METOPROLOL SUCCINATE
Bryant Ranch Prepack
Bryant Ranch Prepack
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets. Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets, USP for Oral use. INITIAL U.S. APPROVAL:1992BOXED WARNINGWARNING: ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE (See Full Prescribing Information for complete boxed warning) Following abrupt cessation of therapy with beta-blocking agents, exacerbations of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction have occurred. Warn patients against interruption or discontinuation of therapy without the physician’s advice. (5.1) INDICATIONS AND USAGE1 Hypertension (1.1) Angina Pectoris (1.2) Heart Failure - for the treatment of stable, symptomatic (NYHA Class II or III) heart failure of ischemic, hypertensive, or cardiomyopathic origin.(1.3) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Administer once daily. Dosing of metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets should be individualized. (2) Heart Failure: Recommended starting dose is 12.5 mg or 25 mg doubled every two weeks to the highest dose tolerated or up to 200 mg. (2.3) Hypertension: Usual initial dosage is 25 to 100 mg once daily. The dosage may be increased at weekly (or longer) intervals until optimum blood pressure reduction is achieved. Dosages above 400 mg per day have not been studied. (2.1) Angina Pectoris: Usual initial dosage is 100 mg once daily. Gradually increase the dosage at weekly intervals until optimum clinical response has been obtained or there is an unacceptable bradycardia. Dosages above 400 mg per day have not been studied. (2.2) Switching from immediate release metoprolol to metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets: use the same total daily dose of metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets. (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets: CONTRAINDICATIONS Known hypersensitivity to product components. (4) Severe bradycardia. (4) Heart block greater than first degree. (4) Cardiogenic shock. (4) Decompensated cardiac failure. (4) Sick sinus syndrome without a pacemaker. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Heart Failure: Worsening cardiac failure may occur. (5.2) Bronchospastic Disease: Avoid beta blockers. (5.3) Pheochromocytoma: If required, first initiate therapy with an alpha blocker. (5.4) Major Surgery: Avoid initiation of high-dose extended release metoprolol in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery because it has been associated with bradycardia, hypotension, stroke and death. Do not routinely withdraw chronic beta blocker therapy prior to surgery. (5.5, 6.1) Diabetes and Hypoglycemia: May mask tachycardia occurring with hypoglycemia (5.6) Patients with Hepatic Impairment: (5.7) Thyrotoxicosis: Abrupt withdrawal in patients with thyrotoxicosis might precipitate a thyroid storm (5.8) Anaphylactic Reactions: Patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reaction (5.9) Peripheral Vascular Disease: Can aggravate symptoms of arterial insufficiency (5.10) Calcium Channel Blockers: Because of significant inotropic and chronotropic effects in patients treated with beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers of the verapamil and diltiazem type, caution should be exercised in patients treated with these agents concomitantly (5.11). Side Effects Most common adverse reactions: tiredness, dizziness, depression, shortness of breath, bradycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, pruritus, rash (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Wockhardt USA LLC., at 1-800-346-6854 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS Catecholamine-depleting drugs may have an additive effect when given with beta-blocking agents (7.1) CYP2D6 Inhibitors are likely to increase metoprolol concentration (7.2) Concomitant use of glycosides, clonidine, and diltiazem and verapamil with beta-blockers can increase the risk of bradycardia (7.3) Beta-blockers including metoprolol, may exacerbate the rebound hypertension that can follow the withdrawal of clonidine (7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Use this drug during pregnancy only if clearly needed. (8.1) Nursing Mothers: Consider possible infant exposure. (8.3) Pediatrics: Safety and effectiveness have not been established in patients < 6 years of age. (8.4) Geriatrics: No notable difference in efficacy or safety vs. younger patients. (8.5) Hepatic Impairment: Consider initiating metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets therapy at low doses and gradually increase dosage to optimize therapy, while monitoring closely for adverse events. (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 METOPROLOL SUCCINATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 METOPROLOL SUCCINATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 METOPROLOL SUCCINATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 METOPROLOL SUCCINATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 METOPROLOL SUCCINATE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 17. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Metoprolol Succ. ER 50mg Tablet
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE: Following abrupt cessation of therapy with certain beta-blocking agents, exacerbations of angina pectoris and, in some cases, myocardial infarction have occurred. When discontinuing chronically administered metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets, particularly in patients with ischemic heart disease, the dosage should be gradually reduced over a period of 1 - 2 weeks and the patient should be carefully monitored. If angina markedly worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets administration should be reinstated promptly, at least temporarily, and other measures appropriate for the management of unstable angina should be taken. Warn patients against interruption or discontinuation of therapy without the physician’s advice. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets therapy abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension (5.1).
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypertension
[see Dosage and Administration (2)].1.2 Angina Pectoris
1.3 Heart Failure
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Hypertension
Adults:Pediatric Hypertensive Patients ≥ 6 Years of age:[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)][see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
2.2 Angina Pectoris
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)].2.3 Heart Failure
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ischemic Heart Disease
5.2 Heart Failure
[see Dosage and Administration (2)].5.3 Bronchospastic Disease
112[see Dosage and Administration (2)].5.4 Pheochromocytoma
5.5 Major Surgery
5.6 Diabetes and Hypoglycemia
5.7 Hepatic Impairment
5.8 Thyrotoxicosis
5.9 Anaphylactic Reaction
5.10 Peripheral Vascular Disease
5.11 Calcium Channel Blockers
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Worsening angina or myocardial infarction. [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
- Worsening heart failure. [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
- Worsening AV block. [see Contraindications (4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Heart Failure:
Adverse Reactions Occurring in the MERIT-HF Study at an Incidence ≥ 1 % in the Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets Group and Greater Than Placebo by More Than 0.5 %
|
|
Metoprolol succinate extended-release tablets n=1990% of patients
|
Placebo n=2001% of patients
|
|---|---|---|
| Dizziness/vertigo
|
1.8
|
1.0
|
| Bradycardia
|
1.5
|
0.4
|
| Accident and/or injury
|
1.4
|
0.8
|
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
Cardiovascular:
Respiratory:
Central Nervous System:
Gastrointestinal:
Hypersensitive Reactions:
Miscellaneous:
Potential Adverse Reactions:
Central Nervous System:
Hematologic:
Hypersensitive Reactions:
6.3 Laboratory Test Findings
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Catecholamine Depleting Drugs
7.2 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
7.3 Digitalis, Clonidine, and Calcium Channel Blockers
[see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
2
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
- Dose-response for reduction in DBP,
- 1.0 mg/kg vs. placebo for change in SBP, and
- 2.0 mg/kg vs. placebo for change in SBP and DBP.
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].10 OVERDOSAGE
2
11 DESCRIPTION
1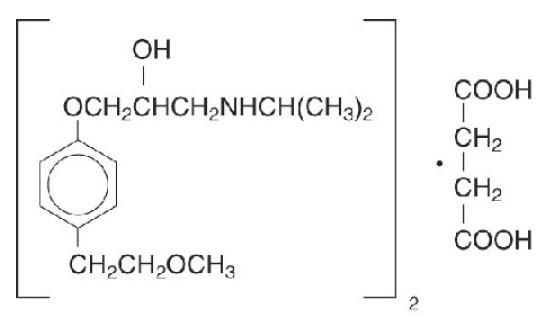
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hypertension:Heart Failure:
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12
1211
max1112
2
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Adults:[see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
1[see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
Pediatrics:
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
22SalmonellaSalmonella
2
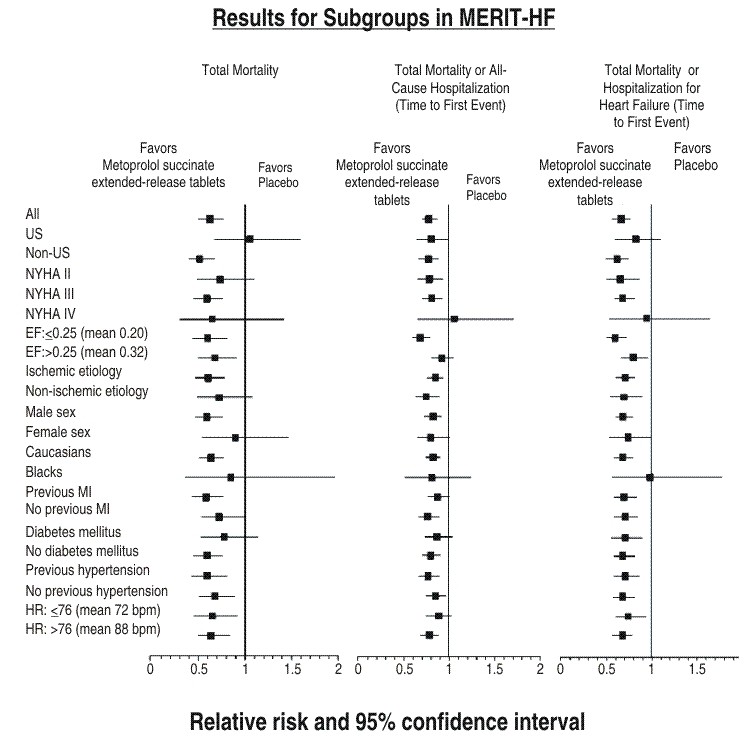
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
11111111®
1
14.1 Angina Pectoris
14.2 Heart Failure
|
Clinical Endpoint |
Number of Patients |
Relative Risk (95% Cl) |
Risk Reduction With Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets |
Nominal P-value |
|
|
Placebo n=2001 |
Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets n=1990 |
||||
|
All-cause mortality plus all-caused hospitalization
|
767 |
641 |
0.81(0.73- 0.90) |
19% |
0.00012 |
|
All-cause mortality |
217 |
145 |
0.66(0.53- 0.81) |
34% |
0.00009 |
|
All-cause mortality plus heart failure hospitalization
|
439 |
311 |
0.69(0.60- 0.80) |
31% |
0.0000008 |
|
Cardiovascular mortality |
203 |
128 |
0.62(0.50- 0.78) |
38% |
0.000022 |
|
Sudden death |
132 |
79 |
0.59(0.45- 0.78) |
41% |
0.0002 |
|
Death due to worsening heart failure |
58 |
30 |
0.51(0.33- 0.79) |
49% |
0.0023 |
|
Hospitalizations due to worsening heart failure
|
451 |
317 |
N/A |
N/A |
0.0000076 |
|
Cardiovascular hospitalization
|
773 |
649 |
N/A |
N/A |
0.00028 |
17. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Manufactured by:
Distributed by:
Metoprolol Succ. ER 50mg Tablet

METOPROLOL SUCCINATEMETOPROLOL SUCCINATE TABLET, FILM COATED, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
