Neulasta
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Neulasta safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Neulasta. Neulasta (pegfilgrastim) injection, for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2002INDICATIONS AND USAGENeulasta is a leukocyte growth factor indicated to decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs associated with a clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia. (1) Neulasta is not indicated for the mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 6 mg administered subcutaneously once per chemotherapy cycle. (2) Do not administer between 14 days before and 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy. (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS6 mg per 0.6 mL in single use prefilled syringe. (3)CONTRAINDICATIONSDo not administer Neulasta to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim. (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Fatal splenic rupture can occur. Evaluate for splenomegaly or splenic rupture in patients with left upper abdominal or shoulder pain. (5.1) Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can occur. Evaluate for ARDS in patients who develop fever, lung infiltrates, or respiratory distress. Discontinue Neulasta in patients with ARDS. (5.2) Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur. Permanently discontinue Neulasta in patients with serious allergic reactions. (5.3) Severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur. (5.4) Side EffectsMost common adverse reactions (≥ 5% difference in incidence) in placebo controlled clinical trials are bone pain and pain in extremity. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amgen Inc. at 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. Physicians are encouraged to enroll pregnant patients in Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program by calling 1-800-772-6436 (1-800-77-AMGEN). (8.1) Nursing Mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman.(8.3) Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Neulasta have not been established. (8.4) Geriatric Use: No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed in patients age 65 and older. (8.5) Renal Impairment: No dose adjustment required. (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 NEULASTA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 NEULASTA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 NEULASTA CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 NEULASTA ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 NEULASTA DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- FDA APPROVED PATIENT LABELING
- PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - prefilled syringe, 6 mg
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Neulasta is indicated to decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs associated with a clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Neulasta is not indicated for the mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of Neulasta is a single subcutaneous injection of 6 mg administered once per chemotherapy cycle in adults. Do not administer Neulasta between 14 days before and 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Visually inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer Neulasta if discoloration or particulates are observed.
NOTE: The needle cover on the single-use prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (latex); persons with latex allergies should not administer this product.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
6 mg per 0.6 mL in single use prefilled syringe.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not administer Neulasta to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Splenic Rupture
Splenic rupture, including fatal cases, can occur following the administration of Neulasta. Evaluate for an enlarged spleen or splenic rupture in patients who report left upper abdominal or shoulder pain after receiving Neulasta.
5.2 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can occur in patients receiving Neulasta. Evaluate patients who develop fever and lung infiltrates or respiratory distress after receiving Neulasta, for ARDS. Discontinue Neulasta in patients with ARDS.
5.3 Serious Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients receiving Neulasta. The majority of reported events occurred upon initial exposure. Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can recur within days after the discontinuation of initial anti-allergic treatment. Permanently discontinue Neulasta in patients with serious allergic reactions. Do not administer Neulasta to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim.
5.4 Use in Patients With Sickle Cell Disorders
Severe sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving Neulasta. Severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving filgrastim, the parent compound of pegfilgrastim.
5.5 Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells
The granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor through which pegfilgrastim and filgrastim act has been found on tumor cell lines. The possibility that pegfilgrastim acts as a growth factor for any tumor type, including myeloid malignancies and myelodysplasia, diseases for which pegfilgrastim is not approved, cannot be excluded.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Splenic Rupture [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serious Allergic Reactions [See Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Use in Patients with Sickle Cell Disorders [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of patients and with a between-group difference of ≥ 5% higher in the pegfilgrastim arm in placebo controlled clinical trials are bone pain and pain in extremity.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Neulasta clinical trials safety data are based upon 932 patients receiving Neulasta in seven randomized clinical trials. The population was 21 to 88 years of age and 92% female. The ethnicity was 75% Caucasian, 18% Hispanic, 5% Black, and 1% Asian. Patients with breast (n = 823), lung and thoracic tumors (n = 53) and lymphoma (n = 56) received Neulasta after nonmyeloablative cytotoxic chemotherapy. Most patients received a single 100 mcg/kg (n = 259) or a single 6 mg (n = 546) dose per chemotherapy cycle over 4 cycles.
The following adverse reaction data in Table 1 are from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with metastatic or non-metastatic breast cancer receiving docetaxel 100 mg/m2 every 21 days (Study 3). A total of 928 patients were randomized to receive either 6 mg Neulasta (n = 467) or placebo (n = 461). The patients were 21 to 88 years of age and 99% female. The ethnicity was 66% Caucasian, 31% Hispanic, 2% Black, and <1% Asian, Native American or other.
Bone pain and pain in extremity occurred at a higher incidence in Neulasta-treated patients as compared with placebo-treated patients.
|
System Organ Class Preferred Term |
Placebo (N= 461) |
Neulasta 6 mg SC on Day 2 (N= 467) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Bone pain | 26% | 31% |
| Pain in extremity | 4% | 9% |
Leukocytosis
In clinical studies, leukocytosis (WBC counts > 100 x 109/L) was observed in less than 1% of 932 patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving Neulasta. No complications attributable to leukocytosis were reported in clinical studies.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. Binding antibodies to pegfilgrastim were detected using a BIAcore assay. The approximate limit of detection for this assay is 500 ng/mL. Pre-existing binding antibodies were detected in approximately 6% (51/849) of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Four of 521 pegfilgrastim-treated subjects who were negative at baseline developed binding antibodies to pegfilgrastim following treatment. None of these 4 patients had evidence of neutralizing antibodies detected using a cell-based bioassay.
The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay, and the observed incidence of antibody positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to Neulasta with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Neulasta. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Decisions to include these reactions in labeling are typically based on one or more of the following factors: (1) seriousness of the reaction, (2) reported frequency of the reaction, or (3) strength of causal relationship to Neulasta.
Gastro-intestinal disorders: Splenic rupture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Blood and lymphatic system disorder: Sickle cell crisis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Hypersensitivity reactions: Allergic reactions/hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, skin rash, and urticaria, generalized erythema and flushing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorder: ARDS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
General disorders and administration site conditions: Injection site reactions
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Sweet’s syndrome, Cutaneous vasculitis
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No formal drug interaction studies between Neulasta and other drugs have been performed. Increased hematopoietic activity of the bone marrow in response to growth factor therapy may result in transiently positive bone-imaging changes. Consider these findings when interpreting bone-imaging results.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Pegfilgrastim was embryotoxic and increased pregnancy loss in pregnant rabbits that received cumulative doses approximately 4 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area). Signs of maternal toxicity occurred at these doses. Neulasta should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In animal reproduction studies, when pregnant rabbits received pegfilgrastim at cumulative doses approximately 4 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area), increased embryolethality and spontaneous abortions occurred. Signs of maternal toxicity (reductions in body weight gain/food consumption) and decreased fetal weights occurred at maternal doses approximately equivalent to the recommended human dose (based on body surface area). There were no structural anomalies observed in rabbit offspring at any dose tested. No evidence of reproductive/developmental toxicity occurred in the offspring of pregnant rats that received cumulative doses of pegfilgrastim approximately 10 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area) [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.3)].
Women who become pregnant during Neulasta treatment are encouraged to enroll in Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program. Patients or their physicians should call 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) to enroll.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether pegfilgrastim is secreted in human milk. Other recombinant G-CSF products are poorly secreted in breast milk and G-CSF is not orally absorbed by neonates. Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Neulasta in pediatric patients have not been established. The adverse reaction profile and pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were studied in 37 pediatric patients with sarcoma. The mean (± standard deviation [SD]) systemic exposure (AUC0-inf) of pegfilgrastim after subcutaneous administration at 100 mcg/kg was 22.0 (± 13.1) mcg·hr/mL in the 6 to 11 years age group (n = 10), 29.3 (± 23.2) mcg·hr/mL in the 12 to 21 years age group (n = 13), and 47.9 (± 22.5) mcg·hr/mL in the youngest age group (0 to 5 years, n = 11). The terminal elimination half-lives of the corresponding age groups were 20.2 (± 11.3) hours, 21.2 (± 16.0) hours, and 30.1 (± 38.2) hours, respectively. The most common adverse reaction was bone pain.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 932 patients with cancer who received Neulasta in clinical studies, 139 (15%) were age 65 and over, and 18 (2%) were age 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients age 65 and older and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
In a study of 30 subjects with varying degrees of renal dysfunction, including end stage renal disease, renal dysfunction had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim. Therefore, pegfilgrastim dose adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction is not necessary [Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
The maximum amount of Neulasta that can be safely administered in single or multiple doses has not been determined. Single subcutaneous doses of 300 mcg/kg have been administered to 8 healthy volunteers and 3 patients with non-small cell lung cancer without serious adverse effects. These patients experienced a mean maximum absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 55 x 109/L, with a corresponding mean maximum WBC of 67 x 109/L. The absolute maximum ANC observed was 96 x 109/L with a corresponding absolute maximum WBC observed of 120 x 109/L. The duration of leukocytosis ranged from 6 to 13 days. The effectiveness of leukapheresis in the management of symptomatic individuals with Neulasta-induced leukocytosis has not been studied.
11 DESCRIPTION
Neulasta (pegfilgrastim) is a covalent conjugate of recombinant methionyl human G-CSF (filgrastim) and monomethoxypolyethylene glycol. Filgrastim is a water-soluble 175 amino acid protein with a molecular weight of approximately 19 kilodaltons (kD). Filgrastim is obtained from the bacterial fermentation of a strain of E coli transformed with a genetically engineered plasmid containing the human G-CSF gene. To produce pegfilgrastim, a 20 kD monomethoxypolyethylene glycol molecule is covalently bound to the N-terminal methionyl residue of filgrastim. The average molecular weight of pegfilgrastim is approximately 39 kD.
Neulasta is supplied in 0.6 mL prefilled syringes for subcutaneous injection. Each syringe contains 6 mg pegfilgrastim (based on protein weight) in a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution (pH 4.0) containing acetate (0.35 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.02 mg), sodium (0.02 mg), and sorbitol (30 mg) in Water for Injection, USP.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pegfilgrastim is a colony-stimulating factor that acts on hematopoietic cells by binding to specific cell surface receptors, thereby stimulating proliferation, differentiation, commitment, and end cell functional activation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were studied in 379 patients with cancer. The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were nonlinear and clearance decreased with increases in dose. Neutrophil receptor binding is an important component of the clearance of pegfilgrastim, and serum clearance is directly related to the number of neutrophils. In addition to numbers of neutrophils, body weight appeared to be a factor. Patients with higher body weights experienced higher systemic exposure to pegfilgrastim after receiving a dose normalized for body weight. A large variability in the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim was observed. The half-life of Neulasta ranged from 15 to 80 hours after subcutaneous injection.
No gender-related differences were observed in the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim, and no differences were observed in the pharmacokinetics of geriatric patients (≥ 65 years of age) compared with younger patients (< 65 years of age) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were studied in pediatric patients with sarcoma [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Renal dysfunction had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. The pharmacokinetic profile in patients with hepatic insufficiency has not been assessed.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or mutagenesis studies have been performed with pegfilgrastim.
Pegfilgrastim did not affect reproductive performance or fertility in male or female rats at cumulative weekly doses approximately 6 to 9 times higher than the recommended human dose (based on body surface area).
13.3 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
Pregnant rabbits were dosed with pegfilgrastim subcutaneously every other day during the period of organogenesis. At cumulative doses ranging from the approximate human dose to approximately 4 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area), treated rabbits exhibited decreased maternal food consumption, maternal weight loss, as well as reduced fetal body weights and delayed ossification of the fetal skull; however, no structural anomalies were observed in the offspring from either study. Increased incidences of post-implantation losses and spontaneous abortions (more than half the pregnancies) were observed at cumulative doses approximately 4 times the recommended human dose, which were not seen when pregnant rabbits were exposed to the recommended human dose.
Three studies were conducted in pregnant rats dosed with pegfilgrastim at cumulative doses up to approximately 10 times the recommended human dose at the following stages of gestation: during the period of organogenesis, from mating through the first half of pregnancy, and from the first trimester through delivery and lactation. No evidence of fetal loss or structural malformations was observed in any study. Cumulative doses equivalent to approximately 3 and 10 times the recommended human dose resulted in transient evidence of wavy ribs in fetuses of treated mothers (detected at the end of gestation but no longer present in pups evaluated at the end of lactation).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Neulasta was evaluated in three randomized, double blind, controlled studies. Studies 1 and 2 were active-controlled studies that employed doxorubicin 60 mg/m2 and docetaxel 75 mg/m2 administered every 21 days for up to 4 cycles for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Study 1 investigated the utility of a fixed dose of Neulasta. Study 2 employed a weight-adjusted dose. In the absence of growth factor support, similar chemotherapy regimens have been reported to result in a 100% incidence of severe neutropenia (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L) with a mean duration of 5 to 7 days and a 30% to 40% incidence of febrile neutropenia. Based on the correlation between the duration of severe neutropenia and the incidence of febrile neutropenia found in studies with filgrastim, duration of severe neutropenia was chosen as the primary endpoint in both studies, and the efficacy of Neulasta was demonstrated by establishing comparability to filgrastim-treated patients in the mean days of severe neutropenia.
In Study 1, 157 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (6 mg) on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle or daily subcutaneous filgrastim (5 mcg/kg/day) beginning on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle. In Study 2, 310 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (100 mcg/kg) on day 2 or daily subcutaneous filgrastim (5 mcg/kg/day) beginning on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle.
Both studies met the major efficacy outcome measure of demonstrating that the mean days of severe neutropenia of Neulasta-treated patients did not exceed that of filgrastim-treated patients by more than 1 day in cycle 1 of chemotherapy. The mean days of cycle 1 severe neutropenia in Study 1 were 1.8 days in the Neulasta arm compared to 1.6 days in the filgrastim arm [difference in means 0.2 (95% CI -0.2, 0.6)] and in Study 2 were 1.7 days in the Neulasta arm compared to 1.6 days in the Filgrastim arm [difference in means 0.1 (95% CI -0.2, 0.4)].
A secondary endpoint in both studies was days of severe neutropenia in cycles 2 through 4 with results similar to those for cycle 1.
Study 3 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that employed docetaxel 100 mg/m2 administered every 21 days for up to 4 cycles for the treatment of metastatic or non-metastatic breast cancer. In this study, 928 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (6 mg) or placebo on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle. Study 3 met the major trial outcome measure of demonstrating that the incidence of febrile neutropenia (defined as temperature ≥ 38.2°C and ANC ≤ 0.5 x109/L) was lower for Neulasta-treated patients as compared to placebo-treated patients (1% versus 17%, respectively, p < 0.001). The incidence of hospitalizations (1% versus 14%) and IV anti-infective use (2% versus 10%) for the treatment of febrile neutropenia was also lower in the Neulasta-treated patients compared to the placebo-treated patients.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Neulasta is supplied in a prefilled single use syringe containing 6 mg pegfilgrastim, supplied with a 27-gauge, 1/2-inch needle with an UltraSafe® Needle Guard.
The needle cover of the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
Neulasta is provided in a dispensing pack containing one syringe
(NDC 55513-190-01).
Store refrigerated between 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) in the carton to protect from light. Do not shake. Discard syringes stored at room temperature for more than 48 hours. Avoid freezing; if frozen, thaw in the refrigerator before administration. Discard syringe if frozen more than once.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients of the following risks:
- Splenic rupture
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Serious allergic reactions
- Sickle cell crisis
Have patients immediately contact their healthcare provider and report:
- Left upper quadrant or shoulder pain
- Shortness of breath
- Signs or symptoms of sickle cell crisis
- Signs or symptoms of infection
- Flushing, dizziness, or rash
[Amgen Logo]
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/neulasta/
© 2002-2014 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
www.neulasta.com
1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436)
1xxxxx
v14
FDA APPROVED PATIENT LABELING
Neulasta®
Pegfilgrastim
Information for Patients and Caregivers
This patient package insert provides information and instructions for people who will be receiving Neulasta or their caregivers. This patient package insert does not tell you everything about Neulasta. You should discuss any questions you have about treatment with Neulasta with your doctor.
What is Neulasta?
Neulasta is a man-made form of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), which is made using the bacteria Escherichia coli. G-CSF is a substance produced by the body. It stimulates the growth of neutrophils (nu-tro-fils), a type of white blood cell important in the body’s fight against infection.
Who should not take Neulasta?
Do not take Neulasta if you have had:
- A serious allergic reaction to Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim) or to Neupogen® (filgrastim).
What important information do I need to know about receiving Neulasta?
Occasionally, pain and redness may occur at the injection site. If there is a lump, swelling, or bruising at the injection site that does not go away, talk to the doctor.
Neulasta should only be injected on the day the doctor has determined and should not be injected until approximately 24 hours after receiving chemotherapy.
The needle cover on the single-use prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (latex), which should not be handled by persons sensitive to this substance.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Neulasta?
If you have a sickle cell disorder, make sure that your doctor knows about it before you start using Neulasta. If you have a sickle cell crisis after getting Neulasta, tell your doctor right away.
If you have any questions, talk to your doctor.
What are possible serious side effects of Neulasta?
- Spleen Rupture. Your spleen may become enlarged and can rupture while taking Neulasta. A ruptured spleen can cause death. The spleen is located in the upper left section of your stomach area. Call your doctor right away if you have pain in the left upper stomach area or left shoulder tip area. This pain could mean your spleen is enlarged or ruptured.
- A serious lung problem called Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Call your doctor or seek emergency care right away if you have shortness of breath, trouble breathing, or a fast rate of breathing.
- Serious Allergic Reactions. Neulasta can cause serious allergic reactions. These reactions can cause shortness of breath, wheezing, dizziness, swelling around the mouth or eyes, fast pulse, sweating, and hives. If you start to have any of these symptoms, call your doctor or seek emergency care right away. If you have an allergic reaction during the injection of Neulasta, stop the injection. Call your doctor right away.
- Sickle Cell Crises. You may have a serious sickle cell crisis if you have a sickle cell disorder and take Neulasta. Serious and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving filgrastim, a medicine similar to Neulasta (pegfilgrastim). Call your doctor right away if you have symptoms of sickle cell crisis such as pain or difficulty breathing.
What are the most common side effects of Neulasta?
The most common side effect you may experience is aching in the bones and muscles. If this happens, it can usually be relieved with a non-aspirin pain reliever, such as acetaminophen.
What about pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Neulasta has not been studied in pregnant women, and its effects on unborn babies are not known. If you take Neulasta while you are pregnant, it is possible that small amounts of it may get into your baby’s blood. It is not known if Neulasta can get into human breast milk. If you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are breastfeeding, you should tell your doctor before using Neulasta. If you become pregnant during Neulasta treatment, you are encouraged to enroll in Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program. You should call 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) to enroll.
HOW TO PREPARE AND GIVE A NEULASTA INJECTION
Neulasta is provided in a prefilled syringe. Neulasta should be stored in its carton to protect from light until use. If you are giving someone else Neulasta injections, it is important that you know how to inject Neulasta. Before getting your Neulasta injection, always check to see that:
- The name Neulasta appears on the carton and prefilled syringe label.
- The expiration date on the prefilled syringe has not passed. You should not use a prefilled syringe after the date on the label.
- The Neulasta liquid should always be clear and colorless. Do not use Neulasta if the contents of the prefilled syringe appear discolored or cloudy, or if the prefilled syringe appears to contain lumps, flakes, or particles.
IMPORTANT: TO HELP AVOID POSSIBLE INFECTION, YOU SHOULD FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Setting up for an injection
Note: The needle cover on the single-use prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (latex), which should not be handled by persons sensitive to this substance.
- Find a clean, flat working surface, such as a table.
- Remove the carton containing the prefilled syringe of Neulasta from the refrigerator. Allow Neulasta to reach room temperature (this takes about 30 minutes). Remove the syringe from the carton before injection. Each prefilled syringe should be used only once. DO NOT SHAKE THE PREFILLED SYRINGE. Shaking may damage Neulasta. If the prefilled syringe has been shaken vigorously, the solution may appear foamy and it should not be used.
- Assemble the supplies you will need for an injection:
- Neulasta prefilled syringe with transparent (clear) plastic blue needle guard attached
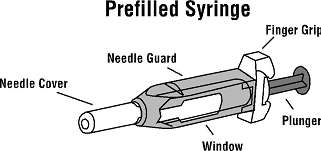
- An alcohol swab and a cotton ball or gauze

- Puncture-proof disposal container
- Neulasta prefilled syringe with transparent (clear) plastic blue needle guard attached
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water.
HOW TO PREPARE FOR INJECTION OF NEULASTA
- Remove the prefilled syringe from the package and the tray. Check to see that the plastic blue needle guard is covering the barrel of the glass syringe. DO NOT push the blue needle guard over the needle cover before injection. This may activate or lock the needle guard. If the blue needle guard is covering the needle that means it has been activated. DO NOT use that syringe. Dispose of that syringe in the puncture-proof disposal container. Use a new prefilled syringe. Do not activate the needle guard prior to injection.
- Hold the syringe barrel through the needle guard windows with the needle pointing up. Holding the syringe with the needle pointing up helps to prevent medicine from leaking out of the needle. Carefully pull the needle cover straight off.
- Check the syringe for air bubbles. If there are air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your fingers until the air bubbles rise to the top of the syringe. Slowly push the plunger up to force the air bubbles out of the syringe.
- Gently place the prefilled syringe with the window flat on your clean working surface so that the needle does not touch anything.
Selecting and preparing the injection site
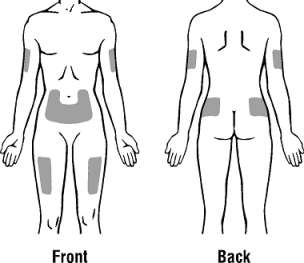
- Choose an injection site. Four recommended injection sites for Neulasta are:
- The outer area of the upper arms
- The abdomen, except for the two-inch area around the navel
- The front of the middle thighs
- The upper outer areas of the buttocks
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab.
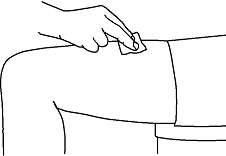
Injecting the dose of Neulasta
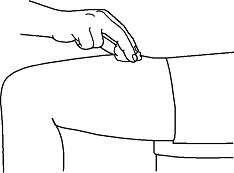
- Pick up the prefilled syringe from your clean, flat working surface by grabbing the sides of the needle guard with your thumb and forefinger.
- Hold the syringe in the hand you will use to inject Neulasta. Use the other hand to pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site. Note: Hold the syringe barrel through the needle guard windows when giving the injection.
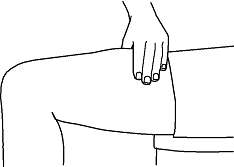
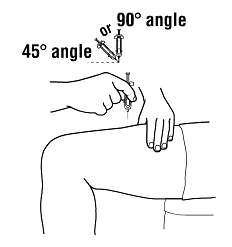
- Holding the syringe like a pencil, use a quick “dart-like” motion to insert the needle either straight up and down (90 degree angle) or at a slight angle (45 degrees) into the skin.
- Inject the prescribed dose subcutaneously as directed by your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
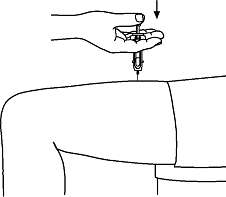
- When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of the skin and place a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site and press for several seconds.
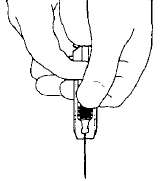
- Use a prefilled syringe with the needle guard only once.
Activating the Needle Guard after the injection has been given
- After injecting Neulasta from the prefilled syringe, do not recap the needle. Keep your hands behind the needle at all times. While holding the clear plastic finger grip of the syringe with one hand, grasp the blue needle guard with your free hand and slide the blue needle guard over the needle until the needle is completely covered and the needle guard clicks into place. NOTE: If an audible click is not heard, the needle guard may not be completely activated.
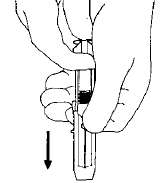
- Place the prefilled syringe with the activated needle guard into a puncture-proof container for proper disposal as described below.
Disposal of prefilled syringes and needle guards
You should always follow the instructions given by your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist on how to properly dispose of containers with used syringes and needle guards. There may be special state and local laws for disposal of used needles and syringes.
- Do not throw the container in the household trash. Do not recycle.
- DO NOT put the needle cover (the cap) back on the needle.
- Place all used needle covers and syringes in a hard plastic container with a screw-on cap or in a metal container with a plastic lid such as a coffee can labeled “used syringes.” If a metal container is used, cut a small hole in the plastic lid and tape the lid to the metal container. If a hard plastic container is used, always screw the cap on tightly after each use.
- Do not use glass or clear plastic containers.
- When the container is full, tape around the cap or lid to make sure the cap or lid does not come off.
- Always keep the container out of the reach of children.
How should Neulasta be stored?
Neulasta should be stored in the refrigerator at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F), but not in the freezer. Neulasta should be protected from light, so you should keep it in its carton until you are ready to use it. Avoid shaking Neulasta. If Neulasta is accidentally frozen, allow it to thaw in the refrigerator before injecting. However, if it is frozen a second time, do not use. Neulasta can be left out at room temperature for up to 48 hours. Do not leave Neulasta in direct sunlight. For all questions about storage, contact your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.
What are the ingredients in Neulasta?
Each syringe contains pegfilgrastim in a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution containing acetate, sorbitol, polysorbate 20, and sodium.
[Amgen logo]
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/neulasta/
© 2002-2014 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
www.neulasta.com
1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436)
Revised: 02/2014
1xxxxx
v10
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - prefilled syringe, 6 mg
NDC 55513-190-01
1 - 0.6 mL Single Use Prefilled Syringe
AMGEN®
Neulasta ®
(pegfilgrastim)
Pegylated Recombinant Methionyl Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
(PEG-r-metHuG-CSF) derived from E Coli
6 mg
6 mg in 0.6 mL Single Use Prefilled Syringe
For Subcutaneous Use Only
This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
Rx Only
Manufactured by Amgen Manufacturing, Limited, a subsidiary of Amgen Inc.
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A.
U.S. License No. 108

Neulastapegfilgrastim INJECTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||