Prazosin Hydrochloride
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- REFERENCES
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
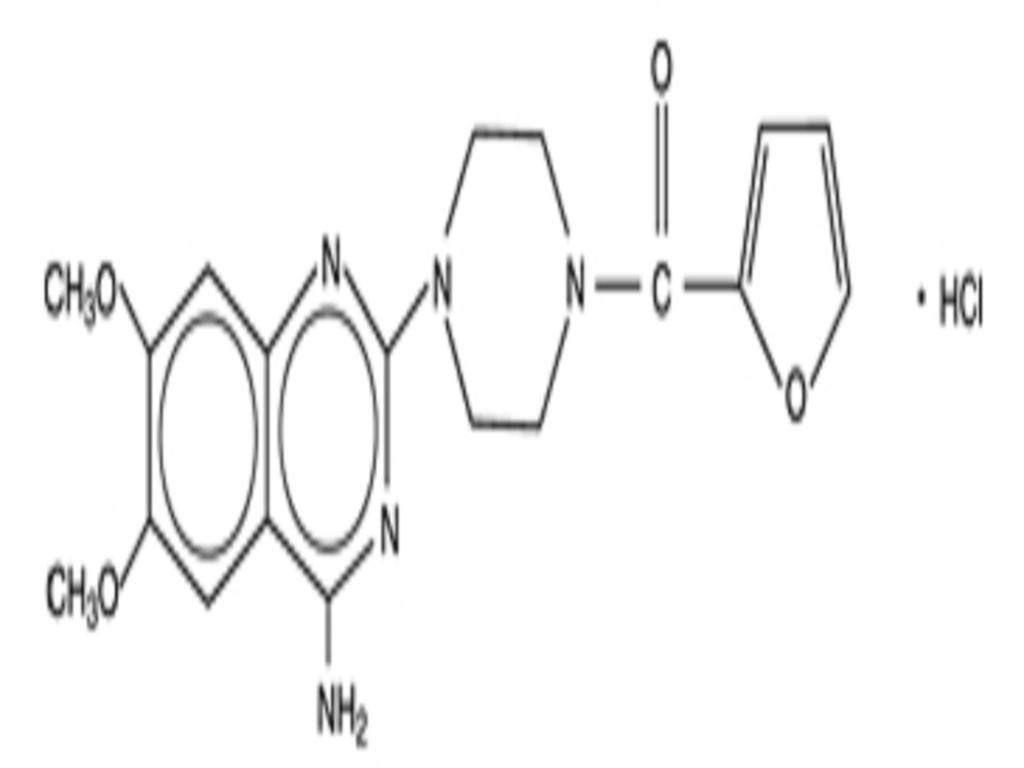
PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
INDICATIONS & USAGE
PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
As with all alpha-blockers, prazosin hydrochloride may cause syncope with suddent loss of consciousness. In most cases this is believed to be due to an excessive postural hypotensive effect, altough occasionally the syncopal episode has been preceded by a bout of severe tachycardia with heart rates of 120 to 160 beats per minute. Syncopal episodes have usually occurred within 30 to 90 minutes of the initial dose of the drug; occasionally they have been reported in association wiht rapid dosage increases or the introduction of another antihypertensive drug into the regimen of a patient taking high doses of prazosin. The incidence of syncopal episodes is approximately 1% in patients given an initial dose of 2 mg or greater. Clinical trials conducted during the investigational phase of this drug suggest that syncopal episodes can be minimized by limiting the initial dose of the drug to 1 mg, by subsequently increasing the dosage slowly, and by indroducing any additional antihypertensive durgs into the patient's regimen with caution (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Hypotension may develop in patients given prazosin who are also receiving a beta-blocker such as propranolol.PRECAUTIONS
GeneralINFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
DRUG INTERACTIONS
WARNINGSAddition of a diuretic or other antihypertensive agent to prazosin has been shown to cause an additive hypotensive effect. This effect can be minimized by reducing the prazosin dose to 1 mg to 2 mg three times a day, by introducing additional antihypertensive drugs cautiously and then by retitrating prazosin based on clinical response.
Concomitant administration of prazosin hydrochloride with a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitor can result in additive blood pressure lowering effects and symptomatic hypotension (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
LABORATORY TESTS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category CNURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
PRAZOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Gastrointestinal:
Cardiovascular:
Central Nervous System:
Dermatologic:
Genitourinary:
EENT:
Gastrointestinal:
Cardiovascular:
Central Nervous System:
Dermatologic:
Genitourinary:
EENT:
Other:
Autonomic Nervous System:
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular:
Endocrine:
Heart Rate/Rhythm:
Psychiatric:
Skin/Appendages:
Vascular (Extracardiac):
Vision:
Special Senses:PRECAUTIONS
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Initial Dose
WARNINGS
Maintenance Dose
Use With Other Drugs
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
REFERENCES
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION


Prazosin HydrochloridePrazosin Hydrochloride CAPSULE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!