Neostigmine Methylsulfate
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE DESCRIPTION
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP, an anticholinesterase agent, is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of neostigmine methylsulfate in Water for Injection intended for intramuscular (IM), intravenous (IV) or subcutaneous (SC) administration.
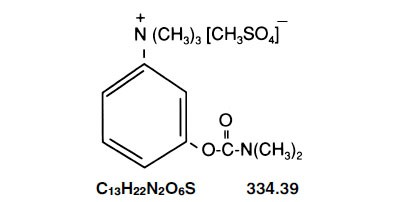
Neostigmine methylsulfate is chemically designated (m-hydroxyphenyl) trimethylammonium methyl sulfate dimethylcarbamate, having the following structural formula:
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection is available in 0.5 and1 mg/mL strengths. The composition per mL is as follows:
|
Ingredients |
mg/mL |
|
|
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Phenol Sodium acetate Water for Injection |
0.5
(1:2000) 4.5 0.2 q.s. |
1
(1:1000) 4.5 0.2 q.s. |
Acetic acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added to adjust pH to approximately 5.9. Phenol is added as a preservative.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Neostigmine inhibits the hydrolysis of acetylcholine by competing with acetylcholine for attachment to acetylcholinesterase at sites of cholinergic transmission. It enhances cholinergic action by facilitating the transmission of impulses across neuromuscular junctions. It also has a direct cholinomimetic effect on skeletal muscle and possibly on autonomic ganglion cells and neurons of the central nervous system (CNS). Neostigmine undergoes hydrolysis by cholinesterase and is also metabolized by microsomal enzymes in the liver. Protein binding to human serum albumin ranges from 15 to 25%.
Following IM administration, neostigmine is rapidly absorbed and eliminated. In a study of five patients with myasthenia gravis, peak plasma levels were observed at 30 minutes, and the half-life ranged from 51 to 90 minutes. Approximately 80% of the drug was eliminated in urine within 24 hours; approximately 50% as the unchanged drug, and 30% as metabolites.
Following IV administration, plasma half-life ranges from 47 to 60 minutes have been reported with a mean halflife of 53 minutes.
The clinical effects of neostigmine usually begin within 20 to 30 minutes after IM injection and last from 2.5 to 4 hours.
NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP is indicated for:
• The symptomatic control of myasthenia gravis when oral therapy is impractical.
• The prevention and treatment of postoperative distention and urinary retention after mechanical obstruction has been excluded.
• Reversal of effects of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents (e.g., tubocurarine, metocurine, gallamine or pancuronium) after surgery.
NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug. It is also contraindicated in patients with peritonitis or mechanical obstruction of the intestinal or urinary tract.
WARNINGS
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection should be used with caution in patients with epilepsy, bronchial asthma, bradycardia, recent coronary occlusion, vagotonia, hyperthyroidism, cardiac arrhythmias or peptic ulcer. When large doses of Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection are administered, the prior or simultaneous injection of atropine sulfate may be advisable. Separate syringes should be used for the neostigmine methylsulfate and atropine. Because of the possibility of hypersensitivity in an occasional patient, atropine and antishock medication should always be readily available.
PRECAUTIONS
General
It is important to differentiate between myasthenic crisis and cholinergic crisis caused by overdosage of Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection. Both conditions result in extreme muscle weakness but require radically different treatment. (See OVERDOSAGE .)
Drug Interactions
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection does not antagonize, and may in fact prolong, the Phase I block of depolarizing muscle relaxants such as succinylcholine or decamethonium. Certain antibiotics, especially neomycin, streptomycin and kanamycin, have a mild but definite nondepolarizing blocking action which may accentuate neuromuscular block. These antibiotics should be used in the myasthenic patient only when definitely indicated, and then careful adjustment should be made of the anticholinesterase dosage. Local and some general anesthetics, antiarrhythmic agents and other drugs that interfere with neuromuscular transmission should be used cautiously, if at all, in patients with myasthenia gravis; the dose of neostigmine methylsulfate may have to be increased accordingly.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
There have been no studies with neostigmine methylsulfate which would permit an evaluation of its carcinogenic or mutagenic potential. Studies on the effect of neostigmine methylsulfate on fertility and reproduction have not been performed.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C — There are no adequate or well-controlled studies of neostigmine methylsulfate in either laboratory animals or in pregnant women. It is not known whether neostigmine methylsulfate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Neostigmine methylsulfate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic Effects —Anticholinesterase drugs may cause uterine irritability and induce premature labor when given IV to pregnant women near term.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether neostigmine methylsulfate is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from neostigmine methylsulfate in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Side effects are generally due to an exaggeration of pharmacological effects of which salivation and fasciculation are the most common. Bowel cramps and diarrhea may also occur.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported following the use of either neostigmine bromide or neostigmine methysulfate.
Allergic
Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis.
Neurologic
Dizziness, convulsions, loss of consciousness, drowsiness, headache, dysarthria, miosis and visual changes.
Cardiovascular
Cardiac arrhythmias (including bradycardia, tachycardia, atrioventricular block and nodal rhythm) and nonspecific electrocardiogram changes have been reported, as well as cardiac arrest, syncope and hypotension. These have been predominantly noted following the use of the injectable form of neostigmine methylsulfate.
Respiratory
Increased oral, pharyngeal and bronchial secretions, dyspnea, respiratory depression, respiratory arrest and bronchospasm.
Dermatologic
Rash and urticaria.
Gastrointestinal
Nausea, emesis, flatulence and increased peristalsis.
Genitourinary
Urinary frequency.
Musculoskeletal
Muscle cramps and spasm, arthralgia.
Miscellaneous
Diaphoresis, flushing and weakness.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of neostigmine methylsulfate can cause cholinergic crisis, which is characterized by increasing muscleweakness, and through involvement of the muscles of respiration, may result in death. Myasthenic crisis, due to an increase in the severity of the disease, is also accompanied by extreme muscle weakness and maybe difficult to distinguish from cholingeric crisis on a symptomatic basis. However, such differentiation is extremely important because increases in the dose of neostigmine methylsulfate or other drugs in this class, in the presence of cholinergic crisis or of a refractory or ‘‘insensitive’’ state, could have grave consequences. The two types of crisis may be differentiated by the use of edrophonium chloride as well as by clinical judgment.
Treatment of the two conditions differs radically. Whereas the presence of myasthenic crisis requires more intensive anticholinesterase therapy, cholinergic crisis calls for the prompt withdrawal of all drugs of this type. The immediate use of atropine in cholinergic crisis is also recommended.
Atropine may also be used to abolish or minimize gastrointestinal side effects or other muscarinic reactions; but such use,by masking signs of overdosage, can lead to inadvertent induction of cholinergic crisis.
The LD50 of neostigmine methylsulfate in mice is 0.3 ± 0.02 mg/kg IV, 0.54 ± 0.03 mg/kg SC and 0.395 ± 0.025 mg/kg IM; in rats the LD50 is 0.315 ± 0.019 mg/kg IV, 0.445 ±0.032 mg/kg SC and 0.423 ± 0.032 mg/kg IM.
NEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Symptomatic Control of Myasthenia Gravis
Symptomatic Control of Myasthenia Gravis One mL of the1:2000 solution (0.5 mg) IM or SC. Subsequent doses should be based on the individual patient’s response.
Prevention of Postoperative Distention and Urinary Retention
One mL of the 1:4000 solution (0.25 mg) IM or SC as soon as possible after operation; repeat every four to six hours for two or three days.
Treatment of Postoperative Distention
One mL of the 1:2000 solution (0.5 mg) IM or SC, as required.
Treatment of Urinary Retention
One mL of the 1:2000 solution (0.5 mg) IM or SC. If urination does not occur within an hour, the patient should be catheterized. After the patient has voided, or the bladder has been emptied, continue the 0.5 mg injections every three hours for at least five injections.
Reversal of Effects of Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
When neostigmine methylsulfate is administered IV, it is recommended that atropine sulfate (0.6 to 1.2 mg) also be given IV using separate syringes. Some authorities have recommended that the atropine be injected several minutes before the neostigmine methylsulfate rather than concomitantly. The usual dose is 0.5 to 2 mg neostigmine methylsulfate given by slow IV injection, repeated as required. Only in exceptional cases should the total dose of neostigmine methylsulfate exceed 5 mg. It is recommended that the patient be well ventilated and a patent airway maintained until complete recovery of normal respiration is assured. The optimum time for administration of the drug is during hyperventilation when the carbon dioxide level of the blood is low. It should never be administered in the presence of high concentrations of halothane or cyclopropane. In cardiac cases and severely ill patients, it is advisable to titrate the exact dose of neostigmine methylsulfate required, using a peripheral nerve stimulator device. In the presence of bradycardia, the pulse rate should be increased to about 80/min with atropine before administering neostigmine methylsulfate.
Parenteral drug products should beinspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP is supplied as:
|
Product No. |
NDC No. |
Strength |
Vial Size |
|
38210 |
63323-382-10 |
0.5 mg/mL (1:2000) |
10 mL multiple dose vial in packages of 10. |
|
38310 |
63323-383-10 |
1 mg/mL (1:1000) |
10 mL multiple dose vial in packages of 10. |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
PROTECT FROM LIGHT .
Retain vial in carton until time of use.

45781C
Revised: April 2008
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Neostigmine Methylsulfate 10 mL Multiple Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-382-10
38210
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP
5 mg/10 mL (1:2000)
(0.5 mg/mL)
For IM, IV or SC Use
10 mL Multiple Dose Vial
Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Neostigmine Methylsulfate 10 mL Multiple Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-382-10
38210
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP
5 mg/10 mL (1:2000)
(0.5 mg/mL)
For IM, IV or SC Use
10 mL Multiple Dose Vial
Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Neostigmine Methylsulfate 10 mL Multiple Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-383-10
38310
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP
10 mg/10 mL (1:1000)
(1 mg/mL)
For IM, IV or SC Use
10 mL Multiple Dose Vial
Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Neostigmine Methylsulfate 10 mL Multiple Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-383-10
38310
Neostigmine Methylsulfate Injection, USP
10 mg/10 mL (1:1000)
(1 mg/mL)
For IM, IV or SC Use
10 mL Multiple Dose Vial
10 Vials Rx only

Neostigmine MethylsulfateNEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neostigmine MethylsulfateNEOSTIGMINE METHYLSULFATE INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||