin pharmacokinetic parameters according to race have been performed. In controlled clinical studies of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes, the antihyperglycemic effect was comparable in whites (n = 249), blacks (n = 51), and Hispanics
(n = 24).
CLINICAL STUDIES
A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, taken once daily with the evening meal, was conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes who had failed to achieve glycemic control with diet and exercise (HbA1c 7to10%, FPG 126 to 270 mg/dL). Patients entering the study had a mean baseline HbA1c of 8% and a mean baseline FPG of 176 mg/dL. After 12 weeks treatment, mean HbA1c had increased from baseline by 0.1% and mean FPG decreased from baseline by 2 mg/dL in the placebo group, compared with a decrease in mean HbA1c of 0.6% and a decrease in mean FPG of 23 mg/dL in patients treated with metformin hydrochloride extended-release 1000 mg once daily. Subsequently, the treatment dose was increased to 1500 mg once daily if HbA1c was ≥7% but <8% (patients with HbA1c ≥8% were discontinued from the study). At the final visit (24-week), mean HbA1c had increased 0.2% from baseline in placebo patients and decreased 0.6% with metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
A 16-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study of metformin hydrochloride extended-release, taken once daily with the evening meal or twice daily with meals, was conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes who had failed to achieve glycemic control with diet and exercise (HbA1c 7to 11%, FPG 126 to 280 mg/dL). Changes in glycemic control and body weight are shown in Table 2.
| Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg Once Daily | 1000 mg Once Daily | 1500 mg Once Daily | 2000 mg Once Daily | 1000 mg Twice Daily | Placebo | |
| *All patients on diet therapy at Baseline | ||||||
| a All comparisons versus Placebo | ||||||
| **Not statistically significant | ||||||
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) Baseline Change at FINAL VISIT p – valuea | (n = 115) 8.2 -0.4 <0.001 | (n = 115) 8.4 -0.6 <0.001 | (n = 111) 8.3 -0.9 <0.001 | (n = 125) 8.4 -0.8 <0.001 | (n = 112) 8.4 -1.1 <0.001 | (n = 111) 8.4 0.1 - |
| FPG (mg/dL) Baseline Change at FINAL VISIT p – valuea | (n = 126) 182.7 -15.2 <0.001 | (n = 118) 183.7 -19.3 <0.001 | (n = 120) 178.9 -28.5 <0.001 | (n = 132) 181.0 -28.5 <0.001 | (n = 122) 181.6 -33.6 <0.001 | (n = 113) 179.6 7.6 - |
| Body Weight (lbs) Baseline Change at FINAL VISIT p – valuea | (n = 125) 192.9 -1.3 NS** | (n = 119) 191.8 -1.3 NS** | (n = 117) 188.3 -0.7 NS** | (n = 131) 195.4 -1.5 NS** | (n = 119) 192.5 -2.2 NS** | (n = 113) 194.3 -1.8 - |
Compared with placebo, improvement in glycemic control was seen at all dose levels of metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets and treatment was not associated with any significant change in weight (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONfor dosing recommendations).
A 24-week, double-blind, randomized study of metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, taken once daily with the evening meal and metformin hydrochloride tablets, taken twice daily (with breakfast and evening meal), was conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes who had been treated with metformin hydrochloride 500 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks prior to study entry.
The metformin dose had not necessarily been titrated to achieve a specific level of glycemic control prior to study entry. Patients qualified for the study if HbA1c was ≤8.5% and FPG was ≤200 mg/dL. Changes in glycemic control and body weight are shown in Table 3.
| Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg Twice Daily | 1000 mg Once Daily | 1500 mg Once Daily | ||
| * All patients on metformin hydrochloride tablets 500 mg twice daily at Baseline | ||||
| a n = 68 | ||||
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | (n = 67) | (n = 72) | (n = 66) | |
| Baseline | 7.06 | 6.99 | 7.02 | |
| Change at 12 Weeks | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.04 | |
| (95% CI) | (-0.03, 0.31) | (0.10, 0.36) | (-0.08, 0.15) | |
| Change at FINAL VISIT | 0.14a | 0.27 | 0.13 | |
| (95% CI) | (-0.04, 0.31) | (0.11, 0.43) | (-0.02, 0.28) | |
| FPG (mg/dL) | (n = 69) | (n = 72) | (n = 70) | |
| Baseline | 127.2 | 131.0 | 131.4 | |
| Change at 12 Weeks | 12.9 | 9.5 | 3.7 | |
| (95% CI) | (6.5, 19.4) | (4.4, 14.6) | (-0.4, 7.8) | |
| Change at FINAL VISIT | 14.0 | 11.5 | 7.6 | |
| (95% CI) | (7.0, 21.0) | (4.4, 18.6) | (1.0, 14.2) | |
| Body Weight (lbs) | (n = 71) | (n = 74) | (n = 71) | |
| Baseline | 210.3 | 202.8 | 192.7 | |
| Change at 12 Weeks | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.7 | |
| (95% CI) | (-0.4, 1.5) | (0.0, 2.0) | (-0.4, 1.8) | |
| Change at FINAL VISIT | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.9 | |
| (95% CI) | (-0.4, 2.2) | (-0.2, 2.4) | (-0.4, 2.0) | |
| Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release | Placebo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg Once Daily | 1000 mg Once Daily | 1500 mg Once Daily | 2000 mg Once Daily | 1000 mg Twice Daily | ||
| *All patients on diet therapy at baseline | ||||||
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | (n = 120) | (n = 113) | (n = 110) | (n = 126) | (n = 117) | (n = 110) |
| Baseline | 210.3 | 218.1 | 214.6 | 204.4 | 208.2 | 208.6 |
| Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT |
1.0% |
1.7% |
0.7% |
-1.6% |
-2.6% |
2.6% |
| Total Triglycerides (mg/dL) | (n = 120) | (n = 113) | (n = 110) | (n = 126) | (n = 117) | (n = 110) |
| Baseline | 220.2 | 211.9 | 198.0 | 194.2 | 179.0 | 211.7 |
| Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT |
14.4% |
9.4% |
15.1% |
14.9% |
9.4% |
10.9% |
| LDL – Cholesterol (mg/dL) | (n = 119) | (n = 113) | (n = 109) | (n = 126) | (n = 117) | (n = 107) |
| Baseline | 131.0 | 134.9 | 135.8 | 125.8 | 131.4 | 131.9 |
| Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT |
-1.4% |
-1.6 |
-3.5% |
-3.3% |
-5.5% |
3.2% |
| HDL – Cholesterol (mg/dL) | (n = 120) | (n = 108) | (n = 108) | (n = 125) | (n = 117) | (n = 108) |
| Baseline | 40.8 | 41.6 | 40.6 | 40.2 | 42.4 | 39.4 |
| Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT |
6.2% |
8.6% |
1.0% |
6.1% |
7.1% |
5.8% |
After 12 weeks of treatment, there was an increase in mean HbA1c in all groups; in the metformin hydrochloride extended-release 1000 mg group, the increase from baseline of 0.23% was statistically significant (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Changes in lipid parameters in the previously described placebo-controlled dose-response study of metformin hydrochloride extended-release are shown in Table 4 above.
Changes in lipid parameters in the previously described study of metformin and metformin extended-release are shown in Table 5.
| Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg Twice Daily | 1000 mg Once Daily | 1500 mg Once Daily | ||
| * All patients on metformin hydrochloride 500 mg twice daily at Baseline | ||||
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) Baseline Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT | (n = 68) 199.0 0.1% | (n = 70) 201.9 1.3% | (n = 66) 201.6 0.1% | |
| Total Triglycerides (mg/dL) Baseline Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT | (n = 68) 178.0 6.3% | (n = 70) 169.2 25.3% | (n = 66) 206.8 33.4% | |
| LDL – Cholesterol (mg/dL) Baseline Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT | (n = 68) 122.1 -1.3% | (n = 70) 126.2 -3.3% | (n = 66) 115.7 -3.7% | |
| HDL – Cholesterol (mg/dL) Baseline Mean % Change at FINAL VISIT | (n = 68) 41.9 4.8% | (n = 70) 41.7 1.0% | (n = 65) 44.6 -2.1% | |
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, are indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
1. Renal disease or renal dysfunction (e.g., as suggested by serum creatinine
levels ≥1.5 mg/dL [males], ≥1.4 mg/dL [females] or abnormal creatinine
clearance) which may also result from conditions such as cardiovascular
collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, and septicemia (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
2. Known hypersensitivity to metformin hydrochloride.
3. Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin.
Metformin should be temporarily discontinued in patients undergoing radiologic studies involving intravascular administration of iodinated contrast materials, because use of such products may result in acute alteration of renal function. (See also PRECAUTIONS.)
BOXED WARNING
WARNINGS
Lactic Acidosis: Lactic acidosis is a rare, but serious, metabolic complication that can occur due to metformin accumulation during treatment with metformin; when it occurs, it is fatal in approximately 50% of cases. Lactic acidosis may also occur in association with a number of pathophysiologic conditions, including diabetes mellitus, and whenever there is significant tissue hypoperfusion and hypoxemia. Lactic acidosis is characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/L), decreased blood pH, electrolyte disturbances with an increased anion gap, and an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio. When metformin is implicated as the cause of lactic acidosis, metformin plasma levels >5 µg/mL are generally found.
The reported incidence of lactic acidosis in patients receiving metformin hydrochloride is very low (approximately 0.03 cases/1000 patient-years, with approximately 0.015 fatal cases/1000 patient years). In more than 20,000 patient-years exposure to metformin in clinical trials, there were no reports of lactic acidosis. Reported cases have occurred primarily in diabetic patients with significant renal insufficiency, including both intrinsic renal disease and renal hypoperfusion, often in the setting of multiple concomitant medical/surgical problems and multiple concomitant medications. Patients with congestive heart failure requiring pharmacologic management, in particular those with unstable or acute congestive heart failure who are at risk of hypoperfusion and hypoxemia, are at increased risk of lactic acidosis. The risk of lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal dysfunction and the patient’s age. The risk of lactic acidosis may, therefore, be significantly decreased by regular monitoring of renal function in patients taking metformin and by use of the minimum effective dose of metformin. In particular, treatment of the elderly should be accompanied by careful monitoring of renal function. Metformin treatment should not be initiated in patients ≥80 years of age unless measurement of creatinine clearance demonstrates that renal function is not reduced, as these patients are more susceptible to developing lactic acidosis. In addition, metformin should be promptly withheld in the presence of any condition associated with hypoxemia, dehydration, or sepsis. Because impaired hepatic function may significantly limit the ability to clear lactate, metformin should generally be avoided in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease. Patients should be cautioned against excessive alcohol intake, either acute or chronic, when taking metformin, since alcohol potentiates the effects of metformin hydrochloride on lactate metabolism. In addition, metformin should be temporarily discontinued prior to any intravascular radiocontrast study and for any surgical procedure (see also PRECAUTIONS ).
The onset of lactic acidosis often is subtle, and accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, increasing somnolence, and nonspecific abdominal distress. There may be associated hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias with more marked acidosis. The patient and the patient’s physician must be aware of the possible importance of such symptoms and the patient should be instructed to notify the physician immediately if they occur (see also PRECAUTIONS ). Metformin should be withdrawn until the situation is clarified. Serum electrolytes, ketones, blood glucose, and if indicated, blood pH, lactate levels, and even blood metformin levels may be useful. Once a patient is stabilized on any dose level of metformin, gastrointestinal symptoms, which are common during initiation of therapy, are unlikely to be drug related. Later occurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms could be due to lactic acidosis or other serious disease.
Levels of fasting venous plasma lactate above the upper limit of normal but less than 5 mmol/L in patients taking metformin do not necessarily indicate impending lactic acidosis and may be explainable by other mechanisms, such as poorly controlled diabetes or obesity, vigorous physical activity, or technical problems in sample handling. (See also PRECAUTIONS .)
Lactic acidosis should be suspected in any diabetic patient with metabolic acidosis lacking evidence of ketoacidosis (ketonuria and ketonemia).
Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency that must be treated in a hospital setting. In a patient with lactic acidosis who is taking metformin, the drug should be discontinued immediately and general supportive measures promptly instituted. Because metformin hydrochloride is dialyzable (with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions), prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove the accumulated metformin. Such management often results in prompt reversal of symptoms and recovery. (See also CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS .)
PRECAUTIONS
General
Macrovascular Outcomes: There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular reduction with metformin or any other anti-diabetic drug.
Monitoring Of Renal Function: Metformin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of impairment of renal function. Thus, patients with serum creatinine levels above the upper limit of normal for their age should not receive metformin. In patients with advanced age, metformin should be carefully titrated to establish the minimum dose for adequate glycemic effect, because aging is associated with reduced renal function. In elderly patients, particularly those =80 years of age, renal function should be monitored regularly and, generally, metformin should not be titrated to the maximum dose (see WARNINGSand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Before initiation of metformin therapy and at least annually thereafter, renal function should be assessed and verified as normal. In patients in whom development of renal dysfunction is anticipated, renal function should be assessed more frequently and metformin discontinued if evidence of renal impairment is present.
Use Of Concomitant Medications That May Affect Renal Function Or Metformin Disposition: Concomitant medication(s) that may affect renal function or result in significant hemodynamic change or may interfere with the disposition of metformin, such as cationic drugs that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions), should be used with caution.
Radiologic Studies Involving The Use Of Intravascular Iodinated Contrast Materials (For Example, Intravenous Urogram, Intravenous Cholangiography, Angiography, And Computed Tomography (CT) Scans With Intravascular Contrast Materials):Intravascular contrast studies with iodinated materials can lead to acute alteration of renal function and have been associated with lactic acidosis in patients receiving metformin (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Therefore, in patients in whom any such study is planned, metformin should be temporarily discontinued at the time of or prior to the procedure, and withheld for 48 hours subsequent to the procedure and reinstituted only after renal function has been re-evaluated and found to be normal.
Hypoxic States:Cardiovascular collapse (shock) from whatever cause, acute congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction and other conditions characterized by hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause pre-renal azotemia. When such events occur in patients on metformin therapy, the drug should be promptly discontinued.
Surgical Procedures:Metformin therapy should be temporarily suspended for any surgical procedure (except minor procedures not associated with restricted intake of food and fluids) and should not be restarted until the patient's oral intake has resumed and renal function has been evaluated as normal.
Alcohol Intake:Alcohol is known to potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Patients, therefore, should be warned against excessive alcohol intake, acute or chronic, while receiving metformin.
Impaired Hepatic Function:Since impaired hepatic function has been associated with some cases of lactic acidosis, metformin should generally be avoided in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease.
Vitamin B12 Levels:In controlled clinical trials of metformin of 29 weeks duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum Vitamin B12 levels, without clinical manifestations, was observed in approximately 7% of patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B12 absorption from the B12-intrinsic factor complex, is, however, very rarely associated with anemia and appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or Vitamin B12 supplementation. Measurement of hematologic parameters on an annual basis is advised in patients on metformin and any apparent abnormalities should be appropriately investigated and managed (see PRECAUTIONS: Laboratory Tests).
Certain individuals (those with inadequate Vitamin B12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal Vitamin B12 levels. In these patients, routine serum Vitamin B12 measurements at two- to three-year intervals may be useful.
Change In Clinical Status Of Patients With Previously Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A patient with type 2 diabetes previously well controlled on metformin who develops laboratory abnormalities or clinical illness (especially vague and poorly defined illness) should be evaluated promptly for evidence of ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis. Evaluation should include serum electrolytes and ketones, blood glucose and, if indicated, blood pH, lactate, pyruvate, and metformin levels. If acidosis of either form occurs, metformin must be stopped immediately and other appropriate corrective measures initiated (see also WARNINGS).
Hypoglycemia:Hypoglycemia does not occur in patients receiving metformin alone under usual circumstances of use, but could occur when caloric intake is deficient, when strenuous exercise is not compensated by caloric supplementation, or during concomitant use with other glucose-lowering agents (such as sulfonylureas and insulin) or ethanol.
Elderly, debilitated, or malnourished patients, and those with adrenal or pituitary insufficiency or alcohol intoxication are particularly susceptible to hypoglycemic effects. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly, and in people who are taking beta-adrenergic blocking drugs.
Loss Of Control Of Blood Glucose:When a patient stabilized on any diabetic regimen is exposed to stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, a temporary loss of glycemic control may occur. At such times, it may be necessary to withhold metformin and temporarily administer insulin. Metformin may be reinstituted after the acute episode is resolved.
The effectiveness of oral antidiabetic drugs in lowering blood glucose to a targeted level decreases in many patients over a period of time. This phenomenon, which may be due to progression of the underlying disease or to diminished responsiveness to the drug, is known as secondary failure, to distinguish it from primary failure in which the drug is ineffective during initial therapy. Should secondary failure occur with metformin or sulfonylurea monotherapy, combined therapy with metformin and sulfonylurea may result in a response. Should secondary failure occur with combined metformin hydrochloride extended-release/sulfonylurea therapy, it may be necessary to consider therapeutic alternatives including initiation of insulin therapy.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the potential risks and benefits of metformin and of alternative modes of therapy. They should also be informed about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, of a regular exercise program, and of regular testing of blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, renal function, and hematologic parameters.
The risks of lactic acidosis, its symptoms, and conditions that predispose to its development, as noted in the WARNINGSand PRECAUTIONSsections, should be explained to patients. Patients should be advised to discontinue metformin immediately and to promptly notify their health practitioner if unexplained hyperventilation, myalgia, malaise, unusual somnolence, or other nonspecific symptoms occur. Once a patient is stabilized on any dose level of metformin, gastrointestinal symptoms, which are common during initiation of metformin therapy, are unlikely to be drug related. Later occurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms could be due to lactic acidosis or other serious disease.
Patients should be counselled against excessive alcohol intake, either acute or chronic, while receiving metformin.
Metformin alone does not usually cause hypoglycemia, although it may occur when metformin is used in conjunction with oral sulfonylureas and insulin. When initiating combination therapy, the risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development should be explained to patients and responsible family members. (See Patient Informationprinted below.)
Patients should be informed that metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and not crushed or chewed.
Laboratory Tests
Response to all diabetic therapies should be monitored by periodic measurements of fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels, with a goal of decreasing these levels toward the normal range. During initial dose titration, fasting glucose can be used to determine the therapeutic response. Thereafter, both glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin should be monitored. Measurements of glycosylated hemoglobin may be especially useful for evaluating long-term control (see also DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Initial and periodic monitoring of hematologic parameters (e.g., hemoglobin/hematocrit and red blood cell indices) and renal function (serum creatinine) should be performed, at least on an annual basis. While megaloblastic anemia has rarely been seen with metformin therapy, if this is suspected, Vitamin B12 deficiency should be excluded.
Drug Interactions
(Clinical Evaluation Of Drug Interactions Conducted With Metformin): Glyburide: In a single-dose interaction study in type 2 diabetes patients, co-administration of metformin and glyburide did not result in any changes in either metformin pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics. Decreases in glyburide AUC and Cmax were observed, but were highly variable. The single-dose nature of this study and the lack of correlation between glyburide blood levels and pharmacodynamic effects, makes the clinical significance of this interaction uncertain (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Concomitant Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release and Oral Sulfonylurea Therapy in Adult Patients).
Furosemide: A single-dose, metformin-furosemide drug interaction study in healthy subjects demonstrated that pharmacokinetic parameters of both compounds were affected by co-administration. Furosemide increased the metformin plasma and blood Cmax by 22% and blood AUC by 15%, without any significant change in metformin renal clearance. When administered with metformin, the Cmax and AUC of furosemide were 31% and 12% smaller, respectively, than when administered alone, and the terminal half-life was decreased by 32%, without any significant change in furosemide renal clearance. No information is available about the interaction of metformin and furosemide when co-administered chronically.
Nifedipine: A single-dose, metformin-nifedipine drug interaction study in normal healthy volunteers demonstrated that co-administration of nifedipine increased plasma metformin Cmax and AUC by 20% and 9%, respectively, and increased the amount excreted in the urine. Tmax and half-life were unaffected. Nifedipine appears to enhance the absorption of metformin. Metformin had minimal effects on nifedipine.
Cationic drugs: Cationic drugs (e.g., amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, trimethoprim, or vancomycin) that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion theoretically have the potential for interaction with metformin by competing for common renal tubular transport systems. Such interaction between metformin and oral cimetidine has been observed in normal healthy volunteers in both single- and multiple-dose, metformin-cimetidine drug interaction studies, with a 60% increase in peak metformin plasma and whole blood concentrations and a 40% increase in plasma and whole blood metformin AUC. There was no change in elimination half-life in the single-dose study. Metformin had no effect on cimetidine pharmacokinetics. Although such interactions remain theoretical (except for cimetidine), careful patient monitoring and dose adjustment of metformin and/or the interfering drug is recommended in patients who are taking cationic medications that are excreted via the proximal renal tubular secretory system.
Other: Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving metformin, the patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving metformin, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
In healthy volunteers, the pharmacokinetics of metformin and propranolol, and metformin and ibuprofen were not affected when co-administered in single-dose interaction studies.
Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins and is, therefore, less likely to interact with highly protein-bound drugs such as salicylates, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, and probenecid, as compared to the sulfonylureas, which are extensively bound to serum proteins.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in rats (dosing duration of 104 weeks) and mice (dosing duration of 91 weeks) at doses up to and including 900 mg/kg/day and 1500 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are both approximately four times the maximum recommended human daily dose of 2000 mg based on body surface area comparisons. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female mice. Similarly, there was no tumorigenic potential observed with metformin in male rats. There was, however, an increased incidence of benign stromal uterine polyps in female rats treated with 900 mg/kg/day.
There was no evidence of mutagenic potential of metformin in the following in vitro tests: Ames test (S. typhimurium), gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), or chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes). Results in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test were also negative.
Fertility of male or female rats was unaffected by metformin when administered at doses as high as 600 mg/kg/day, which is approximately three times the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body surface area comparisons.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category B:Recent information strongly suggests that abnormal blood glucose levels during pregnancy are associated with a higher incidence of congenital abnormalities. Most experts recommend that insulin be used during pregnancy to maintain blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, metformin should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly needed.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women with metformin. Metformin was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day. This represents an exposure of about two and six times the maximum recommended human daily dose of 2000 mg based on body surface area comparisons for rats and rabbits, respectively. Determination of fetal concentrations demonstrated a partial placental barrier to metformin.
Nursing Mothers
Studies in lactating rats show that metformin is excreted into milk and reaches levels comparable to those in plasma. Similar studies have not been conducted in nursing mothers. Because the potential for hypoglycemia in nursing infants may exist, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. If metformin is discontinued, and if diet alone is inadequate for controlling blood glucose, insulin therapy should be considered.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of metformin hydrochloride extended-release in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Controlled clinical studies of metformin did not include sufficient numbers of elderly patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients, although other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Metformin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and because the risk of serious adverse reactions to the drug is greater in patients with impaired renal function, metformin should only be used in patients with normal renal function (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics). Because aging is associated with reduced renal function, metformin should be used with caution as age increases. Care should be taken in dose selection and should be based on careful and regular monitoring of renal function. Generally, elderly patients should not be titrated to the maximum dose of metformin (see also WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In worldwide clinical trials over 900 patients with type 2 diabetes have been treated with metformin hydrochloride extended-release in placebo- and active-controlled studies. In placebo-controlled trials, 781 patients were administered metformin hydrochloride extended-release and 195 patients received placebo. Adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of the metformin hydrochloride extended-release patients, and that were more common in metformin hydrochloride extended-release - than placebo-treated patients, are listed in Table 6.
| Metformin Hydrochloride Extended-Release (n = 781) |
Placebo (n = 195) | |
| Adverse Reaction | % of Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| *Reactions that were common in metformin hydrochloride extended-release - than placebo-treated patients | ||
| Diarrhea | 9.6 | 2.6 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 6.5 | 1.5 |
Diarrhea led to discontinuation of study medication in 0.6% of patients treated with metformin hydrochloride extended-release. Additionally, the following adverse reactions were reported in ≥1% to ≤5% of metformin hydrochloride extended-release patients and were more commonly reported with metformin hydrochloride extended-release than placebo: abdominal pain, constipation, distention abdomen, dyspepsia/heartburn, flatulence, dizziness, headache, upper respiratory infection, taste disturbance.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdose of metformin hydrochloride has occurred, including ingestion of amounts greater than 50 grams. Hypoglycemia was reported in approximately 10% of cases but no causal association with metformin hydrochloride has been established. Lactic acidosis has been reported in approximately 32% of metformin overdose cases (see WARNINGS). Metformin is dialyzable with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions. Therefore, hemodialysis may be useful for removal of accumulated drug from patients in whom metformin overdosage is suspected.
METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
There is no fixed dosage regimen for the management of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes with metformin or any other pharmacologic agent. Dosage of metformin must be individualized on the basis of both effectiveness and tolerance, while not exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose. The maximum recommended daily dose of metformin hydrochloride extended-release in adults is 2000 mg.
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release should generally be given once daily with the evening meal. Metformin should be started at a low dose, with gradual dose escalation, both to reduce gastrointestinal side effects and to permit identification of the minimum dose required for adequate glycemic control of the patient.
During treatment initiation and dose titration (see Recommended Dosing Schedule), fasting plasma glucose should be used to determine the therapeutic response to metformin and identify the minimum effective dose for the patient. Thereafter, glycosylated hemoglobin should be measured at intervals of approximately three months. The therapeutic goal should be to decrease both fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels to normal or near normal by using the lowest effective dose of metformin, either when used as monotherapy or in combination with sulfonylurea or insulin.
Monitoring of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin will also permit detection of primary failure, i.e., inadequate lowering of blood glucose at the maximum recommended dose of medication, and secondary failure, i.e., loss of an adequate blood glucose lowering response after an initial period of effectiveness.
Short-term administration of metformin may be sufficient during periods of transient loss of control in patients usually well-controlled on diet alone.
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed or chewed. (See Patient Informationprinted below.)
Recommended Dosing Schedule:Adults:In general, clinically significant responses are not seen at doses below 1500 mg per day. However, a lower recommended starting dose and gradually increased dosage is advised to minimize gastrointestinal symptoms.
The usual starting dose of metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets is 500 mg once daily with the evening meal. Dosage increases should be made in increments of 500 mg weekly, up to a maximum of 2000 mg once daily with the evening meal. If glycemic control is not achieved on metformin hydrochloride extended-release 2000 mg once daily, a trial of metformin hydrochloride extended-release 1000 mg twice daily should be considered. If higher doses of metformin are required, metformin should be used at total daily doses up to 2550 mg administered in divided daily doses, as described above. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies.)
In a randomized trial, patients currently treated with metformin were switched to metformin hydrochloride extended-release. Results of this trial suggest that patients receiving metformin treatment may be safely switched to metformin hydrochloride extended-release once daily at the same total daily dose, up to 2000 mg once daily. Following a switch from metformin to metformin hydrochloride extended-release, glycemic control should be closely monitored and dosage adjustments made accordingly (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies).
Pediatrics: Safety and effectiveness of metformin hydrochloride extended-release in pediatric patients have not been established.
Transfer From Other Antidiabetic Therapy:When transferring patients from standard oral hypoglycemic agents other than chlorpropamide to metformin, no transition period generally is necessary. When transferring patients from chlorpropamide, care should be exercised during the first two weeks because of the prolonged retention of chlorpropamide in the body, leading to overlapping drug effects and possible hypoglycemia.
Concomitant Metformin And Oral Sulfonylurea Therapy In Adult Patients:If patients have not responded to four weeks of the maximum dose of metformin monotherapy, consideration should be given to gradual addition of an oral sulfonylurea while continuing metformin at the maximum dose, even if prior primary or secondary failure to a sulfonylurea has occurred. Clinical and pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction data are currently available only for metformin plus glyburide (glibenclamide).
With concomitant metformin and sulfonylurea therapy, the desired control of blood glucose may be obtained by adjusting the dose of each drug. However, attempts should be made to identify the minimum effective dose of each drug to achieve this goal. With concomitant metformin and sulfonylurea therapy, the risk of hypoglycemia associated with sulfonylurea therapy continues and may be increased. Appropriate precautions should be taken. (See Package Insert of the respective sulfonylurea.)
If patients have not satisfactorily responded to one to three months of concomitant therapy with the maximum dose of metformin and the maximum dose of an oral sulfonylurea, consider therapeutic alternatives including switching to insulin with or without metformin.
Concomitant Metformin And Insulin Therapy In Adult Patients:The current insulin dose should be continued upon initiation of metformin therapy. Metformin therapy should be initiated at 500 mg once daily in patients on insulin therapy. For patients not responding adequately, the dose of metformin should be increased by 500 mg after approximately 1 week and by 500 mg every week thereafter until adequate glycemic control is achieved. The maximum recommended daily dose is 2000 mg for metformin hydrochloride extended-release. It is recommended that the insulin dose be decreased by 10% to 25% when fasting plasma glucose concentrations decrease to less than 120 mg/dL in patients receiving concomitant insulin and metformin. Further adjustment should be individualized based on glucose-lowering response.
Specific Patient Populations:Metformin is not recommended for use in pregnancy. Metformin hydrochloride extended-release is not recommended in pediatric patients (below the age of 17 years).
The initial and maintenance dosing of metformin should be conservative in patients with advanced age, due to the potential for decreased renal function in this population. Any dosage adjustment should be based on a careful assessment of renal function. Generally, elderly, debilitated, and malnourished patients should not be titrated to the maximum dose of metformin.
Monitoring of renal function is necessary to aid in prevention of lactic acidosis, particularly in the elderly. (See WARNINGS.)
HOW SUPPLIED
750 mg — Each light orange, capsule shaped, film coated tablet imprinted with 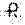 and 728 on one side and plain on the other side contains 750 mg of metformin hydrochloride USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2728-11) with a child-resistant closure and bottles of 500 (NDC 0228-2728-50) without a child-resistant closure.
and 728 on one side and plain on the other side contains 750 mg of metformin hydrochloride USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2728-11) with a child-resistant closure and bottles of 500 (NDC 0228-2728-50) without a child-resistant closure.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at 20 - 25°C (68 - 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
200 Elmora Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA
40-8987
Revised - October 2008
Patient Package Insert
PATIENT INFORMATION METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS, USP
Revised - October 2008
Read this information carefully before you start taking this medicine and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of your doctor’s advice. Ask you doctor or pharmacist if you do not understand some of this information or if you want to know more about this medicine.
What is metformin?
Metformin is used to treat type 2 diabetes. This is also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. People with type 2 diabetes are not able to make enough insulin or respond normally to the insulin their bodies make. When this happens, sugar (glucose) builds up in the blood. This can lead to serious medical problems including kidney damage, amputations, and blindness. Diabetes is also closely linked to heart disease. The main goal of treating diabetes is to lower your blood sugar to a normal level.
High blood sugar can be lowered by diet and exercise, by a number of medicines taken by mouth, and by insulin shots. Before you take metformin, try to control your diabetes by exercise and weight loss. While you take your diabetes medicine, continue to exercise and follow the diet advised for your diabetes. No matter what your recommended diabetes management plan is, studies have shown that maintaining good blood sugar control can prevent or delay complications of diabetes, such as blindness.
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release works longer in your body and helps control your blood sugar in a number of ways. These include helping your body respond better to the insulin it makes naturally, decreasing the amount of sugar your liver makes, and decreasing the amount of sugar your intestines absorb. Metformin does not cause your body to make more insulin. Because of this, when taken alone, it rarely causes hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), and usually does not cause weight gain. However, when taken with a sulfonylurea or with insulin, hypoglycemia is more likely to occur, as is weight gain.
WARNING: A small number of people who have taken metformin have developed a serious condition called lactic acidosis. Lactic acidosis is caused by a build-up of lactic acid in the blood. This happens more often in people with kidney problems. Most people with kidney problems should not take metformin. (See “What are the side effects of metformin?”)
Who should not take metformin?
Some conditions increase your chance of getting lactic acidosis, or cause other problems if you take this medicine. Most of the conditions listed below can increase your chance of getting lactic acidosis.
Do not take metformin if you:
• have kidney problems
• have liver problems
• have heart failure that is treated with medicines, such as Lanoxin® (digoxin) or Lasix® (furosemide)
• drink a lot of alcohol. This means you binge drink for short periods or drink all the time
• are seriously dehydrated (have lost a lot of water from your body)
• are going to have an x-ray procedure with injection of dyes (contrast agents)
• are going to have surgery
• develop a serious condition, such as heart attack, severe infection, or a stroke
• are 80 years or older and you have NOT had your kidney function tested
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Metformin may not be right for you. Talk with your doctor about your choices. You should also discuss your choices with your doctor if you are nursing a child.
Can metformin hydrochloride extended-release be used in children?
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release has not been studied in children.
How should I take metformin?
Your doctor will tell you how much medicine to take and when to take it. You will probably start out with a low dose of the medicine. Your doctor may slowly increase your dose until your blood sugar is better controlled. You should take metformin with meals.
Your doctor may have you take other medicines along with metformin to control your blood sugar. These medicines may include insulin shots. Taking metformin with insulin may help you better control your blood sugar while reducing the insulin dose.
Continue your exercise and diet program and test your blood sugar regularly while taking metformin. Your doctor will monitor your diabetes and may perform blood tests on you from time to time to make sure your kidneys and your liver are functioning normally. There is no evidence that metformin causes harm to the liver or kidneys.
Tell your doctor if you
• have an illness that causes severe vomiting, diarrhea or fever, or if you drink a much lower amount of liquid than normal. These conditions can lead to severe dehydration (loss of water in your body). You may need to stop taking metformin for a short time.
• plan to have surgery or an x-ray procedure with injection of dye (contrast agent). You may need to stop taking metformin for a short time.
• start to take other medicines or change how you take a medicine. Metformin can affect how well other drugs work, and some drugs can affect how well metformin works. Some medicines may cause high blood sugar.
Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed or chewed.
What should I avoid while taking metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets?
Do not drink a lot of alcoholic drinks while taking metformin. This means you should not binge drink for short periods, and you should not drink a lot of alcohol on a regular basis. Alcohol can increase the chance of getting lactic acidosis.
What are the side effects of metformin?
Lactic Acidosis. In rare cases, metformin can cause a serious side effect called lactic acidosis. This is caused by a build-up of lactic acid in your blood. This build-up can cause serious damage. Lactic acidosis caused by metformin is rare and has occurred mostly in people whose kidneys were not working normally. Lactic acidosis has been reported in about one in 33,000 patients taking metformin over the course of a year. Although rare, if lactic acidosis does occur, it can be fatal in up to half the people who develop it.
It is also important for your liver to be working normally when you take metformin. Your liver helps remove lactic acid from your blood.
Make sure you tell your doctor before you use metformin if you have kidney or liver problems. You should also stop using metformin and call your doctor right away if you have signs of lactic acidosis. Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency that must be treated in a hospital.
Signs of lactic acidosis are:
• feeling very weak, tired, or uncomfortable
• unusual muscle pain
• trouble breathing
• unusual or unexpected stomach discomfort
• feeling cold
• feeling dizzy or lightheaded
• suddenly developing a slow or irregular heartbeat
If your medical condition suddenly changes, stop taking metformin and call your doctor right away. This may be a sign of lactic acidosis or another serious side effect.
Other Side Effects. Common side effects of metformin include diarrhea, nausea, and upset stomach. These side effects generally go away after you take the medicine for a while. Taking your medicine with meals can help reduce these side effects. Tell your doctor if the side effects bother you a lot, last for more than a few weeks, come back after they’ve gone away, or start later in therapy. You may need a lower dose or need to stop taking the medicine for a short period or for good.
About 3 out of every 100 people who take metformin have an unpleasant metallic taste when they start taking the medicine. It lasts for a short time.
Metformin rarely causes hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) by itself. However, hypoglycemia can happen if you do not eat enough, if you drink alcohol, or if you take other medicines to lower blood sugar.
General advice about prescription medicines
If you have questions or problems, talk with your doctor or other healthcare provider. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for the information about metformin that is written for healthcare professionals. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a patient information leaflet. Do not use metformin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not share your medicine with other people.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at
1-800-FDA-1088.
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
200 Elmora Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA
Revised - October 2008
Metformin HydrochlorideMetformin Hydrochloride TABLET, EXTENDED RELEASE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||