Naftin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use NAFTIN Gel, 2% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2%. NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% for topical useInitial U.S. Approval: 1988INDICATIONS AND USAGENAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is an allylamine antifungal indicated for the treatment of interdigital tinea pedis caused by the organisms Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum in patients 12 years of age and older. (1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONApply a thin layer of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% once daily to the affected areas plus an approximate ½ inch margin of healthy surrounding skin for 2 weeks. (2)For topical use only. NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use. (2)DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSGel, 2% (3)CONTRAINDICATIONSNone (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSIf redness or irritation develops with the use of NAFTIN Gel, 2% treatment should be discontinued. (5.1)Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions are application site reactions (2%). (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 877-743-8454 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 NAFTIN INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 NAFTIN DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 NAFTIN CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 NAFTIN ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 11 NAFTIN DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is an allylamine antifungal indicated for the treatment of interdigital tinea pedis caused by the organisms Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum in patients 12 years of age and older.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin layer of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% once daily to the affected areas plus an approximate ½ inch margin of healthy surrounding skin for 2 weeks.
For topical use only. NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Gel, 2%. Each gram contains 20 mg of naftifine hydrochloride in a colorless to yellow gel.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Side Effects
If irritation or sensitivity develops with the use of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2%, treatment should be discontinued.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two randomized, vehicle-controlled trials, 1143 subjects were treated with NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% versus 571 subjects treated with the vehicle. The trial subjects were 12 to 92 years old, were primarily male (76%), and were 59% Caucasian, 38% Black or African American, and 23% Hispanic or Latino. Subjects received doses once daily, topically, for 2 weeks to cover the affected skin areas plus a ½-inch margin of surrounding healthy skin. The most common adverse reactions were application site reactions which occurred at the rate of 2% in NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% arm versus 1% in vehicle arm. Most adverse reactions were mild in severity.
In an open-label trial to evaluate the pharmacokentics, safety and efficacy a total of 28 subjects (22 pediatric and six adult subjects) were enrolled and received NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2%. Among pediatric subjects the majority were male (82%) and Black or African American (73%), and were of Hispanic ethnicity (73%). Mean (±SD) pediatric subject age was 15 ± 1.7 years and ranged from 12 to 17 years. Among adult subjects, were male (67%),were Black or African American (67%) or White (33%), and most were not of Hispanic ethnicity (83%). Mean (±SD) adult subject age was 32 ± 11.2 years and ranged from 21 to 51 years. All 22 pediatric subjects and five of the six adult subjects were exposed to naftifine for 14 days; one adult subject was exposed to naftifine for 2 days. The dosing schedule was once-daily, topically, for 2 weeks covering the affected skin areas plus a ½ inch margin of surrounding healthy skin. In this trial, two pediatric subjects (9%) and one adult subject (17%) experienced adverse events. None of these events was serious, led to dose reduction or discontinuation from the study, or was considered treatment-related.
Cumulative irritancy testing revealed the potential for NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% to cause irritation. There was no evidence that NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% causes contact sensitization, phototoxicity, or photoallergenicity in healthy skin.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of naftifine hydrochloride: blisters, burning sensation, crusting, dryness, erythema/redness, inflammation, irritation, maceration, pain, pruritus [mild]/itching, rash and swelling.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B. There are no adequate and well-controlled trials of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on daily dose body surface area comparison (mg/m2) for the reproductive toxicology studies described in this section and in Section 13.1. The Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) was set at 4 g 2% gel per day (1.33 mg/kg/day for a 60 kg individual).
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Oral doses of 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day naftifine hydrochloride were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 15) to pregnant female rats. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (36.5× MRHD). Subcutaneous doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg/day naftifine hydrochloride were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 15) to pregnant female rats. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 30 mg/kg/day (3.7× MRHD). Subcutaneous doses of 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day naftifine hydrochloride were administered during the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 – 18) to pregnant female rabbits. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 30 mg/kg/day (7.3× MRHD).
A peri- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats. Oral doses of 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day naftifine hydrochloride were administered to female rats from gestational day 14 to lactation day 21. Reduced body weight gain of females during gestation and of the offspring during lactation was noted at300 mg/kg/day (36.5× MRHD). No developmental toxicity was noted at 100 mg/kg/day (12.2× MRHD).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Total of 22 pediatric subjects received NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2%. The majority were male (82%) and Black or African American (73%), and were of Hispanic ethnicity (73%). Mean (±SD) age was 15 ± 1.7 years and ranged from 12 to 17 years. All pediatric subjects were exposed to naftifine for 14 days. The dosing schedule was once-daily, topically, for 2 weeks covering the affected skin areas plus a ½ inch margin of surrounding healthy skin. In this trial, two pediatric subjects (9%) experienced adverse events. None of these events was serious, led to dose reduction or discontinuation from the study, or was considered treatment-related.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. The number of pediatric subjects ≤ 12 years of age studied was too small to adequately assess safety and efficacy.
8.5 Geriatric Use
During clinical trials, 99 subjects (9%) aged 65 years and over were exposed to NAFTIN Gel, 2%. Safety and effectiveness were similar to those reported by younger patients.
11 DESCRIPTION
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is a clear to yellow gel for topical use only. Each gram of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% contains 20 mg of naftifine hydrochloride, a synthetic allylamine antifungal compound.
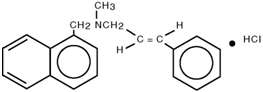
Chemically, naftifine HCl is (E)-N-Cinnamyl-N-methyl-1-napthalenemethylamine hydrochloride.
The molecular formula is C21H21N∙HCl with a molecular weight of 323.86.
The structural formula of naftifine hydrochloride is:
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% contains the following inactive ingredients: alcohol, benzyl alcohol, edentate disodium, hydroxyethyl cellulose, purified water, propylene glycol, polysorbate 20 and trolamine.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is a topical antifungal drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% have not been established.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In vitro and in vivo bioavailability studies have demonstrated that naftifine penetrates the stratum corneum in sufficient concentration to inhibit the growth of dermatophytes.
Pharmacokinetic analysis of plasma samples from 32 tinea pedis subjects treated with a mean dose of of 3.9 grams NAFTIN(naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% applied once daily to both feet for 14 days showed increased exposure over the treatment period, with a geometric mean (CV%) AUC0-24 (area under plasma concentration-versus-time curve from time 0 to 24 hours) of 10.5 (118) ng∙hr/mL on Day 1 and an AUC0-24 of 70 (59) ng∙hr/mL on Day 14. The accumulation ratio based on AUC was approximately 6. Maximum concentration (Cmax) also increased over the treatment period; geometric mean (CV%) Cmax after a single dose was 0.9 (92) ng/mL on Day 1; Cmax on Day 14 was 3.7 (64) ng/mL. Median Tmax was 20.0 hours (range: 8, 20 hours) after a single application on Day 1 and 8.0 hours (range: 0, 24 hours) on Day 14. Trough plasma concentrations increased during the trial period and reached steady state after 11 days. In the same pharmacokinetic trial the fraction of dose excreted in urine was less than or equal to 0.01% of the applied dose.
In a second study, the pharmacokinetics of NAFTIN Gel, 2% was evaluated from pediatric and adult subjects using a maximum dose (4 g total) of NAFT-600 once daily for 14 days for tinea pedis (2 g each foot). The results showed that the systemic exposure increased over the treatment period. Measurable concentrations of naftifine appeared in plasma within 1 hour of application in most pediatric subjects and within 6 hours of application in most of the adult subjects. After 14 days, the geometric mean Ctrough,max(CV%) was 3485.03 pg/mL (CV% 88.9%) in pediatric subjects and 3124.71 pg/mL (CV% 101.8%) in adult subjects. Mean urine concentrations of naftifine increased in pediatric subjects from 380.9 ng on Day 1 to 823.0 ng on Day 14 and in adult subjects from 79.9 ng on Day 1 to 974.5 ng on Day 14. The mean fe% increased during the treatment period from 0.00054% at Day 1 to 0.00116% for pediatric subjects and from 0.00011% at Day 1 to 0.00137% at Day 14 for adult subjects.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Naftifine is an antifungal that belongs to the allylamine class. Although the exact mechanism of action against fungi is not known, naftifine hydrochloride appears to interfere with sterol biosynthesis by inhibiting the enzyme squalene 2, 3-epoxidase. The inhibition of enzyme activity by this allylamine results in decreased amounts of sterols, especially ergosterol, and a corresponding accumulation of squalene in the cells.
Mechanism of Resistance
To date, a mechanism of resistance to naftifine has not been described.
Naftifine has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following fungi, both in vitro and in clinical infections, as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section:
-
-
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% have not been performed.
Naftifine hydrochloride revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay and Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay).
Oral administration of naftifine hydrochloride to rats, throughout mating, gestation, parturition, and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility, or reproduction, at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (12.2× MRHD).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% has been evaluated for efficacy in three pivotal trials.
In two randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter trials that included 1175 subjects with symptomatic and dermatophyte culture-positive tinea pedis. Subjects were randomized to receive NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% or vehicle. Subjects applied naftifine hydrochloride gel 2% or vehicle to the affected area of the foot once daily for 2 weeks. Signs and symptoms of tinea pedis (presence or absence of erythema, pruritus, and scaling) were assessed and potassium hydroxide (KOH) examination and dermatophyte culture were performed 6 weeks after the first treatment.
The mean age of the study population was 45 years; 77% were male; and 60% were Caucasian, 35% were Black or African American, and 26% were Hispanic or Latino. At baseline, subjects were confirmed to have signs and symptoms of tinea pedis, positive KOH exam, and confirmed dermatophyte culture. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of subjects with a complete cure at 6 weeks after the start of treatment (4 weeks after the last treatment). Complete cure was defined as both a clinical cure (absence of erythema, pruritus, and scaling) and mycological cure (negative KOH and dermatophyte culture).
The efficacy results at week 6, four weeks following the end of treatment, are presented in Table 1 below. Naftin Gel demonstrated complete cure in subjects with interdigital type tinea pedis.
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint | NAFTIN Gel, 2% N=382 n (%) |
Vehicle N=179 n (%) |
NAFTIN Gel, 2% N=400 n (%) |
Vehicle N=213 n (%) |
| Complete Cure |
64 (17%) | 3 (2%) | 104 (26%) | 7 (3%) |
| Treatment Effectiveness |
207 (54%) | 11 (6%) | 203 (51%) | 15 (7%) |
| Mycological Cure |
250 (65%) | 25 (14%) | 235 (59%) | 22 (10%) |
An open-label, multi-center, multi-application study was conducted with 28 subjects (22 pediatric and six adult subjects) with tinea pedis. Subjects applied the study agent (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% to the affected area plus a ½-inch margin of healthy skin surrounding the affected area once-daily for 2 weeks. Signs and symptoms of tinea pedis (presence or absence of erythema, pruritus, and scaling) were assessed, and KOH examination and dermatophyte culture were performed at the primary efficacy endpoint at week 4.
Mean (±SD) pediatric subject age was 15 ± 1.7 years and ranged from 12 to 17 years, the majority were male (82%) and Black or African American (73%), and were of Hispanic ethnicity (73%). Among adult subjects, most were male (67%), were Black or African American (67%) or White (33%), and most were not of Hispanic ethnicity (83%). Mean (±SD) adult subject age was 32 ± 11.2 years and ranged from 21 to 51 years.
While positive results were observed as early as Day 7 for some efficacy measures, the proportion of subjects achieving each efficacy endpoint (ie, complete cure, effective treatment, mycological cure, clinical success, and clinical cure) generally increased over time through Day 28. The findings for each of the efficacy parameters are briefly summarized below.
| Endpoint | Pediatric Subjects N=22 |
Adults N=6 |
|---|---|---|
| Tinea Pedis | Tinea Pedis | |
| Complete Cure |
1(4.5%) | 0(0%) |
| Effective Treatment |
7(31.8%) | 0(0.0%) |
| Mycological Cure |
8(36.4%) | 1(20.0%) |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is a colorless to yellow gel supplied in collapsible tubes in the following size:
2g – NDC 0259-1202-02
45g – NDC 0259-1202-45
60g – NDC 0259-1202-60
Storage
Store NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Inform patients that NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is for topical use only. NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is not intended for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
- Patients should be directed to contact their physician if irritation develops with the use of NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% .
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) Gel, 2% is manufactured for Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Greensboro, NC 27410.
NAFTIN (naftifine hydrochloride) is a registered trademark of Merz Pharmaceuticals, LLC.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 45g Tube Carton
NDC 0259-1202-45
NAFTIN
®
(Naftifine Hydrochloride) Gel, 2%
New
Strength
MERZ
For Topical Use Only
Not for Ophthalmic, Oral or Intravaginal Use
45g
Rx Only

NaftinNaftifine Hydrochloride GEL
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||