Modafinil
Modafinil Tablets, USP [C-IV]Rx only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- MODAFINIL DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CLINICAL TRIALS
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- MODAFINIL CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- MODAFINIL ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
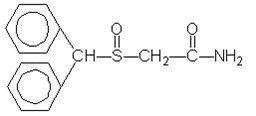
MODAFINIL DESCRIPTION
15152
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action and Pharmacology
1in vitro
in vitroin vivo
Pharmacokinetics
ldldminssldl
Absorption
max
Distribution
in vitromax
Metabolism and Elimination
Metabolism occurs through hydrolytic deamidation, S-oxidation, aromatic ring hydroxylation, and glucuronide conjugation. Less than 10% of an administered dose is excreted as the parent compound. In a clinical study using radiolabeled modafinil, a total of 81% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in 11 days post-dose, predominantly in the urine (80% vs. 1% in the feces). The largest fraction of the drug in urine was modafinil acid, but at least six other metabolites were present in lower concentrations. Only two metabolites reach appreciable concentrations in plasma, i.e., modafinil acid and modafinil sulfone. In preclinical models, modafinil acid, modafinil sulfone, 2-[(diphenylmethyl) sulfonyl]acetic acid and 4-hydroxy modafinil, were inactive or did not appear to mediate the arousal effects of modafinil.
in vitroin vivoPRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions
in vitro
PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactionsin vitro
PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions
in vitroPRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions, Other Drugs
Special Populations
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CLINICAL TRIALS
Narcolepsy
No ChangeVery Much Worse Very Much Improved
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
CLINICAL TRIALS, Narcolepsy
Patients treated with modafinil showed a statistically significant improvement in the ability to remain awake compared to placebo-treated patients as measured by the MWT (p<0.001) at endpoint [Table 1]. Modafinil-treated patients also showed a statistically significant improvement in clinical condition as rated by the CGI-C scale (p<0.001) [Table 2]. The two doses of modafinil performed similarly.
In the second study, a 4-week multicenter placebo-controlled trial, 157 patients were randomized to either modafinil 400 mg/day or placebo. Documentation of regular CPAP use (at least 4 hours/night on 70% of nights) was required for all patients. The primary outcome measure was the change from baseline on the ESS at week 4 or final visit. The baseline ESS scores for the modafinil and placebo groups were 14.2 and 14.4, respectively. At week 4, the ESS was reduced by 4.6 in the modafinil group and by 2.0 in the placebo group, a difference that was statistically significant (p<0.0001).
Shift Work Disorder (SWD)
CLINICAL TRIALS, Narcolepsy
Table 1 Average Baseline Sleep Latency and Change from Baseline at Final Visit in Adults
(MWT and MSLT in minutes)
| Disorder | Measure | Modafinil 200 mg* | Modafinil 400 mg* | Placebo | |||
| Baseline | Change from Baseline | Baseline | Change from Baseline | Baseline | Change from Baseline | ||
| Narcolepsy I | MWT | 5.8 | 2.3 | 6.6 | 2.3 | 5.8 | -0.7 |
| Narcolepsy II | MWT | 6.1 | 2.2 | 5.9 | 2.0 | 6.0 | -0.7 |
| OSA | MWT | 13.1 | 1.6 | 13.6 | 1.5 | 13.8 | -1.1 |
| SWD | MSLT | 2.1 | 1.7 | - | - | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| *Significantly different than placebo for all trials (p<0.01 for all trials but SWD which was p<0.05) |
|||||||
Table 2 Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGI-C) (Percent of Adult Patients Who Improved at Final Visit)
| Disorder | Modafinil 200 mg* | Modafinil 400 mg* | Placebo |
| Narcolepsy I Narcolepsy II |
64% 58% |
72% 60% |
37% 38% |
| OSA | 61% | 68% | 37% |
| SWD | 74% | ---- | 36% |
| *Significantly different than placebo for all trials (p<0.01) | |||
INDICATIONS & USAGE
MODAFINIL CONTRAINDICATIONS
Modafinil is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to modafinil, armodafinil or its inactive ingredients.
WARNINGS
Serious Rash, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Serious rash requiring hospitalization and discontinuation of treatment has been reported in adults and children in association with the use of modafinil.
Modafinil is not approved for use in pediatric patients for any indication.
In clinical trials of modafinil, the incidence of rash resulting in discontinuation was approximately 0.8% (13 per 1,585) in pediatric patients (age <17 years); these rashes included 1 case of possible Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and 1 case of apparent multiorgan hypersensitivity reaction. Several of the cases were associated with fever and other abnormalities (e.g., vomiting, leukopenia). The median time to rash that resulted in discontinuation was 13 days. No such cases were observed among 380 pediatric patients who received placebo. No serious skin rashes have been reported in adult clinical trials (0 per 4,264) of modafinil.
Rare cases of serious or life-threatening rash, including SJS, Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), and Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in adults and children in worldwide postmarketing experience. The reporting rate of TEN and SJS associated with modafinil use, which is generally accepted to be an underestimate due to underreporting, exceeds the background incidence rate. Estimates of the background incidence rate for these serious skin reactions in the general population range between 1 to 2 cases per million-person years.
There are no factors that are known to predict the risk of occurrence or the severity of rash associated with modafinil. Nearly all cases of serious rash associated with modafinil occurred within 1 to 5 weeks after treatment initiation. However, isolated cases have been reported after prolonged treatment (e.g., 3 months). Accordingly, duration of therapy cannot be relied upon as a means to predict the potential risk heralded by the first appearance of a rash.
Although benign rashes also occur with modafinil, it is not possible to reliably predict which rashes will prove to be serious. Accordingly, modafinil should ordinarily be discontinued at the first sign of rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. Discontinuation of treatment may not prevent a rash from becoming life-threatening or permanently disabling or disfiguring.
Angioedema and Anaphylactoid Reactions
Multiorgan Hypersensitivity Reactions
Persistent Sleepiness
Psychiatric Symptoms
PRECAUTIONS
Diagnosis of Sleep Disorders
CLINICAL TRIALS
General
CPAP Use in Patients with OSA
Cardiovascular System
Patients Using Steroidal Contraceptives
PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions
Patients Using Cyclosporine
PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions
Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.
Elderly Patients
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Information for Patients
Pregnancy
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Pregnancy
Nursing
Concomitant Medication
Alcohol
Allergic Reactions
Drug Interactions
CNS Active Drugs
22max0-∞
Other Drugs
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics,
max0-242
Potential Interactions with Drugs That Inhibit, Induce, or are Metabolized by Cytochrome P-450 Isoenzymes and Other Hepatic Enzymes
in vitroin vitroin vivoSee Other Drugs
in vitro Other Drugs,
In vitro
Tricyclic antidepressants
Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis & Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
2
Mutagenesis
in vitroin vivo
Impairment of Fertility
Pregnancy
Labor & Delivery
The effect of modafinil on labor and delivery in humans has not been systematically investigated.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether modafinil or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when modafinil tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
WARNINGS, Serious Rash, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome
WARNINGS, Serious Rash, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Geriatric Use
Experience in a limited number of patients who were greater than 65 years of age in clinical trials showed an incidence of adverse experiences similar to other age groups. In elderly patients, elimination of modafinil and its metabolites may be reduced as a consequence of aging. Therefore, consideration should be given to the use of lower doses in this population (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
MODAFINIL ADVERSE REACTIONS
Incidence in Controlled Trials
Table 3. Incidence Of Treatment-Emergent Adverse Experiences In Parallel-Group, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials1 With Modafinil In Adults With Narcolepsy, OSA, and SWD (200 mg, 300 mg and 400 mg)*
|
Body System
|
Preferred Term
|
Modafinil (n = 934)
|
Placebo (n = 567)
|
| Body as a Whole |
Headache Back Pain Flu Syndrome Chest Pain Chills Neck Rigidity |
34% 6% 4% 3% 1% 1% |
23% 5% 3% 1% 0% 0% |
| Cardiovascular |
Hypertension Tachycardia Palpitation Vasodilatation |
3% 2% 2% 2% |
1% 1% 1% 0% |
| Digestive |
Nausea Diarrhea Dyspepsia Dry Mouth Anorexia Constipation Abnormal Liver Function 2 Flatulence Mouth Ulceration Thirst |
11% 6% 5% 4% 4% 2% 2% 1% 1% 1% |
3% 5% 4% 2% 1% 1% 1% 0% 0% 0% |
| Hemic/Lymphatic |
Eosinophilia |
1% |
0% |
| Metabolic/Nutritional |
Edema |
1% |
0% |
| Nervous |
Nervousness Insomnia Anxiety Dizziness Depression |
7% 5% 5% 5% 2% |
3% 1% 1% 4% 1% |
| Paresthesia Somnolence Hypertonia Dyskinesia3 Hyperkinesia Agitation Confusion Tremor Emotional Lability Vertigo |
2% 2% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% 1% |
0% 1% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% |
|
| Respiratory |
Rhinitis Pharyngitis Lung Disorder Epistaxis Asthma |
7% 4% 2% 1% 1% |
6% 2% 1% 0% 0% |
| Skin/Appendages |
Sweating Herpes Simplex |
1% 1% |
0% 0% |
| Special Senses |
Amblyopia Abnormal Vision Taste Perversion Eye Pain |
1% 1% 1% 1% |
0% 0% 0% 0% |
| Urogenital |
Urine Abnormality Hematuria Pyuria |
1% 1% 1% |
0% 0% 0% |
1
4
2
3
4
Dose Dependency of Adverse Events
Vital Sign Changes
Weight Changes
Laboratory Changes
ECG Changes
Postmarketing Reports
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of modafinil. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Decisions to include these reactions in labeling are typically based on one or more of the following factors: (1) seriousness of the reaction, (2) frequency of the reporting, or (3) strength of causal connection to modafinil.
Hematologic: agranulocytosis
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance Class
Abuse Potential and Dependence
in vitro
Withdrawal
OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience
Overdose Management
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY CLINICAL TRIALS
General Considerations
PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY PRECAUTIONS
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY PRECAUTIONS
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY PRECAUTIONS
HOW SUPPLIED
Modafinil tablets USP
100 mg:
200 mg:
SPL MEDGUIDE
Medication Guide
Modafinil Tablets, USP C-IV
What is the most important information I should know about modafinil?
Modafinil may cause serious side effects including a serious rash or a serious allergic reaction that may affect parts of your body such as your liver or blood cells. Any of these may need to be treated in a hospital and may be life-threatening.
Stop taking modafinil and call your doctor right away or get emergency help if you have any of these symptoms:
- skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or your skin blisters and peels
- swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue, or throat
- trouble swallowing or breathing
- fever, shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, or dark urine.
Modafinil is not approved for use in children for any medical condition.
What is Modafinil?
- narcolepsy
- obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Modafinil is used with other medical treatments for this sleep disorder. Modafinil does not take the place of using your CPAP machine or other treatments that your doctor has prescribed for this condition. It is important that you continue to use these treatments as prescribed by your doctor.
- shift work disorder (SWD)
Modafinil will not cure these sleep disorders. Modafinil may help the sleepiness caused by these conditions, but it may not stop all your sleepiness. Modafinil does not take the place of getting enough sleep. Follow your doctor’s advice about good sleep habits and using other treatments.
| Modafinil is a federally controlled substance (C-IV) because it can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep modafinil in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away modafinil may harm others, and is against the law. Tell your doctor if you have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or street drugs. |
Who should not take modafinil?
- are allergic to any of its ingredients. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in modafinil.
- have had a rash or allergic reaction to either modafinil or armodafinil. These medicines are very similar.
What should I tell my doctor before taking modafinil?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions including, if you:
- have a history of mental health problems, including psychosis
- have heart problems or had a heart attack
- have high blood pressure. Your blood pressure may need to be checked more often while taking modafinil.
- have liver or kidney problems
- have a history of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if modafinil will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if modafinil passes into your milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take modafinil.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take
- a hormonal birth control method, such as birth control pills, shots, implants, patches, vaginal rings, and intrauterine devices (IUDs). Hormonal birth control methods may not work while you take modafinil. Women who use one of these methods of birth control may have a higher chance for getting pregnant while taking modafinil, and for one month after stopping modafinil. Talk to your doctor about birth control choices that are right for you while taking modafinil.
How should I take modafinil?
- Take modafinil exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will prescribe the dose of modafinil that is right for you. Do not change your dose of modafinil without talking to your doctor.
- Your doctor will tell you the right time of day to take modafinil.
- People with narcolepsy or OSA usually take modafinil one time each day in the morning.
- People with SWD usually take modafinil about 1 hour before their work shift.
- Do not change the time of day you take modafinil unless you have talked to your doctor. If you take modafinil too close to your bedtime, you may find it harder to go to sleep.
- You can take modafinil with or without food.
- If you take more than your prescribed dose or if you take an overdose of modafinil, call your doctor or poison control center right away.
Symptoms of an overdose of modafinil may include:
- Trouble sleeping
- Restlessness
- Confusion
- Feeling disoriented
- Feeling excited
- Hearing, seeing, feeling, or sensing things that are not really there (hallucinations)
- Nausea and diarrhea
- A fast or slow heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Increased blood pressure
What should I avoid while taking modafinil?
- Do not drive a car or do other dangerous activities until you know how modafinil affects you. People with sleep disorders should always be careful about doing things that could be dangerous. Do not change your daily habits until your doctor tells you it is okay.
- You should avoid drinking alcohol. It is not known how drinking alcohol will affect you when taking modafinil.
What are possible side effects of modafinil?
Modafinil may cause serious side effects. Stop taking modafinil and call your doctor right away or get emergency help if you get any of the following:
- a serious rash or serious allergic reaction. (See “What is the most important information I should know about modafinil?”)
- mental (psychiatric) symptoms, including:
- depression
- feeling anxious
- hearing, seeing, feeling, or sensing things that are not really there (hallucinations)
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- thoughts of suicide
- aggressive behavior
- other mental problems
- symptoms of a heart problem, including chest pain, abnormal heart beats, and trouble breathing.
Common side effects that can happen in anyone who takes modafinil include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modafinil is not approved for use in children for any medical condition. In studies of modafinil in children with narcolepsy, side effects included:
- Tourette’s syndrome
- hostile behavior
- increase in sudden loss of muscle tone and severe muscle weakness
- increase in seeing and hearing things when falling asleep
- increase in suicidal thoughts
- low white blood count
- painful menstrual periods
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Modafinil Tablets?
- Store modafinil at room temperature between 68° and 77° F (20° and 25°C).
-
Keep modafinil and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about modafinil
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use modafinil for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give modafinil to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them and it is against the law.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about modafinil. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about modafinil that is written for health professionals.For more information, call 1-800-444-4011.
What are the ingredients in modafinil?
Active Ingredient: modafinil
Inactive Ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, povidone, mannitoland magnesium stearate.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL


ModafinilModafinil TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ModafinilModafinil TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||