Plan B
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Plan B safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Plan B. Plan B (levonorgestrel) tablets, 0.75mg, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1982INDICATIONS AND USAGEPlan B is a progestin-only emergency contraceptive, indicated for prevention of pregnancy following unprotected intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure. Plan B is available only by prescription for women younger than age 17 years, and available over the counter for women 17 years and older. Plan B is not intended for routine use as a contraceptive. (1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONThe first tablet is taken orally as soon as possible within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse. The second tablet should be taken 12 hours after the first dose. Efficacy is better if Plan B is taken as soon as possible after unprotected intercourse. (2)DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSA total of two 0.75 mg tablets taken 12 hours apart as a single course of treatment (3)CONTRAINDICATIONSKnown or suspected pregnancy. (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Ectopic Pregnancy: Women who become pregnant or complain of lower abdominal pain after taking Plan B should be evaluated for ectopic pregnancy. (5.1) Plan B is not effective in terminating an existing pregnancy. (5.2 ) Effect on menses: Plan B may alter the next expected menses. If menses is delayed beyond 1 week, pregnancy should be considered. (5.3) STI/HIV: Plan B does not protect against STI/HIV. (5.4) Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) in the clinical trial included menstrual changes (26%), nausea (23%), abdominal pain (18%), fatigue (17%), headache (17%), dizziness (11%) and breast tenderness (11%). (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Barr Laboratories at 1-800-330-1271 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONSDrugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, such as CYP3A4, may decrease the effectiveness of progestin-only pills. (7)USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Nursing Mothers: Small amounts of progestin pass into the breast milk of nursing women taking progestin-only pills for long-term contraception, resulting in detectable steroid levels in infant plasma. (8.3) Plan B is not intended for use in pediatric (premenarcheal) (8.4) or postmenopausal women (8.5). Clinical trials demonstrated a higher pregnancy rate in the Chinese population. (8.6)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 PLAN B INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 PLAN B DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 PLAN B CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 PLAN B ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 PLAN B DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Plan B® is a progestin-only emergency contraceptive indicated for prevention of pregnancy following unprotected intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure. To obtain optimal efficacy, the first tablet should be taken as soon as possible within 72 hours of intercourse. The second tablet should be taken 12 hours later.
Plan B is available only by prescription for women younger than age 17 years, and available over the counter for women 17 years and older.
Plan B is not indicated for routine use as a contraceptive.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Take one tablet of Plan B orally as soon as possible within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure. Efficacy is better if the tablet is taken as soon as possible after unprotected intercourse. The second tablet should be taken 12 hours after the first dose. Plan B can be used at any time during the menstrual cycle.
If vomiting occurs within two hours of taking either dose of medication, consideration should be given to repeating the dose.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each Plan B tablet is supplied as a white, round tablet containing 0.75 mg of levonorgestrel and is marked with INOR on one side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Plan B is contraindicated for use in the case of known or suspected pregnancy.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies account for approximately 2% of all reported pregnancies. Up to 10% of pregnancies reported in clinical studies of routine use of progestin-only contraceptives are ectopic.
A history of ectopic pregnancy is not a contraindication to use of this emergency contraceptive method. Healthcare providers, however, should consider the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy in women who become pregnant or complain of lower abdominal pain after taking Plan B. A follow-up physical or pelvic examination is recommended if there is any doubt concerning the general health or pregnancy status of any woman after taking Plan B.
5.2 Existing Pregnancy
Plan B is not effective in terminating an existing pregnancy.
5.3 Effects on Menses
Some women may experience spotting a few days after taking Plan B. Menstrual bleeding patterns are often irregular among women using progestin-only oral contraceptives and women using levonorgestrel for postcoital and emergency contraception.
If there is a delay in the onset of expected menses beyond 1 week, consider the possibility of pregnancy.
5.4 STI/HIV
Plan B does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
5.5 Physical Examination and Follow-up
A physical examination is not required prior to prescribing Plan B. A follow-up physical or pelvic examination is recommended if there is any doubt concerning the general health or pregnancy status of any woman after taking Plan B.
5.6 Fertility Following Discontinuation
A rapid return of fertility is likely following treatment with Plan B for emergency contraception; therefore, routine contraception should be continued or initiated as soon as possible following use of Plan B to ensure ongoing prevention of pregnancy.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
A double-blind, controlled clinical trial in 1,955 evaluable women compared the efficacy and safety of Plan B (one 0.75 mg tablet of levonorgestrel taken within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse, and one tablet taken 12 hours later) to the Yuzpe regimen (two tablets each containing 0.25 mg levonorgestrel and 0.05 mg ethinyl estradiol, taken within 72 hours of intercourse, and two tablets taken 12 hours later).
The most common adverse events (>10%) in the clinical trial for women receiving Plan B included menstrual changes (26%), nausea (23%), abdominal pain (18%), fatigue (17%), headache (17%), dizziness (11%), and breast tenderness (11%). Table 1 lists those adverse events that were reported in ≥ 5% of Plan B users.
|
Plan B Levonorgestrel N=977 (%) |
|
| Nausea | 23.1 |
| Abdominal Pain | 17.6 |
| Fatigue | 16.9 |
| Headache | 16.8 |
| Heavier Menstrual Bleeding | 13.8 |
| Lighter Menstrual Bleeding | 12.5 |
| Dizziness | 11.2 |
| Breast Tenderness | 10.7 |
| Vomiting | 5.6 |
| Diarrhea | 5.0 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Plan B. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abdominal Pain, Nausea, Vomiting
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Fatigue
Nervous System Disorders
Dizziness, Headache
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders
Dysmenorrhea, Irregular Menstruation, Oligomenorrhea, Pelvic Pain
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs or herbal products that induce enzymes, including CYP3A4, that metabolize progestins may decrease the plasma concentrations of progestins, and may decrease the effectiveness of progestin-only pills. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of progestin-only pills include:
- barbiturates
- bosentan
- carbamazepine
- felbamate
- griseofulvin
- oxcarbazepine
- phenytoin
- rifampin
- St. John’s wort
- topiramate
Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma levels of the progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration with HIV protease inhibitors or with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Consult the labeling of all concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with progestin-only pills or the potential for enzyme alterations.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Many studies have found no harmful effects on fetal development associated with long-term use of contraceptive doses of oral progestins. The few studies of infant growth and development that have been conducted with progestin-only pills have not demonstrated significant adverse effects.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
In general, no adverse effects of progestin-only pills have been found on breastfeeding performance or on the health, growth or development of the infant. However, isolated post-marketing cases of decreased milk production have been reported. Small amounts of progestins pass into the breast milk of nursing mothers taking progestin-only pills for long-term contraception, resulting in detectable steroid levels in infant plasma.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of progestin-only pills for long-term contraception have been established in women of reproductive age. Safety and efficacy are expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents under the age of 16 and for users 16 years and older. Use of Plan B emergency contraception before menarche is not indicated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
This product is not intended for use in postmenopausal women.
8.6 Race
No formal studies have evaluated the effect of race. However, clinical trials demonstrated a higher pregnancy rate in Chinese women with both Plan B and the Yuzpe regimen (another form of emergency contraception). The reason for this apparent increase in the pregnancy rate with emergency contraceptives in Chinese women is unknown.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Plan B.
8.8 Renal Impairment
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Plan B.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Levonorgestrel is not a controlled substance. There is no information about dependence associated with the use of Plan B.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There are no data on overdosage of Plan B, although the common adverse event of nausea and associated vomiting may be anticipated.
11 DESCRIPTION
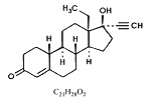
Each Plan B tablet contains 0.75 mg of a single active steroid ingredient, levonorgestrel [18,19-Dinorpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one-13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-, (17α)-(-)-], a totally synthetic progestogen. The inactive ingredients present are colloidal silicon dioxide, potato starch, gelatin, magnesium stearate, talc, corn starch, and lactose monohydrate. Levonorgestrel has a molecular weight of 312.45, and the following structural and molecular formulas:
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Emergency contraceptive pills are not effective if a woman is already pregnant. Plan B is believed to act as an emergency contraceptive principally by preventing ovulation or fertilization (by altering tubal transport of sperm and/or ova). In addition, it may inhibit implantation (by altering the endometrium). It is not effective once the process of implantation has begun.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
No specific investigation of the absolute bioavailability of Plan B in humans has been conducted. However, literature indicates that levonorgestrel is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration (bioavailability about 100%) and is not subject to first pass metabolism.
After a single dose of Plan B (0.75 mg) administered to 16 women under fasting conditions, maximum serum concentrations of levonorgestrel were 14.1 + 7.7 ng/mL (mean + SD) at an average of 1.6 + 0.7 hours.
| Mean (± SD) | ||||||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | CL (L/h) |
Vd (L) | t½ (h) | AUCinf (ng/mL.h) | |
| Levonorgestrel | 14.1 (7.7) | 1.6 ( 0.7) | 7.7 (2.7) | 260.0 | 24.4 (5.3) | 123.1 (50.1) |
|
Cmax = maximum concentration Tmax = time to maximum concentration CL = clearance Vd = volume of distribution t1/2 = elimination half life AUCinf = area under the drug concentration curve from time 0 to infinity |
||||||
Effect of Food: The effect of food on the rate and the extent of levonorgestrel absorption following single oral administration of Plan B has not been evaluated.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of levonorgestrel is reported to be approximately 1.8 L/kg. It is about 97.5 to 99% protein-bound, principally to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and, to a lesser extent, serum albumin.
Metabolism
Following absorption, levonorgestrel is conjugated at the 17β-OH position to form sulfate conjugates and, to a lesser extent, glucuronide conjugates in plasma. Significant amounts of conjugated and unconjugated 3α, 5β-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel are also present in plasma, along with much smaller amounts of 3α, 5α-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel and 16βhydroxylevonorgestrel. Levonorgestrel and its phase I metabolites are excreted primarily as glucuronide conjugates. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for the wide variation observed in levonorgestrel concentrations among users.
Excretion
About 45% of levonorgestrel and its metabolites are excreted in the urine and about 32% are excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates.
Specific Populations
Pediatric: This product is not intended for use in the pediatric (pre-menarcheal) population, and pharmacokinetic data are not available for this population.
Geriatric: This product is not intended for use in postmenopausal women and pharmacokinetic data are not available for this population.
Race: No formal studies have evaluated the effect of race on pharmacokinetics of Plan B. However, clinical trials demonstrated a higher pregnancy rate in Chinese women with both Plan B and the Yuzpe regimen (another form of emergency contraception). The reason for this apparent increase in the pregnancy rate with emergency contraceptives in Chinese women is unknown [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment: No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Plan B.
Renal Impairment: No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Plan B.
Drug-Drug Interactions
No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Plan B [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity: There is no evidence of increased risk of cancer with short-term use of progestins. There was no increase in tumorgenicity following administration of levonorgestrel to rats for 2 years at approximately 5 µg/day, to dogs for 7 years at up to 0.125 mg/kg/day, or to rhesus monkeys for 10 years at up to 250 µg/kg/day. In another 7 year dog study, administration of levonorgestrel at 0.5 mg/kg/day did increase the number of mammary adenomas in treated dogs compared to controls. There were no malignancies.
Genotoxicity: Levonorgestrel was not found to be mutagenic or genotoxic in the Ames Assay, in vitro mammalian culture assays utilizing mouse lymphoma cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in an in vivo micronucleus assay in mice.
Fertility: There are no irreversible effects on fertility following cessation of exposures to levonorgestrel or progestins in general.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
A double-blind, randomized, multinational controlled clinical trial in 1,955 evaluable women (mean age 27) compared the efficacy and safety of Plan B (one 0.75 mg tablet of levonorgestrel taken within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse, and one tablet taken 12 hours later) to the Yuzpe regimen (two tablets each containing 0.25 mg levonorgestrel and 0.05 mg ethinyl estradiol, taken within 72 hours of intercourse, and two additional tablets taken 12 hours later). After a single act of intercourse occurring anytime during the menstrual cycle, the expected pregnancy rate of 8% (with no contraceptive use) was reduced to approximately 1% with Plan B.
Emergency contraceptives are not as effective as routine hormonal contraception since their failure rate, while low based on a single use, would accumulate over time with repeated use [see INDICATIONS AND USAGE (1) ].
At the time of expected menses, approximately 74% of women using Plan B had vaginal bleeding similar to their normal menses, 14% bled more than usual, and 12% bled less than usual. The majority of women (87%) had their next menstrual period at the expected time or within + 7 days, while 13% had a delay of more than 7 days beyond the anticipated onset of menses.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Plan B (levonorgestrel) tablets, 0.75 mg, are available for a single course of treatment in PVC/aluminum foil blister packages of two tablets each. The tablet is white, round and marked INOR on one side.
Available as: Unit-of-use NDC 54868-4894-0
Store Plan B tablets at controlled room temperature, 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Information for Patients
- Take Plan B as soon as possible and not more than 72 hours after unprotected intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure.
- If you vomit within two hours of taking either tablet, immediately contact your healthcare provider to discuss whether to take another tablet.
- Seek medical attention if you experience severe lower abdominal pain 3 to 5 weeks after taking Plan B, in order to be evaluated for an ectopic pregnancy.
- After taking Plan B, consider the possibility of pregnancy if your period is delayed more than one week beyond the date you expected your period.
- Do not use Plan B as routine contraception.
- Plan B is not effective in terminating an existing pregnancy.
- Plan B does not protect against HIV-infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases/infections.
- For women younger than age 17 years, Plan B is available only by prescription.
Mfg. by Gedeon Richter, Ltd., Budapest, Hungary
for Duramed Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Subsidiary of Barr Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Pomona, New York 10970
Phone: 1-800-330-1271 Website: www.go2planb.com
BR- 0038/11001288
Revised July 2009
Additional barcode labeling by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, Oklahoma 74146
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

NDC 54868-4894-0
Plan B®
(LEVONORGESTREL)
tablets 0.75 mg
Emergency Contraceptive
2 Levonorgestrel Tablets
0.75 mg each
The sooner you take the first tablet, the better Plan B® will work
Not for regular birth control.
Plan B® should be used only in emergencies.
1 Take first tablet as soon as possible, within 72 hours (3 days) after unprotected sex.
2 Take second tablet 12 hours after taking first tablet.
TIME REMINDER Write on line below, the time the first tablet is taken. Take second tablet 12 hours later
AM/PM (circle one)
Reduces the chance of pregnancy after unprotected sex (if a regular birth control method fails or after sex without birth control).
Rx only for women younger than age 17
Take the first tablet as soon as possible within 72 hours (3 days) after unprotected sex. The sooner you take the first tablet, the better Plan B® will work. Take the second tablet 12 hours later.
Drug Facts
Active ingredient (in each tablet) Purpose
Levonorgestrel 0.75mg......................Emergency contraceptive
Use reduces chance of pregnancy after unprotected sex (if a contraceptive failed or if you did not use birth control)
Warnings
Allergy alert: Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to levonorgestrel
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) alert: This product does not protect against HIV/AIDS or other STDs
Do not use
- if you are already pregnant (because it will not work)
- for regular birth control
When using this product you may have
- menstrual changes
- nausea
- lower stomach (abdominal) pain
- tiredness
- headache
- dizziness
- breast pain
- vomiting
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control center right away.
Directions
- women 17 years of age or older:
-
take the first tablet as soon as possible within
72 hours (3 days) after unprotected sex. The sooner you
take the first tablet, the better it will work. - take the second tablet 12 hours after you take the first tablet
-
if you vomit within 2 hours of taking the medication, call a
healthcare professional to find out if you should repeat that dose - prescription only for women younger than age 17. If you
are younger than age 17, see a healthcare professional.
Other information
-
before using this product read the enclosed consumer
information leaflet for complete directions and information - this product is not recommended for regular birth control. It
does not work as well as most other birth control methods
used correctly. - this product works mainly by preventing ovulation (egg
release). It may also prevent fertilization of a released egg
(joining of sperm and egg) or attachment of a fertilized egg
to the uterus (implantation). - when used correctly every time you have sex, latex condoms
greatly reduce, but do not eliminate, the risk of pregnancy and
the risk of catching or spreading HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
See condom labeling for additional STD information. - tablets are enclosed in a blister seal. Do not use if the blister
seal is broken. - store at 20-25°C (68-77°F)
Inactive ingredients
colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, gelatin, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, potato starch, talc
Questions or comments?
For more information or to speak to a healthcare professional,
call 1-800-330-1271, 24 hours a day/7 days a week.
Visit our Web site at www.go2planb.com
Plan BLevonorgestrel TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||