Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Short Ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifolia
Jubilant HollisterStier LLC
Jubilant HollisterStier LLC
ALLERGENIC EXTRACT OF RAGWEED POLLEN (Short Ragweed or Giant and Short Ragweed Mixture) Amb a 1 Assayed
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNINGS
- POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE
- LIMITED WARRANTY SECTION
- REFERENCES
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNINGS
This product is intended for use only by licensed medical personnel experienced in administering allergenic extracts and trained to provide immediate emergency treatment in the event of a life-threatening reaction.
Allergenic extracts may potentially elicit a severe life-threatening systemic reaction, rarely resulting in death.1 Therefore, emergency measures and personnel trained in their use must be available immediately in the event of such a reaction. Patients should be instructed to recognize adverse reaction symptoms, be observed in the office for at least 30 minutes after skin testing or treatment, and be cautioned to contact the physician's office if symptoms occur. See ADVERSE REACTION section of this package insert regarding adverse event reporting.
This product should never be injected intravenously.
Patients with cardiovascular diseases and/or pulmonary diseases such as symptomatic unstable, steroid-dependent asthma, and/or those who are receiving cardiovascular drugs such as beta blockers, may be at higher risk for severe adverse reactions. These patients may also be more refractory to the normal allergy treatment regimen. Patients should be treated only if the benefit of treatment outweighs the risks.1
Patients on beta blockers may be more reactive to allergens given for testing or treatment and may be unresponsive to the actual doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reactions. 2
Refer to the WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS and OVERDOSE Sections for further discussion.
POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA DESCRIPTION
3
345,77,8
Ingredients:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism by which hyposensitization is achieved is not known completely. It has been shown that repeated injections of appropriate allergenic extracts will ameliorate the intensity of allergic symptoms upon contact with the allergen.10, 11, 12, 13 Clinical studies which address the efficacy of immunotherapy are available. The allergens which have been studied are cat, mite, venoms, and some pollen extracts.9, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 IgE antibodies bound to receptors on mast cell membranes are required for the allergic reaction, and their level is probably related to serum IgE concentrations. Immunotherapy has been associated with decreased levels of IgE, and also with increases in allergen specific IgG "blocking" antibody.
The histamine release response of circulating basophils to a specific allergen is reduced in some patients by hyposensitization, but the mechanism of this change is not clear.
Further study and clarification of the relationships among changes in blocking antibody, reaginic antibody, and mediator-releasing cells, and between these three factors and successful immunotherapy, is needed.
POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
20, 21, 22, 2324, 252627
POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA CONTRAINDICATIONS
known PRECAUTIONS WARNINGS1
2
WARNINGS
See WARNINGS box at the beginning of this package insert. See also PRECAUTIONS.
Allergenic extracts must be temporarily withheld from patients or the dose adjusted downward if any of the following conditions exist: (1) severe symptoms of rhinitis and/or asthma; (2) infection or flu accompanied by fever; (3) any evidence of an excessively large local or generalized reaction during the initial stages of immunotherapy or during maintenance therapy, and/or (4) exposure to excessive amounts of clinically relevant allergen prior to a scheduled injection.
Do not administer immunotherapy during a period of symptoms due to exposure. Since the individual components of the extract are those to which the patient is allergic, and to which s/he will be exposed, typical allergic symptoms may follow shortly after the injection, particularly when the antigen load from exposure plus the injected antigen exceeds the patient's antigen tolerance.
THE CONCENTRATE MUST NOT BE INJECTED AT ANY TIME UNLESS TOLERANCE HAS BEEN ESTABLISHED. DILUTE CONCENTRATED EXTRACTS WITH STERILE DILUENT FOR INTRADERMAL TESTING AND IMMUNOTHERAPY.
INJECTIONS MUST NEVER BE GIVEN INTRAVENOUSLY. Subcutaneous injection is recommended. Intracutaneous or intramuscular injection may produce large local reactions or be excessively painful. AFTER INSERTING NEEDLE SUBCUTANEOUSLY, BUT BEFORE INJECTING, ALWAYS WITHDRAW THE PLUNGER SLIGHTLY. IF BLOOD APPEARS IN THE SYRINGE, CHANGE NEEDLE AND GIVE THE INJECTION IN ANOTHER SITE.
PRECAUTIONS
1. General
The presence of asthmatic signs and symptoms appear to be an indicator for severe reactions following allergy injections. An assessment of airway obstruction either by measurement of peak flow or an alternate procedure may provide a useful indicator as to the advisability of administering an allergy injection.1, 28, 29, 30, 31
Concentrated extracts must not be injected unless tolerance has been established. Concentrated extracts must be diluted prior to use. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for detailed instructions on the dilution of allergenic extracts.
Any evidence of a local or generalized reaction requires a reduction in dosage during the initial stages of immunotherapy, as well as during maintenance therapy. Allergenic extracts diluted with sterile Albumin Saline with Phenol (0.4%) may be more potent than extracts diluted with diluents which do not contain stabilizers. When changing from non-stabilized to stabilized diluent, consider weaker initial dilutions for both intradermal testing and immunotherapy. Dilutions for both intradermal testing and immunotherapy. Sterile solutions, vials, syringes, etc., should be used and aseptic precautions observed in making dilutions.
To avoid cross-contamination, do not use the same needle to withdraw materials from vials of more than one extract, or extract followed by diluent.
A sterile tuberculin syringe graduated in 0.01 mL units and with a needle at least 5/8" long should be used to measure each dose from the appropriate dilution. Aseptic techniques should always be employed when injections of allergenic extracts are being administered.
A separate sterile syringe should be used for each patient to prevent transmission of hepatitis and other infectious agents from one person to another. Patient reactions to previous injections should be reviewed before each new injection, so that dosage can be adjusted accordingly. See ADVERSE REACTIONS and WARNINGS.
Rarely, a patient is encountered who develops systemic reactions to minute doses of allergen and does not demonstrate increasing tolerance to injections after several months of treatment. If systemic reactions or excessive local responses occur persistently at very small doses, efforts at immunotherapy should be stopped. PATIENTS SHOULD BE OBSERVED IN THE OFFICE FOR AT LEAST 30 MINUTES AFTER SKIN TESTING AND EACH TREATMENT INJECTION. Most severe reactions will occur within this time period, and rapid treatment measures should be instituted. See ADVERSE REACTIONS for these treatment measures.
2. Information for Patients
Patients should be instructed in the recognition of adverse reactions to immunotherapy, and in particular, to the symptoms of shock. (See WARNINGS box at the beginning of this package insert.) Patients should be made to understand the importance of a 30 minute observation period following skin testing or therapeutic injections, and be cautioned to return to the office promptly if symptoms occur after leaving.
Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of exposure to the allergen, so the physician can adjust the dosage appropriately.
3. Drug Interactions
Patients with cardiovascular diseases and/or pulmonary diseases such as symptomatic unstable, steroid-dependent asthma, and/or those who are receiving cardiovascular drugs such as beta blockers, may be at higher risk for severe adverse reactions. These patients may also be more refractory to the normal allergy treatment regimen. Patients should be treated only if the benefit of treatment outweighs the risks. 1
Patients on beta blockers may be more reactive to allergens given for testing or treatment and may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reactions.2 (See WARNINGS.)
Certain medications may lessen the skin test wheal and erythema responses elicited by allergens and histamine for varying time periods. Conventional antihistamines should be discontinued at least 5 days before skin testing. Long acting antihistamines should be discontinued for at least 3 weeks prior to skin testing. 32
Topical steroids should be discontinued at the skin test site for at least 2-3 weeks before skin testing.32, 33
Tricyclic antidepressants such as Doxepin should be withheld for at least 7 days before skin testing.34 Topical local anesthetics may suppress flare responses and should be avoided in skin test sites.35
When using other drugs in patients receiving allergenic extracts, always consult the product labeling of the other drugs to determine any possible interaction with use of allergenic extracts.
4. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been conducted with allergenic extracts to determine their potential for carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility.
5. Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with allergenic extracts. It is also not known whether allergenic extracts can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity.
Allergenic extracts should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. The physician must carefully consider the benefit-to-risk ratio to both patient and fetus, of performing skin testing or continuing immunotherapy during pregnancy. The recommended precautions (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS) for preventing adverse reactions are especially important in the pregnant patient. Based on the physician's discretion, immunotherapy maintenance doses may be continued during pregnancy if the patient has not experienced adverse side effects. Immunotherapy is generally not initiated during pregnancy due to the risks associated with systemic reactions and their treatment.37
6. Nursing Mothers
There are no current studies on the secretion of allergenic extract components in human milk or their effect on the nursing infant. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when allergenic extracts are administered to a nursing woman.
7. Pediatric Use
Since dosage for children is the same as for adults,38, 39 larger volumes of solution may produce excessive discomfort. Therefore, in order to achieve the total dose required, the volume of the dose may need to be divided into more than one injection per visit.
8. Geriatric Use
The reactions from immunotherapy can be expected to be the same in elderly patients as in younger ones. Elderly patients may be more likely to be on medication that could block the effect of epinephrine which could be used to treat serious reactions, or they could be more sensitive to the cardiovascular side effect of epinephrine because of pre-existing cardiovascular disease.40
POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA ADVERSE REACTIONS
WARNINGS1. Local Reactions
2. Systemic Reactions
1, 41
If a systemic or anaphylactic reaction does occur, apply a tourniquet above the site of injection and inject 1:1000 epinephrine-hydrochloride intramuscularly into the opposite arm. Loosen the tourniquet at least every 10 minutes. Do not obstruct arterial blood flow with the tourniquet.
EPINEPHRINE DOSAGE
ADULT:
PEDIATRIC
Ref. J. Allergy and Clinical Immunology
3. Adverse Event Reporting
OVERDOSAGE
See ADVERSE REACTIONS.
POLLENS - WEEDS AND GARDEN PLANTS, SHORT RAGWEED, AMBROSIA ARTEMISIIFOLIA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
21, 22, 23
1. General
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Sterile aqueous diluent containing human serum albumin [Albumin Saline with Phenol (0.4%)] or diluent of 50% glycerin may be used when preparing dilutions of the concentrate for immunotherapy. For intradermal testing dilutions, Albumin Saline with Phenol (0.4%) is recommended. Dilutions should be made accurately and aseptically, using sterile diluent, vials, syringes, etc. Mix thoroughly and gently by rocking or swirling. Maintain stock solutions and dilutions constantly at 2° - 8°C.
2. Pediatric Use
The dose for the pediatric population is the same as for adults. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
3. Geriatric Use
The dose for the elderly patients is the same as for adult patients under 65.40
4. Diagnosis
A positive reaction consists of an urticarial wheal with surrounding erythema (resembling somewhat a mosquito bite reaction) larger than the control site. The smallest reaction considered positive is erythema with a central papule at least 5 mm in diameter, however certain skin test devices may elicit a smaller positive reaction. Check the device manufacturer's recommendations. In some instances with no reaction at the control site, erythema may be considered an indication of sensitivity.
A positive skin reaction to any allergen must be interpreted in light of the patient's history of symptoms, time of year, and known exposures. THE SKIN TESTS ARE IN NO WAY A SUBSTITUTE FOR A CAREFUL ALLERGIC HISTORY. THEY SERVE AS ADDITIONAL INFORMATION TO AID IN IDENTIFYING CAUSATIVE ALLERGENS IN PATIENTS WITH ALLERGIC DISORDERS.
Skin tests are graded in terms of the wheal and erythema response noted at 15 minutes. Wheal and erythema size may be recorded by actual measurement of the extent of both responses.
Refer to the following table to determine the skin test sensitivity class. The corresponding ∑E (sum of the longest diameter and the mid-point orthogonal diameters of erythema) is also presented.
| Class |
Wheal Diameter |
Erythema Diameter |
Corresponding ∑E |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
< 5 mm |
<5 mm |
<10 mm |
| ± |
5-10 mm |
5-10 mm |
10-20 mm |
| 1+ |
5-10 mm |
11-20 mm |
20-40 mm |
| 2+ |
5-10 mm |
21-30 mm |
40-60 mm |
| 3+ |
10-15 mm a
|
31-40 mm |
60-80 mm |
| 4+ |
>15 mm b
|
>40 mm |
>80 mm |
a. Scratch, Prick or Puncture Testing
Scratch tests are performed by first scarifying the skin, then applying the extract to the scratch. Prick tests are performed by placing a drop of extract on the skin and piercing through the drop into the skin with a slight lifting motion. The prick is superficial and should not draw blood. Puncture tests are performed by placing a drop of extract on the skin and piercing through the drop perpendicular to the skin with a device such as a Prick Lancetter. After about 1 minute the extract may be wiped away with a dry sponge.
The diameter of wheal and erythema reactions are measured 15 minutes after the scratch, prick or puncture is made, and the sensitivity class of the patient determined by the table presented at the end of the diagnosis section. Less sensitive individuals (Class 0 to 1+) can be tested intradermally with the recommended dilutions of the extract concentrate (see Intradermal Testing )
b. Intradermal Testing
Intradermal tests should be done only on patients with a negative scratch, prick or puncture test. Patients who do not react to a valid scratch, prick or puncture test should be tested intradermally with 0.02 to 0.05 mL of extract solution. The intradermal strength for Short Ragweed extract is usually 500 PNU which by calculation contains approximately 0.7 to 3 units of Amb a 1/mL. For Giant and Short Ragweed mix, the suggested intradermal strength is 500 PNU which by calculation contains 0.4 to 1.5 units of Amb a 1/mL. These strengths are usually safe for testing patients previously having negative scratch, prick or puncture test reactions. A 1:10 dilution of the stock intradermal strength should be used in preliminary testing of patients not previously screened by scratch, prick or puncture tests. If the intradermal dilutions were prepared from glycerinated concentrate, the negative control used with this latter dilution should contain 5% glycerol. A site should be injected with 0.02 mL of the control solution. False positive reactions are sometimes encountered in intradermal testing and the possibility of irritation reactions should always be taken into consideration.
-1-6
5. Immunotherapy
Dosage of allergenic extracts is a highly individualized matter and varies according to the degree of sensitivity of the patient, his or her clinical response, and tolerance to the extract administered during the early phases of an injection regimen.
Allergen extracts should be administered using a sterile syringe with 0.01 mL gradations and a 25-27 gauge X 1/2" to 5/8" needle. The injections are given subcutaneously. The most common sites of injection are the lateral aspect of the upper arm or thigh. Intracutaneous or intramuscular injections may produce large local reactions which may be very painful.
To prepare dilutions for intradermal and therapeutic use, make a 1:10 dilution by adding 1.0 mL of the concentrate to 9.0 mL of the sterile aqueous diluent. Subsequent serial dilutions are made in a similar manner.
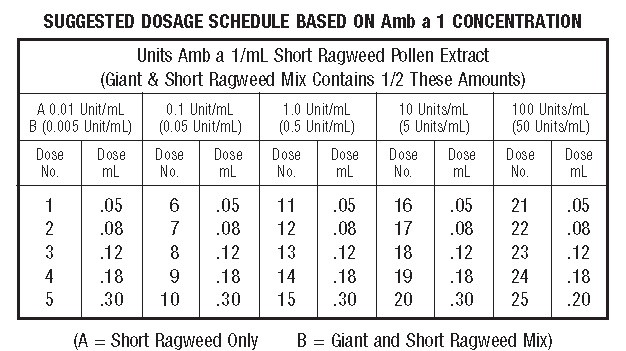
Following is a suggested schedule for average patients that will be satisfactory in most cases. However, the degree of sensitivity varies in many patients. The size of the dose should be adjusted and should be regulated by the patient's tolerance and reaction. Decrease the size of the dose if the previous injection resulted in marked local or the slightest general reaction. Another dose should never be given until all local reactions resulting from the previous dose have disappeared.
The starting dose should be based on skin tests of the extract to be used for immunotherapy. To determine the starting dose, begin intradermal testing with the most dilute extract preparation. Inject 0.02 mL and read the reaction after 15 minutes. Intradermal testing is continued with increasing concentrations of the extract until a reaction of 10-20 mm erythema (∑E 20-40 mm) and/or a 5 mm wheal occurs. This concentration at a dose of 0.03 mL then can serve as a starting dose for immunotherapy and be increased by 0.03 mL to as high as 0.12 mL increments each time until 0.3 mL is reached, at which time a dilution 10 times as strong can be used, starting with 0.03 mL. Proceed in this way until a tolerance dose is reached or symptoms are controlled. Suggested maintenance dose is 0.2 mL of the concentrate. Occasionally, higher doses are necessary to relieve symptoms. Special caution is required in administering doses greater than 0.2 mL. The interval between doses is normally 3 to 7 days during dose building regimen.
In some patients, the dosage may be increased more rapidly than called for in the schedule. In seasonal allergies, treatment should be started and the interval between doses regulated so that at least the first 20 doses will have been administered by the time symptoms are expected. Thus, the shorter the interval between the start of immunotherapy and the expected onset of symptoms, the shorter the interval between each dose. Some patients may even tolerate daily doses.
Should symptoms develop before the next injection is scheduled, the interval between doses should be decreased. Should allergic symptoms or local reactions develop shortly after the dose is administered, the size of the dose should be decreased. In seasonal allergies, it is often advisable to decrease the dose to one-half or one-quarter of the maximum dose previously attained if the patient has any seasonal symptoms.
A maintenance dose, the largest dose tolerated by the patient that relieves symptoms without producing undesirable local or general reactions, is recommended for most patients. The upper limits of dosage have not been established; however, doses larger than 0.2 mL of the glycerinated concentrate may be painful due to the glycerin content. The dosage of allergenic extract does not vary significantly with the respiratory allergic disease under treatment. The size of this dose and the interval between doses will vary and can be adjusted as necessary.
The interval between maintenance doses can be increased gradually from one week to 10 days, to two weeks, to three weeks, or even to four weeks, if tolerated. Repeat the doses at a given interval three or four times to check for untoward reactions before further increasing the interval. Protection is lost rapidly if the interval between doses is more than four weeks. (See WARNINGS Section.)
The usual duration of treatment has not been established. A period of two or three years of injection therapy constitutes an average minimum course of treatment.
In two hyposensitization studies using Amb a 1 27, 43 the amount administered over a pre-seasonal course of injections varied from 4 to 2,000 units of Amb a 1. The maximum individual dose attained ranged up to 170 units in one series.
Formula for calculating dilutions:
1122
1
1
2
2
Formula for determining diluent required:
12
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE
The expiration date is listed on the container label. To insure the maximum potency of Short Ragweed extract and its dilutions, it is recommended that the product be maintained at a temperature of 2° - 8°C at all times, even during use. Dilutions are less stable than the Concentrate. If loss of potency is suspected, the product should be checked by skin testing with equal units of a freshly prepared dilution on known ragweed pollen allergic individuals.
LIMITED WARRANTY SECTION
A number of factors beyond our control could reduce the efficacy of this product or even result in an ill effect following its use. These include storage and handling of the product after it leaves our hands, diagnosis, dosage, method of administration and biological differences in individual patients. Because of these factors, it is important that this product be stored properly and that the directions be followed carefully during use.
No warranty, express or implied, including any warranty of merchantability or fitness, is made. Representatives of the Company are not authorized to vary the terms or the contents of any printed labeling, including the package insert, for this product except by printed notice from the Company's headquarters. The prescriber and user of this product must accept the terms hereof.
REFERENCES
Ambrosia artemisiifolia

Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Short Ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifoliaShort Ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifolia INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Short Ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifoliaShort Ragweed, Ambrosia artemisiifolia INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Ragweed, Mixed AmbrosiaRagweed, Mixed Ambrosia INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Ragweed, Mixed AmbrosiaRagweed, Mixed Ambrosia INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants, Ragweed, Mixed AmbrosiaRagweed, Mixed Ambrosia INJECTION, SOLUTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||