NAFCILLIN
Nafcillin Injection, USP in PL 2040 Plastic Container For Intravenous Use Only GALAXY Container (PL 2040 Plastic)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- NAFCILLIN DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- NAFCILLIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATION
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- NAFCILLIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- NAFCILLIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- DIRECTIONS FOR USE OF GALAXY CONTAINER (PL 2040 PLASTIC)
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABELING - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Nafcillin Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Nafcillin Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
NAFCILLIN DESCRIPTION
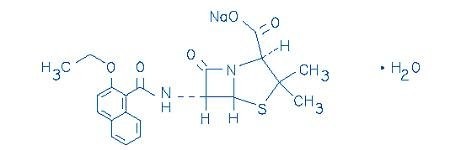
Nafcillin Injection, USP is a sterile injectable product containing nafcillin which is added as Nafcillin Sodium, USP, a semisynthetic penicillin derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid. The chemical name of nafcillin sodium is Monosodium (2S,5R,6R)-6-(2-ethoxy-1-naphthamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1- azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate monohydrate. It is resistant to inactivation by the enzyme penicillinase (beta-lactamase). The molecular formula of Nafcillin Sodium, USP is C21H21N2NaO5S·H2O. The molecular weight is 454.48. The structural formula of nafcillin sodium is as follows:
Nafcillin Injection, USP is a frozen, iso-osmotic, sterile, nonpyrogenic premixed 50 mL or 100 mL solution containing 1 g or 2 g of nafcillin, respectively, added as Nafcillin Sodium, USP. Dextrose, USP has been added to the above dosages to adjust osmolality (approximately 1.8 g and 3.6 g as dextrose hydrous to the 1 g and 2 g dosages, respectively). Sodium Citrate Hydrous, USP has been added as a buffer (approximately 90 mg and 180 mg to the 1 g and 2 g dosages, respectively). The pH has been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and may have been adjusted with sodium hydroxide. The pH is 6.5 (6.0 to 8.5). The solution is intended for intravenous use after thawing to room temperature.
This GALAXY container is fabricated from a specially designed multilayer plastic (PL 2040). Solutions are in contact with the polyethylene layer of this container and can leach out certain chemical components of the plastic in very small amounts within the expiration period. The suitability of the plastic has been confirmed in tests in animals according to the USP biological tests for plastic containers, as well as by tissue culture toxicity studies.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
In a study of five healthy adults administered a single 500 mg dose of nafcillin by intravenous injection over seven minutes, the mean plasma concentration of the drug was approximately 30 mcg/mL at 5 minutes after injection. The mean area under the plasma concentration-versus-time curve (AUC) for nafcillin in this study was 18.06 mcg·h/mL.
The serum half-life of nafcillin administered by the intravenous route ranged from 33 to 61 minutes as measured in three separate studies.
In contrast to the other penicillinase-resistant penicillins, only about 30% of nafcillin is excreted as unchanged drug in the urine of normal volunteers, and most within the first six hours. Nafcillin is primarily eliminated by nonrenal routes, namely hepatic inactivation and excretion in the bile.
Nafcillin binds to serum proteins, mainly albumin. The degree of protein binding reported for nafcillin is 89.9 ± 1.5%. Reported values vary with the method of study and the investigator.
The concurrent administration of probenecid with nafcillin increases and prolongs plasma concentrations of nafcillin. Probenecid significantly reduces the total body clearance of nafcillin with renal clearance being decreased to a greater extent than nonrenal clearance.
The penicillinase-resistant penicillins are widely distributed in various body fluids, including bile, pleural, amniotic and synovial fluids. With normal doses insignificant concentrations are found in the aqueous humor of the eye. High nafcillin CSF levels have been obtained in the presence of inflamed meninges.
Renal failure does not appreciably affect the serum half-life of nafcillin; therefore, no modification of the usual nafcillin dosage is necessary in renal failure with or without hemodialysis. Hemodialysis does not accelerate the rate of clearance of nafcillin from the blood.
A study which assessed the effects of cirrhosis and extrahepatic biliary obstruction in man demonstrated that the plasma clearance of nafcillin was significantly decreased in patients with hepatic dysfunction. In these patients with cirrhosis and extrahepatic obstruction, nafcillin excretion in the urine was significantly increased from about 30 to 50% of the administered dose, suggesting that renal disease superimposed on hepatic disease could further decrease nafcillin clearance.
Microbiology
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins exert a bactericidal action against penicillin-susceptible microorganisms during the state of active multiplication. All penicillins inhibit the biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. The drugs in this class are highly resistant to inactivation by staphylococcal penicillinase and are active against penicillinase producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus. The penicillinase-resistant penicillins are active in vitro against a variety of other bacteria.
Susceptibility Test Methods
When available, the clinical microbiology laboratory should provide the results of in vitro susceptibility test results for antimicrobial drugs used in local hospitals and practice areas to the physician as periodic reports that describe the susceptibility profile of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens. These reports should aid the physician in selecting the most effective antimicrobial.
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure based on dilution method1,2 (broth, agar or microdilution) or equivalent. It has been reported that determination of susceptibility or resistance of a microorganism to all penicillinase-resistant penicillins, including nafcillin, may be deduced by testing microorganisms against either oxacillin or cefoxitin.2 For this reason, routine dilution testing of nafcillin is not advised and susceptibility to nafcillin should be determined by dilution using standardized inoculum and concentrations of oxacillin according to the criteria in Table 1.1,2
|
Staphylococcus
aureus MIC Susceptibility Test
Interpretive Criteria for Oxacillin |
||
|
Minimum Inhibitory
Oxacillin Concentrations (mcg/mL) |
||
| Pathogen | Susceptible (S) | Resistant (R) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ≤ 2.0 | ≥ 4.0 |
Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. One such standardized procedure2,3 requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. It has been reported that determination of susceptibility or resistance of a microorganism to all penicillinase-resistant penicillins, including nafcillin, may be deduced by testing microorganisms against either oxacillin or cefoxitin.2 Disk diffusion results using cefoxitin have been shown to be more reproducible than those obtained with oxacillin,4,5 therefore cefoxitin is the preferred reagent for testing nafcillin susceptibility by diffusion. Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 30 microgram cefoxitin disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria in Table 2.
|
Staphylococcus aureus Disk Diffusion
Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria for Nafcillin Using a 30 mcg Cefoxitin Disk |
||
| Disk Diffusion Diameters (mm) | ||
| Pathogen | Susceptible (S) | Resistant (R) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ≥ 22 | ≤ 21 |
A report of “Susceptible” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited by usually achievable concentrations of the antimicrobial compound in blood. A report of “Resistant” indicates that usually achievable concentrations of the antimicrobial compound in the blood are unlikely to be inhibitory and that other therapy should be selected.
Measurement of MIC or MBC and achieved antimicrobial compound concentrations may be appropriate to guide therapy in some infections. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section for further information on drug concentrations achieved in infected body sites and other pharmacokinetic properties of this antimicrobial drug product.)
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to monitor and ensure the accuracy and precision of the supplies and reagents used in the assay, and the techniques of the individuals performing the test. Appropriate quality control organisms and acceptable corresponding ranges of oxacillin MICs obtained by dilution testing or inhibition zones around 30 mcg cefoxitin disks are provided in Table 3.
| In Vitro Susceptibility Test Quality Control Ranges for Oxacillin and Cefoxitin | ||
| Oxacillin | Cefoxitin | |
| MIC range | disk diffusion | |
| Organism (ATCC #) | (mcg/mL) | range (mm) |
| Staphylococcus aureus (29213) | 0.12 - 0.5 | Not applicable |
| Staphylococcus aureus (25923) | Not applicable | 23 - 29 |
NAFCILLIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Nafcillin is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by penicillinase-producing staphylococci which have demonstrated susceptibility to the drug. Culture and susceptibility tests should be performed initially to determine the causative organism and its susceptibility to the drug (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY - Susceptibility Test Methods).
Nafcillin may be used to initiate therapy in suspected cases of resistant staphylococcal infections prior to the availability of susceptibility test results. Nafcillin should not be used in infections caused by organisms susceptible to penicillin G. If the susceptibility tests indicate that the infection is due to an organism other than a resistant Staphylococcus, therapy should not be continued with Nafcillin Injection, USP.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Nafcillin Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Nafcillin Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
CONTRAINDICATION
A history of a hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reaction to any penicillin is a contraindication.
Solutions containing dextrose may be contraindicated in patients with known allergy to corn or corn products.
WARNINGS
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Before initiating therapy with Nafcillin, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. If an allergic reaction occurs, Nafcillin should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should also be administered as indicated.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Nafcillin Injection, USP, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Nafcillin should generally not be administered to patients with a history of sensitivity to any penicillin.
Penicillin should be used with caution in individuals with histories of significant allergies and/or asthma. Whenever allergic reactions occur, penicillin should be withdrawn unless, in the opinion of the physician, the condition being treated is life-threatening and amenable only to penicillin therapy. The use of antibiotics may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. If new infections due to bacteria or fungi occur, the drug should be discontinued and appropriate measures taken.
The liver/biliary tract is the primary route of nafcillin clearance. Caution should be exercised when patients with concomitant hepatic insufficiency and renal dysfunction are treated with nafcillin. Serum levels should be measured and the dosage adjusted appropriately to avoid possible neurotoxic reactions associated with very high concentrations (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Prescribing Nafcillin Injection, USP in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Laboratory Tests
Bacteriologic studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to nafcillin should be performed (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY - Microbiology). In the treatment of suspected staphylococcal infections, therapy should be changed to another active agent if culture tests fail to demonstrate the presence of staphylococci.
Periodic assessment of organ system function including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic should be made during prolonged therapy with nafcillin. White blood cell and differential cell counts should be obtained prior to initiation of therapy and periodically during therapy with nafcillin. Periodic urinalysis, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine determinations should be performed during therapy with nafcillin. SGOT and SGPT values should be obtained periodically during therapy to monitor for possible liver function abnormalities.
Drug Interactions
Tetracycline, a bacteriostatic antibiotic, may antagonize the bactericidal effect of penicillin, and concurrent use of these drugs should be avoided.
Nafcillin in high dosage regimens, i.e., 2 grams every 4 hours, has been reported to decrease the effects of warfarin. When nafcillin and warfarin are used concomitantly, the prothrombin time should be closely monitored and the dose of warfarin adjusted as necessary. This effect may persist for up to 30 days after nafcillin has been discontinued.
Nafcillin when administered concomitantly with cyclosporine has been reported to result in subtherapeutic cyclosporine levels. The nafcillin-cyclosporine interaction was documented in a patient during two separate courses of therapy. When cyclosporine and nafcillin are used concomitantly in organ transplant patients, the cyclosporine levels should be monitored.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Nafcillin in the urine can cause a false-positive urine reaction for protein when the sulfosalicyclic acid test is used, but not with the dipstick.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long term animal studies have been conducted with these drugs. Studies on reproduction (nafcillin) in rats and mice reveal no fetal or maternal abnormalities before conception and continuously through weaning (one generation).
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in the mouse with oral doses up to 20 times the human dose and orally in the rat at doses up to 40 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the rodent fetus due to nafcillin. There are, however, no adequate or well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, nafcillin should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Penicillins are excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when penicillins are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The liver/biliary tract is the principal route of nafcillin elimination. Because of immature hepatic and renal function in pediatric patients, nafcillin excretion may be impaired, with abnormally high serum levels resulting. Serum levels should be monitored and the dosage adjusted appropriately. There are no approved pediatric patient dosage regimens for intravenous nafcillin. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
The potential for toxic effects in pediatric patients from chemicals that may leach from the single dose premixed intravenous preparation in plastic containers has not been determined.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Nafcillin Injection, USP did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Nafcillin Injection, USP contains 76.6 mg (3.33 mEq) of sodium per gram. At the usual recommended doses, patients would receive between 230 and 460 mg/day (10.0 and 20.0 mEq) of sodium. The geriatric population may respond with a blunted natriuresis to salt loading. This may be clinically important with regard to such diseases as congestive heart failure.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Nafcillin Injection, USP should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Nafcillin Injection, USP is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Nafcillin Injection, USP or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
NAFCILLIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
Body as a Whole
The reported incidence of allergic reactions to penicillin ranges from 0.7 to 10 percent (see WARNINGS). Sensitization is usually the result of treatment, but some individuals have had immediate reactions to penicillin when first treated. In such cases, it is thought that the patients may have had prior exposure to the drug via trace amounts present in milk or vaccines. Two types of allergic reactions to penicillins are noted clinically, immediate and delayed.
Immediate reactions usually occur within 20 minutes of administration and range in severity from urticaria and pruritus to angioneurotic edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, hypotension, vascular collapse, and death. Such immediate anaphylactic reactions are very rare (see WARNINGS) and usually occur after parenteral therapy but have occurred in patients receiving oral therapy. Another type of immediate reaction, an accelerated reaction, may occur between 20 minutes and 48 hours after administration and may include urticaria, pruritus, and fever.
Although laryngeal edema, laryngospasm, and hypotension occasionally occur, fatality is uncommon. Delayed allergic reactions to penicillin therapy usually occur after 48 hours and sometimes as late as 2 to 4 weeks after initiation of therapy. Manifestations of this type of reaction include serum sickness-like symptoms (i.e., fever, malaise, urticaria, myalgia, arthralgia, abdominal pain) and various skin rashes. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis, black or hairy tongue, and other symptoms of gastrointestinal irritation may occur, especially during oral penicillin therapy.
Local Reactions
Pain, swelling, inflammation, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, and occasional skin sloughing at the injection site have occurred with intravenous administration of nafcillin (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Severe tissue necrosis with sloughing secondary to subcutaneous extravasation of nafcillin has been reported.
Nervous System Reactions
Neurotoxic reactions similar to those observed with penicillin G could occur with large intravenous or intraventricular doses of nafcillin especially in patients with concomitant hepatic insufficiency and renal dysfunction (see PRECAUTIONS).
Urogenital Reactions
Renal tubular damage and interstitial nephritis have been associated infrequently with the administration of nafcillin. Manifestations of this reaction may include rash, fever, eosinophilia, hematuria, proteinuria, and renal insufficiency.
Gastrointestinal Reactions
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with the use of nafcillin. The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment (see WARNINGS).
Metabolic Reactions
Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and bone marrow depression have been associated with the use of nafcillin.
OVERDOSAGE
Neurotoxic reactions similar to those observed with penicillin G may arise with intravenous doses of nafcillin especially in patients with concomitant hepatic insufficiency and renal dysfunction (see PRECAUTIONS).
In the case of overdosage, discontinue nafcillin, treat symptomatically and institute supportive measures as required. Hemodialysis does not increase the rate of clearance of nafcillin from the blood.
NAFCILLIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Nafcillin Injection, USP supplied as a premixed frozen solution is to be administered as an intravenous infusion. The usual I.V. dosage for adults is 500 mg every 4 hours. For severe infections, 1 g every 4 hours is recommended. Administer slowly over at least 30 to 60 minutes to minimize the risk of vein irritation and extravasation. Bacteriologic studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to nafcillin should always be performed. Duration of therapy varies with the type and severity of infection as well as the overall condition of the patient; therefore, it should be determined by the clinical and bacteriological response of the patient. In severe staphylococcal infections, therapy with nafcillin should be continued for at least 14 days. Therapy should be continued for at least 48 hours after the patient has become afebrile, asymptomatic, and cultures are negative. The treatment of endocarditis and osteomyelitis may require a longer duration of therapy.
Nafcillin-probenecid therapy is generally limited to those infections where very high serum levels of nafcillin are necessary.
No dosage alterations are necessary for patients with renal dysfunction, including those on hemodialysis. Hemodialysis does not accelerate nafcillin clearance from the blood.
For patients with hepatic insufficiency and renal failure, measurement of nafcillin serum levels should be performed and dosage adjusted accordingly.
With intravenous administration, particularly in elderly patients, care should be taken because of the possibility of thrombophlebitis.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Do not add supplementary medication to Nafcillin Injection, USP.
Store in a freezer capable of maintaining a temperature of -20°C (-4°F) or less.
DIRECTIONS FOR USE OF GALAXY CONTAINER (PL 2040 PLASTIC)
Nafcillin Injection, USP in GALAXY container (PL 2040 Plastic) is for intravenous administration using sterile equipment.
Storage
Store in a freezer capable of maintaining a temperature of -20°C/-4°F.
Thawing of Plastic Containers
Thaw frozen container at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). [DO NOT FORCE THAW BY IMMERSION IN WATER BATHS OR BY MICROWAVE IRRADIATION.] Check for minute leaks by squeezing bag firmly. If leaks are detected, discard solution as sterility may be impaired.
Do not add supplementary medication.
The container should be visually inspected. Components of the solution may precipitate in the frozen state and will dissolve upon reaching room temperature with little or no agitation. Potency is not affected. Agitate after solution has reached room temperature. If after visual inspection the solution remains cloudy or if an insoluble precipitate is noted or if any seals or outlet ports are not intact, the container should be discarded.
The thawed 1 g and 2 g solutions are stable for 21 days under refrigeration (5°C/41°F) or 72 hours at room temperature (25°C/77°F). Do not refreeze.
Caution: Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Such use could result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete.
Preparation for intravenous administration
- Suspend container from eyelet support.
- Remove protector from outlet port at bottom of container.
- Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
HOW SUPPLIED
Nafcillin Injection, USP is supplied as a premixed frozen iso-osmotic solution in 50 mL and 100 mL single dose GALAXY containers (PL 2040 Plastic) as follows:
2G3540 NDC 0338-1017-41 1 gram nafcillin in 50 mL
2G3556 NDC 0338-1019-48 2 grams nafcillin in 100 mL
STORAGE AND HANDLING
Store at or below -20°C/-4°F. See Directions for Use of GALAXY Container (PL 2040 Plastic).
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
REFERENCES
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard- Eighth Edition. CLSI Document M07-A8 (ISBN 1-56238-689-1). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1898 USA, 2009.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-First Informational Supplement. CLSI Document M100-S21 (ISBN 1-56238-742-1). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1898 USA, 2011.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard-Tenth Edition. CLSI Document M02-A10 (ISBN 1-56238-688-3). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1898 USA, 2009.
- Palazzo ICV, Darini ALC. Evaluation of methods for detecting oxacillin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci including cefoxitin disc diffusion. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2006;257:299-305.
- Swenson JM, Tenover FC; Cefoxitin Disk Study Group. Results of disk diffusion testing with cefoxitin correlate with presence of mecA in Staphylococcus spp. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:3818-23.
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
ATCC is a trademark of American Type Culture Collection.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015
USA
Printed in
USA
07-19-66-125
Rev. October 2011
PACKAGE LABELING - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Baxter Logo
Nafcillin Injection, USP
12 - 50 mL
Single Dose Containers Iso-osmotic
Store at or
below -20°C/-4°F. Do not
refreeze.
1 g
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL
60015 USA
NDC
0338-1071-41
Code 2G3540
FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01)
20303381017419
Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). DO NOT FORCE THAW BY IMMERSION IN WATER BATHS OR BY MICROWAVE
IRRADIATION. Thawed solution is stable for 21 days under
refrigeration (5°C/41°F) or 72 hours at room
temperature
(25°C/77°F). Do not
refreeze
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
PL 2040
Plastic
07-04-65-185
GALAXY
Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 50 mL contains: Nafcillin
Sodium, USP equivalent to 1 g Nafcillin with approx. 1.8 g Dextrose
Hydrous, USP added to adjust osmolality and 90 mg Sodium Citrate
Hydrous, USP added as a buffer. pH adjusted with hydrochloric acid and
may have been adjusted with sodium hydroxide. pH 6.5 (6.0 to
8.5).
Dosage: Intravenously as directed by a physician. See insert.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication. Must not be used in series connections. Check for minute leaks by squeezing thawed bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard bag as sterility may be impaired. Do not use unless solution is clear. Rx only.
NAFCILLINNAFCILLIN INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NAFCILLINNAFCILLIN INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||