Proparacaine Hydrochloride
Proparacaine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 0.5% (Sterile)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- PROPARACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION:
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
- PROPARACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
- PROPARACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- WARNINGS:
- PRECAUTIONS:
- PROPARACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS:
- PROPARACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
- HOW SUPPLIED:
- Storage
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx only
DESCRIPTION:
Proparacaine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 0.5% is a topical anesthetic prepared as a sterile aqueous ophthalmic solution. The active ingredient is represented by the following structural formula:
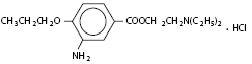
C16H26N2O3 • HCI
Mol. wt.: 330.85
Chemical name: Benzoic acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-,2-(diethylamino) ethyl ester, monohydrochloride.
Each mL Contains:
ACTIVE: Proparacaine Hydrochloride 5 mg (0.5%); INACTIVES: Glycerin, Hydrochloric Acid, Purified Water. Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide may be added to adjust pH (3.5 – 6.0). PRESERVATIVE ADDED: Benzalkonium Chloride 0.01%.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Proparacaine is a rapid acting local anesthetic suitable for ophthalmic use. With a single drop, the onset of anesthesia usually begins within 30 seconds and persists for 15 minutes or longer.
The main site of anesthetic action is the nerve cell membrane where proparacaine interferes with the large transient increase in the membrane permeability to sodium ions that is normally produced by a slight depolarization of the membrane. As the anesthetic action progressively develops in a nerve, the threshold for electrical stimulation gradually increases and the safety factor for conduction decreases. When this action is sufficiently well developed, block of conduction is produced.
The exact mechanism whereby proparacaine and other local anesthetics influence the permeability of the cell membrane is unknown; however, several studies indicate that local anesthetics may limit sodium ion permeability by closing the pores through which the ions migrate in the lipid layer of the nerve cell membrane. This limitation prevents the fundamental change necessary for the generation of the action potential.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Proparacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is indicated for topical anesthesia in ophthalmic practice. Representative ophthalmic procedures in which the preparation provides good local anesthesia include measurement of intraocular pressure (tonometry), removal of foreign bodies and sutures from the cornea, conjunctival scraping in diagnosis and gonioscopic examination; it is also indicated for use as a topical anesthetic prior to surgical operations such as cataract extraction.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
This preparation is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of the solution.
WARNINGS:
NOT FOR INJECTION - FOR TOPICAL OPHTHALMIC USE ONLY
Prolonged use of a topical ocular anesthetic may produce permanent corneal opacifiction with accompanying loss of vision.
PRECAUTIONS:
General:
Proparacaine should be used cautiously and sparingly in patients with known allergies, cardiac disease, or hyperthyroidism. The long-term toxicity of proparacaine is unknown; prolonged use may possibly delay wound healing. Although exceedingly rare with ophthalmic application of local anesthetics, it should be borne in mind that systemic toxicity (manifested by central nervous system stimulation followed by depression) may occur.
Protection of the eye from irritating chemicals, foreign bodies and rubbing during the period of anesthesia is very important. Tonometers soaked in sterilizing or detergent solutions should be thoroughly rinsed with sterile distilled water prior to use. Patients should be advised to avoid touching the eye until the anesthesia has worn off. Do not touch dropper tip to any surface as this may contaminate the solution.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenicity, or possible impairment of fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with proparacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. It is also not known whether proparacaine hydrochloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Proparacaine hydrochloride should be administered to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers:
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when proparacaine hydrochloride is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use:
Controlled clinical studies have not been performed with proparacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution to establish safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients; however, the literature cites the use of proparacaine hydrochloride as a topical ophthalmic anesthetic agent in pediatric patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Pupillary dilation or cycloplegic effects have rarely been observed with proparacaine hydrochloride. The drug appears to be safe for use in patients sensitive to other local anesthetics, but local or systemic sensitivity occasionally occurs. Instillation of proparacaine in the eye at recommended concentration and dosage usually produces little or no initial irritation, stinging, burning, conjunctival redness, lacrimation or increased winking. However, some local irritation and stinging may occur several hours after the instillation.
Rarely, a severe, immediate-type, apparently hyperallergic corneal reaction may occur which includes acute, intense and diffuse epithelial keratitis; a gray, ground-glass appearance; sloughing of large areas of necrotic epithelium; corneal filaments and, sometimes, iritis with descemetitis.
Allergic contact dermatitis with drying and fissuring of the fingertips has been reported.
Softening and erosion of the corneal epithelium and conjunctival congestion and hemorrhage have been reported.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Deep anesthesia as in cataract extraction:
Instill 1 drop every 5 to 10 minutes for 5 to 7 doses.
Removal of sutures:
Instill 1 or 2 drops 2 or 3 minutes before removal of stitches.
Removal of foreign bodies:
Instill 1 or 2 drops prior to operating.
Tonometry:
Instill 1 or 2 drops immediately before measurement
FOR OPHTHALMIC USE ONLY
HOW SUPPLIED:
Proparacaine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 0.5% is supplied in a plastic bottle with a controlled drop tip in the following size:
15 mL bottle - Prod. No. 04711
Storage
Refrigerate at 2°-8°C (36°- 46°F). Protect from light. Keep tightly closed.
Do not use if the solution shows more than a faint yellow color.
DO NOT USE IF IMPRINTED NECKBAND IS NOT INTACT.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Rx only
Bausch & Lomb Incorporated
Tampa, FL 33637
©Bausch & Lomb Incorporated
Revised November 2007
9114400 (Folded)
9114500 (Flat)
Principal Display Panel
NDC 24208-730-06
Bausch & Lomb
Proparacaine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 0.5% (Sterile)
Rx only
[icon- eye] [icon- 0.5%] [icon-solution] [icon- 15 mL]
Repacked by:
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
Nipomo, CA 93444
Proparacaine HydrochlorideProparacaine Hydrochloride SOLUTION/ DROPS
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||