Paroxetine Hydrochloride
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- LABOR & DELIVERY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
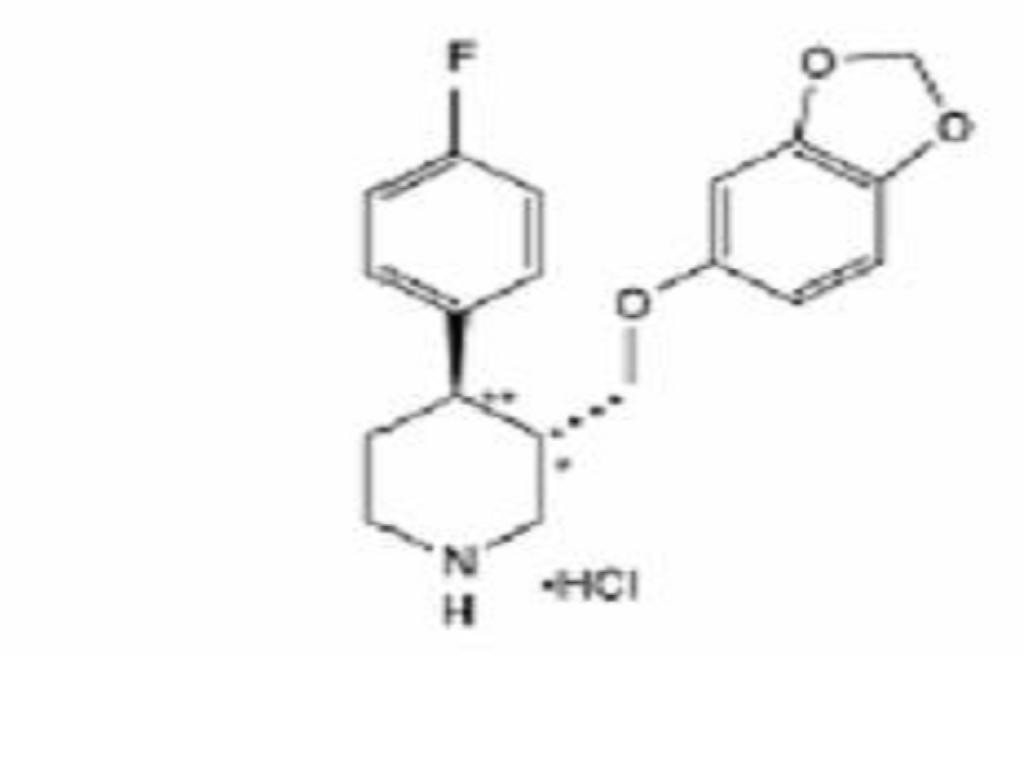
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics:Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption and Distribution:
Metabolism and Excretion:
PRECAUTIONSDrugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
Other Clinical Pharmacology Information:
Specific Populations:
Renal and Liver Disease:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Elderly Patients:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Drug-Drug Interactions:
Drug Interactions
Clinical Trials:
Major Depressive Disorder:
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder:
Panic Disorder:
Social Anxiety Disorder:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Major Depressive Disorder:CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials
The effects of paroxetine tablets, USP in hospitalized depressed patients have not been adequately studied.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP in maintaining a response in major depressive disorder for up to 1 year was demonstrated in a placebo-controlled trial (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine tablets, USP for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder:
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of obsessions and compulsions in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) as defined in the DSM-IV. The obsessions or compulsions cause marked distress, are time-consuming, or significantly interfere with social or occupational functioning.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP were established in two 12-week trials with obsessive compulsive outpatients whose diagnoses corresponded most closely to the DSM-IIIR category of obsessive compulsive disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials).
Obsessive compulsive disorder is characterized by recurrent and persistent ideas, thoughts, impulses, or images (obsessions) that are ego-dystonic and/or repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors (compulsions) that are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable.
Long-term maintenance of efficacy was demonstrated in a 6-month relapse prevention trial. In this trial, patients assigned to paroxetine showed a lower relapse rate compared to patients on placebo (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine tablets, USP for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Panic Disorder:
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, as defined in DSM-IV. Panic disorder is characterized by the occurrence of unexpected panic attacks and associated concern about having additional attacks, worry about the implications or consequences of the attacks, and/or a significant change in behavior related to the attacks.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP were established in three 10- to 12-week trials in panic disorder patients whose diagnoses corresponded to the DSM-IIIR category of panic disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials).
Panic disorder (DSM-IV) is characterized by recurrent unexpected panic attacks, i.e., a discrete period of intense fear or discomfort in which 4 (or more) of the following symptoms develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes: (1) palpitations, pounding heart, or accelerated heart rate; (2) sweating; (3) trembling or shaking; (4) sensations of shortness of breath or smothering; (5) feeling of choking; (6) chest pain or discomfort; (7) nausea or abdominal distress; (8) feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint; (9) derealization (feelings of unreality) or depersonalization (being detached from oneself); (10) fear of losing control; (11) fear of dying; (12) paresthesias (numbness or tingling sensations); (13) chills or hot flushes.
Long-term maintenance of efficacy was demonstrated in a 3-month relapse prevention trial. In this trial, patients with panic disorder assigned to paroxetine demonstrated a lower relapse rate compared to patients on placebo (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who prescribes paroxetine tablets, USP for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Social Anxiety Disorder:
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, as defined in DSM-IV (300.23). Social anxiety disorder is characterized by a marked and persistent fear of 1 or more social or performance situations in which the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. Exposure to the feared situation almost invariably provokes anxiety, which may approach the intensity of a panic attack. The feared situations are avoided or endured with intense anxiety or distress. The avoidance, anxious anticipation, or distress in the feared situation(s) interferes significantly with the person's normal routine, occupational or academic functioning, or social activities or relationships, or there is marked distress about having the phobias. Lesser degrees of performance anxiety or shyness generally do not require psychopharmacological treatment.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP were established in three 12-week trials in adult patients with social anxiety disorder (DSM-IV). Paroxetine tablets, USP have not been studied in children or adolescents with social phobia (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials).
The effectiveness of paroxetine tablets, USP in long-term treatment of social anxiety disorder, i.e., for more than 12 weeks, has not been systematically evaluated in adequate and well-controlled trials. Therefore, the physician who elects to prescribe paroxetine tablets, USP for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
Paroxetine tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), as defined in DSM-IV. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP in the treatment of GAD was established in two 8-week placebo-controlled trials in adults with GAD. Paroxetine tablets, USP have not been studied in children or adolescents with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials).
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (DSM-IV) is characterized by excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation) that is persistent for at least 6 months and which the person finds difficult to control. It must be associated with at least 3 of the following 6 symptoms: Restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge, being easily fatigued, difficulty concentrating or mind going blank, irritability, muscle tension, sleep disturbance.
The efficacy of paroxetine tablets, USP in maintaining a response in patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder, who responded during an 8-week acute treatment phase while taking paroxetine tablets, USP and were then observed for relapse during a period of up to 24 weeks, was demonstrated in a placebocontrolled trial (seeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials). Nevertheless, the physician who elects to use paroxetine tablets, USP for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGSPRECAUTIONSPRECAUTIONS
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk:PRECAUTIONSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDiscontinuation of Treatment With Paroxetine
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder:
Potential for Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors:
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Serotonin Syndrome:
Potential Interaction with Thioridazine:
CONTRAINDICATIONSPRECAUTIONS
Usage in Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects:
PRECAUTIONSDiscontinuation of Treatment With paroxetine
Animal Findings:
Nonteratogenic Effects:
WARNINGSSerotonin SyndromePotential for Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PRECAUTIONS
General:Activation of Mania Hypomania
Seizures:
Discontinuation of Treatment with Paroxetine Tablets:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Pediatric Use
Akathisia:
Hyponatremia:
PRECAUTIONSGeriatric Use
Abnormal Bleeding:
Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk:
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g.,NSAIDs, Aspirin and Warfarin):
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance:
Completing Course of Therapy:
Concomitant Medication:
Alcohol:
Pregnancy:
Usage in PregnancyTeratogenic EffectsNonteratogenic Effects
Nursing:
PRECAUTIONSNursing Mothers
Laboratory Tests:
Drug Interactions:
Tryptophan:
WARNINGSSerotonin Syndrome
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors:
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
Pimozide:
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Serotonergic Drugs:
WARNINGSSerotonin SyndromeCONTRAINDICATIONSPRECAUTIONSDrug Interactions Tryptophan
Thioridazine:
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
Warfarin:
PRECAUTIONSDrugs That Interfere with Hemostasis
Triptans:
WARNINGSSerotonin Syndrome
Drugs Affecting Hepatic Metabolism:
Cimetidine:
Phenobarbital:
Phenytoin:
Postmarketing Reports
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6:
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP3A4:
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs):
PRECAUTIONSDrugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP2D6
Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Protein:
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin and Warfarin):
Alcohol:
Lithium:
Digoxin:
Diazepam:
Procyclidine:
Beta-Blockers:
Postmarketing Reports
Theophylline:
Fosamprenavir/Ritonavir:
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT):
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
Mutagenesis:
Impairment of Fertility:
PREGNANCY
WARNINGSUsage in PregnancyTeratogenic effectsNonteratogenic EffectsLABOR & DELIVERY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
BOX WARNINGWARNINGSDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDiscontinuation of Treatment with Paroxetine Tablets
GERIATRIC USE
HyponatremiaCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment:***
Commonly Observed Adverse Events:
Table 2
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder:
Table 3
Panic Disorder:
Table 3
Social Anxiety Disorder:
Table 3
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
Table 4
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials:
Major Depressive Disorder:
*
*##
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder:
*
*
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
*
*
Dose Dependency of Adverse Events:
*
*
Adaptation to Certain Adverse Events:
Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction with SSRIs:
Weight and Vital Sign Changes:
ECG Changes:
Liver Function Tests:
Hallucinations:
Other Events Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Paroxetine Tablets:
PRECAUTIONS
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular System:
Digestive System:
Endocrine System:
Hemic and Lymphatic Systems:
Metabolic and Nutritional:
Musculoskeletal System:
Nervous System:
Respiratory System:
Skin and Appendages:
Special Senses:
Urogenital System:
Postmarketing Reports:
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance Class:Physical and Psychologic Dependence:
OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience:Overdosage Management:
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP2D6
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Major Depressive Disorder:Maintenance Therapy:
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder:
Maintenance Therapy:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials
Panic Disorder:
Maintenance Therapy:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials
Social Anxiety Disorder:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials
Maintenance Therapy:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder:
Maintenance Therapy:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYClinical Trials
Special Populations:
WARNINGSUsage in Pregnancy
Dosage for Elderly or Debilitated Patients, and Patients with Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment:
Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor:
Discontinuation of Treatment with Paroxetine Tablets:
PRECAUTIONS
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
SPL MEDGUIDE
-
● All risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
-
● All treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
-
● Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
-
● Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
-
● Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
-
● Thoughts about suicide or dying
-
● Attempts to commit suicide
-
● New or worse depression
-
● New or worse anxiety
-
● Feeling very agitated or restless
-
● Panic attacks
-
● Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
-
● New or worse irritability
-
● Acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
-
● Acting on dangerous impulses
-
● An extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
-
● Other unusual changes in behavior or mood
-
● Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
-
● Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
-
● Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
-
● Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
-
● Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child's healthcare provider for more information.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Paroxetine HydrochlorideParoxetine Hydrochloride TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!