PREZISTA
State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use PREZISTA safely and effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for PREZISTA. PREZISTA (darunavir) Tablet, Film Coated for Oral use Initial U.S. Approval – 2006RECENT MAJOR CHANGES • Contraindications (4) 04/2010 • Warnings and Precautions • Severe Skin Reactions (5.3) 01/2010 INDICATIONS AND USAGEPREZISTA is a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease inhibitor indicated for the treatment of HIV infection in adult patients. PREZISTA is also indicated for the treatment of HIV infection in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir (PREZISTA/ritonavir) and with other antiretroviral agents. (1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Treatment-naïve adult patients: 800 mg (two 400 mg tablets) taken with ritonavir 100 mg once daily and with food. (2.1) Treatment-experienced adult patients: 600 mg (one 600 mg tablet or two 300 mg tablets) taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily and with food. (2.1) Pediatric patients (6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg)): dosage of PREZISTA and ritonavir is based on body weight and should not exceed the treatment-experienced adult dose. Do not use once daily dosing in pediatric patients. PREZISTA tablets should be taken with ritonavir twice daily and with food. (2.2) PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS75 mg tablets, 150 mg tablets, 300 mg tablets, 400 mg tablets, and 600 mg tablets (3)CONTRAINDICATIONSCo-administration with alfuzosin, dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine, cisapride, pimozide, oral midazolam, triazolam, St. Johns Wort, lovastatin, simvastatin, rifampin and sildenafil (for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension). (4) Due to the need for co-administration of PREZISTA with 100 mg of ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for a description of ritonavir contraindications. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Drug-induced hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis) has been reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Monitor liver function before and during therapy, especially in patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases. (5.2, 6) Skin reactions ranging from mild to severe, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported. Discontinue treatment if severe reaction develops. (5.3, 6) Use with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy. (5.4) Patients may develop new onset diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia. Initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents may be required. (5.6) Patients may develop redistribution/accumulation of body fat (5.7) or immune reconstitution syndrome. (5.8) Patients with hemophilia may develop increased bleeding events. (5.9) PREZISTA/ritonavir should not be used in pediatric patients below 3 years of age. (5.11) Side Effects The most common clinical adverse drug reactions to PREZISTA/ritonavir (incidence ≥ 5%) of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) were diarrhea, nausea, rash, headache, abdominal pain and vomiting. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Tibotec Therapeutics at 1-877-REACH-TT or 1-877-732-2488 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir with other drugs can alter the concentration of other drugs and other drugs may alter the concentrations of darunavir. The potential drug-drug concentrations must be considered prior to and during therapy. (4, 5.5, 7, 12.3). USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Use during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. (8.1) An Antiviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263. Mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed due to the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. (8.3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 PREZISTA INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 PREZISTA DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 PREZISTA CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 PREZISTA ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 6.1 Clinical Trials Experience: Treatment-Naïve Adults
- 6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Treatment-Experienced Adults
- 6.3 Serious ADRs
- 6.4 Additional ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir identified in adult subjects in other clinical trials
- 6.5 Patients co-infected with hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus
- 6.6 Clinical Trials Experience: Pediatric Patients
- 6.7 Postmarketing Experience
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 PREZISTA DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Adult Patients
PREZISTA®, co-administered with ritonavir (PREZISTA/ritonavir), and with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
This indication is based on analyses of plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4+ cell counts from 2 controlled Phase 3 trials of 48 weeks duration in antiretroviral treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients and 2 controlled Phase 2 trials of 96 weeks duration in clinically advanced, treatment-experienced adult patients.
1.2 Pediatric Patients
PREZISTA, co-administered with ritonavir (PREZISTA/ritonavir), and with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of HIV infection in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ].
This indication is based on 24-week analyses of plasma HIV RNA levels and CD4+ cell counts from an open-label Phase 2 trial in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients 6 to < 18 years of age.
In treatment-experienced adult and pediatric patients, the following points should be considered when initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir:
- Treatment history and, when available, genotypic or phenotypic testing should guide the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ].
- The use of other active agents with PREZISTA/ritonavir is associated with a greater likelihood of treatment response [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) and Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Patients
PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir to exert its therapeutic effect. Failure to correctly co-administer PREZISTA with ritonavir will result in plasma levels of darunavir that will be insufficient to achieve the desired antiviral effect and will alter some drug interactions.
Treatment-Naïve Adult Patients
The recommended oral dose of PREZISTA tablets is 800 mg (two 400 mg tablets) taken with ritonavir 100 mg once daily and with food.
Treatment-Experienced Adult Patients
The recommended oral dose of PREZISTA tablets is 600 mg (one 600 mg tablet or two 300 mg tablets) taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily and with food. Once daily administration of PREZISTA is not recommended in treatment-experienced adult patients.
2.2 Pediatric Patients (age 6 to < 18 years)
Do not use once daily dosing in pediatric patients.
Healthcare professionals should pay special attention to accurate dose selection of PREZISTA, transcription of the medication order, dispensing information and dosing instruction to minimize risk for medication errors, overdose, and underdose.
Prescribers should select the appropriate dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir for each individual child based on body weight (kg) and should not exceed the recommended dose for treatment-experienced adults.
Before prescribing PREZISTA, children should be assessed for the ability to swallow tablets. If a child is unable to reliably swallow a tablet, the use of PREZISTA tablets may not be appropriate.
The recommended dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir for pediatric patients (6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg)) is based on body weight (see Table 1) and should not exceed the recommended treatment-experienced adult dose (PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg b.i.d.). PREZISTA tablets should be taken with ritonavir twice daily and with food.
| Body Weight | Dose | |
|---|---|---|
| (kg) | (lbs) | |
| ≥ 20 kg – < 30 kg | ≥ 44 lbs – < 66 lbs | 375 mg PREZISTA/50 mg ritonavir twice daily |
| ≥ 30 kg – < 40 kg | ≥ 66 lbs – < 88 lbs | 450 mg PREZISTA/60 mg ritonavir twice daily |
| ≥ 40 kg | ≥ 88 lbs | 600 mg PREZISTA/100 mg ritonavir twice daily |
The safety and efficacy of PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients 3 to < 6 years of age have not been established.
Do not use PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ].
2.3 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. No data are available regarding the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir when co-administered to subjects with severe hepatic impairment; therefore, PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
3.1 PREZISTA 75 mg Tablets
PREZISTA (darunavir) 75 mg tablets are supplied as white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 75 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "75" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
3.2 PREZISTA 150 mg Tablets
PREZISTA (darunavir) 150 mg tablets are supplied as white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 150 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "150" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
3.3 PREZISTA 300 mg Tablets
PREZISTA (darunavir) 300 mg tablets are supplied as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 300 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "300" on one side and "TMC114" on the other side.
3.4 PREZISTA 400 mg Tablets
PREZISTA (darunavir) 400 mg tablets are supplied as light orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 400 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "400" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
3.5 PREZISTA 600 mg Tablets
PREZISTA (darunavir) 600 mg tablets are supplied as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 600 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "600" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (narrow therapeutic index). These drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of darunavir) are listed in Table 2 [also see Drug Interactions (7.3) , Table 7].
| Drug Class | Drugs Within Class That Are Contraindicated With PREZISTA/ritonavir | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist | Alfuzosin | Potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as hypotension. |
| Ergot Derivatives | Dihydroergotamine, Ergonovine, Ergotamine, Methylergonovine | Potential for serious and/or life-threatening events such as acute ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues. |
| GI Motility Agent | Cisapride | Potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| Neuroleptic | Pimozide | Potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| Sedative/hypnotics | Orally administered Midazolam, Triazolam | Triazolam and orally administered midazolam are extensively metabolized by CYP3A. Co-administration of triazolam or orally administered midazolam with PREZISTA/ritonavir may cause large increases in the concentrations of these benzodiazepines. Potential for serious and/or life-threatening events such as prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression. |
| Herbal Products | St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) | Patients taking PREZISTA/ritonavir should not use products containing St. John's wort because co-administration may result in reduced plasma concentrations of darunavir. This may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance. |
| HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors | Lovastatin, Simvastatin | Potential for serious reactions such as myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. For dosing recommendation regarding atorvastatin and pravastatin, see Table 7: Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions: Alterations in Dose or Regimen May Be Recommended Based on Drug Interaction Studies or Predicted Interaction. |
| Antimycobacterial | Rifampin | Rifampin is a potent inducer of CYP450 metabolism. PREZISTA/ritonavir should not be used in combination with rifampin, as this may cause significant decreases in darunavir plasma concentrations. This may result in loss of therapeutic effect to PREZISTA. |
| PDE-5 inhibitor | Sildenafil for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension | A safe and effective dose for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension has not been established with PREZISTA/ritonavir. There is an increased potential for sildenafil-associated adverse events (which include visual disturbances, hypotension, prolonged erection, and syncope). |
Due to the need for co-administration of PREZISTA with ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for a description of ritonavir contraindications.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 General
PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir and food to achieve the desired antiviral effect. Failure to administer PREZISTA with ritonavir and food may result in a loss of efficacy of darunavir.
Please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for additional information on precautionary measures.
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis) has been reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir. During the clinical development program (N=3063), hepatitis was reported in 0.5% of patients receiving combination therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Patients with pre-existing liver dysfunction, including chronic active hepatitis B or C, have an increased risk for liver function abnormalities including severe hepatic adverse events.
Post-marketing cases of liver injury, including some fatalities, have been reported. These have generally occurred in patients with advanced HIV-1 disease taking multiple concomitant medications, having co-morbidities including hepatitis B or C co-infection, and/or developing immune reconstitution syndrome. A causal relationship with PREZISTA/ritonavir therapy has not been established.
Appropriate laboratory testing should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir and patients should be monitored during treatment. Increased AST/ALT monitoring should be considered in patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases, especially during the first several months of PREZISTA/ritonavir treatment.
Evidence of new or worsening liver dysfunction (including clinically significant elevation of liver enzymes and/or symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, dark urine, liver tenderness, hepatomegaly) in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir should prompt consideration of interruption or discontinuation of treatment.
5.3 Severe Skin Reactions
During the clinical development program (n=3063), severe skin reactions, accompanied by fever and/or elevations of transaminases in some cases, have been reported in 0.4% of subjects. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome was rarely (<0.1%) reported during the clinical development program. During post-marketing experience toxic epidermal necrolysis has been reported. Discontinue PREZISTA/rtv immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions develop. These can include but are not limited to severe rash or rash accompanied with fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, hepatitis and/or eosinophilia.
Rash (all grades, regardless of causality) occurred in 10.3% of subjects treated with PREZISTA/rtv [also see Adverse Reactions (6) ]. Rash was mostly mild-to-moderate, often occurring within the first four weeks of treatment and resolving with continued dosing. The discontinuation rate due to rash in subjects using PREZISTA/rtv was 0.5%.
5.4 Sulfa Allergy
Darunavir contains a sulfonamide moiety. PREZISTA should be used with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy. In clinical studies with PREZISTA/ritonavir, the incidence and severity of rash was similar in subjects with or without a history of sulfonamide allergy.
5.5 Drug Interactions
See Table 2 for a listing of drugs that are contraindicated for use with PREZISTA/ritonavir due to potentially life-threatening adverse events, significant drug-drug interactions, or loss of therapeutic effect to PREZISTA [see Contraindications (4) ]. Please refer to Table 7 for established and other potentially significant drug-drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ].
5.6 Diabetes Mellitus / Hyperglycemia
New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in HIV-infected patients receiving protease inhibitor (PI) therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued PI therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and causal relationships between PI therapy and these events have not been established.
5.7 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
5.8 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
During the initial phase of treatment, patients responding to antiretroviral therapy may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium complex, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, and tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
5.9 Hemophilia
There have been reports of increased bleeding, including spontaneous skin hematomas and hemarthrosis in patients with hemophilia type A and B treated with PIs. In some patients, additional factor VIII was given. In more than half of the reported cases, treatment with PIs was continued or reintroduced if treatment had been discontinued. A causal relationship between PI therapy and these episodes has not been established.
5.10 Resistance/Cross-Resistance
Because the potential for HIV cross-resistance among PIs has not been fully explored in PREZISTA/ritonavir treated patients, the effect therapy with PREZISTA will have on the activity of subsequently administered PIs is unknown [see Microbiology (12.4) ].
5.11 Pediatric Patients
Do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age in view of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir (from 20 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg) up to days 23 to 26 of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 and 8.4) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ]. The safety and efficacy of PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients 3 to < 6 years of age have not been established.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The safety assessment is based on all safety data from the Phase 2b studies (Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, TMC114-C215, and TMC114-C208) and Phase 3 studies (TMC114-C211, TMC114-C214, TMC114-C209, DUET-1 (TMC125-C206), and DUET-2 (TMC125-C216)) reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir in a total of 3063 subjects.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Due to the need for co-administration of PREZISTA with ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for ritonavir-associated adverse reactions.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience: Treatment-Naïve Adults
Study TMC114-C211
The safety assessment is based on all safety data from the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C211 comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day in 689 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects. The total mean exposure for subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily arm and in the lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day arm was 95.0 and 91.4 weeks, respectively.
The majority of the adverse drug reactions (ADRs) reported during treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily were mild in severity. The most common clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily (≥ 5%) of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) were diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain and rash. 2.3% of subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm discontinued treatment due to ADRs.
ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) in antiretroviral treatment naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects are presented in Table 3 and subsequent text below the table.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C211 |
||
|---|---|---|
| System Organ Class, Preferred Term, % |
PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily + TDF/FTC N = 343 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day + TDF/FTC N = 346 |
| N=total number of subjects per treatment group TDF = tenofovir disoproxil fumarate FTC = emtricitabine |
||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Abdominal pain | 5% | 6% |
| Diarrhea | 8% | 15% |
| Nausea | 3% | 4% |
| Vomiting | 2% | 3% |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
| Fatigue | < 1% | 3% |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Anorexia | 2% | < 1% |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 6% | 5% |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rash | 5% | 6% |
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Treatment-emergent ADRs of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) occurring in less than 2% of antiretroviral treatment-naïve subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily are listed below by body system:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: acute pancreatitis, dyspepsia, flatulence
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: asthenia
Hepatobiliary Disorders: acute hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis, hepatotoxicity)
Immune System Disorders: (drug) hypersensitivity
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: diabetes mellitus
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myalgia
Psychiatric Disorders: abnormal dreams
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: angioedema, pruritus, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, urticaria
Laboratory abnormalities:
Selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline observed in antiretroviral treatment-naïve adult subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily are presented in Table 4.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C211 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term, % |
Limit | PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily + TDF/FTC |
lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day + TDF/FTC |
| N=total number of subjects per treatment group TDF = tenofovir disoproxil fumarate FTC = emtricitabine |
|||
| Biochemistry | |||
| Alanine Aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 7% | 6% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | 3% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | < 1% | 3% |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 6% | 6% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | 4% | 2% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | 1% | 2% |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | 0% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | 0% | 0% |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 2.5 X ULN | < 1% | 4% |
| Grade 3 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | 0% | 0% |
| Triglycerides | |||
| Grade 2 | 5.65-8.48 mmol/L 500-750 mg/dL |
3% | 8% |
| Grade 3 | 8.49-13.56 mmol/L 751-1200 mg/dL |
1% | 5% |
| Grade 4 | > 13.56 mmol/L > 1200 mg/dL |
< 1% | < 1% |
| Total Cholesterol | |||
| Grade 2 | 6.20-7.77 mmol/L 240-300 mg/dL |
16% | 23% |
| Grade 3 | > 7.77 mmol/L > 300 mg/dL |
1% | 5% |
| Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | |||
| Grade 2 | 4.13-4.90 mmol/L 160-190 mg/dL |
14% | 10% |
| Grade 3 | ≥ 4.91 mmol/L ≥ 191 mg/dL |
5% | 5% |
| Elevated Glucose Levels | |||
| Grade 2 | 6.95-13.88 mmol/L 126-250 mg/dL |
7% | 8% |
| Grade 3 | 13.89-27.75 mmol/L 251-500 mg/dL |
< 1% | 0% |
| Grade 4 | > 27.75 mmol/L > 500 mg/dL |
0% | 0% |
| Pancreatic Lipase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 3.0 X ULN | 2% | 1% |
| Grade 3 | > 3.0 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | 0% | < 1% |
| Pancreatic Amylase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 2.0 X ULN | 5% | 2% |
| Grade 3 | > 2.0 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 3% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | 0% | < 1% |
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Treatment-Experienced Adults
Study TMC114-C214
The safety assessment is based on all safety data from the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C214 comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily in 595 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects. The total mean exposure for subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm and in the lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily arm was 80.7 and 76.4 weeks, respectively.
The majority of the ADRs reported during treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily were mild in severity. The most common clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (≥ 5%) of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) were diarrhea, nausea, rash, abdominal pain and vomiting. 4.7% of subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm discontinued treatment due to ADRs.
ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects are presented in Table 5 and subsequent text below the table.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C214 |
||
|---|---|---|
| System Organ Class, Preferred Term, % |
PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 298 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 297 |
| N=total number of subjects per treatment group OBR = optimized background regimen |
||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Abdominal distension | 2% | < 1% |
| Abdominal pain | 6% | 3% |
| Diarrhea | 14% | 20% |
| Dyspepsia | 2% | 1% |
| Nausea | 7% | 6% |
| Vomiting | 5% | 3% |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
| Asthenia | 3% | 1% |
| Fatigue | 2% | 1% |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
| Anorexia | 2% | 2% |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2% | < 1% |
| Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Headache | 3% | 3% |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rash | 7% | 3% |
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Treatment-emergent ADRs of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) occurring in less than 2% of antiretroviral treatment-experienced subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily are listed below by body system:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: acute pancreatitis, flatulence
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myalgia
Psychiatric Disorders: abnormal dreams
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: pruritus, urticaria
Laboratory abnormalities:
Selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline observed in antiretroviral treatment-experienced adult subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily are presented in Table 6.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C214 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term, % |
Limit | PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR |
lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily + OBR |
| N=total number of subjects per treatment group OBR = optimized background regimen |
|||
| Biochemistry | |||
| Alanine Aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 7% | 5% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | 2% | 2% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | 1% | 2% |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 6% | 6% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | 2% | 2% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | < 1% | 2% |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | 0% |
| Grade 3 | > 5.0 to ≤ 10.0 X ULN | < 1% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 10.0 X ULN | 0% | 0% |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 2.5 X ULN | < 1% | 2% |
| Grade 3 | > 2.5 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | 0% |
| Triglycerides | |||
| Grade 2 | 5.65-8.48 mmol/L 500-750 mg/dL |
10% | 11% |
| Grade 3 | 8.49-13.56 mmol/L 751-1200 mg/dL |
7% | 10% |
| Grade 4 | > 13.56 mmol/L > 1200 mg/dL |
3% | 6% |
| Total Cholesterol | |||
| Grade 2 | 6.20-7.77 mmol/L 240-300 mg/dL |
25% | 23% |
| Grade 3 | > 7.77 mmol/L > 300 mg/dL |
10% | 14% |
| Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | |||
| Grade 2 | 4.13-4.90 mmol/L 160-190 mg/dL |
14% | 14% |
| Grade 3 | ≥ 4.91 mmol/L ≥ 191 mg/dL |
8% | 9% |
| Elevated Glucose Levels | |||
| Grade 2 | 6.95-13.88 mmol/L 126-250 mg/dL |
10% | 11% |
| Grade 3 | 13.89-27.75 mmol/L 251-500 mg/dL |
1% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 27.75 mmol/L > 500 mg/dL |
< 1% | 0% |
| Pancreatic Lipase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 3.0 X ULN | 3% | 4% |
| Grade 3 | > 3.0 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 2% | < 1% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | < 1% | 0% |
| Pancreatic Amylase | |||
| Grade 2 | > 1.5 to ≤ 2.0 X ULN | 6% | 7% |
| Grade 3 | > 2.0 to ≤ 5.0 X ULN | 7% | 3% |
| Grade 4 | > 5.0 X ULN | 0% | 0% |
6.3 Serious ADRs
The following serious ADRs of at least moderate intensity (≥ Grade 2) occurred in the Phase 2b studies (Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, TMC114-C215, and TMC114-C208) and Phase 3 studies (TMC114-C211, TMC114-C214, TMC114-C209, DUET-1 (TMC125-C206), and DUET-2 (TMC125-C216)) with PREZISTA/ritonavir: abdominal pain, acute hepatitis, acute pancreatitis, anorexia, asthenia, diabetes mellitus, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, hepatic enzyme increased, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, immune reconstitution syndrome, low density lipoprotein increased, nausea, pancreatic enzyme increased, rash, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and vomiting.
6.4 Additional ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir identified in adult subjects in other clinical trials
The additional ADR of interest identified from other clinical trials was osteonecrosis.
6.5 Patients co-infected with hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus
In subjects co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir, the incidence of adverse events and clinical chemistry abnormalities was not higher than in subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir who were not co-infected, except for increased hepatic enzymes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]. The pharmacokinetic exposure in co-infected subjects was comparable to that in subjects without co-infection.
6.6 Clinical Trials Experience: Pediatric Patients
PREZISTA/ritonavir has been studied in 80 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg) in combination with other antiretroviral agents [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ].
Frequency, type, and severity of ADRs in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults. ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir (all grades, ≥ 3%), excluding laboratory abnormalities reported as ADRs, were vomiting (13%), diarrhea (11%), abdominal pain (10%), headache (9%), rash (5%), nausea (4%) and fatigue (3%).
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were ALT increased (Grade 3: 3%; Grade 4: 1%), AST increased (Grade 3: 1%), pancreatic amylase increased (Grade 3: 4%, Grade 4: 1%), pancreatic lipase increased (Grade 3: 1%), total cholesterol increased (Grade 3: 1%), and LDL increased (Grade 3: 3%).
6.7 Postmarketing Experience
The following events have been identified during postmarketing use of PREZISTA. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Redistribution of body fat has been reported.
Rarely, rhabdomyolysis (associated with co-administration with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and PREZISTA/ritonavir) and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
See also Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) .
7.1 Potential for PREZISTA/ritonavir to Affect Other Drugs
PREZISTA co-administered with ritonavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP2D6. Co-administration of PREZISTA and ritonavir with drugs that are primarily metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2D6 may result in increased plasma concentrations of such drugs, which could increase or prolong their therapeutic effect and adverse events (see Table 7).
7.2 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Darunavir
Darunavir and ritonavir are metabolized by CYP3A. Drugs that induce CYP3A activity would be expected to increase the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir, resulting in lowered plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir and other drugs that inhibit CYP3A may decrease the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir and may result in increased plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir (see Table 7).
7.3 Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Table 7 provides dosing recommendations as a result of drug interactions with PREZISTA/ritonavir. These recommendations are based on either drug interaction studies or predicted interactions due to the expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious adverse events or loss of efficacy.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name |
Effect on Concentration of Darunavir or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) | ||
| didanosine | ↔ darunavir ↔ didanosine |
Didanosine should be administered one hour before or two hours after PREZISTA/ritonavir (which are administered with food). |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: HIV-Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | ||
| indinavir (The reference regimen for indinavir was indinavir/ritonavir 800/100 mg twice daily.) |
↑ darunavir ↑ indinavir |
The appropriate dose of indinavir in combination with PREZISTA/ritonavir has not been established. |
| lopinavir/ritonavir | ↓ darunavir ↔ lopinavir |
Appropriate doses of the combination have not been established. Hence, it is not recommended to co-administer lopinavir/ritonavir and PREZISTA, with or without ritonavir. |
| saquinavir | ↓ darunavir ↔ saquinavir |
Appropriate doses of the combination have not been established. Hence, it is not recommended to co-administer saquinavir and PREZISTA, with or without ritonavir. |
| HIV-Antiviral Agents: CCR5 co-receptor antagonists | ||
| Maraviroc | ↑ maraviroc | Maraviroc concentrations are increased when co-administered with PREZISTA/rtv. When used in combination with PREZISTA/rtv, the dose of maraviroc should be 150 mg twice daily. |
| Other Agents | ||
|
Antiarrhythmics: bepridil, lidocaine (systemic), quinidine, amiodarone, flecainide, propafenone |
↑ antiarrhythmics | Concentrations of these drugs may be increased when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Caution is warranted and therapeutic concentration monitoring, if available, is recommended for antiarrhythmics when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
| digoxin | ↑ digoxin | The lowest dose of digoxin should initially be prescribed. The serum digoxin concentrations should be monitored and used for titration of digoxin dose to obtain the desired clinical effect. |
|
Anticoagulant: warfarin |
↓ warfarin ↔ darunavir |
Warfarin concentrations are decreased when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. It is recommended that the international normalized ratio (INR) be monitored when warfarin is combined with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Anticonvulsant: carbamazepine |
↔ darunavir ↑ carbamazepine |
The dose of either darunavir/ritonavir or carbamazepine does not need to be adjusted when initiating co-administration with darunavir/ritonavir and carbamazepine. Clinical monitoring of carbamazepine concentrations and its dose titration is recommended to achieve the desired clinical response. |
|
Anticonvulsant: phenobarbital, phenytoin |
↔ darunavir ↓ phenytoin ↓ phenobarbital |
Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir may cause decrease in the steady-state concentrations of phenytoin and phenobarbital. Phenytoin and phenobarbital levels should be monitored when co-administering with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Antidepressant: trazodone, desipramine |
↑ trazodone ↑ desipramine |
Concomitant use of trazodone or desipramine and PREZISTA/ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of trazodone or desipramine which may lead to adverse events such as nausea, dizziness, hypotension and syncope. If trazodone or desipramine is used with PREZISTA/ritonavir, the combination should be used with caution and a lower dose of trazodone or desipramine should be considered. |
|
Anti-infective: clarithromycin |
↔ darunavir ↑ clarithromycin |
No dose adjustment of the combination is required for patients with normal renal function. For patients with renal impairment, the following dose adjustments should be considered:
|
|
Antifungals: ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole |
↑ ketoconazole ↑ darunavir ↑ itraconazole (not studied) ↓ voriconazole (not studied) |
Ketoconazole and itraconazole are potent inhibitors as well as substrates of CYP3A. Concomitant systemic use of ketoconazole, itraconazole, and darunavir/ritonavir may increase plasma concentration of darunavir. |
| Plasma concentrations of ketoconazole or itraconazole may be increased in the presence of darunavir/ritonavir. When co-administration is required, the daily dose of ketoconazole or itraconazole should not exceed 200 mg. | ||
| Plasma concentrations of voriconazole may be decreased in the presence of darunavir/ritonavir. Voriconazole should not be administered to patients receiving darunavir/ritonavir unless an assessment of the benefit/risk ratio justifies the use of voriconazole. | ||
|
Anti-gout: colchicine |
↑ colchicine |
Treatment of gout-flares – co-administration of colchicine in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir:
0.6 mg (1 tablet) × 1 dose, followed by 0.3 mg (half tablet) 1 hour later. Treatment course to be repeated no earlier than 3 days.
Prophylaxis of gout-flares – co-administration of colchicine in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir:
Treatment of familial Mediterranean fever – co-administration of colchicine in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir:
|
|
Antimycobacterial: rifabutin |
↑ darunavir ↑ rifabutin ↑ 25-O-desacetylrifabutin |
Dose reduction of rifabutin by at least 75% of the usual dose (300 mg once daily) is recommended (i.e., a maximum dose of 150 mg every other day). Increased monitoring for adverse events is warranted in patients receiving this combination and further dose reduction of rifabutin may be necessary. |
| The reference regimen for rifabutin was 300 mg once daily | ||
|
β-Blockers: metoprolol, timolol |
↑ beta-blockers | Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring of patients is recommended. A dose decrease may be needed for these drugs when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Benzodiazepines: parenterally administered midazolam |
↑ midazolam | Concomitant use of parenteral midazolam with PREZISTA/ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of midazolam. Co-administration should be done in a setting which ensures close clinical monitoring and appropriate medical management in case of respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation. Dosage reduction for midazolam should be considered, especially if more than a single dose of midazolam is administered. Co-administration of oral midazolam with PREZISTA/ritonavir is CONTRAINDICATED. |
|
Calcium Channel
Blockers: felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine |
↑ calcium channel blockers | Plasma concentrations of calcium channel blockers (e.g., felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine) may increase when PREZISTA/ritonavir are co-administered. Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring of patients is recommended. |
|
Corticosteroid: Systemic: dexamethasone |
↓ darunavir | Systemic dexamethasone induces CYP3A and can thereby decrease darunavir plasma concentrations. This may result in loss of therapeutic effect to PREZISTA. |
|
Corticosteroid: Inhaled/Nasal: fluticasone |
↑ fluticasone | Concomitant use of inhaled fluticasone and PREZISTA/ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of fluticasone. Alternatives should be considered, particularly for long term use. |
|
Endothelin receptor antagonists: bosentan |
↑ bosentan |
Co-administration of bosentan in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir:
Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir in patients on bosentan:
|
|
HMG-CoA
Reductase Inhibitors: pravastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin |
↑ pravastatin ↑ atorvastatin ↑ rosuvastatin |
Use the lowest possible dose of atorvastatin, pravastatin or rosuvastatin with careful monitoring, or consider other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors such as fluvastatin in combination with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Immunosuppressants: cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus |
↑ immunosuppressants | Plasma concentrations of cyclosporine, tacrolimus or sirolimus may be increased when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Therapeutic concentration monitoring of the immunosuppressive agent is recommended when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Inhaled beta agonist: salmeterol |
↑ salmeterol | Concurrent administration of salmeterol and PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended. The combination may result in increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events associated with salmeterol, including QT prolongation, palpitations and sinus tachycardia. |
|
Narcotic Analgesic/Treatment of Opioid Dependence: methadone, buprenorphine, buprenorphine/naloxone |
↓ methadone ↔ buprenorphine, naloxone ↑ norbuprenorphine (metabolite) |
No adjustment of methadone dosage is required when initiating co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir. However, clinical monitoring is recommended as the dose of methadone during maintenance therapy may need to be adjusted in some patients. No dose adjustment for buprenorphine or buprenorphine/naloxone is required with concurrent administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir. Clinical monitoring is recommended if PREZISTA/ritonavir and buprenorphine or buprenorphine/naloxone are coadministered. |
|
Neuroleptics: risperidone, thioridazine |
↑ neuroleptics | A dose decrease may be needed for these drugs when co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir. |
|
Oral Contraceptives/estrogen: ethinyl estradiol, norethindrone |
↓ ethinyl estradiol ↓ norethindrone |
Plasma concentrations of ethinyl estradiol are decreased due to induction of its metabolism by ritonavir. Alternative methods of nonhormonal contraception are recommended. |
|
PDE-5 inhibitors: sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil |
↑ PDE-5 inhibitors (only the use of sildenafil at doses used for treatment of erectile dysfunction has been studied with PREZISTA/ritonavir) |
Co-administration with PREZISTA/ritonavir may result in an increase in PDE-5 inhibitor-associated adverse events, including hypotension, syncope, visual disturbances and priapism. Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH):
Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction:
|
|
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): sertraline, paroxetine |
↔ darunavir ↓ sertraline ↓ paroxetine |
If sertraline or paroxetine is co-administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir, the recommended approach is a careful dose titration of the SSRI based on a clinical assessment of antidepressant response. In addition, patients on a stable dose of sertraline or paroxetine who start treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir should be monitored for antidepressant response. |
In addition to the drugs included in Table 7, the interaction between PREZISTA/ritonavir and the following drugs were evaluated in clinical studies and no dose adjustments are needed for either drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]: atazanavir, efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine, omeprazole, ranitidine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs):
Based on the different elimination pathways of the other NRTIs (zidovudine, zalcitabine, emtricitabine, stavudine, lamivudine and abacavir) that are primarily renally excreted, no drug interactions are expected for these drugs and PREZISTA/ritonavir.
Other PIs:
The co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir and PIs other than lopinavir/ritonavir, saquinavir, atazanavir, and indinavir has not been studied. Therefore, such co-administration is not recommended.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: PREZISTA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.
No adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted in pregnant women. Reproduction studies conducted with darunavir showed no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity in mice, rats and rabbits. However, due to limited bioavailability and/or dosing limitations, animal exposures (based on AUC) were only 50% (mice and rats) and 5% (rabbit) of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir.
In the rat pre- and postnatal development study, a reduction in pup body weight gain was observed with darunavir alone or in combination with ritonavir during lactation. This was due to exposure of pups to drug substances via the milk. Sexual development, fertility and mating performance of offspring were not affected by maternal treatment with darunavir alone or in combination with ritonavir. The maximal plasma exposures achieved in rats were approximately 50% of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir.
In the juvenile toxicity study where rats were directly dosed with darunavir, deaths occurred from post-natal day 5 through 11 at plasma exposure levels ranging from 0.1 to 1.0 of the human exposure levels. In a 4-week rat toxicology study, when dosing was initiated on post-natal day 23 (the human equivalent of 2 to 3 years of age), no deaths were observed with a plasma exposure (in combination with ritonavir) of 0.1 of the human plasma exposure levels.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry : To monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to PREZISTA, an Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers in the United States not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. Although it is not known whether darunavir is secreted in human milk, darunavir is secreted into the milk of lactating rats. Because of both the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed if they are receiving PREZISTA.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age because of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir (from 20 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg) up to days 23 to 26 of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2) ].
The pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability, and efficacy of PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients 3 to < 6 years of age have not been established.
Do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir once daily in pediatric patients.
The safety, pharmacokinetic profile, and virologic and immunologic responses of PREZISTA/ritonavir were evaluated in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg) [see Adverse Reactions (6.6) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ]. Frequency, type, and severity of adverse drug reactions in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.6) ]. Please see Dosage and Administration (2.2) for dosing recommendations for pediatric subjects 6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of PREZISTA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, caution should be exercised in the administration and monitoring of PREZISTA in elderly patients reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment of PREZISTA/ritonavir is necessary for patients with either mild or moderate hepatic impairment. No pharmacokinetic or safety data are available regarding the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir in subjects with severe hepatic impairment, therefore, PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that the pharmacokinetics of darunavir were not significantly affected in HIV-infected subjects with moderate renal impairment (CrCL between 30-60 mL/min, n=20). No pharmacokinetic data are available in HIV-1-infected patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease; however, because the renal clearance of darunavir is limited, a decrease in total body clearance is not expected in patients with renal impairment. As darunavir and ritonavir are highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that they will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Human experience of acute overdose with PREZISTA/ritonavir is limited. Single doses up to 3200 mg of the oral solution of darunavir alone and up to 1600 mg of the tablet formulation of darunavir in combination with ritonavir have been administered to healthy volunteers without untoward symptomatic effects.
No specific antidote is available for overdose with PREZISTA. Treatment of overdose with PREZISTA consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed active substance is to be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage. Administration of activated charcoal may also be used to aid in removal of unabsorbed active substance. Since PREZISTA is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to be beneficial in significant removal of the active substance.
11 DESCRIPTION
PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease.
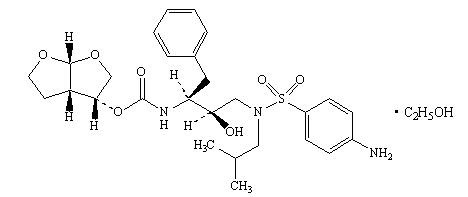
PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-carbamic acid (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester monoethanolate. Its molecular formula is C27H37N3O7S • C2H5OH and its molecular weight is 593.73. Darunavir ethanolate has the following structural formula:
Darunavir ethanolate is a white to off-white powder with a solubility of approximately 0.15 mg/mL in water at 20°C.
PREZISTA 75 mg tablets are available as white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 150 mg tablets are available as white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 300 mg and PREZISTA 600 mg tablets are available as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 400 mg is available as a light orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet for oral administration.
Each 75 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 75 mg of darunavir. Each 150 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 150 mg of darunavir. Each 300 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 300 mg of darunavir. Each 400 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 400 mg of darunavir. Each 600 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 600 mg of darunavir. During storage, partial conversion from ethanolate to hydrate may occur; however, this does not affect product quality or performance. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film coating, OPADRY® White, contains polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide. The tablet film coating, OPADRY® Orange, contains FD&C Yellow No. 6, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
All dosages for PREZISTA are expressed in terms of the free form of darunavir.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Darunavir is an HIV antiviral drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) ].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In an open-label, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled, four-way crossover trial, 40 healthy subjects were administered supratheraputic doses of darunavir/ritonavir 1600/100 mg once daily and 800/100 mg twice daily for seven days.
At the mean maximum darunavir concentration of 6599 ng/mL observed in this study, the mean increase in QTcF was 2.2 ms with a 90% two-sided confidence interval (CI) of -2.0 to 6.3 ms. When evaluating the 2-sided 90% CI on the time-matched mean changes in QTcF versus placebo control, the upper bounds of both darunavir/ritonavir groups never exceeded the 10 ms boundary. In the setting of this trial, darunavir/ritonavir did not appear to prolong the QTc interval.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics in Adults
General
Darunavir is primarily metabolized by CYP3A. Ritonavir inhibits CYP3A, thereby increasing the plasma concentrations of darunavir. When a single dose of PREZISTA 600 mg was given orally in combination with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, there was an approximate 14-fold increase in the systemic exposure of darunavir. Therefore, PREZISTA should only be used in combination with 100 mg of ritonavir to achieve sufficient exposures of darunavir.
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir, co-administered with low dose ritonavir (100 mg), has been evaluated in healthy adult volunteers and in HIV-1-infected subjects. Table 8 displays the population pharmacokinetic estimates of darunavir after oral administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily [based on sparse sampling in 285 patients in study TMC114-C214 and 119 patients (integrated data) from Studies TMC114-C202 and TMC114-C213] and PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily [based on sparse sampling in 335 patients in Study TMC114-C211] to HIV-1-infected patients.
| Parameter | Study TMC114-C211 PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily N = 335 |
Study TMC114-C214 PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily N = 285 |
Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 (integrated data) PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily N =119 |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = number of subjects with data. | |||
| AUC24h (ng∙h/mL) |
|||
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | 93026 ± 27050 | 116796 ± 33594 | 124698 ± 32286 |
| Median (Range) | 87854 (45000-219240) | 111632 (64874-355360) | 123336 (67714-212980) |
| C0h (ng/mL) | |||
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | 2282 ± 1168 | 3490 ± 1401 | 3578 ± 1151 |
| Median (Range) | 2041 (368-7242) | 3307 (1517-13198) | 3539 (1255-7368) |
Absorption and Bioavailability
Darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, was absorbed following oral administration with a Tmax of approximately 2.5-4 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of a single 600 mg dose of darunavir alone and after co-administration with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily was 37% and 82%, respectively. In vivo data suggests that darunavir/ritonavir is an inhibitor of the p-glycoprotein (p-gp) transporters.
Effects of Food on Oral Absorption
When administered with food, the Cmax and AUC of darunavir, co-administered with ritonavir, is approximately 30% higher relative to the fasting state. Therefore, PREZISTA tablets, co-administered with ritonavir, should always be taken with food. Within the range of meals studied, darunavir exposure is similar. The total caloric content of the various meals evaluated ranged from 240 Kcal (12 gms fat) to 928 Kcal (56 gms fat).
Distribution
Darunavir is approximately 95% bound to plasma proteins. Darunavir binds primarily to plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG).
Metabolism
In vitro experiments with human liver microsomes (HLMs) indicate that darunavir primarily undergoes oxidative metabolism. Darunavir is extensively metabolized by CYP enzymes, primarily by CYP3A. A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after a single dose administration of 400 mg 14C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir, the majority of the radioactivity in the plasma was due to darunavir. At least 3 oxidative metabolites of darunavir have been identified in humans; all showed activity that was at least 90% less than the activity of darunavir against wild-type HIV.
Elimination
A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after single dose administration of 400 mg 14C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir, approximately 79.5% and 13.9% of the administered dose of 14C-darunavir was recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged darunavir accounted for approximately 41.2% and 7.7% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively. The terminal elimination half-life of darunavir was approximately 15 hours when co-administered with ritonavir. After intravenous administration, the clearance of darunavir, administered alone and co-administered with 100 mg twice daily ritonavir, was 32.8 L/h and 5.9 L/h, respectively.
Special Populations
Hepatic Impairment
Darunavir is primarily metabolized by the liver. The steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of darunavir were similar after multiple dose co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily to subjects with normal hepatic function (n=16), mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, n=8), and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, n=8). The effect of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of darunavir has not been evaluated [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus Co-infection
The 48-week analysis of the data from Studies TMC114-C211 and TMC114-C214 in HIV-1-infected subjects indicated that hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infection status had no apparent effect on the exposure of darunavir.
Renal Impairment
Results from a mass balance study with 14C-darunavir/ritonavir showed that approximately 7.7% of the administered dose of darunavir is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug. As darunavir and ritonavir are highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that they will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that the pharmacokinetics of darunavir were not significantly affected in HIV-infected subjects with moderate renal impairment (CrCL between 30-60 mL/min, n=20). There are no pharmacokinetic data available in HIV-1-infected patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ].
Gender
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed higher mean darunavir exposure in HIV-infected females compared to males. This difference is not clinically relevant.
Race
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of darunavir in HIV-infected subjects indicated that race had no apparent effect on the exposure to darunavir.
Geriatric Patients
Population pharmacokinetic analysis in HIV-infected subjects showed that darunavir pharmacokinetics are not considerably different in the age range (18 to 75 years) evaluated in HIV-infected subjects (n = 12, age ≥ 65) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ].
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir in combination with ritonavir in 74 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 6 to < 18 years of age and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg) showed that the administered weight-based dosages resulted in darunavir exposure comparable to that in treatment-experienced adults receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
| Parameter Median (Range) |
PREZISTA/ritonavir twice daily N = 74 |
|---|---|
| N = number of subjects with data. * AUC24h is calculated as AUC12h*2 |
|
| AUC24h (ng∙h/mL) | 127340 (67054-230720) |
| C0h (ng/mL) | 3888 (1836-7821) |
Drug Interactions
[See also Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.5), and Drug Interactions (7) .]
Darunavir co-administered with ritonavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP2D6. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir with drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2D6 may result in increased plasma concentrations of such drugs, which could increase or prolong their therapeutic effect and adverse events.
Darunavir and ritonavir are metabolized by CYP3A. Drugs that induce CYP3A activity would be expected to increase the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir, resulting in lowered plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir and other drugs that inhibit CYP3A may decrease the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir and may result in increased plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir.
Drug interaction studies were performed with darunavir and other drugs likely to be co-administered and some drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of co-administration of darunavir on the AUC, Cmax, and Cmin values are summarized in Table 10 (effect of other drugs on darunavir) and Table 11 (effect of darunavir on other drugs). For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7) .
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose/Schedule | N | PK | LS Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Darunavir Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without Co-administered Drug No Effect =1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Administered Drug | Darunavir/ ritonavir |
Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |||
| N = number of subjects with data; - = no information available. | |||||||
| Co-Administration With Other Protease Inhibitors | |||||||
| Atazanavir | 300 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
13 | ↔ | 1.02 (0.96-1.09) |
1.03 (0.94-1.12) |
1.01 (0.88-1.16) |
| Indinavir | 800 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 9 | ↑ | 1.11 (0.98-1.26) |
1.24 (1.09-1.42) |
1.44 (1.13-1.82) |
| Lopinavir/ Ritonavir | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 1200/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 | ↓ | 0.79 (0.67-0.92) |
0.62 (0.53-0.73) |
0.49 (0.39-0.63) |
| 533/133.3 mg b.i.d. | 1200 mg b.i.d. |
15 | ↓ | 0.79 (0.64-0.97) |
0.59 (0.50-0.70) |
0.45 (0.38-0.52) |
|
| Saquinavir hard gel capsule |
1000 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 14 | ↓ | 0.83 (0.75-0.92) |
0.74 (0.63-0.86) |
0.58 (0.47-0.72) |
| Co-Administration With Other Antiretrovirals | |||||||
| Didanosine | 400 mg q.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 17 | ↔ | 0.93 (0.86-1.00) |
1.01 (0.95-1.07) |
1.07 (0.95-1.21) |
| Efavirenz | 600 mg q.d. | 300/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↓ | 0.85 (0.72-1.00) |
0.87 (0.75-1.01) |
0.69 (0.54-0.87) |
| Etravirine | 200 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 15 | ↔ | 1.11 (1.01-1.22) |
1.15 (1.05-1.26) |
1.02 (0.90-1.17) |
| Nevirapine | 200 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 8 | ↑ | 1.40  (1.14-1.73) |
1.24  (0.97-1.57) |
1.02  (0.79-1.32) |
| Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate | 300 mg q.d. | 300/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↑ | 1.16 (0.94-1.42) |
1.21 (0.95-1.54) |
1.24 (0.90-1.69) |
| Co-Administration With Other Drugs | |||||||
| Carbamazepine | 200 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↔ | 1.04 (0.93-1.16) |
0.99 (0.90-1.08) |
0.85 (0.73-1.00) |
| Clarithromycin | 500 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 17 | ↔ | 0.83 (0.72-0.96) |
0.87 (0.75-1.01) |
1.01 (0.81-1.26) |
| Ketoconazole | 200 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 14 | ↑ | 1.21 (1.04-1.40) |
1.42 (1.23-1.65) |
1.73 (1.39-2.14) |
| Omeprazole | 20 mg q.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↔ | 1.02 (0.95-1.09) |
1.04 (0.96-1.13) |
1.08 (0.93-1.25) |
| Paroxetine | 20 mg q.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↔ | 0.97 (0.92-1.02) |
1.02 (0.95-1.10) |
1.07 (0.96-1.19) |
| Ranitidine | 150 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↔ | 0.96 (0.89-1.05) |
0.95 (0.90-1.01) |
0.94 (0.90-0.99) |
| Rifabutin | 150 mg q.o.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. | 11 | ↑ | 1.42 (1.21-1.67) |
1.57 (1.28-1.93) |
1.75 (1.28-2.37) |
| Sertraline | 50 mg q.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 13 | ↔ | 1.01 (0.89-1.14) |
0.98 (0.84-1.14) |
0.94 (0.76-1.16) |
| Co-Administered Drug | Dose/Schedule | N | PK | LS Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Co-Administered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without Darunavir No effect =1.00 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Administered Drug | Darunavir/ ritonavir |
Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |||
| N = number of subjects with data;- = no information available. | |||||||
| A cocktail study was conducted in 12 healthy volunteers to evaluate the effect of steady state pharmacokinetics of darunavir/ritonavir on the activity of CYP2D6 (using dextromethorphan as probe substrate), CYP2C9 (using warfarin as probe substrate), and CYP2C19 (using omeprazole as probe substrate). The pharmacokinetic results are shown in Table 11. | |||||||
| Co-Administration With Other Protease Inhibitors | |||||||
| Atazanavir | 300 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
13 | ↔ | 0.89 (0.78-1.01) |
1.08 (0.94-1.24) |
1.52 (0.99-2.34) |
| 300 mg q.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
| Indinavir | 800 mg b.i.d. /100 mg ritonavir b.i.d. when administered alone | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 9 | ↑ | 1.08 (0.95-1.22) |
1.23 (1.06-1.42) |
2.25 (1.63-3.10) |
| 800 mg b.i.d. when administered with darunavir/ ritonavir |
|||||||
| Lopinavir/Ritonavir | 400/100 mg b.i.d. |
1200/100 mg b.i.d. | 14 | ↔ | 0.98 (0.78-1.22) |
1.09 (0.86-1.37) |
1.23 (0.90-1.69) |
533/133.3 mg b.i.d. |
1200 mg b.i.d. | 15 | ↔ | 1.11 (0.96-1.30) |
1.09 (0.96-1.24) |
1.13 (0.90-1.42) |
|
| Saquinavir hard gel capsule | 1000 mg b.i.d. /100 mg ritonavir b.i.d. when administered alone | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↔ | 0.94 (0.78-1.13) |
0.94 (0.76-1.17) |
0.82 (0.52-1.30) |
| 1000 mg b.i.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
| Co-Administration With Other Antiretrovirals | |||||||
| Didanosine | 400 mg q.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 17 | ↔ | 0.84 (0.59-1.20) |
0.91 (0.75-1.10) |
- |
| Efavirenz | 600 mg q.d. | 300/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↑ | 1.15 (0.97-1.35) |
1.21 (1.08-1.36) |
1.17 (1.01-1.36) |
| Etravirine | 100 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 14 | ↓ | 0.68 (0.57-0.82) |
0.63 (0.54-0.73) |
0.51 (0.44-0.61) |
| Nevirapine | 200 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 8 | ↑ | 1.18 (1.02-1.37) |
1.27 (1.12-1.44) |
1.47 (1.20-1.82) |
| Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate | 300 mg q.d. | 300/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↑ | 1.24 (1.08-1.42) |
1.22 (1.10-1.35) |
1.37 (1.19-1.57) |
| Maraviroc | 150 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↑ | 2.29 (1.46-3.59) |
4.05 (2.94-5.59) |
8.00 (6.35-10.1) |
| Maraviroc | 150 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. with 200 mg b.i.d. etravirine | 10 | ↑ | 1.77 (1.20-2.60) |
3.10 (2.57-3.74) |
5.27 (4.51-6.15) |
| Co-Administration With Other Drugs | |||||||
| Atorvastatin | 40 mg q.d. when administered alone | 300/100 mg b.i.d. | 15 | ↑ | 0.56 (0.48-0.67) |
0.85 (0.76-0.97) |
1.81 (1.37-2.40) |
| 10 mg q.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
| Buprenorphine/ Naloxone | 8/2 mg to 16/4 mg q.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 17 | ↔ | 0.92  (0.79-1.08) |
0.89  (0.78-1.02) |
0.98  (0.82-1.16) |
| Norbuprenorphine | 17 | ↑ | 1.36 (1.06-1.74) |
1.46 (1.15-1.85) |
1.71 (1.29-2.27) |
||
| Carbamazepine | 200 mg b.i.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↑ | 1.43 (1.34-1.53) |
1.45 (1.35-1.57) |
1.54 (1.41-1.68) |
| Carbamazepine epoxide | 16 | ↓ | 0.46 (0.43-0.49) |
0.46 (0.44-0.49) |
0.48 (0.45-0.51) |
||
| Clarithromycin | 500 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 17 | ↑ | 1.26 (1.03-1.54) |
1.57 (1.35-1.84) |
2.74 (2.30-3.26) |
| Dextromethorphan | 30 mg | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↑ | 1.27 (1.58-3.25) |
1.70 (1.80-4.05) |
- |
| Dextrorphan | ↓ | 0.86 (0.76-0.97) |
0.96 (0.89-1.03) |
- | |||
| Digoxin | 0.4 mg | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 8 | ↑ | 1.15 (0.89-1.48) |
1.36 (0.81-2.27) |
- |
| Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) | Ortho-Novum 1/35 (35 µg EE / 1 mg NE) |
600/100 mg b.i.d. | 11 | ↓ | 0.68 (0.61-0.74) |
0.56 (0.50-0.63) |
0.38 (0.27-0.54) |
| Norethindrone (NE) | 11 | ↓ | 0.90 (0.83-0.97) |
0.86 (0.75-0.98) |
0.70 (0.51-0.97) |
||
| Ketoconazole | 200 mg b.i.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 15 | ↑ | 2.11 (1.81-2.44) |
3.12 (2.65-3.68) |
9.68 (6.44-14.55) |
| R-Methadone | 55-150 mg q.d. | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↓ | 0.76 (0.71-0.81) |
0.84 (0.78-0.91) |
0.85 (0.77-0.94) |
| Omeprazole | 40 mg single dose | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↓ | 0.66 (0.48-0.90) |
0.58 (0.50-0.66) |
- |
| 5-hydroxy omeprazole | ↓ | 0.93 (0.71-1.21) |
0.84 (0.77-0.92) |
- | |||
| Paroxetine | 20 mg q.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↓ | 0.64 (0.59-0.71) |
0.61 (0.56-0.66) |
0.63 (0.55-0.73) |
| Pravastatin | 40 mg single dose | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 14 | ↑ | 1.63 (0.95-2.82) |
1.81 (1.23-2.66) |
- |
| Rifabutin | 150 mg q.o.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
11 | ↑ | 0.72 (0.55-0.93) |
0.93 (0.80-1.09) |
1.64 (1.48-1.81) |
| 25-O-desacetyl-rifabutin | 300 mg q.d. when administered alone | 11 | ↑ | 4.77 (4.04-5.63) |
9.81 (8.09-11.9) |
27.1 (22.2-33.2) |
|
| Sertraline | 50 mg q.d. | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 13 | ↓ | 0.56 (0.49-0.63) |
0.51 (0.46-0.58) |
0.51 (0.45-0.57) |
| Sildenafil | 100 mg (single dose) administered alone | 400/100 mg b.i.d. | 16 | ↑ | 0.62 (0.55-0.70) |
0.97 (0.86-1.09) |
- |
| 25 mg (single dose) when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
| S-warfarin | 10 mg single dose | 600/100 mg b.i.d. | 12 | ↓ | 0.92 (0.86-0.97) |
0.79 (0.73-0.85) |
- |
| 7-OH-S-warfarin | 12 | ↑ | 1.42 (1.24-1.63) |
1.23 (0.97-1.57) |
- | ||
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. It selectively inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded Gag-Pol polyproteins in infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature virus particles.
Antiviral Activity
Darunavir exhibits activity against laboratory strains and clinical isolates of HIV-1 and laboratory strains of HIV-2 in acutely infected T-cell lines, human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and human monocytes/macrophages with median EC50 values ranging from 1.2 to 8.5 nM (0.7 to 5.0 ng/mL). Darunavir demonstrates antiviral activity in cell culture against a broad panel of HIV-1 group M (A, B, C, D, E, F, G), and group O primary isolates with EC50 values ranging from < 0.1 to 4.3 nM. The EC50 value of darunavir increases by a median factor of 5.4 in the presence of human serum. Darunavir did not show antagonism when studied in combination with the PIs amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, or tipranavir, the N(t)RTIs abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir, zalcitabine, or zidovudine, the NNRTIs delavirdine, efavirenz, etravirine, or nevirapine, and the fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide.
Resistance
Cell Culture: HIV-1 isolates with a decreased susceptibility to darunavir have been selected in cell culture and obtained from subjects treated with darunavir/ritonavir. Darunavir-resistant virus derived in cell culture from wild-type HIV had 21- to 88-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir and developed 2 to 4 of the following amino acid substitutions S37D, R41E/T, K55Q, H69Q, K70E, T74S, V77I, or I85V in the protease. Selection in cell culture of darunavir resistant HIV-1 from nine HIV-1 strains harboring multiple PI resistance-associated mutations resulted in the overall emergence of 22 mutations in the protease gene, coding for amino acid substitutions L10F, V11I, I13V, I15V, G16E, L23I, V32I, L33F, S37N, M46I, I47V, I50V, F53L, L63P, A71V, G73S, L76V, V82I, I84V, T91A/S, and Q92R, of which L10F, V32I, L33F, S37N, M46I, I47V, I50V, L63P, A71V, and I84V were the most prevalent. These darunavir-resistant viruses had at least eight protease substitutions and exhibited 50- to 641-fold decreases in darunavir susceptibility with final EC50 values ranging from 125 nM to 3461 nM.
Clinical studies of PREZISTA/ritonavir in treatment-experienced subjects: In a pooled analysis of the 600/100 mg PREZISTA/ritonavir twice daily arms of Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, TMC114-C215, and the control arms of etravirine studies TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216, the amino acid substitutions V32I and I54L or M developed most frequently on PREZISTA/ritonavir in 41% and 25%, respectively, of the treatment-experienced subjects who experienced virologic failure, either by rebound or by never being suppressed (< 50 copies/mL). Other substitutions that developed frequently in PREZISTA/ritonavir virologic failure isolates occurred at amino acid positions V11I, I15V, L33F, I47V, I50V, and L89V. These amino acid substitutions were associated with decreased susceptibility to darunavir; 90% of the virologic failure isolates had a > 7-fold decrease in susceptibility to darunavir at failure. The median darunavir phenotype (fold change from reference) of the virologic failure isolates was 4.3-fold at baseline and 85-fold at failure. Amino acid substitutions were also observed in the protease cleavage sites in the Gag polyprotein of some PREZISTA/ritonavir virologic failure isolates. In Study TMC114-C212 of treatment-experienced pediatric subjects, the amino acid substitutions V32I, I54L and L89M developed most frequently in virologic failures on PREZISTA/ritonavir.
In the 96-week as-treated analysis of the Phase 3 Study TMC114-C214, the percent of virologic failures (never suppressed, rebounders and discontinued before achieving suppression) was 21% (62/298) in the group of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily compared to 32% (96/297) of subjects receiving lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily. Examination of subjects who failed on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily and had post-baseline genotypes and phenotypes showed that 7 subjects (7/43; 16%) developed PI substitutions on darunavir/ritonavir treatment resulting in decreased susceptibility to darunavir. Six of the 7 had baseline PI resistance-associated substitutions and baseline darunavir phenotypes > 7. The most common emerging PI substitutions in these virologic failures were V32I, L33F, M46I or L, I47V, I54L, T74P and L76V. These amino acid substitutions were associated with 59- to 839-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir at failure. Examination of individual subjects who failed in the comparator arm on lopinavir/ritonavir and had post-baseline genotypes and phenotypes showed that 31 subjects (31/75; 41%) developed substitutions on lopinavir treatment resulting in decreased susceptibility to lopinavir (> 10-fold) and the most common substitutions emerging on treatment were L10I or F, M46I or L, I47V or A, I54V and L76V. Of the 31 lopinavir/ritonavir virologic failure subjects, 14 had reduced susceptibility (> 10-fold) to lopinavir at baseline.
Clinical studies of PREZISTA/ritonavir in treatment-naive subjects: In the 96-week as-treated analysis of the Phase 3 Study TMC114-C211, the percentage of virologic failures (never suppressed, rebounders and discontinued before achieving suppression) was 15% (53/343) in the group of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily compared to 22% (77/346) of subjects receiving lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day. In the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm, emergent PI substitutions were identified in 5 of the virologic failures with post-baseline genotypic data (n=14). However, none of the darunavir virologic failures had a decrease in darunavir susceptibility (> 7-fold change) at failure. In the comparator lopinavir/ritonavir arm, emergent PI substitutions were identified in 15 of the virologic failures with post-baseline genotypic data (n=28), but none of the lopinavir/ritonavir virologic failures had decreased susceptibility to lopinavir (> 10-fold change) at failure. The reverse transcriptase M184V substitution and resistance to emtricitabine, which was included in the fixed background regimen, was identified in 2 virologic failures of the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm and 3 virologic failures in the lopinavir/ritonavir arm.
Cross-resistance
Cross-resistance among PIs has been observed. Darunavir has a < 10-fold decreased susceptibility in cell culture against 90% of 3309 clinical isolates resistant to amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and/or tipranavir showing that viruses resistant to these PIs remain susceptible to darunavir.
Darunavir-resistant viruses were not susceptible to amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir or saquinavir in cell culture. However, six of nine darunavir-resistant viruses selected in cell culture from PI-resistant viruses showed a fold change in EC50 values < 3 for tipranavir, indicative of limited cross-resistance between darunavir and tipranavir. In Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215, 34% (64/187) of subjects in the darunavir/ritonavir arm whose baseline isolates had decreased susceptibility to tipranavir (tipranavir fold change > 3) achieved < 50 copies/mL serum HIV RNA levels at Week 96. Of the viruses isolated from subjects experiencing virologic failure on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (> 7 fold change), 41% were still susceptible to tipranavir and 10% were susceptible to saquinavir while less than 2% were susceptible to the other protease inhibitors (amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir or nelfinavir).
In Study TMC114-C214, the 7 darunavir/ritonavir virologic failures with reduced susceptibility to darunavir at failure were also resistant to the approved PIs (fos)amprenavir, atazanavir, lopinavir, indinavir, and nelfinavir at failure. Six of these 7 were resistant to saquinavir and 5 were resistant to tipranavir. Four of these virologic failures were already PI-resistant at baseline.
Cross-resistance between darunavir and nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, fusion inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor antagonists, or integrase inhibitors is unlikely because the viral targets are different.
Baseline Genotype/Phenotype and Virologic Outcome Analyses
Genotypic and/or phenotypic analysis of baseline virus may aid in determining darunavir susceptibility before initiation of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily therapy. The effect of baseline genotype and phenotype on virologic response at 96 weeks was analyzed in as-treated analyses using pooled data from the Phase 2b studies (Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215) (n=439). The findings were confirmed with additional genotypic and phenotypic data from the control arms of etravirine Studies TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216 at Week 24 (n=591).
Diminished virologic responses were observed in subjects with 5 or more baseline IAS-defined primary protease inhibitor resistance-associated substitutions (D30N, V32I, L33F, M46I/L, I47A/V, G48V, I50L/V, I54L/M, L76V, V82A/F/L/S/T, I84V, N88S, L90M) (see Table 12).
| Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, TMC114-C215 < 50 copies/mL at Week 96 N=439 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| # IAS-Defined Primary PI Substitutions | Overall | De Novo ENF | Re-Used/ No ENF |
| All | 44% (192/439) | 54% (61/112) | 40% (131/327) |
| 0 - 4 | 50% (162/322) | 58% (49/85) | 48% (113/237) |
| 5 | 22% (16/74) | 47% (9/19) | 13% (7/55) |
| ≥ 6 | 9% (3/32) | 17% (1/6) | 8% (2/26) |
IAS Primary PI Substitutions (2008): D30N, V32I, L33F, M46I/L, I47A/V, G48V, I50L/V, I54L/M, L76V, V82A/F/L/S/T, I84V, N88S, L90M
The presence at baseline of two or more of the substitutions V11I, V32I, L33F, I47V, I50V, I54L or M, T74P, L76V, I84V or L89V was associated with a decreased virologic response to PREZISTA/ritonavir. In subjects not taking enfuvirtide de novo, the proportion of subjects achieving viral load < 50 plasma HIV RNA copies/mL at 96 weeks was 59%, 29%, and 12% when the baseline genotype had 0-1, 2 and ≥ 3 of these substitutions, respectively.
Baseline darunavir phenotype (shift in susceptibility relative to reference) was shown to be a predictive factor of virologic outcome. Response rates assessed by baseline darunavir phenotype are shown in Table 13. These baseline phenotype groups are based on the select patient populations in the Studies TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215, and are not meant to represent definitive clinical susceptibility breakpoints for PREZISTA/ritonavir. The data are provided to give clinicians information on the likelihood of virologic success based on pre-treatment susceptibility to darunavir.
| Proportion of Subjects with < 50 copies/mL at Week 96 N=417 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline DRV Phenotype | All | De Novo ENF | Re-Used/ No ENF |
| Overall | 175/417 (42%) | 61/112 (54%) | 131/327 (40%) |
| 0 - 7 | 148/270 (55%) | 44/65 (68%) | 104/205 (51%) |
| > 7 - 20 | 16/53 (30%) | 7/17 (41%) | 9/36 (25%) |
| > 20 | 11/94 (12%) | 6/23 (26%) | 5/71 (7%) |
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Darunavir was evaluated for carcinogenic potential by oral gavage administration to mice and rats up to 104 weeks. Daily doses of 150, 450 and 1000 mg/kg were administered to mice and doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg were administered to rats. A dose-related increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas were observed in males and females of both species as well as an increase in thyroid follicular cell adenomas in male rats. The observed hepatocellular findings in rodents are considered to be of limited relevance to humans. Repeated administration of darunavir to rats caused hepatic microsomal enzyme induction and increased thyroid hormone elimination, which predispose rats, but not humans, to thyroid neoplasms. At the highest tested doses, the systemic exposures to darunavir (based on AUC) were between 0.4- and 0.7-fold (mice) and 0.7- and 1-fold (rats), relative to those observed in humans at the recommended therapeutic doses (600/100 mg twice daily or 800/100 mg once daily).
Darunavir was not mutagenic or genotoxic in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays including bacterial reserve mutation (Ames), chromosomal aberration in human lymphocytes and in vivo micronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
No effects on fertility or early embryonic development were observed with darunavir in rats and darunavir has shown no teratogenic potential in mice (in the presence or absence of ritonavir), rats and rabbits.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In juvenile rats single doses of darunavir (20 mg/kg to 160 mg/kg at ages 5-11 days) or multiple doses of darunavir (40 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg at age 12 days) caused mortality. The mortalities were associated with convulsions in some of the animals. Within this age range exposures in plasma, liver and brain were dose and age dependent and were considerably greater than those observed in adult rats. These findings were attributed to the ontogeny of the CYP450 liver enzymes involved in the metabolism of darunavir and the immaturity of the blood-brain barrier. No treatment-related mortalities were noted in juvenile rats after a single dose of darunavir at 1000 mg/kg on day 26 of age or after repeat dosing at 500 mg/kg from day 23 to 50 of age. The exposures and toxicity profile in the older animals (day 23 or day 26) were comparable to those observed in adult rats. Due to uncertainties regarding the rate of development of the human blood-brain barrier and liver enzymes, do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Description of Adult Clinical Studies
The evidence of efficacy of PREZISTA/ritonavir is based on the analyses of 96-week data from 2 randomized, controlled open-label Phase 3 trials in treatment-naïve (TMC114-C211) and antiretroviral treatment-experienced (TMC114-C214) HIV-1-infected adult subjects. In addition, 96-week data is included from 2 randomized, controlled Phase 2b trials, TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202, in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects.
14.2 Treatment-Naïve Adult Subjects
Study TMC114-C211
Study TMC114-C211 is a randomized, controlled, open-label Phase 3 trial comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day (given as a twice daily or as a once daily regimen) in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects. Both arms used a fixed background regimen consisting of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg once daily (TDF) and emtricitabine 200 mg once daily (FTC).
HIV-1-infected subjects who were eligible for this trial had plasma HIV-1 RNA ≥ 5000 copies/mL. Randomization was stratified by screening plasma viral load (HIV-1 RNA < 100,000 copies/mL or ≥ 100,000 copies/mL) and screening CD4+ cell count (< 200 cells/mm3 or ≥ 200 cells/mm3). Virologic response was defined as a confirmed plasma HIV-1 RNA viral load < 50 copies/mL. Analyses included 689 subjects in Study TMC114-C211 who had completed 96 weeks of treatment or discontinued earlier.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were balanced between the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm and the lopinavir/ritonavir arm (see Table 14). Table 14 compares the demographic and baseline characteristics between subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily arm and subjects in the lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day arm in Study TMC114-C211.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C211 | ||
|---|---|---|
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily + TDF/FTC N = 343 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day + TDF/FTC N = 346 |
|
| Demographic Characteristics | ||
| Median Age (years) (range, years) |
34 (18-70) |
33 (19-68) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 70% | 70% |
| Female | 30% | 30% |
| Race | ||
| White | 40% | 45% |
| Black | 23% | 21% |
| Hispanic | 23% | 22% |
| Asian | 13% | 11% |
| Baseline Characteristics | ||
| Mean Baseline Plasma HIV-1 RNA (log10 copies/mL) | 4.86 | 4.84 |
| Median Baseline CD4+ Cell Count (cells/mm3) (range, cells/mm3) |
228 (4-750) |
218 (2-714) |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline Viral Load ≥ 100,000 copies/mL | 34% | 35% |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline CD4+ Cell Count < 200 cells/mm3 | 41% | 43% |
Week 96 outcomes for subjects on PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily from Study TMC114-C211 are shown in Table 15.
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily + TDF/FTC N = 343 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day + TDF/FTC N = 346 |
|
|---|---|---|
| N = total number of subjects with data | ||
| Virologic success HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL | 78% | 74% |
| Virologic failure |
11% | 12% |
| No virologic data at Week 96 window Reasons |
||
| Discontinued study due to adverse event or death |
4% | 9% |
| Discontinued study for other reasons |
6% | 5% |
| Missing data during window but on study | 1% | < 1% |
In Study TMC114-C211 at 96 weeks of treatment, the median increase from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was 171 cells/mm3 in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily arm and 188 cells/mm3 in the lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day arm.
14.3 Treatment-Experienced Adult Subjects
Study TMC114-C214
Study TMC114-C214 is a randomized, controlled, open-label Phase 3 trial comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily in antiretroviral treatment-experienced, lopinavir/ritonavir-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects. Both arms used an optimized background regimen (OBR) consisting of at least 2 antiretrovirals (NRTIs with or without NNRTIs).
HIV-1-infected subjects who were eligible for this trial had plasma HIV-1 RNA > 1000 copies/mL and were on a highly active antiretroviral therapy regimen (HAART) for at least 12 weeks. Virologic response was defined as a confirmed plasma HIV-1 RNA viral load < 400 copies/mL. Analyses included 595 subjects in Study TMC114-C214 who had completed 96 weeks of treatment or discontinued earlier.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were balanced between the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm and the lopinavir/ritonavir arm (see Table 16). Table 16 compares the demographic and baseline characteristics between subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm and subjects in the lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily arm in Study TMC114-C214.
| Randomized Study TMC114-C214 | ||
|---|---|---|
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 298 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 297 |
|
| Demographic Characteristics | ||
| Median Age (years) (range, years) |
40 (18-68) |
41 (22-76) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 77% | 81% |
| Female | 23% | 19% |
| Race | ||
| White | 54% | 57% |
| Black | 18% | 17% |
| Hispanic | 15% | 15% |
| Asian | 9% | 9% |
| Baseline Characteristics | ||
| Mean Baseline Plasma HIV-1 RNA (log10 copies/mL) | 4.33 | 4.28 |
| Median Baseline CD4+ Cell Count (cells/mm3) (range, cells/mm3) |
235 (3-831) |
230 (2-1096) |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline Viral Load ≥ 100,000 copies/mL | 19% | 17% |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline CD4+ Cell Count < 200 cells/mm3 | 40% | 40% |
| Median Darunavir Fold Change (range) |
0.60 (0.10-37.40) |
0.60 (0.1-43.8) |
| Median Lopinavir Fold Change (range) |
0.70 (0.40-74.40) |
0.80 (0.30-74.50) |
Median Number of Resistance-Associated |
||
| PI mutations | 4 | 4 |
| NNRTI mutations | 1 | 1 |
| NRTI mutations | 2 | 2 |
Percentage of Subjects with Number of Baseline Primary Protease Inhibitor Mutations |
||
| ≤ 1 | 78% | 80% |
| 2 | 8% | 9% |
| ≥ 3 | 13% | 11% |
| Median Number of ARVs Previously Used |
||
| NRTIs | 4 | 4 |
| NNRTIs | 1 | 1 |
| PIs (excluding low-dose ritonavir) | 1 | 1 |
| Percentage of Subjects Resistant |
2% | 3% |
Week 96 outcomes for subjects on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily from Study TMC114-C214 are shown in Table 17.
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 298 |
lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 297 |
|
|---|---|---|
| N = total number of subjects with data | ||
| Virologic success HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL | 58% | 52% |
| Virologic failure |
26% | 33% |
| No virologic data at Week 96 window Reasons |
||
| Discontinued study due to adverse event or death |
7% | 8% |
| Discontinued study for other reasons |
8% | 7% |
| Missing data during window but on study | 1% | < 1% |
In Study TMC114-C214 at 96 weeks of treatment, the median increase from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was 81 cells/mm3 in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm and 93 cells/mm3 in the lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily arm.
Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202
Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 are randomized, controlled, Phase 2b trials in adult subjects with a high level of PI resistance consisting of 2 parts: an initial partially-blinded, dose-finding part and a second long-term part in which all subjects randomized to PREZISTA/ritonavir received the recommended dose of 600/100 mg twice daily.
HIV-1-infected subjects who were eligible for these trials had plasma HIV-1 RNA > 1000 copies/mL, had prior treatment with PI(s), NNRTI(s) and NRTI(s), had at least one primary PI mutation (D30N, M46I/L, G48V, I50L/V, V82A/F/S/T, I84V, L90M) at screening, and were on a stable PI-containing regimen at screening for at least 8 weeks. Randomization was stratified by the number of PI mutations, screening viral load, and the use of enfuvirtide.
The virologic response rate was evaluated in subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir plus an OBR versus a control group receiving an investigator-selected PI(s) regimen plus an OBR. Prior to randomization, PI(s) and OBR were selected by the investigator based on genotypic resistance testing and prior ARV history. The OBR consisted of at least 2 NRTIs with or without enfuvirtide. Selected PI(s) in the control arm included: lopinavir in 36%, (fos)amprenavir in 34%, saquinavir in 35% and atazanavir in 17%; 98% of control subjects received a ritonavir boosted PI regimen out of which 23% of control subjects used dual-boosted PIs. Approximately 47% of all subjects used enfuvirtide, and 35% of the use was in subjects who were ENF-naïve. Virologic response was defined as a decrease in plasma HIV-1 RNA viral load of at least 1 log10 versus baseline.
In the pooled analysis for TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202, demographics and baseline characteristics were balanced between the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm and the comparator PI arm (see Table 18). Table 18 compares the demographic and baseline characteristics between subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm and subjects in the comparator PI arm in the pooled analysis of Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202.
| Randomized Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 |
||
|---|---|---|
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR N = 131 |
Comparator PI(s) + OBR N = 124 |
|
| Demographic Characteristics | ||
| Median Age (years) (range, years) |
43 (27-73) |
44 (25-65) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 89% | 88% |
| Female | 11% | 12% |
| Race | ||
| White | 81% | 73% |
| Black | 10% | 15% |
| Hispanic | 7% | 8% |
| Baseline Characteristics | ||
| Mean Baseline Plasma HIV-1 RNA (log10 copies/mL) |
4.61 | 4.49 |
| Median Baseline CD4+ Cell Count (cells/mm3) (range, cells/mm3) |
153 (3-776) |
163 (3-1274) |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline Viral Load > 100,000 copies/mL | 24% | 29% |
| Percentage of Patients with Baseline CD4+ Cell Count < 200 cells/mm3 | 67% | 58% |
| Median Darunavir Fold Change | 4.3 | 3.3 |
Median Number of Resistance-Associated |
||
| PI mutations | 12 | 12 |
| NNRTI mutations | 1 | 1 |
| NRTI mutations | 5 | 5 |
Percentage of Subjects with Number of Baseline Primary Protease Inhibitor Mutations |
||
| ≤ 1 | 8% | 9% |
| 2 | 22% | 21% |
| ≥ 3 | 70% | 70% |
Median Number of ARVs Previously Used |
||
| NRTIs | 6 | 6 |
| NNRTIs | 1 | 1 |
| PIs (excluding low-dose ritonavir) | 5 | 5 |
Percentage of Subjects Resistant |
63% | 61% |
| Percentage of Subjects with Prior Use of Enfuvirtide |
20% | 17% |
Week 96 outcomes for subjects on the recommended dose PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily from the pooled Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 are shown in Table 19.
| Randomized Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 |
||
|---|---|---|
| PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily + OBR N=131 |
Comparator PI + OBR N=124 |
|
| Virologic Responders confirmed at least 1 log10 HIV-1 RNA below baseline through Week 96 (< 50 copies/mL at Week 96) |
57% (39%) |
10% (9%) |
| Virologic failures | 29% | 80% |
| Lack of initial response |
8% | 53% |
| Rebounder |
17% | 19% |
| Never Suppressed |
4% | 8% |
| Death or discontinuation due to adverse events | 9% | 3% |
| Discontinuation due to other reasons | 5% | 7% |
In the pooled Studies TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202 through 48 weeks of treatment, the proportion of subjects with HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL in the arm receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily compared to the comparator PI arm was 55.0% and 14.5%, respectively. In addition, the mean changes in plasma HIV-1 RNA from baseline were –1.69 log10 copies/mL in the arm receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily and –0.37 log10 copies/mL for the comparator PI arm. The mean increase from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was higher in the arm receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (103 cells/mm3) than in the comparator PI arm (17 cells/mm3).
14.4 Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetic profile, safety and antiviral activity of PREZISTA/ritonavir were evaluated in a randomized, open-label, multicenter study. This study enrolled treatment-experienced pediatric subjects between the ages of 6 and < 18 years and weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg). Patients were stratified according to their weight (≥ 20 - < 30 kg, ≥ 30 - < 40 kg, ≥ 40 kg) and received PREZISTA/ritonavir plus background therapy consisting of at least two non-protease inhibitor antiretroviral drugs. Eighty patients were randomized and received at least one dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir. Pediatric subjects who were at risk of discontinuing therapy due to intolerance of ritonavir oral solution (e.g., taste aversion) were allowed to switch to the capsule formulation. Of the 44 pediatric subjects taking ritonavir oral solution, 23 subjects switched to the 100 mg capsule formulation and exceeded the weight-based ritonavir dose without changes in observed safety.
The 80 randomized pediatric subjects had a median age of 14 (range 6 - < 18 years), and were 71% male, 54% Caucasian, 30% Black, 9% Hispanic and 8% other. The mean baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.64 log10 copies/mL, and the median baseline CD4+ cell count was 330 cells/mm3 (range: 6 to 1505 cells/mm3). Overall, 38% of pediatric subjects had baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA ≥ 100,000 copies/mL. Most pediatric subjects (79%) had previous use of at least one NNRTI and 96% of pediatric subjects had previously used at least one PI.
Seventy-seven pediatric subjects (96%) completed the 24 week period. Of the patients who discontinued, one patient discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. An additional 2 patients discontinued for other reasons, one patient due to compliance and another patient due to relocation.
The proportion of pediatric subjects with HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL and < 50 copies/mL was 64% and 50%, respectively. The mean CD4+ cell count increase from baseline was 117 cells/mm3.
The dose selection was based on the following:
- Similar darunavir plasma exposures in children compared to adults
- Similar virologic response rates and safety profile in children compared to adults
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PREZISTA (darunavir) 75 mg tablets are supplied as white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 75 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "75" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA (darunavir) 150 mg tablets are supplied as white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 150 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "150" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA (darunavir) 300 mg tablets are supplied as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 300 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "300" on one side and "TMC114" on the other side.
PREZISTA (darunavir) 400 mg tablets are supplied as light orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 400 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "400" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA (darunavir) 600 mg tablets are supplied as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets containing darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 600 mg of darunavir per tablet. Each tablet is debossed with "600" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
They are supplied by State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy as follows:
| NDC | Strength | Quantity/Form | Color | Source Prod. Code |
| 53808-0672-1 | 400 mg | 30 Tablets in a Blister Pack | light orange | 59676-561 |
| 53808-0773-1 | 600 mg | 30 Tablets in a Blister Pack | ORANGE | 59676-562 |
Storage:
Store PREZISTA tablets at 25°C (77°F); with excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling]
A statement to patients and healthcare providers is included on the product's bottle label: ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with PREZISTA. A Patient Package Insert for PREZISTA is available for patient information.
17.1 General
Patients should be informed that PREZISTA is not a cure for HIV infection and that they may continue to develop opportunistic infections and other complications associated with HIV disease. Patients should be told that there are currently no data demonstrating that therapy with PREZISTA can reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to others.
Patients should be told that sustained decreases in plasma HIV RNA have been associated with a reduced risk of progression to AIDS and death. Patients should remain under the care of a physician while using PREZISTA.
17.2 Instructions for Use
General
Patients should be advised to take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) with food every day as prescribed. Patients should be instructed to swallow whole tablets with a drink such as water or milk. PREZISTA must always be used with ritonavir (NORVIR®) in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Patients should not alter the dose of either PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®), discontinue ritonavir (NORVIR®), or discontinue therapy with PREZISTA without consulting their physician.
Patients Taking PREZISTA Once Daily
If a patient misses a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by more than 12 hours, the patient should be told to wait and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If the patient misses a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by less than 12 hours, the patient should be told to take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) immediately, and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose. Inform the patient that he or she should not take more or less than the prescribed dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®).
Patients Taking PREZISTA Twice Daily
If a patient misses a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by more than 6 hours, the patient should be told to wait and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If the patient misses a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by less than 6 hours, the patient should be told to take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) immediately, and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose. Inform the patient that he or she should not take more or less than the prescribed dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®).
17.3 Drug Interactions
PREZISTA/ritonavir may interact with many drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their healthcare provider the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medication or herbal products, including St. John's wort.
Patients receiving estrogen-based contraceptives should be instructed to use alternate contraceptive measures during therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir because hormonal levels may decrease.
17.4 Fat Redistribution
Patients should be informed that redistribution or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy, including PREZISTA/ritonavir, and that the cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time.
Manufactured for Tibotec, Inc. by:
JOLLC, Gurabo, Puerto Rico
Distributed by:
Tibotec Therapeutics, Division of Centocor Ortho Biotech Products, L.P., Raritan NJ 08869
Patent Numbers: 5,843,946; 6,248,775; 6,335,460 and other US patents pending
NORVIR® is a registered trademark of its respective owner.
PREZISTA® is a registered trademark of Tibotec Pharmaceuticals
© Tibotec, Inc. 2006
This Product was Repackaged By:
State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy
104-2 Hamilton Park Drive
Tallahassee, FL 32304
United States
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
PREZISTA® (darunavir) Tablets
Patient Information about
PREZISTA (pre-ZIS-ta)
for HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) Infection
Generic name: darunavir (da-ROO-nuh-veer)
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with PREZISTA. Please also read the section "Who should not take PREZISTA?".
Please read this information before you start taking PREZISTA. Also, read the leaflet each time you renew your prescription, just in case anything has changed. Remember, this leaflet does not take the place of careful discussions with your doctor. You and your doctor should discuss your treatment with PREZISTA prior to the first time you take your medicine and at regular checkups. You should remain under a doctor's care when using PREZISTA and should not change or stop treatment without first talking with a doctor.
WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT INFORMATION I SHOULD KNOW ABOUT PREZISTA?
PREZISTA, together with NORVIR® (ritonavir), has rarely been observed to cause liver problems which may be life-threatening. It was not always clear if PREZISTA caused these liver problems because some patients had other illnesses or were taking other medicines. Your healthcare professional should do blood tests prior to initiating combination treatment including PREZISTA. If you have chronic hepatitis B or C infection, your healthcare professional should check your blood tests more often because you have an increased chance of developing liver problems. Please also read the section "What are the possible side effects of PREZISTA?".
Rarely, PREZISTA has been reported to cause a severe or life-threatening rash. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you develop a rash. Your healthcare provider will advise you whether your symptoms can be managed on therapy or whether PREZISTA should be stopped.
WHAT IS PREZISTA?
PREZISTA is an oral tablet used for the treatment of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection in adults and children 6 years of age and older. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). PREZISTA is a type of anti-HIV medicine called a protease (PRO-tee-ase) inhibitor.
HOW DOES PREZISTA WORK?
PREZISTA blocks HIV protease, an enzyme which is needed for HIV to multiply. When used with other anti-HIV medicines, PREZISTA can help to reduce the amount of HIV in your blood (called "viral load") and increase your CD4 (T) cell count. HIV infection destroys CD4 (T) cells, which are important to the immune system. The immune system helps fight infection. Reducing the amount of HIV and increasing the CD4 (T) cell count may improve your immune system and, thus, reduce the risk of death or infections that can happen when your immune system is weak (opportunistic infections).
PREZISTA is always taken with and at the same time as ritonavir (NORVIR®), in combination with other anti-HIV medicines. PREZISTA should also be taken with food.
DOES PREZISTA CURE HIV OR AIDS?
PREZISTA does not cure HIV infection or AIDS. At present, there is no cure for HIV infection. People taking PREZISTA may still develop infections or other conditions associated with HIV infection. Because of this, it is very important for you to remain under the care of a doctor. Although PREZISTA is not a cure for HIV or AIDS, PREZISTA can help reduce your risks of getting illnesses associated with HIV infection (AIDS and opportunistic infection) and eventually dying from these conditions.
DOES PREZISTA REDUCE THE RISK OF PASSING HIV TO OTHERS?
PREZISTA does not reduce the risk of passing HIV to others through sexual contact, sharing needles, or being exposed to your blood. For your health and the health of others, it is important to always practice safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier method to lower the chance of sexual contact with any body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, or blood. Never re-use or share needles.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions on how to prevent passing HIV to other people.
WHAT SHOULD I TELL MY DOCTOR BEFORE I TAKE PREZISTA?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- are allergic to sulfa medicines.
- have diabetes. In general, anti-HIV medicines, such as PREZISTA, might increase sugar levels in the blood.
- have liver problems, including hepatitis B and/or C.
- have hemophilia. Anti-HIV medicines, such as PREZISTA, might increase the risk of bleeding.
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. The effects of PREZISTA on pregnant women or their unborn babies are not known. You and your doctor will need to decide if taking PREZISTA is right for you. If you take PREZISTA while you are pregnant, talk to your doctor about how you can be included in the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry.
- are breastfeeding. Do not breastfeed if you are taking PREZISTA. You should not breastfeed if you have HIV because of the chance of passing HIV to your baby. Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby.
WHO SHOULD NOT TAKE PREZISTA?

Together with your doctor, you need to decide whether taking PREZISTA is right for you.
Do not take or administer PREZISTA:
- to children younger than 6 years of age
- if you are or your child is allergic to darunavir or any of the other ingredients in PREZISTA
- if you are or your child is allergic to ritonavir (NORVIR®)
- if you take or your child takes any of the following types of medicines because you could experience serious side effects:
| Type of Drug | Examples of Generic Names (Brand Names) |
|---|---|
| Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist | alfuzosin (Uroxatral®) |
| Ergot Derivatives (to treat migraine and headaches) |
dihydroergotamine (D.H.E. 45®, Migranal®) ergonovine ergotamine (Cafergot®, Ergomar®) methylergonovine |
| Gastrointestinal Motility Agent (to treat some digestive conditions) |
cisapride |
| Neuroleptic (to treat psychiatric conditions) |
pimozide (Orap®) |
| Sedative/hypnotics (to treat trouble with sleeping and/or anxiety) |
oral midazolam triazolam (Halcion®) |
| Herbal Product | St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (also known as statins) (to lower cholesterol levels) |
lovastatin (Mevacor®, Altoprev®, Advicor®) simvastatin (Zocor®, Simcor®, Vytorin®) |
| Antimycobacterial (to treat tuberculosis or Mycobacterium avium complex) |
rifampin (Rifadin®, Rifater®, Rifamate®, Rimactane®) |
| PDE-5 inhibitor (to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension) |
sildenafil (Revatio®) |
CAN PREZISTA BE TAKEN WITH OTHER MEDICATIONS?

Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. PREZISTA and many other medicines can interact. Sometimes serious side effects will happen if PREZISTA is taken with certain other medicines (see "Who should not take PREZISTA?").
Tell your doctor if you are taking estrogen-based contraceptives (birth control). PREZISTA might reduce the effectiveness of estrogen-based contraceptives. You must take additional precautions for birth control such as a condom.
Tell your doctor if you take other anti-HIV medicines. PREZISTA can be combined with some other anti-HIV medicines while other combinations are not recommended.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines:
| Type of Drug | Examples of Generic Names (Brand Names) |
|---|---|
| Antiarrhythmics (to treat abnormal heart rhythms) |
bepridil lidocaine quinidine amiodarone (Cordarone®) digoxin (Lanoxin®) flecainide (Tambocor®) propafenone (Rythmol®) |
| Anticoagulants (to treat and prevent blood clots) |
warfarin (Coumadin®) |
| Anticonvulsants (to treat epilepsy and prevent seizures) |
carbamazepine (Tegretol®, Carbatrol®) phenobarbital phenytoin (Dilantin®, Phenytek®) |
| Antidepressants (to treat depression) |
trazodone (Desyrel®) desipramine (Norpramin®) |
| Antigout (to treat gout and familial Mediterranean fever) |
colchicine (Colcrys®) |
| Anti-infectives (to treat bacterial infections) |
clarithromycin (Biaxin®) |
| Antifungals (to treat fungal infections) |
ketoconazole (Nizoral®) itraconazole (Sporanox®) voriconazole (Vfend®) |
| Antimycobacterials (to treat tuberculosis or Mycobacterium avium complex) |
rifabutin (Mycobutin®) |
| β-Blockers (to treat high blood pressure, heart attack, or heart failure or to lower pressure in the eye) |
metoprolol (Lopressor®, Toprol-XL®) timolol (Betimol®, Combigan®, Istalol®, Cosopt®, Timoptic®) |
| Benzodiazepines (to treat anxiety and/or trouble with sleeping) |
midazolam administered by injection |
| Calcium Channel Blockers (to treat heart disease) |
felodipine (Plendil®) nifedipine (Adalat®) nicardipine (Cardene®) |
| Corticosteroids (to treat inflammation or asthma) |
dexamethasone fluticasone (Advair Diskus®, Cutivate®, Flonase®, Flovent Diskus®) |
| Endothelin receptor antagonist (to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension) |
bosentan (Tracleer®) |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (also known as statins) (to lower cholesterol levels) |
atorvastatin (Lipitor®) pravastatin (Pravachol®) rosuvastatin (Crestor®) |
| Immunosuppressants (to prevent organ transplant rejection) |
cyclosporine (Sandimmune®, Neoral®) tacrolimus (Prograf®) sirolimus (Rapamune®) |
| Inhaled beta agonist | salmeterol (Serevent®) |
| Narcotic Analgesics/Treatment of Opioid Dependence (to treat narcotic withdrawal and dependence) |
methadone buprenorphine/naloxone |
| Neuroleptics (to treat schizophrenia or bipolar disorder) |
risperidone (Risperdal®, Risperdal® Consta®, Risperdal® M-TAB®) thioridazine |
| PDE-5 Inhibitors (to treat erectile dysfunction) |
sildenafil (Viagra®) vardenafil (Levitra®) tadalafil (Cialis®) |
| PDE-5 Inhibitors (to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension) |
tadalafil (Adcirca®) |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) (to treat depression, anxiety, or panic disorder) |
paroxetine (Paxil®) sertraline (Zoloft®) |
Tell your doctor if you are taking any medicines that you obtained without a prescription.
This is not a complete list of medicines that you should tell your doctor that you are taking. Know and keep track of all the medicines you take and have a list of them with you. Show this list to all of your doctors and pharmacists any time you get a new medicine. Both your doctor and your pharmacist can tell you if you can take these other medicines with PREZISTA. Do not start any new medicines while you are taking PREZISTA without first talking with your doctor or pharmacist. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of medicines that can interact with PREZISTA.
HOW SHOULD I TAKE PREZISTA?
Take PREZISTA tablets every day exactly as prescribed by your doctor. You must take ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the same time as PREZISTA.
- For adults who have never taken anti-HIV medicines, the usual dose is 800 mg (two 400 mg tablets) of PREZISTA, together with 100 mg (one 100 mg capsule) of ritonavir (NORVIR®), once daily every day.
- For adults who have taken anti-HIV medicines in the past, the usual dose is 600 mg (one 600 mg tablet or two 300 mg tablets) of PREZISTA, together with 100 mg (one 100 mg capsule) of ritonavir (NORVIR®), twice daily every day. Do not take PREZISTA once daily if you have taken anti-HIV medicines in the past.
- For children at least 6 years of age weighing at least 44 lbs (20 kg), your child's doctor will decide the right dose based on your child's weight. Your child's doctor will inform you exactly on how many PREZISTA tablets and how much ritonavir (NORVIR®) (capsules or solution) your child should take. In case your child does not tolerate ritonavir oral solution, ask your child's doctor for advice. Do not give PREZISTA once daily to your child.
PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) should be taken together at the same time every day. If you have questions about when to take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®), your doctor can help you decide which schedule works for you.
Take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) with food. Swallow the whole tablets with a drink such as water or milk. Do not chew the tablets.
Continue taking PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) unless your doctor tells you to stop. Take the exact amount of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) that your doctor tells you to take, right from the very start. To help make sure you will benefit from PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®), you must not skip doses or interrupt therapy. If you don't take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) as prescribed, the beneficial effects of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) may be reduced or even lost.
Patients taking PREZISTA once daily
If you miss a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by more than 12 hours, wait and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If you miss a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by less than 12 hours, take your missed dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) immediately. Then take your next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time.
Patients taking PREZISTA twice daily
If you miss a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by more than 6 hours, wait and then take the next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time. If you miss a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) by less than 6 hours, take your missed dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) immediately. Then take your next dose of PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) at the regularly scheduled time.
You should always take PREZISTA and ritonavir (NORVIR®) together with food.
If a dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) is skipped, do not double the next dose. Do not take more or less than your prescribed dose of PREZISTA or ritonavir (NORVIR®) at any one time.
WHAT ARE THE POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS OF PREZISTA?
Like all prescription drugs, PREZISTA can cause side effects. The following is not a complete list of side effects reported with PREZISTA when taken either alone or with other anti-HIV medicines. Do not rely on this leaflet alone for information about side effects. Your doctor can discuss with you a more complete list of side effects.
PREZISTA, together with NORVIR® (ritonavir), has rarely been observed to cause liver problems which may be life-threatening. It was not always clear if PREZISTA caused these liver problems because some patients had other illnesses or were taking other medicines. Your healthcare professional should do blood tests prior to initiating combination treatment including PREZISTA. If you have chronic hepatitis B or C infection, your healthcare professional should check your blood tests more often because you have an increased chance of developing liver problems.
Talk to your healthcare professional about the signs and symptoms of liver problems. These may include yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes, dark (tea colored) urine, pale colored stools (bowel movements), nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, or pain, aching or sensitivity on your right side below your ribs.
Rash has been reported in 10.3% of patients receiving PREZISTA. In few patients, PREZISTA has been reported to cause a severe or life-threatening rash. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you develop a rash. Your healthcare provider will advise you whether your symptoms can be managed on therapy or whether PREZISTA should be stopped.
Other relevant severe side effects reported at an uncommon or rare frequency were inflammation of the liver or pancreas, increased blood fat levels, diabetes, and changes in body fat.
Some side effects are typical for anti-HIV medicines in the same family as PREZISTA. These are:
- high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and diabetes. This can happen in patients taking PREZISTA or other protease inhibitor medicines. Some patients have diabetes before starting treatment with PREZISTA which gets worse. Some patients get diabetes during treatment with PREZISTA. Some patients will need changes in their diabetes medicine. Some patients may need new diabetes medicine.
- increased bleeding in patients with hemophilia.
- changes in body fat. These changes can happen in patients taking anti-HIV medicines, including PREZISTA. The changes may include an increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck, breast, and around the back, chest, and stomach area. Loss of fat from the legs, arms, and face may also happen. The exact cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known.
- immune reconstitution syndrome. In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) and a history of opportunistic infection, signs and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment, including PREZISTA, is started. It is believed that these symptoms are due to an improvement in the body's immune response, enabling the body to fight infections that may have been present with no obvious symptoms.
The most common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, rash, headache, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Tell your doctor promptly about these or any other unusual symptoms. If the condition persists or worsens, seek medical attention.
WHAT DO PREZISTA TABLETS LOOK LIKE?
PREZISTA 75 mg tablets are white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets mentioning "75" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA 150 mg tablets are white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets mentioning "150" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA 300 mg tablets are orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets mentioning "300" on one side and "TMC114" on the other side.
PREZISTA 400 mg tablets are light orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets mentioning "400" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA 600 mg tablets are orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets mentioning "600" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
HOW SHOULD I STORE PREZISTA TABLETS?
Store PREZISTA tablets at room temperature (77°F (25°C)). Short-term exposure to higher or lower temperatures [from 59°F (15°C) to 86°F (30°C)] is acceptable. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about storing your tablets.
This medication is prescribed for your particular condition. Do not use it for any other condition or give it to anybody else. Keep PREZISTA and all of your medicines out of the reach of children. If you suspect that more than the prescribed dose of this medicine has been taken, contact your local poison control center or emergency room immediately.
This leaflet provides a summary of information about PREZISTA. If you have any questions or concerns about either PREZISTA or HIV, talk to your doctor.
For additional information, you may also call Tibotec Therapeutics at 1-877-REACH-TT or 1-877-732-2488.
Manufactured for Tibotec, Inc. by:
JOLLC, Gurabo, Puerto Rico
Distributed by:
Tibotec Therapeutics, Division of Centocor Ortho Biotech Products, L.P., Raritan NJ 08869
Patent Numbers: 5,843,946; 6,248,775; 6,335,460 and other US patents pending
NORVIR® is a registered trademark of its respective owner.
PREZISTA® is a registered trademark of Tibotec Pharmaceuticals
© Tibotec, Inc. 2006
Revised: May 2010
This Product was Repackaged By:
State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy
104-2 Hamilton Park Drive
Tallahassee, FL 32304
United States
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 400 mg Tablet Label
30 Tablets NDC 53808-0672-1
PREZISTA®
(darunavir) tablets
Each tablet contains darunavir ethanolate
equivalent to 400 mg of darunavir.
Rx only
_4cde01bb.jpg)
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 600 mg Tablet Label
30 Tablets NDC 53808-0773-1
PREZISTA®
(darunavir) tablets
Each tablet contains darunavir ethanolate
equivalent to 600 mg of darunavir.
Rx only
_4cde01bb.jpg)
PREZISTAdarunavir ethanolate TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PREZISTAdarunavir ethanolate TABLET, FILM COATED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||