METRONIDAZOLE
Metronidazole Topical Lotion 0.75%
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- METRONIDAZOLE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PHARMACOKINETICS
- METRONIDAZOLE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
- METRONIDAZOLE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS, IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- METRONIDAZOLE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- METRONIDAZOLE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE
- Metronidazole Topical Lotion 0.75%
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx Only
FOR TOPICAL USE ONLY
(NOT FOR OPHTHALMIC USE)
METRONIDAZOLE DESCRIPTION
Metronidazole Topical Lotion contains metronidazole, USP, at a concentration of 7.5 mg per gram (0.75% w/w) in a lotion consisting of benzoyl alcholol, carbomer 941, cyclomethicone, glycerin, glyceryI stearate, light mineral oil, PEG·100 stearate, polyethylene glycol 400, potassium sorbate, purified water, steareth 21, stearyl alcohol, and sodium hydroxyde and/or lactic acid to adjust pH.
Metronidazole is an imidazole and is classified therapeutically as an antiprotozoal and antibacterial agent. Chemically, metronidazole is 2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazole-1-ethanol. The molecular formula is C6H9N303, and molecular weight is 171.16. Metronidazole is represented by the following structural formula:
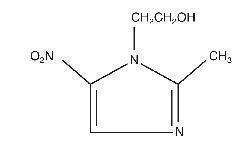
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanisms by which metronidazole acts in the treatment of rosacea are unknown, but appear to include an anti-inflammatory effect.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption of metronidazole after topical application of Metronidazole Topical Lotion is less complete and more prolonged than after oral admistration. Delectable plasma levels were found in all subjects follwoing the adminislralion of a 1 gram dose of Metronidazole Topical Lotion (containing 7.5 mg of metronidazole) applied every morning and evening for 4 days to the faces of 8 patients. The highest concentration (96 ng/mL) seen following the morning dose on Day 5 was approximately 80 times lower than the peak concentrations produced by a single 250 mg tablet of metronidazole. The mean (± SD) AUC after twice daily administration was 962 ± 373 ng.hr/mL.
METRONIDAZOLE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Metronidazole Topical Lotion is indicated for topical application in treatment of inflammatory papules and pustules of rosacea.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
A controlled clinical study was conducted in 144 patients with moderate to severe rosacea, in which Metronidazole Topical Lotion was compared with its vehicle. Applications were made twice daily for 12 weeks during which patients were instructed to avoid spicy foods, thermally hot foods and drinks, alcoholic beverages and caffeine. Patients were also provided samples of a soapless cleansing Iotion and, if requested, a moisturizer. Metronidazole Topical Lotion was significantly more effective than its vehicle in mean percent reduction of inflammatory lesions associated with rosacea and in the investigators global assessment of improvement. The results of the mean percent reduction in inflammatory Iesion counts from baseline after 12 weeks of treatment and the investigators global assessment of improvement at week 12 are presented in the following table:
Efficacy Outcomes at Week 12
| Mean Percent Reduction in Inflammatory Lesion Counts from Baseline | |
|---|---|
| Metronidazole Topical Lotion N = 65 |
Vehicle Lotion N = 60 |
| 55% | 20% |
| Investigators' Global Assessment of Improvement (percent change from baseline) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worse | No Change |
Minimal Improvement |
Definite Improvement |
Marked Improvement |
Clear | |
| Metronidazole Topical Lotion N = 65 |
5% | 12% | 11% | 32% | 32% | 8% |
| Vehicle Lotion N = 60 |
15% | 27% | 23% | 15% | 20% | 0% |
The scale is based on the following definitions:
Worse: Exacerbation of either erythema or quantitative assessment of papules and/or postules.
No change: Condition remains the same.
Minimal Improvement: Slight improvement in the quantitative assessment of papules and/or pustules, and/or slight improvement in erythema.
Definite improvement: More pronounced improvement in the quantitative assessment of papules and/or pustules, and/or more pronounced improvement in erythema.
Marked Improvement: Obvious improvement in the quantitative assessment of papules and/or postules, and/or obvious improvement in erythema.
Clear: No papules or postules and minimal residual or no erythema.
METRONIDAZOLE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Metronidazole Topical Lotion is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or to other ingredients of the formulation.
PRECAUTIONS
General: Topical metronidazole formulations have been reported to cause tearing of the eyes. Therefore, contact with the eyes should be avoided. If a reaction suggesting local irritation occurs, patients should be directed to use the medication less frequently or discontinue use. Metronidazole is a nitroimidazoIe and should be used with care in patients with evidence or history of blood dyscracia.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Patients using Metronidazole Topical Lotion should receive the following information and instructions:
1 This medication is to be used only as directed by the physician.
2. It is for external use only.
3. Avoid contact with the eyes.
4. Cleanse affected area(s) before applying this medication.
5. Patients should report any adverse reaction to their physician.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Oral metronidazole has been reported to potentiate the anticoagulant effect of warfarin and coumarin anticoagulants, resulting in a prolongation of prothrombin time. The effect of topical metronidazole on prothrombin time is not known.
CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS, IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
Metronidazole has shown evidence of carcinogenic activity in a number of studies involving chronic, oral administration in mice and rats. Metronidazole has not been assessed for carcinogenic activity following topical administration. In several long term studies in mice, oral doses of approximately 200 mg/m2/day (approximately 20 times the exposure of a patient that received the estimated maximum human topical daily dose (assuming 100% of bioavailability and following normalization of the data on the basis of the body surface area)) or greater were associated with increase incidences of lung tumors in male mice and Iymphomas in female mice. In several long-term studies in rats oral administration of metronidazole resulted in increased incidences of mammary and hepatic tumors in female rats and tumors pituitary adenomas in male rats at dosages of approximately 1600 mg/m2/day (approximately 170 times the exposure or a patient that received the estimated maximum human topical daily dose (assuming 100% of bioavailability and following normalization of the data on the basis of the body surface area)) or greater. In another oral study, an increase of mammary tumors was observed in female rats that received approximately 160 mg/m2/day (approximately 17 times the exposure or a patient that received the estimated maximum human topical daily dose (assuming 100% of bioavailability and following normalization of the data on the basis of the body surface area)).
Ultraviolet radiation-induced carcinogenesis was enhanced in albino mice by intraperitoneal injection of metronidazole at a dosage of 45 mg/m2/day, 5 days per week, for 10 weeks, as indicated by a decreased latency period to the development of skin noeoplasms. It is unclear how this level of exposure compares to the clinical situation with respect to the concentration of the drug or metabolics in the skin. This study did not determine if metronidazole must be present during exposure to ultraviolet radiation in order to enhance tumor formation; metronidazole may promote tumor formation in cells that have been previously initialed by ultraviolet radiation.
Metronidazole exhibited mutagenic activity in several in vitro bacterial and mammalian assay systems. Intraperitoneal administration of metronidazole to mice resulted in dosage dependent increase in the incidence of chromosomal aberrations in peripheral lymphocytes was reported in patients with Crohn’s disease who were treated with metronidazole for 1 to 2 months at a dosage of 200 to 1200 mg/day. However similar results were not observed in another study in which humans treated for 8 months.
In rats, oral metronidazole at a dosage of approximately 1800 mg/m2/day day (approximately 200 times the exposure or a patient that received the estimated maximum human topical daily dose (assuming 100% of bioavailability and following normalization of the data on the basis of the body surface area)) included inhibition of spermatogenesis and sever testicular degeneration.
PREGNANCY
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with the use of Metronidazole Topical Lotion in pregnant women. Metronidazole crosses the placental barrier and enters the fetal circulation rapidly. No fetotoxicity was observed after oral administration of metronidazole in rats or mice. However because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response and since oral metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogen in some rodents, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
NURSING MOTHERS
After oral administration, metronidazole is secreted in breast milk in concentrations similar to those found in the plasma. Even though blood levels are significantly lower with topically applied metronidazole than those achieved after oral administration of metronidazole, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
PEDIATRIC USE
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
METRONIDAZOLE ADVERSE REACTIONS
In a controlled clinical trial, safety data from 141 patients who used Metronidazole Topical Lotion (n = 71), or the lotion vehicle (n = 70), twice daily and experienced a local cutaneous adverse event which may or may not have been related to the treatments include: Iocal allergic reaction, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 2 (3%), lotion vehicle 0; contact dermatitis, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 2 (3%), lotion vehicle 1 (1%); pruritus, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 1 (1%), lotion vehicle 0; skin discomfort (burning and stinging), Metronidazole Topical Lotion 1 (1%), lotion vehicle 2 (3%); erythema, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 4 (6%), lotion vehicle 0; dry skin, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 0, lotion vehicle 1 (1%); and worsening of rosasea, Metronidazole Topical Lotion 1 (1%), lotion vehicle 7 (10%).
The following additional adverse experiences have been reported with the topical use of metronidazole skin irritation, transient redness, metallic taste, tingling or numbness of extremities, and nausea.
METRONIDAZOLE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin layer to the affected areas after washing. Use morning and evening or as directed by physician. Avoid application close to the eyes. Patients may use cosmetics after waiting for the Metronidazole Topical Lotion to dry (not less than 5 minutes).
HOW SUPPLIED
Metronidazole Topical Lotion 0.75% is supplied in the following size:
2 fl. Oz (59 mL) plastic bottle - NDC 0472-0912-02
STORAGE
Store at controlled room temperature 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C)
Protect from freezing.
Distributed by:
Actavis Mid Atlantic LLC
1877 Kawai Road
Lincolnton, NC 28092 USA
Manufactured by:
DPT Laboratories, Ltd.
San Antonio, Texas 78215 USA
325098-0209 Revised: February 2009
Metronidazole Topical Lotion 0.75%

METRONIDAZOLEMETRONIDAZOLE LOTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||