Paroxetine Hydrochloride
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- LABOR & DELIVERY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
BOXED WARNING
Suicidality and Antidepressant DrugsAntidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of paroxetine tablets or any other antidepressants in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves assoicated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriver. Paroxetine is not approved for usein pediatric patients. (See WARNINGS: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk,PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients, andPRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use.)
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
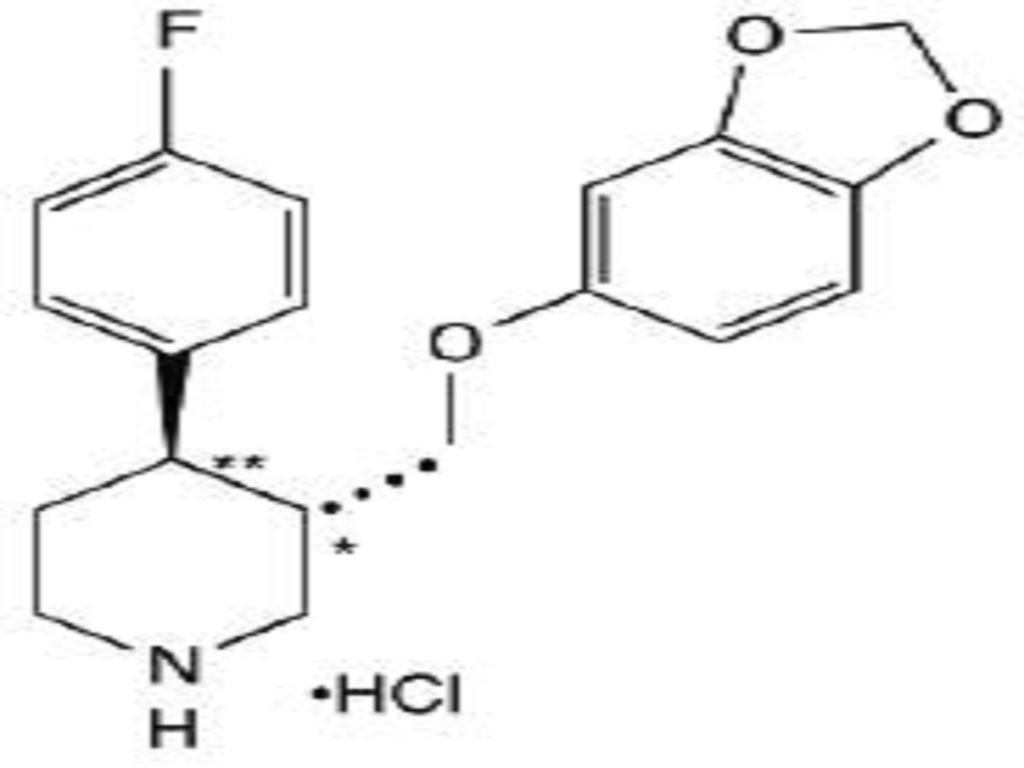
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
PharmacodynamicsPharmacokinetics
PRECAUTIONS: Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
Other Clinical Pharmacology Information
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions
Clinical Trials
Outcome Classification (%) on CGI-Global Improvement Item for Completers in Study 1Outcome ClassificationPlacebo (n = 74)Paroxetine 20 mg (n = 75)Paroxetine 40 mg (n = 66)Paroxetine 60 mg (n = 66)
INDICATIONS & USAGE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials
The effects of paroxetine in hospitalized depressed patients have not been adequately studied.
The efficacy of paroxetine in maintaining a response in major depressive disorder for up to 1 year was demonstrated in a placebo-controlled trial (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of obsessions and compulsions in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) as defined in the DSM-IV. The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time-consuming, or significantly interfere with social or occupational functioning.
The efficacy of paroxetine was established in two 12-week trials with obsessive compulsive outpatients whose diagnoses corresponded most closely to the DSM-IIIR category of obsessive compulsive disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials).
Obsessive compulsive disorder is characterized by recurrent and persistent ideas, thoughts, impulses, or images (obsessions) that are ego-dystonic and/or repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors (compulsions) that are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable.
Long-term maintenance of efficacy was demonstrated in a 6-month relapse prevention trial. In this trial, patients assigned to paroxetine showed a lower relapse rate compared to patients on placebo (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Panic Disorder
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, as defined in DSM-IV. Panic disorder is characterized by the occurrence of unexpected panic attacks and associated concern about having additional attacks, worry about the implications or consequences of the attacks, and/or a significant change in behavior related to the attacks.
The efficacy of paroxetine was established in three 10- to 12-week trials in panic disorder patients whose diagnoses corresponded to the DSM-IIIR category of panic disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials).
Long-term maintenance of efficacy was demonstrated in a 3-month relapse prevention trial. In this trial, patients with panic disorder assigned to paroxetine demonstrated a lower relapse rate compared to patients on placebo (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who prescribes paroxetine for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), as defined in DSM-IV. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
The efficacy of paroxetine in the treatment of GAD was established in two 8-week placebo-controlled trials in adults with GAD. Paroxetine has not been studied in children or adolescents with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials).
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (DSM-IV) is characterized by excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation) that is persistent for at least 6 months and which the person finds difficult to control. It must be associated with at least 3 of the following 6 symptoms: Restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge, being easily fatigued, difficulty concentrating or mind going blank, irritability, muscle tension, sleep disturbance.
The efficacy of paroxetine in maintaining a response in patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder, who responded during an 8-week acute treatment phase while taking paroxetine and were then observed for relapse during a period of up to 24 weeks, was demonstrated in a placebo-controlled trial (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGSPRECAUTIONSPRECAUTIONS
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide RiskTable 1
PRECAUTIONSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
Potential for Interaction With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
Potential Interaction With Thioridazine
CONTRAINDICATIONSPRECAUTIONS
Usage in Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
PRECAUTIONS: Discontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
Animal Findings
Nonteratogenic Effects
WARNINGS: Serotonin SyndromePotential for Interaction With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralDiscontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use
Hyponatremia
PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Drugs That Interfere With Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin, and Warfarin)
WARNINGS: Usage in Pregnancy: Teratogenic EffectsNonteratogenic Effects
PRECAUTIONS: Nursing Mothers
LABORATORY TESTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
TryptophanWARNINGS: Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS: Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like ReactionsCONTRAINDICATIONSPRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions, Tryptophan
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS: Drugs That Interfere With Hemostasis
WARNINGS: Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like Reactions
ADVERSE REACTIONS: Postmarketing Reports
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS: Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
PRECAUTIONS: Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP2D6
ADVERSE REACTIONS: Postmarketing Reports
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
WARNINGS: Usage in Pregnancy: Teratogenic EffectsNonteratogenic Effects
LABOR & DELIVERY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
BOX WARNINGWARNINGS: Clinical Worsening and Suicide RiskDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
GERIATRIC USE
PRECAUTIONS: HyponatremiaCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Major Depressive DisorderOCDPanic DisorderGeneralized Anxiety DisorderParoxetinePlaceboParoxetinePlaceboParoxetinePlaceboParoxetinePlacebo
Body SystemPreferred TermParoxetine (n=421)Placebo (n=421)
Body SystemPreferred TermObsessive Compulsive DisorderPanic DisorderParoxetine (n = 542)Placebo (n = 265)Paroxetine (n = 469)Placebo (n = 324)
Body SystemPreferred TermGeneralized Anxiety DisorderParoxetine (n=735)Placebo (n=529)
Body System/Preferred TermPlaceboParoxetinen = 5110 mg n = 10220 mg n = 10430 mg n = 10140 mg n = 102
ParoxetinePlacebon (males)14461042
PRECAUTIONS
Postmarketing Reports
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance ClassPhysical and Psychologic Dependence
OVERDOSAGE
PRECAUTIONS: Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP2D6
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Clinical Trials
WARNINGS: Usage in Pregnancy
Discontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
PRECAUTIONS: Discontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine Tablets
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
SPL MEDGUIDE
-
● all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
-
● all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
-
● Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
-
● Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
-
● Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
-
● thoughts about suicide or dying
-
● attempts to commit suicide
-
● new or worse depression
-
● new or worse anxiety
-
● feeling very agitated or restless
-
● panic attacks
-
● trouble sleeping (insomnia)
-
● new or worse irritability
-
● acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
-
● acting on dangerous impulses
-
● an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
-
● other unusual changes in behavior or mood
-
● Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
-
● Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
-
● Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
-
● Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
-
● Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child's healthcare provider for more information.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Paroxetine HydrochlorideParoxetine Hydrochloride TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!