METHERGINE
Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) Tablets, USP Rx only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- METHERGINE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICTIONS AND USAGE
- METHERGINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- METHERGINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- METHERGINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABEL, PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
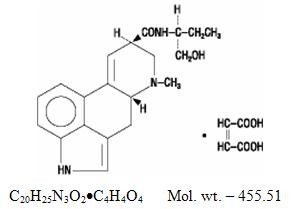
METHERGINE DESCRIPTION
Active ingredient
Inactive Ingredients
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) acts directly on the smooth muscle of the uterus and increases the tone, rate, and amplitude of rhythmic contractions. Thus, it induces a rapid and sustained tetanic uterotonic effect which shortens the third stage of labor and reduces blood loss. The onset of action after I.V. administration is immediate; after I.M. administration, 2-5 minutes, and after oral administration, 5-10 minutes.
Pharmacokinetic studies following an I.V. injection have shown that methylergonovine is rapidly distributed from plasma to peripheral tissues within 2-3 minutes or less. The bioavailability after oral administration was reported to be about 60% with no accumulation after repeated doses. During delivery, with intramuscular injection, bioavailability increased to 78%. Ergot alkaloids are mostly eliminated by hepatic metabolism and excretion, and the decrease in bioavailability following oral administration is probably a result of first-pass metabolism in the liver.
Bioavailability studies conducted in fasting healthy female volunteers have shown that oral absorption of a 0.2 mg methylergonovine tablet was fairly rapid with a mean peak plasma concentration of 3243 ± 1308 pg/mL observed at 1.12 ± 0.82 hours. For a 0.2 mg intramuscular injection, a mean peak plasma concentration of 5918 ± 1952 pg/mL was observed at 0.41 ± 0.21 hours. The extent of absorption of the tablet, based upon methylergonovine plasma concentrations, was found to be equivalent to that of the I.M. solution given orally, and the extent of oral absorption of the I.M. solution was proportional to the dose following administration of 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 mg. When given intramuscularly, the extent of absorption of Methergine solution was about 25% greater than the tablet. The volume of distribution (Vdss/F) of methylergonovine was calculated to be 56.1 ± 17.0 liters, and the plasma clearance (CLp/F) was calculated to be 14.4 ± 4.5 liters per hour. The plasma level decline was biphasic with a mean elimination half-life of 3.39 hours (range 1.5 to 12.7 hours). A delayed gastrointestinal absorption (Tmax about 3 hours) of Methergine tablet might be observed in postpartum women during continuous treatment with this oxytocic agent.
INDICTIONS AND USAGE
METHERGINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypertension; toxemia; pregnancy; and hypersensitivity.
WARNINGS
This drug should not be administered I.V. routinely because of the possibility of inducing sudden hypertensive and cerebrovascular accidents. If I.V. administration is considered essential as a lifesaving measure, Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) should be given slowly over a period of no less than 60 seconds with careful monitoring of blood pressure. Intra-arterial or periarterial injection should be strictly avoided.
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralCaution should be exercised in the presence of sepsis, obliterative vascular disease, hepatic or renal involvement. Also use with caution during the second stage of labor. The necessity for manual removal of a retained placenta should occur only rarely with proper technique and adequate allowance of time for its spontaneous separation.
Drug Interactions
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors)There have been rare reports of serious adverse events in connection with the coadministration of certain ergot alkaloid drugs (e.g., dihydroergotamine and ergotamine) and potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors, resulting in vasospasm leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities. Although there have been no reports of such interactions with methylergonovine alone, potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors should not be coadministered with methylergonovine. Examples of some of the more potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors include macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, troleandomycin, clarithromycin), HIV protease or reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, delavirdine) or azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole). Less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors should be administered with caution. Less potent inhibitors include saquinavir, nefazodone, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, zileuton, and clotrimazole. These lists are not exhaustive, and the prescriber should consider the effects on CYP 3A4 of other agents being considered for concomitant use with methylergonovine.
No pharmacokinetic interactions involving other cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are known.
Caution should be exercised when Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) is used concurrently with other vasoconstrictors or ergot alkaloids
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term studies have been performed in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential. The effect of the drug on mutagenesis or fertility has not been determined.
Pregnancy
Category C. Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with Methergine. It is also not known whether methylergonovine maleate can cause fetal harm or can affect reproductive capacity. Use of Methergine is contraindicated during pregnancy because of its uterotonic effects. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE.)
Labor and Delivery
The uterotonic effect of Methergine is utilized after delivery to assist involution and decrease hemorrhage, shortening the third stage of labor.
Nursing Mothers
®Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
METHERGINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reaction is hypertension associated in several cases with seizure and/or headache. Hypotension has also been reported. Nausea and vomiting have occurred occasionally. Rarely observed reactions have included: acute myocardial infarction, transient chest pains, arterial spasm (coronary and peripheral), bradycardia, tachycardia, dyspnea, hematuria, thrombophlebitis, water intoxication, hallucinations, leg cramps, dizziness, tinnitus, nasal congestion, diarrhea, diaphoresis, palpitation, rash, and foul taste.1
There have been rare isolated reports of anaphylaxis, without a proven causal relationship to the drug product.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) has not been associated with drug abuse or dependence of either a physical or psychological nature.
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms of acute overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, numbness, tingling of the extremities, rise in blood pressure, in severe cases followed by hypotension, respiratory depression, hypothermia, convulsions, and coma.
Because reports of overdosage with Methergine® (methylergonovine maleate) are infrequent, the lethal dose in humans has not been established. The oral LD50 (in mg/kg) for the mouse is 187, the rat 93, and the rabbit 4.5.2 Several cases of accidental Methergine injection in newborn infants have been reported, and in such cases 0.2 mg represents an overdose of great magnitude. However, recovery occurred in all but one case following a period of respiratory depression, hypothermia, hypertonicity with jerking movements, and, in one case, a single convulsion.
Also, several children 1-3 years of age have accidentally ingested up to 10 tablets (2 mg) with no apparent ill effects. A postpartum patient took 4 tablets at one time in error and reported paresthesias and clamminess as her only symptoms.
Treatment of acute overdosage is symptomatic and includes the usual procedures of:
- removal of offending drug by inducing emesis, gastric lavage, catharsis, and
supportive diuresis.
- maintenance of adequate pulmonary ventilation, especially if convulsions or
coma develop.
- correction of hypotension with pressor drugs as needed.
- control of convulsions with standard anticonvulsant agents.
- control of peripheral vasospasm with warmth to the extremities if needed.3
METHERGINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
Orally
One tablet, 0.2 mg, 3 or 4 times daily in the puerperium for a maximum of 1 week.
HOW SUPPLIED
Tablets
0.2 mg round, coated, orchid, branded “78-54” one side, “SANDOZ” other side.
Bottles of 6............ NDC 12634-179-96
Bottles of 8............ NDC 12634-179-98
Bottles of 10 ..........NDC 12634-179-00
Bottles of 12 ..........NDC 12634-179-82
Bottles of 15.......... NDC 12634-179-85
Bottles of 20...........NDC 12634-179-80
Blister Pack of 1.... NDC 12634-179-91
Store and Dispense
TabletsREFERENCES
- Information on Adverse Reactions supplied by Medical Services Department,
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, E. Hanover, N.J., based on computerized clinical
reports.
- Berde, B. and Schild, H.O.: Ergot Alkaloids and Related
Compounds, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1978, p. 810.
- Treatment of Acute Overdosage. Novartis Consumer Health, Inc. Rx Products. Novartis, Medical Services Department.
T2006-91
REV: OCTOBER 2006 Printed in the U.S.A. 5000981
5000982
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
Methergine® Trademark Registrant Sandoz Chemical Works, Inc.
By change of name, by merger, by assignment, List Owner Novartis Pharmaceutcals Corporation.
PACKAGE LABEL, PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
6 TabletsNDC 12634-179-96
Rx Only
Keep This and all Medications Out of the Reach of Children
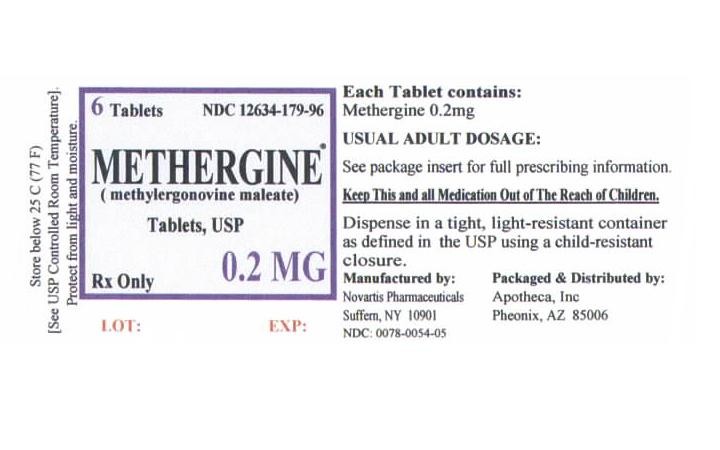
METHERGINEMETHYLERGONOVINE MALEATE TABLET, COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||