Olanzapine
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use olanzapine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for olanzapine tablets. Olanzapine Tablets, for Oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 1996 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES none BOXED WARNINGWARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Olanzapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. ( 5.1 , 5.14 , 17.2 ) When using olanzapine and fluoxetine in combination, also refer to the Boxed Warning section of the package insert for Symbyax*. INDICATIONS AND USAGEAs oral formulation for the: Treatment of schizophrenia. (1.1) Adults: Efficacy was established in three clinical trials in patients with schizophrenia: two 6-week trials and one maintenance trial. (14.1) Acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder and maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder. (1.2) Adults: Efficacy was established in three clinical trials in patients with manic or mixed episodes of bipolar I disorder: two 3- to 4-week trials and one maintenance trial. (14.2) Adjunct to valproate or lithium in the treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder. (1.2) Efficacy was established in two 6-week clinical trials in adults (14.2). Maintenance efficacy has not been systematically evaluated. As Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination for the: Treatment of depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder. (1.5) Efficacy was established with Symbyax* (olanzapine and fluoxetine in combination) in adults; refer to the product label for Symbyax*. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Schizophrenia in adults (2.1) Oral: Start at 5 mg to 10 mg once daily; Target: 10 mg/day within several days Bipolar I Disorder (manic or mixed episodes) in adults (2.2) Oral: Start at 10 mg or 15 mg once daily Bipolar I Disorder (manic or mixed episodes) with lithium or valproate in adults (2.2) Oral: Start at 10 mg once daily Depressive Episodes associated with Bipolar I Disorder in adults (2.5) Oral in combination with fluoxetine: Start at 5 mg of oral olanzapine and 20 mg of fluoxetine once daily Lower starting dose recommended in debilitated or pharmacodynamically sensitive patients or patients with predisposition to hypotensive reactions, or with potential for slowed metabolism. (2.1) Olanzapine may be given without regard to meals. (2.1) Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Dosage adjustments, if indicated, should be made with the individual components according to efficacy and tolerability. (2.5) Olanzapine monotherapy is not indicated for the treatment of depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder. (2.5) Safety of coadministration of doses above 18 mg olanzapine with 75 mg fluoxetine has not been evaluated. (2.5) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets (not scored): 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS None with olanzapine monotherapy. When using olanzapine and fluoxetine in combination, also refer to the Contraindications section of the package insert for Symbyax®*. (4) When using olanzapine in combination with lithium or valproate, refer to the Contraindications section of the package inserts for those products. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased risk of death and increased incidence of cerebrovascular adverse events (e.g., stroke, transient ischemic attack). (5.1) Suicide: The possibility of a suicide attempt is inherent in schizophrenia and in bipolar I disorder, and close supervision of high-risk patients should accompany drug therapy, when using in combination with fluoxetine, also refer to the Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions sections of the package insert for Symbyax*. (5.2) Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Manage with immediate discontinuation and close monitoring. (5.3) Hyperglycemia: In some cases extreme and associated with ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma or death, has been reported in patients taking olanzapine. Patients taking olanzapine should be monitored for symptoms of hyperglycemia and undergo fasting blood glucose testing at the beginning of, and periodically during, treatment. (5.4) Hyperlipidemia: Undesirable alterations in lipids have been observed. Appropriate clinical monitoring is recommended, including fasting blood lipid testing at the beginning of, and periodically during, treatment. (5.5) Weight Gain: Potential consequences of weight gain should be considered. Patients should receive regular monitoring of weight. (5.6) Tardive Dyskinesia: Discontinue if clinically appropriate. (5.7) Orthostatic Hypotension: Orthostatic hypotension associated with dizziness, tachycardia, bradycardia and, in some patients, syncope, may occur especially during initial dose titration. Use caution in patients with cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and those conditions that could affect hemodynamic responses. (5.8) Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: Has been reported with antipsychotics, including olanzapine. Patients with a history of a clinically significant low white blood cell count (WBC) or drug induced leukopenia/neutropenia should have their complete blood count (CBC) monitored frequently during the first few months of therapy and discontinuation of olanzapine should be considered at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors. (5.9) Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold. (5.11) Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Has potential to impair judgment, thinking, and motor skills. Use caution when operating machinery. (5.12) Hyperprolactinemia: May elevate prolactin levels. (5.15) Use in Combination with Fluoxetine, Lithium or Valproate: Also refer to the package inserts for Symbyax*, lithium, or valproate. (5.16) Laboratory Tests: Monitor fasting blood glucose and lipid profiles at the beginning of, and periodically during, treatment. (5.17) Side Effects Oral Olanzapine Monotherapy: Schizophrenia (Adults) – postural hypotension, constipation, weight gain, dizziness, personality disorder, akathisia (6.1) Schizophrenia (Adolescents) – sedation, weight increased, headache, increased appetite, dizziness, abdominal pain, pain in extremity, fatigue, dry mouth (6.1) Manic or Mixed Episodes, Bipolar I Disorder (Adults) – asthenia, dry mouth, constipation, increased appetite, somnolence, dizziness, tremor (6.1) Manic or Mixed Episodes, Bipolar I Disorder (Adolescents) – sedation, weight increased, increased appetite, headache, fatigue, dizziness, dry mouth, abdominal pain, pain in extremity (6.1) Combination of Olanzapine and Lithium or Valproate: Manic or Mixed Episodes, Bipolar I Disorder (Adults) – dry mouth, weight gain, increased appetite, dizziness, back pain, constipation, speech disorder, increased salivation, amnesia, paresthesia (6.1) Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Also refer to the Adverse Reactions section of the package insert for Symbyax*. (6)To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CARACO Pharmaceutical Laboratories Ltd. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatchDRUG INTERACTIONS Diazepam: May potentiate orthostatic hypotension. (7.1, 7.2) Alcohol: May potentiate orthostatic hypotension. (7.1) Carbamazepine: Increased clearance of olanzapine. (7.1) Fluvoxamine: May increase olanzapine levels. (7.1) Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Also refer to the Drug Interactions section of the package insert for Symbyax*. (7.1) CNS Acting Drugs: Caution should be used when taken in combination with other centrally acting drugs and alcohol. (7.2) Antihypertensive Agents: Enhanced antihypertensive effect. (7.2) Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists: May antagonize levodopa/dopamine agonists. (7.2) Other Concomitant Drug Therapy: When using olanzapine in combination with lithium or valproate, refer to the Drug Interactions sections of the package insert for those products. (7.2) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Olanzapine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1) Nursing Mothers: Breast-feeding is not recommended. (8.3) Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of olanzapine in children
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
- 1 OLANZAPINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 OLANZAPINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 OLANZAPINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
- 5.2 Suicide
- 5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
- 5.4 Hyperglycemia
- 5.5 Hyperlipidemia
- 5.6 Weight Gain
- 5.7 Tardive Dyskinesia
- 5.8 Orthostatic Hypotension
- 5.9 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
- 5.10 Dysphagia
- 5.11 Seizures
- 5.12 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
- 5.13 Body Temperature Regulation
- 5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
- 5.15 Hyperprolactinemia
- 5.16 Use in Combination with Fluoxetine, Lithium, or Valproate
- 5.17 Laboratory Tests
- 6 OLANZAPINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 OLANZAPINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- 17.1 Information on Medication Guide
- 17.2 Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased Mortality and Cerebrovascular Adverse Events (CVAE), Including Stroke
- 17.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
- 17.4 Hyperglycemia
- 17.5 Hyperlipidemia
- 17.6 Weight Gain
- 17.7 Orthostatic Hypotension
- 17.8 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
- 17.9 Body Temperature Regulation
- 17.10 Concomitant Medication
- 17.11 Alcohol
- 17.13 Use in Specific Populations
- 17.14 Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program in Pediatric Patients
- Medication Guide
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 2.5MG
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 5MG
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 7.5MG
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 10MG
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 15MG
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 20MG
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of seventeen placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. Olanzapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.14) and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)].
When using olanzapine and fluoxetine in combination, also refer to the Boxed Warning section of the package insert for Symbyax*.
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Schizophrenia
Oral [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
When [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]
Information describing the use of olanzapine tablets in pediatric patients with schizophrenia is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
1.2 Bipolar I Disorder (Manic or Mixed Episodes)
Monotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
When [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]
Information describing the use of olanzapine tablets in pediatric patients with bipolar 1 disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
Adjunctive Therapy to Lithium or Valproate [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
1.3 Special Considerations in Treating Pediatric Schizophrenia and Bipolar I Disorder
Informat ion on treating pediatric patients with schizophrenia and bipolar 1 disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
1.5 Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Schizophrenia
Adults
Dose Selection
Dosing in Special Populations[see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Drug Interactions (7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Maintenance Treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
Adolescents
Pediatric dosing information in pediatric patients with schizophrenia is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
2.2 Bipolar I Disorder (Manic or Mixed Episodes)
Adults
Dose Selection for Monotherapy
[see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Maintenance Monotherapy[see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Dose Selection for Adjunctive Treatment
Antimanic efficacy [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
Adolescents
Pediatric dosing information in pediatric patients with bipolar I disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
2.5 Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar I Disorder
| For Symbyax* (mg/day) |
Use in Combination | |
|---|---|---|
| Olanzapine (mg/day) |
Fluoxetine (mg/day) |
|
|
a Symbyax* (olanzapine/fluoxetine hydrochloride) is a fixed-dose combination of olanzapine and fluoxetine. |
||
| 3 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
2.5 |
20 |
| 6 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
5 |
20 |
| 12 mg olanzapine/25 mg fluoxetine |
10+2.5 |
20 |
| 6 mg olanzapine/50 mg fluoxetine |
5 |
40+10 |
| 12 mg olanzapine/50 mg fluoxetine |
10+2.5 |
40+10 |
Olanzapine
2.7 Olanzapine and Fluoxetine in Combination: Dosing in Special Populations
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Drug Interactions (7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None with olanzapine monotherapy.
- When using olanzapine and fluoxetine in combination, also refer to the Contraindications section of the package insert for Symbyax*.
- For specific information about the contraindications of lithium or valproate, refer to the Contraindications section of the package inserts for these other products.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Increased Mortality — Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Olanzapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.14), and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)].
Cerebrovascular Adverse Events (CVAE), Including Stroke [see Boxed Warning and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)]
5.2 Suicide
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.3)]
5.4 Hyperglycemia
17.4
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adults
| Up to 12 weeks exposure | At least 48 weeks exposure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Analyte | Category Change (at least once) from Baseline | Treatment Arm | N | Patients | N | Patients |
| Fasting Glucose |
Normal to High (<100 mg/dL to ≥126 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
543 |
2.2% |
345 |
12.8% |
| Placebo |
293 |
3.4% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥100 mg/dL and <126 mg/dL to ≥126 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
178 |
17.4% |
127 |
26% |
|
| Placebo |
96 |
11.5% |
NA |
NA |
||
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adolescents
| Up to 12 weeks exposure | At least 24 weeks exposure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Analyte | Category Change (at least once) from Baseline | Treatment Arm | N | Patients | N | Patients |
| Fasting Glucose |
Normal to High (<100 mg/dL to ≥126 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
124 |
0% |
108 |
0.9% |
| Placebo |
53 |
1.9% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥100 mg/dL and <126 mg/dL to ≥126 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
14 |
14.3% |
13 |
23.1% |
|
| Placebo |
13 |
0% |
NA |
NA |
||
5.5 Hyperlipidemia
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.5)]
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adults
| Up to 12 weeks exposure | At least 48 weeks exposure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Analyte | Category Change (at least once) from Baseline | Treatment Arm | N | Patients | N | Patients |
| Fasting Triglycerides |
Increase by ≥50 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
745 |
39.6% |
487 |
61.4% |
| Placebo |
402 |
26.1% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<150 mg/dL to ≥200 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
457 |
9.2% |
293 |
32.4% |
|
| Placebo |
251 |
4.4% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥150 mg/dL and <200 mg/dL to ≥200 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
135 |
39.3% |
75 |
70.7% |
|
| Placebo |
65 |
20% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Fasting Total Cholesterol |
Increase by ≥40 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
745 |
21.6% |
489 |
32.9% |
| Placebo |
402 |
9.5% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<200 mg/dL to ≥240 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
392 |
2.8% |
283 |
14.8% |
|
| Placebo |
207 |
2.4% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥200 mg/dL and <240 mg/dL to ≥240 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
222 |
23% |
125 |
55.2% |
|
| Placebo |
112 |
12.5% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Fasting LDL Cholesterol |
Increase by ≥30 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
536 |
23.7% |
483 |
39.8% |
| Placebo |
304 |
14.1% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<100 mg/dL to ≥160 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
154 |
0% |
123 |
7.3% |
|
| Placebo |
82 |
1.2% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥100 mg/dL and <160 mg/dL to ≥160 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
302 |
10.6% |
284 |
31% |
|
| Placebo |
173 |
8.1% |
NA |
NA |
||
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adolescents
| Up to 6 weeks exposure | At least 24 weeks exposure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Analyte | Category Change (at least once) from Baseline |
Treatment Arm |
N |
Patients |
N |
Patients |
| Fasting Triglycerides |
Increase by ≥50 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
138 |
37% |
122 |
45.9% |
| Placebo |
66 |
15.2% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<90 mg/dL to >130 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
67 |
26.9% |
66 |
36.4% |
|
| Placebo |
28 |
10.7% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥90 mg/dL and ≤130 mg/dL to >130 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
37 |
59.5% |
31 |
64.5% |
|
| Placebo |
17 |
35.3% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Fasting Total Cholesterol |
Increase by ≥40 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
138 |
14.5% |
122 |
14.8% |
| Placebo |
66 |
4.5% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<170 mg/dL to ≥200 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
87 |
6.9% |
78 |
7.7% |
|
| Placebo |
43 |
2.3% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥170 mg/dL and <200 mg/dL to ≥200 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
36 |
38.9% |
33 |
57.6% |
|
| Placebo |
13 |
7.7% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Fasting LDL Cholesterol |
Increase by ≥30 mg/dL |
Olanzapine |
137 |
17.5% |
121 |
22.3% |
| Placebo |
63 |
11.1% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Normal to High (<110 mg/dL to ≥130 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
98 |
5.1% |
92 |
10.9% |
|
| Placebo |
44 |
4.5% |
NA |
NA |
||
| Borderline to High (≥110 mg/dL and <130 mg/dL to ≥130 mg/dL) |
Olanzapine |
29 |
48.3% |
21 |
47.6% |
|
| Placebo |
9 |
0% |
NA |
NA |
||
5.6 Weight Gain
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.6)]
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adults
| Amount Gained kg (lb) | 6 Weeks (N=7465) (%) | 6 Months (N=4162) (%) | 12 Months (N=1345) (%) | 24 Months (N=474) (%) | 36 Months (N=147) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0 |
26.2 |
24.3 |
20.8 |
23.2 |
17 |
| 0 to ≤5 (0 to 11 lb) |
57 |
36 |
26 |
23.4 |
25.2 |
| >5 to ≤10 (11 to 22 lb) |
14.9 |
24.6 |
24.2 |
24.1 |
18.4 |
| >10 to ≤15 (22 to 33 lb) |
1.8 |
10.9 |
14.9 |
11.4 |
17 |
| >15 to ≤20 (33 to 44 lb) |
0.1 |
3.1 |
8.6 |
9.3 |
11.6 |
| >20 to ≤25 (44 to 55 lb) |
0 |
0.9 |
3.3 |
5.1 |
4.1 |
| >25 to ≤30 (55 to 66 lb) |
0 |
0.2 |
1.4 |
2.3 |
4.8 |
| >30 (>66 lb) |
0 |
0.1 |
0.8 |
1.2 |
2 |
| Olanzapine-treated patients | Placebo-treated patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean change in body weight from baseline (median exposure = 3 weeks) |
4.6 kg (10.1 lb) |
0.3 kg (0.7 lb) |
| Percentage of patients who gained at least 7% of baseline body weight |
40.6% (median exposure to 7% = 4 weeks) |
9.8% (median exposure to 7% = 8 weeks) |
| Percentage of patients who gained at least 15% of baseline body weight |
7.1% (median exposure to 15% = 19 weeks) |
2.7% (median exposure to 15% = 8 weeks) |
| Amount Gained kg (lb) | 6 Weeks (N=243) (%) | 6 Months (N=191) (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ≤0 |
2.9 |
2.1 |
| 0 to ≤5 (0 to 11 lb) |
47.3 |
24.6 |
| >5 to ≤10 (11 to 22 lb) |
42.4 |
26.7 |
| >10 to ≤15 (22 to 33 lb) |
5.8 |
22 |
| >15 to ≤20 (33 to 44 lb) |
0.8 |
12.6 |
| >20 to ≤25 (44 to 55 lb) |
0.8 |
9.4 |
| >25 to ≤30 (55 to 66 lb) |
0 |
2.1 |
| >30 to ≤35 (66 to 77 lb) |
0 |
0 |
| >35 to ≤40 (77 to 88 lb) |
0 |
0 |
| >40 (>88 lb) |
0 |
0.5 |
5.7 Tardive Dyskinesia
5.8 Orthostatic Hypotension
1[see Patient Counseling Information (17.7)]
[see Dosage and Administration (2)]
Caution [see Drug Interactions (7)]
5.9 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
Class Effect
3
5.10 Dysphagia
5.11 Seizures
5.12 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.8)]
5.13 Body Temperature Regulation
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.9)]
5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
in vitro
[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)]
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
5.15 Hyperprolactinemia
As with
Tissue culture in vitro[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]
In placebo1 2 3
In placebo123[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
1
2
3
5.16 Use in Combination with Fluoxetine, Lithium, or Valproate
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
5.17 Laboratory Tests
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5) and Patient Counseling Information (17.4, 17.5)]
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trials in Adults
Incidence of Adverse Reactions in Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled and Combination Trials
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment in Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled Trials
Schizophrenia
Bipolar I Disorder (Manic or Mixed Episodes) Monotherapy
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment in Short-Term Combination Trials
Bipolar I Disorder (Manic or Mixed Episodes), Olanzapine as Adjunct to Lithium or Valproate
Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions in Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled Trials
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | Olanzapine (N=248) | Placebo (N=118) |
| Postural hypotension |
5 |
2 |
| Constipation |
9 |
3 |
| Weight gain |
6 |
1 |
| Dizziness |
11 |
4 |
Personality disorder |
8 |
4 |
| Akathisia |
5 |
1 |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Olanzapine | Placebo | |
| Adverse Reaction | (N=125) | (N=129) |
| Asthenia |
15 |
6 |
| Dry mouth |
22 |
7 |
| Constipation |
11 |
5 |
| Dyspepsia |
11 |
5 |
| Increased appetite |
6 |
3 |
| Somnolence |
35 |
13 |
| Dizziness |
18 |
6 |
| Tremor |
6 |
3 |
| Body System/Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | |
|---|---|---|
| Olanzapine (N=532) |
Placebo (N=294) |
|
|
Body as a Whole
|
||
| Accidental injury |
12 |
8 |
| Asthenia |
10 |
9 |
| Fever |
6 |
2 |
| Back pain
|
5 |
2 |
| Chest pain
|
3 |
1 |
|
Cardiovascular System
|
||
| Postural hypotension
|
3 |
1 |
| Tachycardia |
3 |
1 |
| Hypertension |
2 |
1 |
|
Digestive System
|
||
| Dry mouth
|
9 |
5 |
| Constipation |
9 |
4 |
| Dyspepsia |
7 |
5 |
| Vomiting |
4 |
3 |
| Increased appetite |
3 |
2 |
|
Hemic and Lymphatic System
|
||
| Ecchymosis |
5 |
3 |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
|
||
| Weight gain
|
5 |
3 |
| Peripheral edema
|
3 |
1 |
|
Musculoskeletal System
|
||
| Extremity pain (other than joint)
|
5 |
3 |
| Joint pain
|
5 |
3 |
|
Nervous System
|
||
| Somnolence |
29 |
13 |
| Insomnia |
12 |
11 |
| Dizziness |
11 |
4 |
| Abnormal gait |
6 |
1 |
| Tremor |
4 |
3 |
| Akathisia |
3 |
2 |
| Hypertonia |
3 |
2 |
| Articulation impairment |
2 |
1 |
|
Respiratory System
|
||
| Rhinitis |
7 |
6 |
| Cough increased |
6 |
3 |
| Pharyngitis
|
4 |
3 |
|
Special Senses
|
||
| Amblyopia |
3 |
2 |
|
Urogenital System
|
||
| Urinary incontinence |
2 |
1 |
| Urinary tract infection |
2 |
1 |
| Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | |
|---|---|---|
| Olanzapine with lithium or valproate (N=229) |
Placebo with lithium or valproate (N=115) |
|
| Dry mouth |
32 |
9 |
| Weight gain |
26 |
7 |
| Increased appetite |
24 |
8 |
| Dizziness |
14 |
7 |
| Back pain |
8 |
4 |
| Constipation |
8 |
4 |
| Speech disorder |
7 |
1 |
| Increased salivation |
6 |
2 |
| Amnesia |
5 |
2 |
| Paresthesia |
5 |
2 |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System/Adverse Reaction | Olanzapine with lithium or valproate (N=229) |
Placebo with lithium or valproate (N=115) |
|
Body as a Whole
|
||
| Asthenia |
18 |
13 |
| Back pain |
8 |
4 |
| Accidental injury |
4 |
2 |
| Chest pain |
3 |
2 |
|
Cardiovascular System
|
||
| Hypertension |
2 |
1 |
|
Digestive System
|
||
| Dry mouth |
32 |
9 |
| Increased appetite |
24 |
8 |
| Thirst |
10 |
6 |
| Constipation |
8 |
4 |
| Increased salivation |
6 |
2 |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
|
||
| Weight gain |
26 |
7 |
| Peripheral edema |
6 |
4 |
| Edema |
2 |
1 |
|
Nervous System
|
||
| Somnolence |
52 |
27 |
| Tremor |
23 |
13 |
| Depression |
18 |
17 |
| Dizziness |
14 |
7 |
| Speech disorder |
7 |
1 |
| Amnesia |
5 |
2 |
| Paresthesia |
5 |
2 |
| Apathy |
4 |
3 |
| Confusion |
4 |
1 |
| Euphoria |
3 |
2 |
| Incoordination |
2 |
0 |
|
Respiratory System
|
||
| Pharyngitis |
4 |
1 |
| Dyspnea |
3 |
1 |
|
Skin and Appendages
|
||
| Sweating |
3 |
1 |
| Acne |
2 |
0 |
| Dry skin |
2 |
0 |
|
Special Senses
|
||
| Amblyopia |
9 |
5 |
| Abnormal vision |
2 |
0 |
|
Urogenital System
|
||
Dysmenorrhea |
2 |
0 |
Vaginitis |
2 |
0 |
Additional Findings Observed in Clinical Trials
Dose Dependency of Adverse Reactions in Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled Trials
Extrapyramidal Symptoms:
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | Olanzapine 5 ± 2.5 mg/day |
Olanzapine 10 ± 2.5 mg/day |
Olanzapine 15 ± 2.5 mg/day |
|
Parkinsonism |
15 |
14 |
12 |
14 |
Akathisia |
23 |
16 |
19 |
27 |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=68) | Olanzapine 5 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=65) |
Olanzapine 10 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=64) |
Olanzapine 15 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=69) |
|
Dystonic events |
1 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
Parkinsonism events |
10 |
8 |
14 |
20 |
Akathisia events |
1 |
5 |
11 |
10 |
Dyskinetic events |
4 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
Residual events |
1 |
2 |
5 |
1 |
| Any extrapyramidal event |
16 |
15 |
25 |
32 |
Categories |
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=89) | Olanzapine (N=179) | ||
| Dystonic events |
0 |
1 |
|
| Parkinsonism events |
2 |
1 |
|
| Akathisia events |
4 |
6 |
|
| Dyskinetic events |
0 |
1 |
|
| Nonspecific events |
0 |
4 |
|
| Any extrapyramidal event |
6 |
10 |
|
Other Adverse Reactions:
| Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=68) |
Olanzapine 5 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=65) |
Olanzapine 10 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=64) |
Olanzapine 15 ± 2.5 mg/day (N=69) |
|
| Asthenia |
15 |
8 |
9 |
20 |
| Dry mouth |
4 |
3 |
5 |
13 |
| Nausea |
9 |
0 |
2 |
9 |
| Somnolence |
16 |
20 |
30 |
39 |
| Tremor |
3 |
0 |
5 |
7 |
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Clinical Trial Evaluation of Oral Olanzapine
Body as a Whole Infrequent: 1Rare: 1
Cardiovascular System Infrequent:
Digestive System Infrequent: Rare:
Hemic and Lymphatic System Infrequent:
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders Infrequent:
Musculoskeletal System Rare:
Nervous System Infrequent: Rare:
Respiratory System Infrequent: Rare:
Skin and Appendages Infrequent:
Special Senses Infrequent: Rare:
Urogenital System Infrequent: 222222
1
2
Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions in Oral Olanzapine Short-Term, Placebo-Controlled Trials
| Adverse Reactions | Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 Week Trial % Schizophrenia Patients |
3 Week Trial % Bipolar Patients |
|||
| Olanzapine (N=72) |
Placebo (N=35) |
Olanzapine (N=107) |
Placebo (N=54) |
|
Sedation |
39 |
9 |
48 |
9 |
| Weight increased |
31 |
9 |
29 |
4 |
| Headache |
17 |
6 |
17 |
17 |
| Increased appetite |
17 |
9 |
29 |
4 |
| Dizziness |
8 |
3 |
7 |
2 |
Abdominal pain |
6 |
3 |
6 |
7 |
| Pain in extremity |
6 |
3 |
5 |
0 |
| Fatigue |
3 |
3 |
14 |
6 |
| Dry mouth |
4 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
| Percentage of Patients Reporting Event | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | Olanzapine (N=179) |
Placebo (N=89) |
Sedation |
44 |
9 |
| Weight increased |
30 |
6 |
| Increased appetite |
24 |
6 |
| Headache |
17 |
12 |
| Fatigue |
9 |
4 |
| Dizziness |
7 |
2 |
| Dry mouth |
6 |
0 |
| Pain in extremity |
5 |
1 |
| Constipation |
4 |
0 |
| Nasopharyngitis |
4 |
2 |
| Diarrhea |
3 |
0 |
| Restlessness |
3 |
2 |
Liver enzymes increased |
8 |
1 |
| Dyspepsia |
3 |
1 |
| Epistaxis |
3 |
0 |
Respiratory tract infection |
3 |
2 |
| Sinusitis |
3 |
0 |
| Arthralgia |
2 |
0 |
| Musculoskeletal stiffness |
2 |
0 |
6.2 Vital Signs and Laboratory Studies
Vital Sign Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]
Laboratory Changes Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adults:
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
Olanzapine Monotherapy in Adolescents:
ECG Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Olanzapine
Diazepam [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]
Cimetidine and Antacids
Inducers of CYP1A2
Alcohol [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]
Inhibitors of CYP1A2
Fluvoxamine: max
Inhibitors of CYP2D6
Fluoxetine:
Warfarin [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]
Inducers of CYP1A2 or Glucuronyl Transferase
Charcoal max
7.2 Potential for Olanzapine to Affect Other Drugs
CNS Acting Drugs
Antihypertensive Agents
Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists
Lithium [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
Valproate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
Effect of Olanzapine on Drug Metabolizing Enzymes In vitro
Imipramine
Warfarin [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
Diazepam [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
Alcohol [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]
Biperiden
Theophylline
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects, Pregnancy Category C 2 2 2 2
Nonteratogenic Effects, Class Effect
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6, 5.15, 5.17) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
[see Patient Counseling Information (17.13)]
Pediatric use information in pediatric patients with schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Boxed Warning, Dosage and Administration (2.1), and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.3 Dependence
2
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience
10.2 Management of Overdose
max
11 DESCRIPTION
Hb17204
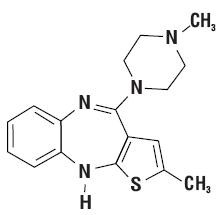
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
2A/2C6i1-4i1i1i3i1-5iAi
21-511
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Oral Administration, Monotherapy
1
Metabolism and Elimination 14
In vitroin vivo
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
Hepatic Impairment
Geriatric [see Dosage and Administration (2)]
Gender
Smoking Status
Race In vivo
Combined Effects [see Dosage and Administration (2)]
Adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years)
Pharmacokinetic information in pediatric patients is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis 2 2 2 2 2 2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
Mutagenesis in vivoin vivo
Impairment of Fertility 2 2 2
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
2 2 2 2
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Schizophrenia
Adults
Adolescents
Clinical trial information in pediatric patients with schizophrenia is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
14.2 Bipolar I Disorder (Manic or Mixed Episodes)
Adults
Monotherapy
Adjunct to Lithium or Valproate
Adolescents
Clinical trial information in pediatric patients with bipolar I disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved Medication Guide for the oral formulations.
17.1 Information on Medication Guide
17.2 Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased Mortality and Cerebrovascular Adverse Events (CVAE), Including Stroke
[see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
17.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
17.4 Hyperglycemia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
17.5 Hyperlipidemia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
17.6 Weight Gain
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
17.7 Orthostatic Hypotension
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7)]
17.8 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
17.9 Body Temperature Regulation
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
17.10 Concomitant Medication
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
17.11 Alcohol
[see Drug Interactions (7)]
17.13 Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
Nursing Mothers [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Pediatric Use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
Pediatric use information in pediatric patients with schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
17.14 Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program in Pediatric Patients
Pediatric use information in pediatric patients with schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
Medication Guide
Olanzapine Tablets
What is the most important information I should know about olanzapine tablets?
Olanzapine tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
- Increased risk of death in elderly people who are confused, have memory loss and have lost touch with reality (dementia-related psychosis).
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
- High fat levels in your blood (increased cholesterol and triglycerides), especially in teenagers age 13 to 17.
- Weight gain, especially in teenagers age 13 to 17.
1. Increased risk of death in elderly people who are confused, have memory loss and have lost touch with reality (dementia-related psychosis).
2. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
- a build up of acid in your blood due to ketones (ketoacidosis)
- coma
- death
Call your doctor
- feel very thirsty
- need to urinate more than usual
- feel very hungry
- feel weak or tired
- feel sick to your stomach
- feel confused or your breath smells fruity
4. Weight gain.
What are olanzapine tablets?
Olanzapine tablets are prescription medicines used to treat:
- schizophrenia.
- bipolar disorder, including:
- manic or mixed episodes that happen with bipolar I disorder.
- manic or mixed episodes that happen with bipolar I disorder, when used with the medicine lithium or valproate, in adults.
- long-term treatment of bipolar I disorder in adults.
- episodes of depression that happen with bipolar I disorder, when used with the medicine fluoxetine (Prozac®*), in adults.
Pediatric use information is approved for Eli Lilly and Company’s olanzapine drug product labeling. However, due to Eli Lilly and Company’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
What should I tell my doctor before taking olanzapine tablets?
- heart problems
- seizures
- diabetes or high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia)
- high cholesterol or triglyceride levels in your blood
- liver problems
- low or high blood pressure
- strokes or “mini-strokes” also called transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
- Alzheimer’s disease
- narrow-angle glaucoma
- enlarged prostate in men
- bowel obstruction
- breast cancer
- thoughts of suicide or hurting yourself
- any other medical condition
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if olanzapine tablets will harm your unborn baby.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Olanzapine can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. You should not breast-feed while taking olanzapine tablets. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take olanzapine tablets.
thoughts of suicide
Tell your doctor about all the medicines that you take,
How should I take olanzapine tablets?
- Take olanzapine tablets exactly as prescribed. Your doctor may need to change (adjust) the dose of olanzapine tablets until it is right for you.
- If you miss a dose of olanzapine tablets, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, just skip the missed dose and take your next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses of olanzapine tablets at the same time.
- To prevent serious side effects, do not stop taking olanzapine tablets suddenly. If you need to stop taking olanzapine tablets, your doctor can tell you how to safely stop taking it.
- If you take too many olanzapine tablets, call your doctor or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away, or get emergency treatment.
- Olanzapine tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Olanzapine tablets are usually taken one time each day.
- Call your doctor if you do not think you are getting better or have any concerns about your condition while taking olanzapine tablets.
What should I avoid while taking olanzapine tablets?
- Olanzapine tablets can cause sleepiness and may affect your ability to make decisions, think clearly, or react quickly. You should not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how olanzapine tablets affect you.
- Avoid drinking alcohol while taking olanzapine tablets. Drinking alcohol while you take olanzapine tablets may make you sleepier than if you take olanzapine tablets alone.
Serious side effects may happen when you take olanzapine tablets, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about olanzapine tablets?”, which describes the increased risk of death in elderly people with dementia-related psychosis and the risks of high blood sugar, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and weight gain.
- Increased incidence of stroke or “mini-strokes” called transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) in elderly people with dementia-related psychosis (elderly people who have lost touch with reality due to confusion and memory loss). Olanzapine tablets are not approved for these patients.
-
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): NMS is a rare but very serious condition that can happen in people who take antipsychotic medicines, including olanzapine tablets. NMS can cause death and must be treated in a hospital. Call your doctor right away if you become severely ill and have any of these symptoms:
- high fever
- excessive sweating
- rigid muscles
- confusion
- changes in your breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
- Tardive Dyskinesia: This condition causes body movements that keep happening and that you can not control. These movements usually affect the face and tongue. Tardive dyskinesia may not go away, even if you stop taking olanzapine tablets. It may also start after you stop taking olanzapine tablets. Tell your doctor if you get any body movements that you can not control.
- Decreased blood pressure when you change positions, with symptoms of dizziness, fast or slow heartbeat, or fainting.
- Difficulty swallowing, that can cause food or liquid to get into your lungs.
- Seizures: Tell your doctor if you have a seizure during treatment with olanzapine tablets.
-
Problems with control of body temperature: You could become very hot, for instance when you exercise a lot or stay in an area that is very hot. It is important for you to drink water to avoid dehydration. Call your doctor right away if you become severely ill and have any of these symptoms of dehydration:
- sweating too much or not at all
- dry mouth
- feeling very hot
- feeling thirsty
- not able to produce urine.
Other common side effects in teenagers (13 to 17 years old) include:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store olanzapine tablets?
- Store olanzapine tablets at room temperature, at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F).
- Keep olanzapine tablets away from light.
- Keep olanzapine tablets dry and away from moisture.
General information about olanzapine tablets
What are the ingredients in olanzapine tablets?
Active ingredient:
Inactive ingredients:
Olanzapine Tablets
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Caraco Pharmaceutical Laboratories, Ltd.
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
PJPI0378B
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 2.5MG
NDC 62756-551-88
Olanzapine Tablets
2.5 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 5MG

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 7.5MG

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 10MG
NDC 62756-554-88
Olanzapine Tablets
10 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 15MG
NDC 62756-555-88
Olanzapine Tablets
15 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL - 20MG
NDC 62756-556-88
Olanzapine Tablets
20 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Medication Guide provided separately to each patient.

OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OlanzapineOlanzapine TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!