Mupirocin
MUPIROCIN OINTMENT USP, 2%1010For Dermatologic Use
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- MUPIROCIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- MUPIROCIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- MUPIROCIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- MUPIROCIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- MUPIROCIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
MUPIROCIN DESCRIPTION
Each gram of Mupirocin Ointment 2% contains 20 mg mupirocin in a bland water miscible ointment base (polyethylene glycol ointment, N.F.) consisting of polyethylene glycol 400 and polyethylene glycol 3350. Mupirocin is a naturally occurring antibiotic. The chemical name is (E)-(2S,3R,4R,5S)-5-[(2S,3S,4S,5S)-2,3-Epoxy-5-hydroxy-4-methylhexyl]tetrahydro-3,4-dihydroxy-β- methyl-2H-pyran-2-crotonic acid, ester with 9-hydroxynonanoic acid. The chemical structure is:
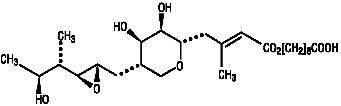
C26H44O9 M.W. 500.63
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Application of 14C-labeled mupirocin ointment to the lower arm of normal male subjects followed by occlusion for 24 hours showed no measurable systemic absorption (< 1.1 nanogram mupirocin per milliliter of whole blood). Measurable radioactivity was present in the stratum corneum of these subjects 72 hours after application.
Following intravenous or oral administration, mupirocin is rapidly metabolized. The principal metabolite, monic acid, is eliminated by renal excretion, and demonstrates no antibacterial activity. In a study conducted in seven healthy adult male subjects, the elimination half-life after intravenous administration of mupirocin was 20 to 40 minutes for mupirocin and 30 to 80 minutes for monic acid. The pharmacokinetics of mupirocin has not been studied in individuals with renal insufficiency.
Microbiology
Mupirocin is an antibacterial agent produced by fermentation using the organism Pseudomonas fluorescens. It is active against a wide range of gram-positive bacteria including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is also active against certain gram-negative bacteria. Mupirocin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by reversibly and specifically binding to bacterial isoleucyl transfer-RNA synthetase. Due to this unique mode of action, mupirocin demonstrates no in vitro cross-resistance with other classes of antimicrobial agents.
Resistance occurs rarely. However, when mupirocin resistance does occur, it appears to result from the production of a modified isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. High-level plasmid-mediated resistance (MIC > 1024 mcg/mL) has been reported in some strains of S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci.
Mupirocin is bactericidal at concentrations achieved by topical administration. However, the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) against relevant pathogens is generally eight-fold to thirty-fold higher than the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). In addition, mupirocin is highly protein bound (> 97%), and the effect of wound secretions on the MICs of mupirocin has not been determined. Mupirocin has been shown to be active against most strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, both in vitro and in clinical studies. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE.) The following in vitro data are available, BUT THEIR CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE IS UNKNOWN. Mupirocin is active against most strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
MUPIROCIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Mupirocin ointment 2% is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo due to: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
MUPIROCIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
This drug is contraindicated in individuals with a history of sensitivity reactions to any of its components.
WARNINGS
Mupirocin ointment is not for ophthalmic use.
PRECAUTIONS
If a reaction suggesting sensitivity or chemical irritation should occur with use of mupirocin ointment 2%, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate alternative therapy for the infection instituted.
As with other antibacterial products prolonged use may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi.
Mupirocin ointment is not formulated for use on mucosal surfaces. Intranasal use has been associated with isolated reports of stinging and drying. A paraffin-based formulation – *Bactroban® Nasal (mupirocin calcium ointment) – is available for intranasal use.
Polyethylene glycol can be absorbed from open wounds and damaged skin and is excreted by the kidneys. In common with other polyethylene glycol-based ointments, mupirocin ointment should not be used in conditions where absorption of large quantities of polyethylene glycol is possible, especially if there is evidence of moderate or severe renal impairment.
Information for Patients
Use this medication only as directed by your health provider. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes. The medication should be stopped and your health care practitioner contacted if irritation, severe itching, or rash occurs.
If impetigo has not improved in 3 to 5 days, contact your health care practitioner.
Drug Interactions
The effect of the concurrent application of mupirocin ointment and other drug products has not been studied.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential of mupirocin have not been conducted.
Results of the following studies performed with mupirocin calcium or mupirocin sodium in vitro and in vivo did not indicate a potential for genotoxicity: rat primary hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis, sediment analysis for DNA strand breaks, Salmonella reversion test (Ames), Escherichia coli mutation assay, metaphase analysis of human lymphocytes, mouse lymphoma assay, and bone marrow micronuclei assay in mice.
Reproduction studies were performed in male and female rats with mupirocin administered subcutaneously at doses up to 14 times a human topical dose (approximately 60 mg mupirocin per day) on a mg/m2 basis and revealed no evidence of impaired fertility and reproductive performance from mupirocin.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits with mupirocin administered subcutaneously at doses up to 22 and 43 times, respectively, the human topical dose (approximately 60 mg mupirocin per day) on a mg/m2 basis and revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to mupirocin. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when mupirocin ointment is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of mupirocin ointment have been established in the age range of 2 months to 16 years. Use of mupirocin ointment in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of mupirocin ointment in impetigo in pediatric patients studied as a part of the pivotal clinical trials (see CLINICAL STUDIES).
MUPIROCIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following local adverse reactions have been reported in connection with the use of mupirocin ointment: burning, stinging, or pain in 1.5% of patients; itching in 1% of patients; rash, nausea, erythema, dry skin, tenderness, swelling, contact dermatitis, and increased exudate in less than 1% of patients.
MUPIROCIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
A small amount of mupirocin ointment should be applied to the affected area three times daily. The area treated may be covered with a gauze dressing if desired. Patients not showing a clinical response within 3 to 5 days should be reevaluated.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of topical mupirocin ointment in impetigo was tested in two studies. In the first, patients with impetigo were randomized to receive either mupirocin ointment or vehicle placebo t.i.d. for 8 to 12 days. Clinical efficacy rates at end of therapy in the evaluable populations (adults and pediatric patients included) were 71% for mupirocin ointment (n = 49) and 35% for vehicle placebo (n = 51). Pathogen eradication rates in the evaluable populations were 94% for mupirocin ointment and 62% for vehicle placebo. There were no side effects reported in the group receiving mupirocin ointment.
In the second study, patients with impetigo were randomized to receive either mupirocin ointment t.i.d. or 30 to 40 mg/kg oral erythromycin ethylsuccinate per day (this was an unblinded study) for 8 days. There was a follow-up visit 1 week after treatment ended. Clinical efficacy rates at the follow-up visit in the evaluable populations (adults and pediatric patients included) were 93% for mupirocin ointment (n = 29) and 78.5% for erythromycin (n = 28). Pathogen eradication rates in the evaluable patient populations were 100% for both test groups. There were no side effects reported in the mupirocin ointment group.
Pediatrics
There were 91 pediatric patients aged 2 months to 15 years in the first study described above. Clinical efficacy rates at end of therapy in the evaluable populations were 78% for mupirocin ointment (n = 42) and 36% for vehicle placebo (n = 49). In the second study described above, all patients were pediatric except two adults in the group receiving mupirocin ointment. The age range of the pediatric patients was 7 months to 13 years. The clinical efficacy rate for mupirocin ointment (n = 27) was 96%, and for the erythromycin it was unchanged (78.5%).
HOW SUPPLIED
Mupirocin Ointment USP, 2% is supplied in 22 gram tubes.
Store at 20o to 25oC (68o to 77oF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
*Bactroban® Nasal is a registered trademark of SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals.
Manufactured In Croatia By:
PLIVA HRVATSKA d.o.o
Zagreb, Croatia
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. F 3/2005
Repackaged by:
REBEL DISTRIBUTORS COPR
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
MupirocinMupirocin OINTMENT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||