Nevirapine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use nevirapine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for nevirapine oral suspension, USP. Nevirapine Oral Suspension, USPInitial U.S. Approval: 1996BOXED WARNING WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Fatal and non-fatal hepatotoxicity (5.1) Fatal and non-fatal skin reactions (5.2) Discontinue immediately if experiencing: Signs or symptoms of hepatitis (5.1) Increased transaminases combined with rash or other systemic symptoms (5.1) Severe skin or hypersensitivity reactions (5.2) Any rash with systemic symptoms (5.2) Monitoring during the first 18 weeks of therapy is essential. Extra vigilance is warranted during the first 6 weeks of therapy, which is the period of greatest risk of these events (5).INDICATIONS AND USAGE Nevirapine is an NNRTI indicated for combination antiretroviral treatment of HIV-1 infection (1) Initiation of treatment is not recommended in the following populations unless the benefits outweigh the risks (1, 5.1) adult females with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3 adult males with CD4+ cell counts greater than 400 cells/mm3 The 14-day lead-in period must be strictly followed; it has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency of rash (2.4, 5.2) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION If any patient experiences rash during the 14-day lead-in period, do not increase dose until the rash has resolved. Do not continue the lead-in dosing regimen beyond 28 days (2.4) If dosing is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart 14-day lead-in dosing (2.4) *Total daily dose should not exceed 400 mg for any patient. Adults (≥16 yrs) Pediatric* (>15 days) First 14 days 200 mg once daily 150 mg/m2 once daily After 14 days 200 mg twice daily 150 mg/m2 twice daily DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 50 mg per 5 mL oral suspension (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Patients with moderate or severe (Child-Pugh Class B or C, respectively) hepatic impairment (4.1, 5.1, 8.7) Use as part of occupational and non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimens, an unapproved use (4.2, 5.1) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hepatotoxicity: Fatal and non-fatal hepatotoxicity has been reported. Monitor liver function tests before and during therapy. Permanently discontinue nevirapine if clinical hepatitis or transaminase elevations combined with rash or other systemic symptoms occur. Do not restart nevirapine after recovery (5.1) Rash: Fatal and non-fatal skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions, have been reported. Permanently discontinue nevirapine if severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions occur. Check transaminase immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment (5.2) Monitor patients for immune reconstitution syndrome and fat redistribution (5.5, 5.6) Side Effects The most common adverse reaction is rash. In adults the incidence of rash is 15% vs. 6% with placebo, with Grade 3/4 rash occurring in 2% of subjects (6.1) In pediatric subjects the incidence of rash (all causality) was 21% (6.2) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS(5.4712.3)USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Monitor patients with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis carefully for evidence of drug induced toxicity. Do not administer nevirapine to patients with Child-Pugh B or C (5.1, 8.7) No dose adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment. Patients on dialysis receive an additional dose of 200 mg following each dialysis treatment (8.6) Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry available (8.1)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS
- 1 NEVIRAPINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 NEVIRAPINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 NEVIRAPINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 NEVIRAPINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 NEVIRAPINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg/5 mL (240 mL Bottle)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING (INCLUDING FATAL) HEPATOTOXICITY and SKIN REACTIONS
HEPATOTOXICITY
Severe, life-threatening, and in some cases fatal hepatotoxicity, particularly in the first 18 weeks, has been reported in patients treated with nevirapine. In some cases, patients presented with non-specific prodromal signs or symptoms of hepatitis and progressed to hepatic failure. These events are often associated with rash. Female gender and higher CD4+ cell counts at initiation of therapy place patients at increased risk; women with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3, including pregnant women receiving nevirapine in combination with other antiretrovirals for the treatment of HIV-1 infection, are at the greatest risk. However, hepatotoxicity associated with nevirapine use can occur in both genders, all CD4+ cell counts and at any time during treatment. Hepatic failure has also been reported in patients without HIV taking nevirapine for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). Use of nevirapine for occupational and non-occupational PEP is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.2)]. Patients with signs or symptoms of hepatitis, or with increased transaminases combined with rash or other systemic symptoms, must discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
SKIN REACTIONS
Severe, life-threatening skin reactions, including fatal cases, have occurred in patients treated with nevirapine. These have included cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and hypersensitivity reactions characterized by rash, constitutional findings, and organ dysfunction. Patients developing signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions must discontinue nevirapine and seek medical evaluation immediately. Transaminase levels should be checked immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment. The 14-day lead-in period with nevirapine 200 mg daily dosing has been observed to decrease the incidence of rash and must be followed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
MONITORING
Patients must be monitored intensively during the first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine to detect potentially life-threatening hepatotoxicity or skin reactions. Extra vigilance is warranted during the first 6 weeks of therapy, which is the period of greatest risk of these events. Do not restart nevirapine following clinical hepatitis, or transaminase elevations combined with rash or other systemic symptoms, or following severe skin rash or hypersensitivity reactions. In some cases, hepatic injury has progressed despite discontinuation of treatment.
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Based on serious and life-threatening hepatotoxicity observed in controlled and uncontrolled trials, nevirapine oral suspension, USP should not be initiated in adult females with CD4+ cell counts greater than 250 cells/mm3 or in adult males with CD4+ cell counts greater than 400 cells/mm3 unless the benefit outweighs the risk [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- The 14-day lead-in period with nevirapine oral suspension USP, 200 mg daily dosing must be strictly followed; it has been demonstrated to reduce the frequency of rash [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- If rash persists beyond the 14-day lead-in period, do not dose escalate to 200 mg twice daily. The 200 mg once-daily dosing regimen should not be continued beyond 28 days, at which point an alternative regimen should be sought.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
2.2 Pediatric Patients
22
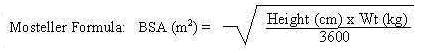
| BSA range (m2) | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|
| 0.06 – 0.12 |
1.25 |
| 0.12 – 0.25 |
2.5 |
| 0.25 – 0.42 |
5 |
| 0.42 – 0.58 |
7.5 |
| 0.58 – 0.75 |
10 |
| 0.75 – 0.92 |
12.5 |
| 0.92 – 1.08 |
15 |
| 1.08 – 1.25 |
17.5 |
| 1.25+ |
20 |
2.3 Monitoring of Patients
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
2.4 Dosage Adjustment
Patients with Rash
Discontinue nevirapine oral suspension if a patient experiences severe rash or any rash accompanied by constitutional findings [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)]Do not increase nevirapine oral suspension dose if a patient experiences mild to moderate rash without constitutional symptoms during the 14-day lead-in period of 200 mg/day (150 mg/m2/day in pediatric patients) until the rash has resolved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17.1) ] The total duration of the once daily lead-in dosing period should not exceed 28 days at which point an alternative regimen should be sought.
Patients with Hepatic Events
If a clinical (symptomatic) hepatic event occurs, permanently discontinue nevirapine oral suspension. Do not restart nevirapine oral suspension after recovery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Patients with Dose Interruption
22
Patients with Renal Impairment
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hepatic Impairment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ]
4.2 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
The first 18 weeks of therapy with nevirapine are a critical period during which intensive clinical and laboratory monitoring of patients is required to detect potentially life-threatening hepatic events and skin reactions.[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
5.1 Hepatotoxicity and Hepatic Impairment
Transaminases should be checked immediately if a patient experiences signs or symptoms suggestive of hepatitis and/or hypersensitivity reaction. Transaminases should also be checked immediately for all patients who develop a rash in the first 18 weeks of treatment. Physicians and patients should be vigilant for the appearance of signs or symptoms of hepatitis, such as fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, bilirubinuria, acholic stools, liver tenderness or hepatomegaly. The diagnosis of hepatotoxicity should be considered in this setting, even if transaminases are initially normal or alternative diagnoses are possible [see Boxed Warning, Dosage and Administration (2.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)]
+++3+3+3+3++
[see Contraindications (4.2)].
[see Contraindications (4.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
5.2 Skin Reactions
[see Boxed Warning and Patient Counseling Information (17.1) ]
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
22. [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]
5.3 Resistance
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]
5.4 Drug Interactions
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
Hypericum perforatum
5.5 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Mycobacterium avium Pneumocystis jiroveci
5.6 Fat Redistribution
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials in Adults
[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Hepatic Reaction
+33[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Skin Reaction
[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)][see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
| Trial 10901 | Trials 1037, 1038, 10462 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nevirapine (n=1121) |
Placebo (n=1128) |
Nevirapine (n=253) |
Placebo (n=203) |
|
|
1 Background therapy included 3TC for all subjects and combinations of NRTIs and PIs. Subjects had CD4+ cell counts less than 200 cells/mm3. 2 Background therapy included ZDV and ZDV+ddI; nevirapine monotherapy was administered in some subjects. Subjects had CD4+ cell count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3. |
||||
| Median exposure (weeks) |
58 |
52 |
28 |
28 |
| Any adverse event |
15% |
11% |
32% |
13% |
| Rash |
5 |
2 |
7 |
2 |
| Nausea |
1 |
1 |
9 |
4 |
| Granulocytopenia |
2 |
3 |
<1 |
0 |
| Headache |
1 |
<1 |
4 |
1 |
| Fatigue |
<1 |
<1 |
5 |
4 |
| Diarrhea |
<1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
| Abdominal pain |
<1 |
<1 |
2 |
0 |
| Myalgia |
<1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
Laboratory Abnormalities
| Laboratory Abnormality | Trial 10901 | Trials 1037, 1038, 10462 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nevirapine (n=1121) |
Placebo (n=1128) |
Nevirapine (n=253) |
Placebo (n=203) |
|
|
1 Background therapy included 3TC for all subjects and combinations of NRTIs and PIs. Subjects had CD4+ cell counts less than 200 cells/mm3. 2 Background therapy included ZDV and ZDV+ddI; nevirapine monotherapy was administered in some subjects. Subjects had CD4+ cell count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3. |
||||
|
Blood Chemistry
|
||||
| SGPT (ALT) >250 U/L |
5 |
4 |
14 |
4 |
| SGOT (AST) >250 U/L |
4 |
3 |
8 |
2 |
| Bilirubin >2.5 mg/dL |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Hematology
|
||||
| Hemoglobin <8 g/dL |
3 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
| Platelets <50,000/mm3
|
1 |
1 |
<1 |
2 |
| Neutrophils <750/mm3
|
13 |
14 |
4 |
1 |
6.2 Clinical Trials in Pediatric Subjects
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)][see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.2)]
6.3 Post-Marketing Experience
Body as a Whole: [see Drug Interactions (7)], [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Gastrointestinal:
Liver and Biliary:
Hematology:
Investigations:
Musculoskeletal:
Neurologic:
Skin and Appendages: [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Clinical Pharmacology,
in vitro
| Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Nevirapine or Concomitant Drug |
Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Atazanavir/Ritonavir |
↓ Atazanavir ↑ Nevirapine |
Do not co-administer nevirapine with atazanavir because nevirapine substantially decreases atazanavir exposure. |
| Clarithromycin |
↓ Clarithromycin ↑ 14-OH clarithromycin |
Clarithromycin exposure was significantly decreased by nevirapine; however, 14-OH metabolite concentrations were increased. Because clarithromycin active metabolite has reduced activity against Mycobacterium avium- intracellulare complex, overall activity against this pathogen may be altered. Alternatives to clarithromycin, such as azithromycin, should be considered. |
| Efavirenz |
↓ Efavirenz |
There has been no determination of appropriate doses for the safe and effective use of this combination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]. |
| Ethinyl estradiol and Norethindrone |
↓ Ethinyl estradiol ↓ Norethindrone |
Oral contraceptives and other hormonal methods of birth control should not be used as the sole method of contraception in women taking nevirapine, since nevirapine may lower the plasma levels of these medications. An alternative or additional method of contraception is recommended. |
| Fluconazole |
↑ Nevirapine |
Because of the risk of increased exposure to nevirapine, caution should be used in concomitant administration, and patients should be monitored closely for nevirapine -associated adverse events. |
| Fosamprenavir |
↓Amprenavir ↑Nevirapine |
Co-administration of nevirapine and fosamprenavir without ritonavir is not recommended. |
| Fosamprenavir/Ritonavir |
↓Amprenavir ↑Nevirapine |
No dosing adjustments are required when nevirapine is co-administered with 700/100 mg of fosamprenavir/ritonavir twice daily. |
| Indinavir |
↓ Indinavir |
Appropriate doses for this combination are not established, but an increase in the dosage of indinavir may be required. |
| Ketoconazole |
↓ Ketoconazole |
Nevirapine and ketoconazole should not be administered concomitantly because decreases in ketoconazole plasma concentrations may reduce the efficacy of the drug. |
| Lopinavir/Ritonavir |
↓Lopinavir |
A dose increase of lopinavir/ritonavir tablets to 500/125 mg twice-daily is recommended when used in combination with nevirapine. A dose increase of lopinavir/ritonavir oral solution to 533/133 mg twice daily with food is recommended in combination with nevirapine. In children 6 months to 12 years of age receiving lopinavir/ritonavir solution, consideration should be given to increasing the dose of lopinavir/ritonavir to 13/3.25 mg/kg for those 7 to <15 kg; 11/2.75 mg/kg for those 15 to 45 kg; and up to a maximum dose of 533/ 133 mg twice daily. Refer to the lopinavir/ritonavir package insert for complete pediatric dosing instructions when lopinavir/ritonavir tablets are used in combination with nevirapine. |
| Methadone |
↓ Methadone |
Methadone levels were decreased; increased dosages may be required to prevent symptoms of opiate withdrawal. Methadone-maintained patients beginning nevirapine therapy should be monitored for evidence of withdrawal and methadone dose should be adjusted accordingly. |
| Nelfinavir |
↓ Nelfinavir M8 Metabolite ↓ Nelfinavir Cmin
|
The appropriate dose for nelfinavir in combination with nevirapine, with respect to safety and efficacy, has not been established. |
| Rifabutin |
↑ Rifabutin |
Rifabutin and its metabolite concentrations were moderately increased. Due to high intersubject variability, however, some patients may experience large increases in rifabutin exposure and may be at higher risk for rifabutin toxicity. Therefore, caution should be used in concomitant administration. |
| Rifampin |
↓ Nevirapine |
Nevirapine and rifampin should not be administered concomitantly because decreases in nevirapine plasma concentrations may reduce the efficacy of the drug. Physicians needing to treat patients co-infected with tuberculosis and using a nevirapine-containing regimen may use rifabutin instead. |
| Saquinavir/Ritonavir |
The interaction between nevirapine and saquinavir/ritonavir has not been evaluated |
The appropriate doses of the combination of nevirapine and saquinavir/ritonavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
|
Potential Drug Interactions:
|
||
|
Drug Class
|
Examples of Drugs
|
|
| Antiarrhythmics |
Amiodarone, disopyramide, lidocaine |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Anticonvulsants |
Carbamazepine, clonazepam, ethosuximide |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Antifungals |
Itraconazole |
Plasma concentrations of some azole antifungals may be decreased. Nevirapine and itraconazole should not be administered concomitantly due to a potentialdecrease in itraconazole plasma concentrations. |
| Calcium channel blockers |
Diltiazem, nifedipine, verapamil |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Cancer chemotherapy |
Cyclophosphamide |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Ergot alkaloids |
Ergotamine |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Immunosuppressants |
Cyclosporin, tacrolimus, sirolimus |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Motility agents |
Cisapride |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Opiate agonists |
Fentanyl |
Plasma concentrations may be decreased. |
| Antithrombotics |
Warfarin |
Plasma concentrations may be increased. Potential effect on anticoagulation. Monitoring of anticoagulation levels is recommended. |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects, Pregnancy Category B.
+3[see Boxed Warning]
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry
8.3 Nursing Mothers
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-1 infected mothers not breast-feed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV-1. Nevirapine is excreted in breast milk. Because of both the potential for HIV-1 transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breast-feed if they are receiving nevirapine.
8.4 Pediatric Use
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Clinical Studies (14.2)][see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Clinical Studies (14.2)]
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Clinical Studies (14.2) ]
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
[see Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
15144
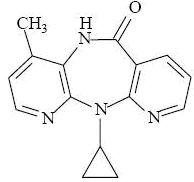
Nevirapine oral suspension, USP is for oral administration. Each 5 mL of nevirapine oral suspension contains 50 mg of nevirapine (as nevirapine hemihydrate). The suspension also contains the following excipients: carbopol 974PNF, methylparaben, propylparaben, non crystallizing sorbitol solution, sucrose, propylene glycol, polysorbate 80, sodium hydroxide, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Adults
Absorption and Bioavailability
®τ
Distribution
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Metabolism/Elimination
In vivo in vitro In vitro 14
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]
Hepatic Impairment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
[see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]
Gender
Race
minss =
Geriatric Subjects
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]
Pediatric Subjects
22[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)]22
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Drug Interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)]
in vitro i
maxmin
| Co-administered Drug | Dose of Co-administered Drug |
Dose Regimen of Nevirapine |
n | % Change of Co-administered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiretrovirals | AUC | Cmax | Cmin | ||||||
| § = Cmin below detectable level of the assay ↑ = Increase, ↓= Decrease, ↔ = No Effect a For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7). b Pediatric subjects ranging in age from 6 months to 12 years. c Parallel group design; n for nevirapine+lopinavir/ritonavir, n for lopinavir/ritonavir alone. d Parallel group design; n=23 for atazanavir/ritonavir + nevirapine, n=22 for atazanavir/ritonavir without nevirapine. Changes in atazanavir PK are relative to atazanavir/ritonavir 300/100 mg alone. e Based on between-trial comparison. f Based on historical controls. |
|||||||||
| Atazanavir/Ritonavira,d
|
300/100 mg QD day 4 to 13, then 400/100 mg QD, day 14 to 23 |
200 mg BID day 1 to 23. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry. |
23 |
Atazanavir 300/100 mg ↓42 (↓52 to ↓29) |
Atazanavir 300/100 mg ↓28 (↓40 to ↓14) |
Atazanavir 300/100 mg ↓72 (↓80 to ↓60) |
|||
| Atazanavir 400/100 mg ↓19 (↓35 to ↑2) |
Atazanavir 400/100 mg ↑2 (↓15 to ↑24) |
Atazanavir 400/100 mg ↓59 (↓73 to ↓40) |
|||||||
| Darunavir/Ritonavire
|
400/100 mg BID |
200 mg BID |
8 |
↑24 (↓3 to ↑57) |
↑40 (↑14 to ↑73) |
↑2 (↓21 to ↑32) |
|||
| Didanosine |
100 to 150 mg BID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
18 |
↔ |
↔ |
§ |
|||
| Efavirenza
|
600 mg QD |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 400 mg QD x 14 days |
17 |
↓28 (↓34 to ↓14) |
↓12 (↓23 to ↑1) |
↓32 (↓35 to ↓19) |
|||
| Fosamprenavir |
1400 mg BID |
200 mg BID. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry. |
17 |
↓33 (↓45 to ↓20) |
↓25 (↓37 to ↓10) |
↓35 (↓50 to ↓15) |
|||
| Fosamprenavir/Ritonavir |
700/100 mg BID |
200 mg BID. Subjects were treated with nevirapine prior to trial entry |
17 |
↓11 (↓23 to ↑3) |
↔ |
↓19 (↓32 to ↓4) |
|||
| Indinavira
|
800 mg q8H |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
19 |
↓31 (↓39 to ↓22) |
↓15 (↓24 to ↓4) |
↓44 (↓53 to ↓33) |
|||
| Lopinavira, b
|
300/75 mg/m2
(lopinavir/ ritonavir)b |
7 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg QD x 2 weeks; BID x 1 week |
12, 15c
|
↓22 (↓44 to ↑9) |
↓14 (↓36 to ↑16) |
↓55 (↓75 to ↓19) |
|||
| Lopinavira
|
400/100 mg BID (lopinavir/ ritonavir) |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID >1 year |
22, 19c
|
↓27 (↓47 to ↓2) |
↓19 (↓38 to ↑5) |
↓51 (↓72 to ↓26) |
|||
| Maravirocf
|
300 mg SD |
200 mg BID |
8 |
↑1 (↓35 to ↑55) |
↑54 (↓6 to ↑151) |
↔ |
|||
| Nelfinavira
Nelfinavir-M8 metabolite |
750 mg TID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
23 |
↔ |
↔ |
↓32 (↓50 to ↑5) |
|||
| ↓62 (↓70 to ↓53) |
↓59 (↓68 to ↓48) |
↓66 (↓74 to ↓55) |
|||||||
| Ritonavir |
600 mg BID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
18 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||
| Stavudine |
30 to 40 mg BID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
22 |
↔ |
↔ |
§ |
|||
| Zalcitabine |
0.125 to 0.25 mg TID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
6 |
↔ |
↔ |
§ |
|||
| Zidovudine |
100 to 200 mg TID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
11 |
↓28 (↓40 to ↓4) |
↓30 (↓51 to ↑14) |
§ |
|||
|
Other Medications
|
|
|
|
AUC
|
Cmax
|
Cmin
|
|||
| Clarithromycina
Metabolite 14-OH-clarithromycin |
500 mg BID |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
15 |
↓31 (↓38 to ↓24) |
↓23 (↓31 to ↓14) |
↓56 (↓70 to ↓36) |
|||
| ↑42 (↑16 to ↑73) |
↑47 (↑21 to ↑80) |
↔ |
|||||||
| Ethinyl estradiola and Norethindronea |
0.035 mg (as Ortho-Novum® 1/35) 1 mg (as Ortho-Novum® 1/35) |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
10 |
↓20 (↓33 to ↓3) |
↔ |
§ |
|||
| ↓19 (↓30 to ↓7) |
↓16 (↓27 to ↓3) |
§ |
|||||||
| Depomedroxy- progesterone acetate |
150 mg every 3 months |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
32 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||
| Fluconazole |
200 mg QD |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
19 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||
| Ketoconazolea
|
400 mg QD |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
21 |
↓72 (↓80 to ↓60) |
↓44 (↓58 to ↓27) |
§ |
|||
| Methadonea
|
Individual Subject Dosing |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID ≥7 days |
9 |
In a controlled pharmacokinetic trial with 9 subjects receiving chronic methadone to whom steady-state nevirapine therapy was added, the clearance of methadone was increased by 3-fold, resulting in symptoms of withdrawal, requiring dose adjustments in 10 mg segments, in 7 of the 9 subjects. Methadone did not have any effect on nevirapine clearance. |
|||||
| Rifabutina
Metabolite 25-O-desacetyl-rifabutin |
150 or 300 mg QD |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
19 |
↑17 (↓2 to ↑40) |
↑28 (↑9 to ↑51) |
↔ |
|||
| ↑24 (↓16 to ↑84) |
↑29 (↓2 to ↑68) |
↑22 (↓14 to ↑74) |
|||||||
| Rifampina
|
600 mg QD |
200 mg QD x 14 days; 200 mg BID x 14 days |
14 |
↑11 (↓4 to ↑28) |
↔ |
§ |
|||
max[see Drug Interactions (7)]
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Antiviral Activity
50th 5050
Resistance
Cross-resistance
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
-in vitroin vivoE. coli
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trials in Adults
+3+ 310
| Outcome | Nevirapine (N=1121) % |
Placebo (N=1128) % |
|---|---|---|
|
1 including change to open-label nevirapine 2 includes withdrawal of consent, lost to follow-up, non-compliance with protocol, other administrative reasons |
||
| Responders at 48 weeks: HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL |
18 |
2 |
| Treatment Failure |
82 |
98 |
| Never suppressed viral load |
45 |
66 |
| Virologic failure after response |
7 |
4 |
| CDC category C event or death |
10 |
11 |
| Added antiretroviral therapy1 while <50 copies/mL |
5 |
1 |
| Discontinued trial therapy due to AE |
7 |
6 |
| Discontinued trial <48 weeks2
|
9 |
10 |
+310+3
+333
14.2 Clinical Trials in Pediatric Subjects
2[see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
10+ 3
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Nevirapine Oral Suspension, USP is a white to off-white homogenous suspension containing 50 mg nevirapine (as nevirapine hemihydrate) in each 5 mL. Nevirapine suspension is supplied in HDPE bottles with child-resistant closures.
100 mL Bottle NDC 65862-057-11
240 mL Bottle NDC 65862-057-24
Nevirapine Oral Suspension, USP should be stored at 20
°
to 25
°
C (68
°
to 77
°
F); excursions permitted to 15
°
to 30
°
C (59
°
to 86
°
F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in a safe place out of the reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Hepatotoxicity and Skin Reactions
Inform patients of the possibility of severe liver disease or skin reactions associated with nevirapine that may result in death. Instruct patients developing signs or symptoms of liver disease or severe skin reactions to discontinue nevirapine and seek medical attention immediately, including performance of laboratory monitoring. Symptoms of liver disease include fatigue, malaise, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, acholic stools, liver tenderness or hepatomegaly. Symptoms of severe skin or hypersensitivity reactions include rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, and/or hepatitis.
+33[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
17.2 Administration
17.3 Drug Interactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7)]
17.4 Contraceptives
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
17.5 Methadone
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
17.6 Fat Redistribution
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
MEDICATION GUIDE
Nevirapine Oral Suspension, USP
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking nevirapine oral suspension and each time you get a refill.
What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine oral suspension?
Nevirapine oral suspension can cause serious side effects. These include severe liver and skin problems that can cause death. These problems can happen at any time during treatment, but your risk is highest during the first 18 weeks of treatment.
Severe liver problems:
+
- Women with CD4+ counts higher than 250 cells/mm3. This group has the highest risk.
- Men with CD4+ counts higher than 400 cells/mm3.
+ 3+ 3
Stop taking nevirapine oral suspension and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
- dark (tea colored) urine
- yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes
- light-colored bowel movements (stools)
- fever
- nausea (feeling sick to your stomach)
- feel unwell or like you have the flu
- pain or tenderness on your right side below your ribs
- tiredness
- loss of appetite
2. Severe rash and skin reactions:Rashes and skin reactions may be severe, life-threatening, and in some people, may lead to death. Stop using nevirapine oral suspension and call your doctor right away if you get a rash with any of the following symptoms:
- blisters
- mouth sores
- red or inflamed eyes, like “pink eye” (conjunctivitis)
- liver problems (see symptoms of liver problems above)
- swelling of your face
- fever
- feel unwell or like you have the flu
- tiredness
- muscle or joint aches
If your doctor tells you to stop treatment with nevirapine oral suspension because you have had any of the serious liver or skin problems described above, you should never take nevirapine oral suspension again.
“What are the possible side effects of nevirapine oral suspension?”
What is nevirapine oral suspension?
You must take nevirapine oral suspension with other anti-HIV medicines.++
Who should not take nevirapine oral suspension?
What should I tell my doctor before taking nevirapine oral suspension?
Before you take nevirapine oral suspension, tell your doctor if you:
- have or have had hepatitis (inflammation of your liver) or problems with your liver. See “What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine oral suspension?” and “Who should not take nevirapine oral suspension?”
- receive dialysis
- have skin problems, such as a rash
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if nevirapine oral suspension will harm your unborn baby.
- Pregnancy Registry: There is a pregnancy registry for women who take antiviral medicines during pregnancy. The purpose of the registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your doctor about how you can take part in this registry.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Nevirapine can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. It is also recommended that HIV-positive women should not breast-feed their babies. Do not breast-feed during treatment with nevirapine oral suspension. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the medicines you take,
- St. John’sWort. St. John’s Wort can lower the amount of nevirapine oral suspension in your body.
- efavirenz (Sustiva®, Atripla®). Efavirenz may cause you to have an increased chance of side effects.
- atazanavir (Reyataz®)
- lopinavir and ritonavir (Kaletra®)
- fosamprenavir calcium (Lexiva®)
- itraconazole (Sporanox®)
- ketoconazole (Nizoral®)
- rifampin (Rifadin®, Rifamate®, Rifater®)
- Birth control pills. Birth control pills taken by mouth (oral contraceptives) and other hormone types of birth control may not work to prevent pregnancy. Talk with your doctor about other types of birth control that you can use to prevent pregnancy during treatment with nevirapine oral suspension.
- clarithromycin (Biaxin®)
- fluconazole (Diflucan®)
- indinavir sulfate (Crixivan®)
- methadone
- nelfinavir mesylate (Viracept®)
- rifabutin (Mycobutin®)
- warfarin (Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
- saquinavir mesylate (Invirase®)
If you are not sure if you take a medicine above, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How should I take nevirapine oral suspension?
- Nevirapine oral suspension is always taken in combination with other anti-HIV medications.
- Take nevirapine oral suspension exactly as your doctor tells you to take it. Do not change your dose unless your doctor tells you to.
- You should never take more than one form of nevirapine at the same time. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions
- You may take nevirapine oral suspension with or without food.
- Do not miss a dose of nevirapine oral suspension, because this could make HIV harder to treat. If you miss a dose of nevirapine oral suspension, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, do not take the missed dose, just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take two doses at the same time.
- If you stop taking nevirapine oral suspension for more than 7 days, ask your doctor how much to take before you start taking it again. You may need to begin taking the nevirapine oral suspension starting dose again, which is taken 1 time each day for 14 days.
- Your doctor should start you with 1 dose each day to lower your chance of getting a serious rash. It is important that you only take one dose of nevirapine oral suspension each day for the first 14 days.
- Call your doctor right away if you get a skin rash during the first 14 days of nevirapine oral suspension treatment and do not increase your dose to 2 times a day.
- You should never take your starting dose for longer than 28 days. If after 28 days you are still receiving this starting dose because you have a rash, you and your doctor should talk about prescribing another HIV medicine for you instead of nevirapine oral suspension.
- Do not increase your dose to 2 times a day if you have a rash.
- If you or your child takes nevirapine oral suspension (liquid), shake it gently before each use. Use an oral dosing syringe or dosing cup to measure the right dose. The oral dosing syringe and dosing cup are not provided with nevirapine oral suspension. Ask your pharmacist for a syringe or cup if you do not have one.
- After drinking the medicine, fill the dosing cup with water and drink it to make sure you get all the medicine.
- If the dose is less than 1 teaspoon (5 mL), use the syringe instead of the dosing cup.
What are the possible side effects of nevirapine oral suspension?
- See “What is the most important information I should know about nevirapine oral suspension ?”
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your doctor if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV medicine.
- Changes in body fat can happen in some people who take antiretroviral therapy. These changes may include increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck (“buffalo hump”), breast, and around the middle of your body (trunk). Loss of fat from your legs, arms, and face can also happen. The cause and long-term health effects of these problems are not known at this time.
How should I store nevirapine oral suspension?
- Nevirapine oral suspension should be stored at 20° to 25° C (68° to 77° F) excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
- Throw away nevirapine oral suspension that is no longer needed or out-of-date.
Keep nevirapine oral suspension and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about nevirapine oral suspension.
What are the ingredients in nevirapine oral suspension?
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg/5 mL (240 mL Bottle)
NDC 65862-057-24
Nevirapine Oral Suspension, USP
50 mg/5 mL*
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompying
Medication Guide to each patient.
Rx only 240 mL
AUROBINDO

NevirapineNevirapine SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||