Primidone
PRIMIDONE TABLETS, USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PRIMIDONE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- PRIMIDONE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- PRIMIDONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- PRIMIDONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- PRIMIDONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL 50 mg
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL 250 mg
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx Only
PRIMIDONE DESCRIPTION
Primidone is a white crystalline, highly stable substance, M.P. 279-284° C. It is poorly soluble in water (60 mg per 100 ML at 37° C) and in most organic solvents. It possesses no acidic properties, in contrast to its barbiturate analog.
Chemical name: 5-ethyldihydro-5-phenyl-4,6 (1H, 5H)-pyrimidinedione.
Structural formula:
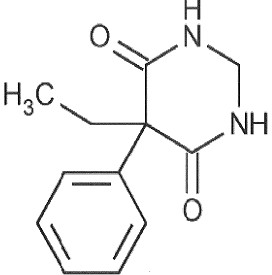
Primidone 50 mg and 250 mg tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, methyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Primidone raises electro- or chemoshock seizure thresholds or alters seizure patterns in experimental animals. The mechanisms(s) of primidone’s antiepileptic action is not known.
Primidone per se has anticonvulsant activity as do its two metabolites, phenobarbital and phenylethylmalonamide (PEMA). In addition to its anticonvulsant activity, PEMA potentiates the anticonvulsant activity of phenobarbital in experimental animals.
PRIMIDONE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Primidone, used alone or concomitantly with other anticonvulsants, is indicated in the control of grand mal, psychomotor, and focal epileptic seizures. It may control grand mal seizures refractory to other anticonvulsant therapy.
PRIMIDONE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Primidone is contraindicated in:
1) patients with porphyria and
2) patients who are hypersensitive to phenobarbital
(see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ).
WARNINGS
The abrupt withdrawal of antiepileptic medication may precipitate status epilepticus. The therapeutic efficacy of a dosage regimen takes several weeks before it can be assessed.
Usage in Pregnancy
The effects of primidone in human pregnancy and nursing infants are unknown.
Recent reports suggest an association between the use of anticonvulsant drugs by women with epilepsy and an elevated incidence of birth defects in children born to these women. Data are more extensive with respect to diphenylhydantoin and phenobarbital, but these are also the most commonly prescribed anticonvulsants; less systematic or anecdotal reports suggest a possible similar association with the use of all known anticonvulsant drugs.
The reports suggesting an elevated incidence of birth defects in children of drug-treated epileptic women cannot be regarded as adequate to prove a definate cause-and-effect relationship. There are intrinsic methodologic problems in obtaining adequate data on drug teratogenicity in humans: the possibility also exists that other factors leading to birth defects, e.g., genetic factors or the epileptic condition itself, may be more important than drug therapy. The majority of mothers on anticonvulsant medication deliver normal infants. It is important to note that anticonvulsant drugs should not be discontinued in patients in whom the drug is administered to prevent major seizures because of the strong possibility of precipitating status epilepticus with attendant hypoxia and threat to life. In individual cases where the severity and frequency of the seizure disorders are such that the removal of medication does not pose a serious threat to the patient, discontinuation of the drug may be considered prior to and during pregnancy, although it cannot be said with any confidence that even minor seizures do not pose some hazard to the developing embryo or fetus.
The prescribing physician will wish to weigh these considerations in treating or counseling epileptic women of childbearing potential.
Neonatal hemorrhage, with a coagulation defect resembling vitamin K deficiency, has been described in newborns whose mothers were taking primidone and other anticonvulsants. Pregnant women under anticonvulsant therapy should receive prophylactic vitamin K therapy for one month prior to, and during, delivery.
PRECAUTIONS
The total daily dosage should not exceed 2g. Since primidone therapy generally extends over prolonged periods, a complete blood count and a sequential multiple analysis-12 (SMA-12) test should be made every six months.
In Nursing Mothers
There is evidence that in mothers treated with primidone, the drug appears in the milk in substantial quantities. Since tests for the presence of primidone in biological fluids are too complex to be carried out in the average clinical laboratory, it is suggested that the presence of undue somnolence and drowsiness in nursing newborns of primidone-treated mothers be taken as an indication that nursing should be discontinued.
PRIMIDONE ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently occuring early side effects are ataxia and vertigo. These tend to disappear with continued therapy, or with reduction of initial dosage. Occasionally, the following have been reported: nausea, anorexia, vomiting, fatigue, hyperirritability, emotional disturbances, sexual impotency, diplopia, nystagmus, drowsiness, and morbilliform skin erruptions. Granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and red-cell hypoplasia and aplasia, have been reported rarely. These and, occasionally, other persistent or severe side effects may necessitate withdrawal of the drug. Megaloblastic anemia may occur as a rare idiosyncrasy to primidone and to other anticonvulsants. The anemia responds to folic acid without necessity of discontinuing medication.
PRIMIDONE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult Dosage
Patients 8 years of age and older who have received no previous treatment may be started on primidone according to the following regimen using either 50 mg or scored 250 mg primidone tablets:
Days 1 to 3: 100 to 125 mg at bedtime.
Days 4 to 6: 100 to 125 mg b.i.d.
Days 7 to 9: 100 to 125 mg t.i.d.
Day 10 to Maintenance: 250 mg t.i.d.
For most adults and children 8 years of age and over, the usual maintenance dosage is three to four 250 mg primidone tablets daily in divided doses (250 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d.). If required, an increase to five or six 250 mg tablets daily may be made but daily doses should not exceed 500 mg q.i.d.
| KEY: | • = 50 MG TABLET; | ●= 250 MG TABLET | ||||
| DAY | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| AM | •• | •• | •• | |||
| NOON | ||||||
| PM | •• | •• | •• | •• | •• | •• |
| DAY | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| AM | •• | •• | •• | ● | ||
| NOON | •• | •• | •• | ● | Adjust to Maintenance | |
| PM | •• | •• | •• | ● | ||
Dosage should be individualized to provide maximum benefit. In some cases, serum blood level determinations of primidone may be necessary for optimal dosage adjustment. The clinically effective serum level for primidone is between 5 to 12 µg/mL.
In Patients Already Receiving Other Anticonvulsants
Primidone should be started at 100 to 125 mg at bedtime and gradually increased to maintenance level as the other drug is gradually decreased. This regimen should be continued until satisfactory dosage level is achieved for the combination, or the other medication is completely withdrawn. When therapy with primidone alone is the objective, the transition from concomitant therapy should not be completed in less than two weeks.
Pediatric Dosage
For children under 8 years of age, the following regimen may be used:
Days 1 to 3: 50 mg at bedtime.
Days 4 to 6: 50 mg b.i.d.
Days 7 to 9: 100 mg b.i.d.
Day 10 to maintenance: 125 mg t.i.d. to 250 mg t.i.d.
For children under 8 years of age, the usual maintenance dosage is 125 to 250
mg three times daily or 10 to 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses.
HOW SUPPLIED
Primidone Tablets USP 50 mg are supplied as white, round, flat faced tablets, debossed AN above 44 on one side and cut bisected on the other side.
Bottles of 100 NDC 42291-509-01
Bottles of 500 NDC 42291-509-50
Primidone Tablets USP 250 mg are supplied as white, round, flat faced tablets, debossed AN bisect 545 on one side and plain on the other side.
Bottles of 100 NDC 42291-511-01
Bottles of 500 NDC 42291-511-50
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F- 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense contents with a child-resistant closure (as required) and in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals
Paterson, New Jersey 07504
Packaged by:
APACE Packaging, LLC
Fountain Run, Kentucky 42133
MF# 296 REV03/2008
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL 50 mg
NDC 42291-509-50
Primidone
Tablets, USP
50 mg
500 Tablets
Rx Only
Each tablet contains:
Primidone, USP...... 50 mg
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Usual Dosage and Complete Prescribing Information: See accompanying literature.
Dispense contents with a child-resistant closure (as required) and in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C - 30°C (59°F - 86°F).
[See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
MF508 06/09
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL 250 mg
NDC 42291-511-50
Primidone
Tablets, USP
250 mg
500 Tablets
Rx Only
Each tablet contains:
Primidone, USP...... 250 mg
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Usual Dosage and Complete Prescribing Information: See accompanying literature.
Dispense contents with a child-resistant closure (as required) and in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C - 30°C (59°F - 86°F).
[See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
MF508 06/09
PrimidonePrimidone TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PrimidonePrimidone TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||