Quillivant
NextWave Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use QUILLIVANT™ XR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for QUILLIVANT XR. QUILLIVANT™ XR (methylphenidate hydrochloride) for extended-release oral suspension, CIIInitial U.S. Approval: 1955RECENT MAJOR CHANGES Warnings and Precautions Priapism (5.5) 12/2013 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon (5.6) 8/2013 BOXED WARNINGWARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. CNS stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR, have a high potential for abuse and dependence (5.1, 9.2, 9.3) Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy (5.1, 9.2) INDICATIONS AND USAGEQUILLIVANT XR is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). (1)The efficacy of QUILLIVANT XR was established in a 2-week, placebo-controlled trial in children aged 6–12 years with a diagnosis of ADHD. Accumulated efficacy data from other methylphenidate products were also considered. (1, 14)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Before administering the dose, vigorously shake bottle for at least 10 seconds. (2.1) May be taken with or without food. (2.1) For patients 6 years and above, recommended starting dose is 20 mg given orally once daily in the morning. Dosage may be increased weekly in increments of 10 mg to 20 mg per day. Daily dosage above 60 mg is not recommended. (2.1) Reconstitution instructions for the pharmacist: Tap bottle until powder flows freely. Remove bottle cap, add specified amount of water for reconstitution. Insert bottle adapter into neck of bottle. Replace bottle cap. Shake with vigorous back and forth motion for at least 10 seconds to prepare suspension. (2.5) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSExtended-release oral suspension (after reconstitution with water): 25 mg per 5 mL (5 mg per mL) (3)CONTRAINDICATIONS Known hypersensitivity to methylphenidate or product components (4.1) Concurrent treatment with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), or use of an MAOI within the preceding 14 days (4.2, 7.1) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Serious Cardiovascular Reactions: Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulants at recommended doses in children and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. In adults, sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmias, or coronary artery disease (5.2) Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases: Monitor blood pressure and pulse. Consider the benefits and risks in patients for whom an increase in blood pressure or heart rate would be problematic.(5.3) Psychiatric Adverse Reactions: Use of stimulants may cause psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or exacerbation of symptoms in patients with pre-existing psychiatric illness. Evaluate for bipolar disorder prior to QUILLIVANT XR use. (5.4) Priapism: Cases of painful and prolonged penile erections and priapism have been reported with methylphenidate products. Immediate medical attention should be sought if signs or symptoms of prolonged penile erections or priapism are observed (5.5) Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon: Stimulants used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants (5.6) Long-Term Suppression of Growth:. Monitor height and weight at appropriate intervals in pediatric patients. (5.7) Side EffectsBased on accumulated data from other methylphenidate products, the most common (≥5% and twice the rate of placebo) adverse reactions are appetite decreased, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, weight decreased, anxiety, dizziness, irritability, affect lability, tachycardia, and blood pressure increased. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact NextWave Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-206-8115 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1). Nursing Mothers: Discontinue drug or discontinue nursing, taking into consideration the importance of the drug to the mother. (8.3).
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 QUILLIVANT INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 QUILLIVANT DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 QUILLIVANT CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 QUILLIVANT ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 QUILLIVANT DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
CNS stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
QUILLIVANT XR is indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
The efficacy of QUILLIVANT XR was established in a 2-week, placebo-controlled, laboratory classroom, crossover study in children aged 6–12 years with a diagnosis of ADHD. Patients in the trial met DSM-IV® criteria for ADHD. Accumulated efficacy data from other methylphenidate products were also considered [see Clinical Studies (14) ].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
QUILLIVANT XR should be orally administered once daily in the morning with or without food. The dose should be individualized according to the needs and responses of the patient. Before administering the dose, vigorously shake the bottle of QUILLIVANT XR for at least 10 seconds, to ensure that the proper dose is administered.
The recommended starting dose of QUILLIVANT XR for patients 6 years and above is 20 mg once daily in the morning. The dose may be titrated weekly in increments of 10 mg to 20 mg. Daily doses above 60 mg have not been studied and are not recommended.
2.2 Maintenance/Extended Treatment
There is no body of evidence available from controlled trials to indicate how long the patient with ADHD should be treated with QUILLIVANT XR. It is generally agreed, however, that pharmacological treatment of ADHD may be needed for extended periods. The effectiveness of QUILLIVANT XR for longer-term use has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. The physician who elects to use QUILLIVANT XR for extended periods in patients with ADHD should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient with trials off medication to assess the patient's functioning without pharmacotherapy. Improvement may be sustained when the drug is either temporarily or permanently discontinued.
2.3 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation
If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse effects occur, reduce dosage, or, if necessary, discontinue the drug. QUILLIVANT XR should be periodically discontinued to assess the child's condition. If improvement is not observed after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period, the drug should be discontinued.
2.4 Important Information Prior to Initiating Treatment
Prior to treating children, adolescents, and adults with CNS stimulants including QUILLIVANT XR, assess for the presence of cardiac disease (i.e., perform a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam) [see Warnings and Precautions 5.2].
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy. Maintain careful prescription records, educate patients about abuse, monitor for signs of abuse and overdose, and periodically re-evaluate the need for QUILLIVANT XR use [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
2.5 Reconstitution Instructions for the Pharmacist
QUILLIVANT XR is supplied as a powder for oral suspension which must be reconstituted with water prior to dispensing. Preparation instructions: Tap bottle until powder flows freely. Remove bottle cap, and add specified amount of water to the bottle (see Table 1 below). Insert bottle adapter into neck of bottle. Replace bottle cap. Shake with vigorous back and forth motion for at least 10 seconds to prepare suspension.
| Amount of drug in bottle |
Amount of water to add to bottle |
Final reconstituted volume (yield) |
|---|---|---|
| 300 mg | 53 mL | 60 mL |
| 600 mg | 105 mL | 120 mL |
| 750 mg | 131 mL | 150 mL |
| 900 mg | 158 mL | 180 mL |
Store reconstituted QUILLIVANT XR at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted from 15º to 30ºC (59º to 86ºF). Dispense in original container. QUILLIVANT XR is stable for up to 4 months after reconstitution.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-release oral suspension (after reconstitution with water): 25 mg per 5 mL (5 mg per mL).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Methylphenidate or other Components of QUILLIVANT XR
QUILLIVANT XR is contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to methylphenidate, or other components of QUILLIVANT XR. Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with other methylphenidate products [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
4.2 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
QUILLIVANT XR is contraindicated during treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and also within 14 days following discontinuation of treatment with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), because of the risk of hypertensive crisis [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
CNS stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Reactions
Stroke and myocardial infarction have occurred in adults treated with CNS stimulants at recommended doses. Sudden death has occurred in children and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities and other serious cardiac problems, and in adults taking CNS stimulants at recommended doses for ADHD. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, or other serious cardiac problems. Further evaluate patients who develop exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or arrhythmias during treatment with QUILLIVANT XR.
5.3 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
CNS stimulants cause an increase in blood pressure (mean increase approximately 2 to 4 mmHg) and heart rate (mean increase approximately 3 to 6 bpm). Individuals may have larger increases. Monitor all patients for hypertension and tachycardia
5.4 Psychiatric Side Effects
Exacerbation of Pre-Existing Psychosis
CNS stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought disorder in patients with a pre-existing psychotic disorder.
Induction of a Manic Episode in Patients with Bipolar Disorder
CNS stimulants may induce a manic or mixed episode in patients. Prior to initiating treatment, screen patients for risk factors for developing a manic episode (e.g., comorbid or history of depressive symptoms or a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, or depression).
New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
CNS stimulants, at recommended doses, may cause psychotic or manic symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania) in patients without a prior history of psychotic illness or mania. If such symptoms occur, consider discontinuing QUILLIVANT XR. In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo-controlled studies of CNS stimulants, psychotic or manic symptoms occurred in approximately 0.1% of CNS stimulant-treated patients, compared to 0 in placebo-treated patients.
5.5 Priapism
Prolonged and painful erections, sometimes requiring surgical intervention, have been reported with methylphenidate products in both pediatric and adult patients. Priapism was not reported with drug initiation but developed after some time on the drug, often subsequent to an increase in dose. Priapism has also appeared during a period of drug withdrawal (drug holidays or during discontinuation). Patients who develop abnormally sustained or frequent and painful erections should seek immediate medical attention.
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon
Stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation of digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.7 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
CNS stimulants have been associated with weight loss and slowing of growth rate in pediatric patients. Closely monitor growth (weight and height) in pediatric patients treated with CNS stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR. Careful follow-up of weight and height in children ages 7 to 10 years who were randomized to either methylphenidate or nonmedication treatment groups over 14 months, as well as in naturalistic subgroups of newly methylphenidate-treated and nonmedication-treated children over 36 months (to the ages of 10 to 13 years), suggests that consistently medicated children (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout the year) have a temporary slowing in growth rate (on average, a total of about 2 cm less growth in height and 2.7 kg less growth in weight over 3 years), without evidence of growth rebound during this period of development..
Published data are inadequate to determine whether chronic use of amphetamines may cause a similar suppression of growth; however, it is anticipated that they likely have this effect as well. Therefore, growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, and patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Clinical Trials Experience with Other Methylphenidate Products in Children, Adolescents, and Adults with ADHD
Commonly reported (≥2% of the methylphenidate group and at least twice the rate of the placebo group) adverse reactions from placebo-controlled trials of methylphenidate products include: appetite decreased, weight decreased, nausea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, dry mouth, vomiting, insomnia, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, affect lability, agitation, irritability, dizziness, vertigo, tremor, blurred vision, blood pressure increased, heart rate increased, tachycardia, palpitations, hyperhidrosis, and pyrexia.
Clinical Trials Experience with QUILLIVANT XR in Children and Adolescents with ADHD
There is limited experience with QUILLIVANT XR in controlled trials. Based on this limited experience, the adverse reaction profile of QUILLIVANT XR appears similar to other methylphenidate extended-release products. The most common (≥2% in the QUILLIVANT XR group and greater than placebo) adverse reactions reported in the Phase 3 controlled study conducted in 45 ADHD patients (ages 6–12 years) were affect lability, excoriation, initial insomnia, tic, decreased appetite, vomiting, motion sickness, eye pain, and rash.
| Adverse reaction | QUILLIVANT XR N= 45 |
Placebo N= 45 |
|---|---|---|
| Affect lability | 9% | 2% |
| Excoriation | 4% | 0 |
| Initial Insomnia | 2% | 0 |
| Tic | 2% | 0 |
| Decreased appetite | 2% | 0 |
| Vomiting | 2% | 0 |
| Motion sickness | 2% | 0 |
| Eye pain | 2% | 0 |
| Rash | 2% | 0 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of methylphenidate products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions are as follows:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Pancytopenia, Thrombocytopenia, Thrombocytopenic purpura
Cardiac Disorders: Angina pectoris, Bradycardia, Extrasystole, Supraventricular tachycardia, Ventricular extrasystole
Eye Disorders: Diplopia, Mydriasis, Visual impairment
General Disorders: Chest pain, Chest discomfort, Hyperpyrexia
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions such as Angioedema, Anaphylactic reactions, Auricular swelling, Bullous conditions, Exfoliative conditions, Urticarias, Pruritus NEC, Rashes, Eruptions, and Exanthemas NEC
Investigations: Alkaline phosphatase increased, Bilirubin increased, Hepatic enzyme increased, Platelet count decreased, White blood cell count abnormal
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders: Arthralgia, Myalgia, Muscle twitching
Nervous System Disorders: Convulsion, Grand mal convulsion, Dyskinesia
Psychiatric Disorders: Disorientation, Hallucination, Hallucination auditory, Hallucination visual, Libido changes, Mania
Urogenital System: Priapism
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia, Erythema
Vascular Disorders: Raynaud's phenomenon
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 MAO Inhibitors
Do not administer QUILLIVANT XR concomitantly with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or within 14 days after discontinuing MAOI treatment. Concomitant use of MAOIs and CNS stimulants can cause hypertensive crisis. Potential outcomes include death, stroke, myocardial infarction, aortic dissection, ophthalmological complications, eclampsia, pulmonary edema, and renal failure.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Risk Summary
There are no adequate or well-controlled studies with QUILLIVANT XR in pregnant women. Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including premature delivery and low birth weight, have been seen in mothers dependent on other stimulant products such as amphetamines. Methylphenidate showed some potential for teratogenicity when pregnant animals were treated during organogenesis: an increased incidence of fetal spina bifida in rabbits at 40 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), on a mg/m2 basis, and an increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations in rats at 7 times the MRHD. A decrease in body weight gain was seen in the offspring of rats treated with methylphenidate throughout pregnancy and lactation at 4 times the MRHD. QUILLIVANT XR should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Clinical Considerations
Stimulant medications, such as QUILLIVANT XR, cause vasoconstriction and thereby decrease placental perfusion. Infants born to amphetamine dependent mothers have an increased risk of premature delivery and low birth weight. Monitor infants for symptoms of withdrawal such as feeding difficulties, irritability, agitation, and excessive drowsiness.
Animal Data
In studies conducted in rats and rabbits, methylphenidate was administered orally at doses of up to 75 and 200 mg/kg/day, respectively, during the period of organogenesis. Teratogenic effects (increased incidence of fetal spina bifida) were observed in rabbits at the highest dose, which is approximately 40 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis. The no effect level for embryo-fetal development in rabbits was 60 mg/kg/day (11 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). There was no evidence of specific teratogenic activity in rats, although increased incidences of fetal skeletal variations were seen at the highest dose level (7 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis), which was also maternally toxic. The no effect level for embryo-fetal development in rats was 25 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). When methylphenidate was administered to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation at doses of up to 45 mg/kg/day, offspring body weight gain was decreased at the highest dose (4 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis), but no other effects on postnatal development were observed. The no effect level for pre- and postnatal development in rats was 15 mg/kg/day (equal to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Methylphenidate is present in human milk. Long-term neurodevelopmental effects on infants from stimulant exposure are unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of QUILLIVANT XR have been established in pediatric patients ages 6 to 17 years. Use of QUILLIVANT XR in pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age is supported by adequate and well-controlled studies [see Clinical Studies (14) ]. Use in 12 to 17 year olds is supported by the adequate and well-controlled studies of QUILLIVANT XR in younger pediatric patients and additional pharmacokinetic data in adolescents, along with safety information from other methylphenidate-containing products. The long-term efficacy of methylphenidate in pediatric patients has not been established. Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years have not been established.
Long Term Suppression of Growth
Growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, including QUILLIVANT XR. Children who are not growing or gaining weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Juvenile Animal Data
Rats treated with methylphenidate early in the postnatal period through sexual maturation demonstrated a decrease in spontaneous locomotor activity in adulthood. A deficit in acquisition of a specific learning task was observed in females only. The doses at which these findings were observed are at least 6 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis.
In the study conducted in young rats, methylphenidate was administered orally at doses of up to 100 mg/kg/day for 9 weeks, starting early in the postnatal period (postnatal day 7) and continuing through sexual maturity (postnatal week 10). When these animals were tested as adults (postnatal weeks 13–14), decreased spontaneous locomotor activity was observed in males and females previously treated with 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis) or greater, and a deficit in the acquisition of a specific learning task was observed in females exposed to the highest dose (12 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The no effect level for juvenile neurobehavioral development in rats was 5 mg/kg/day (half the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of the long-term behavioral effects observed in rats is unknown.
8.5 Geriatric Use
QUILLIVANT XR has not been studied in patients over the age of 65 years.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
QUILLIVANT XR contains methylphenidate, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
CNS stimulants including QUILLIVANT XR, other methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines have a high potential for abuse. Abuse is characterized by impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving.
Signs and symptoms of CNS stimulant abuse include increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and/or sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, insomnia, decreased appetite, loss of coordination, tremors, flushed skin, vomiting, and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been observed. Abusers of CNS stimulants may chew, snort, inject, or use other unapproved routes of administration which can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
To reduce the abuse of CNS stimulants including QUILLIVANT XR, assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing. After prescribing, keep careful prescription records, educate patients and their families about abuse and on proper storage and disposal of CNS stimulants, monitor for signs of abuse while on therapy, and re-evaluate the need for QUILLIVANT XR use.
9.3 Dependence
Tolerance
Tolerance (a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug results in a reduction of the drug's desired and/or undesired effects over time) can occur during chronic therapy with CNS stimulants including QUILLIVANT XR.
Dependence
Physical dependence (a state of adaptation manifested by a withdrawal syndrome produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, or administration of an antagonist) can occur in patients treated with CNS stimulants including QUILLIVANT XR. Withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation following prolonged high-dosage administration of CNS stimulants include extreme fatigue and depression.
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of acute methylphenidate overdosage, resulting principally from overstimulation of the CNS and from excessive sympathomimetic effects, may include the following: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, restlessness, anxiety, agitation, tremors, hyperreflexia, muscle twitching, convulsions (may be followed by coma), euphoria, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, sweating, flushing, headache, hyperpyrexia, tachycardia, palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, hypotension, tachypnea, mydriasis, and dryness of mucous membranes.
10.2 Management of Overdose
Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center for up-to-date guidance and advice on the management of overdosage with methylphenidate (1-800-222-1222.) Provide supportive care, including close medical supervision and monitoring. Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug. Consider the possibility of multiple drug overdosage. Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. Use supportive and symptomatic measures.
11 DESCRIPTION
QUILLIVANT XR is a powder that, after reconstitution with water, forms an extended-release oral suspension formulation of methylphenidate intended for once daily oral administration. QUILLIVANT XR contains approximately 20% immediate-release and 80% extended-release methylphenidate. After reconstitution, QUILLIVANT XR is available in a 25 mg per 5 mL (5 mg per mL) extended-release oral suspension.
Methylphenidate HCl is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. The chemical name is methyl α-phenyl-2-piperidineacetate hydrochloride, and its structural formula is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Methylphenidate HCl structure
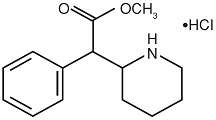
Methylphenidate HCl is a white, odorless crystalline powder. Its solutions are acid to litmus. It is freely soluble in water and in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in chloroform and in acetone.
QUILLIVANT XR also contains the following inactive ingredients: sodium polystyrene sulfonate, povidone, triacetin, polyvinyl acetate, sucrose, anhydrous trisodium citrate, anhydrous citric acid, sodium benzoate, sucralose, poloxamer 188, corn starch, xanthan gum, talc, banana flavor, and silicon dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate HCl is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Methylphenidate is a racemic mixture comprised of the d- and l-isomers. The d-isomer is more pharmacologically active than the l-isomer. Methylphenidate is thought to block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a single, 60 mg oral dose of QUILLIVANT XR in 28 healthy adult subjects in a crossover study under fasting conditions, d-methylphenidate (d-MPH) mean (± SD) peak plasma concentrations of 13.6 (± 5.8) ng/mL occurred at a median time of 5.0 hours after dosing (Figure 2). The relative bioavailability of QUILLIVANT XR compared to Methylphenidate IR oral solution (2×30 mg, q6h) is 95%.
Figure 2. Mean d-Methylphenidate Plasma Concentration-Time Profiles

The single dose pharmacokinetics of d-MPH under fed conditions are summarized (Table 3) from studies in children and adolescents with ADHD, and healthy adults following an oral dose of 60 mg QUILLIVANT XR.
| PK Parameter | Children |
Adolescent |
Adult (n=27) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax (hr) |
4.05 (3.98–6.0) | 2.0 (1.98–4.0) | 4.0 (1.3–7.3) |
| T1/2 (hr) | 5.2±0.1 | 5.0±0.2 | 5.2±1.0 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 34.4±14.0 | 21.1±5.9 | 17.0±7.7 |
| AUCinf (hr*ng/mL) | 378±175 | 178±54.2 | 163.2±80.3 |
| Cl (L/hr/kg) | 4.27±0.70 | 5.06±1.42 | 5.66±2.15 |
Metabolism and Excretion
Following a single 60 mg oral dose of QUILLIVANT XR in 28 healthy adult subjects under fasting conditions, the mean plasma terminal elimination half-life of d-methylphenidate was 5.6 (± 0.8) hours.
In humans, methylphenidate is metabolized primarily via deesterification to alpha-phenyl-piperidine acetic acid (PPAA). The metabolite has little or no pharmacologic activity.
After oral dosing of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, about 90% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine. The main urinary metabolite was PPAA, accounting for approximately 80% of the dose.
Food Effects
In a study in adult volunteers to investigate the effects of a high-fat meal on the bioavailability of QUILLIVANT XR at a dose of 60 mg, the presence of food reduced the time to peak concentration by approximately 1 hour (fed: 4 hours vs. fasted: 5 hours). Overall, a high-fat meal increased the average Cmax of QUILLIVANT XR by about 28% and the AUC by about 19%. These changes are not considered clinically significant.
Gender
There is insufficient experience with the use of QUILLIVANT XR to detect gender variations in pharmacokinetics.
Race
There is insufficient experience with the use of QUILLIVANT XR to detect ethnic variations in pharmacokinetics.
Age
The pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate after QUILLIVANT XR administration were studied in pediatric patients with ADHD between 9 and 15 years of age. After a single oral dose of 60 mg QUILLIVANT XR, plasma concentrations of methylphenidate in children (9–12 years old; n=3) were approximately twice the concentrations observed in adults. The plasma concentrations in adolescent patients (13–15 years old; n=4) were similar to those in adults.
Renal Insufficiency
There is no experience with the use of QUILLIVANT XR in patients with renal insufficiency. After oral administration of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, methylphenidate was extensively metabolized and approximately 80% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine in the form of PPAA. Since renal clearance is not an important route of methylphenidate clearance, renal insufficiency is expected to have little effect on the pharmacokinetics of QUILLIVANT XR.
Hepatic Insufficiency
There is no experience with the use of QUILLIVANT XR in patients with hepatic insufficiency.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in B6C3F1 mice, methylphenidate caused an increase in hepatocellular adenomas and, in males only, an increase in hepatoblastomas, at a daily dose of approximately 60 mg/kg/day. This dose is approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis. Hepatoblastoma is a relatively rare rodent malignant tumor type. There was no increase in total malignant hepatic tumors. The mouse strain used is sensitive to the development of hepatic tumors, and the significance of these results to humans is unknown.
Methylphenidate did not cause any increase in tumors in a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in F344 rats; the highest dose used was approximately 45 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 5 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Mutagenesis
Methylphenidate was not mutagenic in the in vitro Ames reverse mutation assay or in the in vitro mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay. Sister chromatid exchanges and chromosome aberrations were increased, indicative of a weak clastogenic response, in an in vitro assay in cultured Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. The genotoxic potential of methylphenidate has not been evaluated in an in vivo assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Methylphenidate did not impair fertility in male or female mice that were fed diets containing the drug in an 18-week Continuous Breeding study. The study was conducted at doses of up to 160 mg/kg/day, approximately 8-fold the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of QUILLIVANT XR was evaluated in a laboratory classroom study conducted in 45 pediatric patients (ages 6 to 12 years) with ADHD. The study began with an open-label dose optimization period (4 to 6 weeks) with an initial QUILLIVANT XR dose of 20 mg once daily in the morning. The dose could be titrated weekly in increments of 10 or 20 mg until an optimal dose or the maximum dose of 60 mg/day was reached. Subjects then entered a 2-week randomized, double-blind, crossover treatment with the individually optimized dose of QUILLIVANT XR or placebo. At the end of each week, school teachers and raters evaluated the attention and behavior of the subjects in a laboratory classroom using the Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham (SKAMP) rating scale. The primary efficacy endpoint was the SKAMP-Combined score at 4 hours post-dosing. The key secondary efficacy endpoints were the SKAMP-Combined scores at 0.75, 2, 8, 10, and 12 hours post-dosing.
Results from the first double-blind, placebo-controlled week of the study are summarized in Figure 3. SKAMP-Combined scores were statistically significantly lower (improved) at all time points (0.75, 2, 4, 8, 10, 12 hours) post-dosing with QUILLIVANT XR compared to placebo.
Figure 3. Absolute SKAMP-Combined Score after treatment with QUILLIVANT XR or Placebo during Period 1.

16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
QUILLIVANT XR is supplied as powder that, after reconstitution with water, forms an extended-release oral suspension. The product is supplied in a carton. Each carton also contains one bottle, one oral dosing dispenser, and one bottle adapter.
The product must be reconstituted only by the pharmacist and not by the patient or caregiver. After reconstitution, the product is a light beige to tan viscous suspension containing 25 mg per 5 mL (5 mg per mL) of methylphenidate hydrochloride.
| Bottles of 300 mg powder (to prepare 60 mL suspension) | NDC 24478-190-10 |
| Bottles of 600 mg powder (to prepare 120 mL suspension) | NDC 24478-200-20 |
| Bottles of 750 mg powder (to prepare 150 mL suspension) | NDC 24478-205-25 |
| Bottles of 900 mg powder (to prepare 180 mL suspension) | NDC 24478-210-30 |
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted from 15º to 30ºC (59º to 86ºF). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in original container.
Disposal
Comply with laws and regulations on drug disposal. Use a medicine take-back program if available.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
17.1 Information for Patients
Information on the Medication Guide
Inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with QUILLIVANT XR, and counsel them on its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide is available for QUILLIVANT XR. Instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide, and assist them in understanding its contents. Give patients the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is attached to the prescribing information.
Instructions for Using the Enclosed Oral Dosing Dispenser
Provide the following instructions on administration to the patient or caregiver:
- Use only with the oral dosing dispenser provided with this product
- Vigorously shake the bottle of QUILLIVANT XR for at least 10 seconds before each dose, to ensure that the proper dose is administered.
- Remove the bottle cap. Confirm that the bottle adapter has been inserted into top of the bottle.
- Insert the tip of the oral dosing dispenser provided with this product into the bottle adapter.
- Turn bottle upside down and withdraw prescribed amount of QUILLIVANT XR into the oral dosing dispenser.
- Remove filled oral dosing dispenser from bottle and dispense QUILLIVANT XR directly into mouth.
- Replace bottle cap and store bottle as directed.
- Wash oral dosing dispenser after each use (components are dishwasher-safe).
Controlled Substance Status/Potential for Abuse and Dependence
Advise patients and their caregivers that QUILLIVANT XR is a federally controlled substance, and it can be abused and lead to dependence [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.1, 9.2, and 9.3)]. Instruct patients that they should not give QUILLIVANT XR to anyone else. Advise patients to store QUILLIVANT XR in a safe place, preferably locked, to prevent abuse. Advise patients to comply with laws and regulations on drug disposal. Advise patients to dispose of remaining, unused, or expired QUILLIVANT XR through a medicine take-back program if available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
Serious Cardiovascular Risks
Advise patients, caregivers, and family members that there is a potential for serious cardiovascular risks including sudden death, myocardial infarction, and stroke with QUILLIVANT XR use. Instruct patients to contact a healthcare provider immediately if they develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
Advise patients that QUILLIVANT XR can elevate blood pressure and heart rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Psychiatric Risks
Advise patients that QUILLIVANT XR, at recommended doses, can cause psychotic or manic symptoms, even in patients without a prior history of psychotic symptoms or mania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Suppression of Growth
Advise patients, families, and caregivers that QUILLIVANT XR can cause slowing of growth and weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Priapism
Advise patients, caregivers, and family members of the possibility of painful or prolonged penile erections (priapism). Instruct the patient to seek immediate medical attention in the event of priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Circulation Problems in Fingers and Toes [Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon]
- Instruct patients beginning treatment with QUILLIVANT XR about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon, and associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful, and/or may change color from pale, to blue, to red.
- Instruct patients to report to their physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes.
- Instruct patients to call their physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking QUILLIVANT XR.
- Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
Pregnancy
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with QUILLIVANT XR. Advise patients of the potential fetal effects from the use of QUILLIVANT XR during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Nursing Mothers
Advise nursing mothers to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue QUILLIVANT XR [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
For the Pharmacist
Dispense a Medication Guide to patients receiving a QUILLIVANT XR prescription.

Manufactured by:
Tris Pharma, Inc., Monmouth Junction, NJ 08852
LAB-0656-4.0
Medication Guide
QUILLIVANT™ XR (\kwil-ə-vant\)
(methylphenidate hydrochloride)
for extended-release oral suspension CII
Read this Medication Guide that comes with QUILLIVANT XR before you or your child starts taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your or your child's treatment with QUILLIVANT XR.
| What is the most important information I should know about QUILLIVANT XR? |
| The following have been reported with use of methylphenidate hydrochloride and other stimulant medicines. |
1. Heart-related problems:
|
| Tell your doctor if you or your child have any heart problems, heart defects, high blood pressure, or a family history of these problems. |
| Your doctor should check you or your child carefully for heart problems before starting QUILLIVANT XR. |
| Your doctor should check your or your child's blood pressure and heart rate regularly during treatment with QUILLIVANT XR. |
| Call your doctor right away if you or your child has any signs of heart problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting while taking QUILLIVANT XR. |
| 2. Mental (Psychiatric) problems: |
All Patients
|
Children and Teenagers
|
| Tell your doctor about any mental problems you or your child have, or about a family history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression. |
| Call your doctor right away if you or your child have any new or worsening mental symptoms or problems while taking QUILLIVANT XR, especially seeing or hearing things that are not real, believing things that are not real, or are suspicious. |
| 3. Circulation problems in fingers and toes [Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon]: |
|
| Tell your doctor if you have or your child has numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in the fingers or toes. |
| Call your doctor right away if you have or your child has any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking QUILLIVANT XR. |
What is QUILLIVANT XR?
QUILLIVANT XR is a central nervous system stimulant prescription medicine. QUILLIVANT XR is a liquid medicine that you take by mouth. It is used for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). QUILLIVANT XR may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in patients with ADHD.
QUILLIVANT XR should be used as a part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include counseling or other therapies.
| QUILLIVANT XR is a federally controlled substance (CII) because it can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep QUILLIVANT XR in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away QUILLIVANT XR may harm others, and is against the law. |
| Tell your doctor if you or your child have (or have a family history of) ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or street drugs. |
It is not known if QUILLIVANT XR is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.
Who should not take QUILLIVANT XR?
QUILLIVANT XR should not be taken if you or your child:
- are allergic to methylphenidate hydrochloride, or any of the ingredients in QUILLIVANT XR. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in QUILLIVANT XR.
- are taking or have taken within the past 14 days an antidepression medicine called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor or MAOI.
QUILLIVANT XR may not be right for you or your child. Before starting QUILLIVANT XR tell your or your child's doctor about all health conditions (or a family history of) including:
- heart problems, heart defects, high blood pressure
- mental problems including psychosis, mania, bipolar illness, or depression
- circulation problems in fingers and toes
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if QUILLIVANT XR will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed. QUILLIVANT XR passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take QUILLIVANT XR or breast feed.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines that you or your child take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. QUILLIVANT XR and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines will need to be adjusted while taking QUILLIVANT XR.
Your doctor will decide whether QUILLIVANT XR can be taken with other medicines.
Especially tell your doctor if you or your child takes:
- anti-depression medicines including MAOIs
- cold or allergy medicines that contain decongestants
Know the medicines that you or your child takes. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist.
Do not start any new medicine while taking QUILLIVANT XR without talking to your doctor first.
How should QUILLIVANT XR be taken?
- Take QUILLIVANT XR exactly as prescribed. Your doctor may adjust the dose until it is right for you or your child.
- Take QUILLIVANT XR once each day in the morning. QUILLIVANT XR is an extended-release suspension. It releases medicine into your body throughout the day.
- QUILLIVANT XR should be used with the oral dosing dispenser provided with the product. If the oral dosing dispenser is missing or not provided, please contact your pharmacist for a replacement.
- QUILLIVANT XR can be taken with or without food. Taking QUILLIVANT XR with food may shorten the time it takes for the medicine to start working.
- From time to time, your doctor may stop QUILLIVANT XR treatment for a while to check ADHD symptoms.
- Your doctor may do regular checks of the blood, heart, and blood pressure while taking QUILLIVANT XR.
- Children should have their height and weight checked often while taking QUILLIVANT XR. QUILLIVANT XR treatment may be stopped if a problem is found during these check-ups.
- In case of poisoning call your poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are possible side effects of QUILLIVANT XR?
See "What is the most important information I should know about QUILLIVANT XR?" for information on reported heart and mental problems.
Other serious side effects include:
- painful and prolonged erections (priapism) have occurred with methylphenidate. If you or your child develop priapism seek medical help right away. Because of the potential for lasting damage, priapism should be evaluated by a doctor immediately
- slowing of growth (height and weight) in children
Common side effects include:
- decreased appetite
- weight loss
- nausea
- stomach pain
- dry mouth
- vomiting
- trouble sleeping
- anxiety
- nervousness
- restlessness
- mood swings
- agitation
- irritability
- dizziness
- shaking (tremor)
- blurred vision
- increased blood pressure
- fast heart beat
- increased sweating
- fever
Talk to your doctor if you or your child has side effects that are bothersome or do not go away.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store QUILLIVANT XR?
- Store QUILLIVANT XR in a safe place at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep QUILLIVANT XR and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of QUILLIVANT XR
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use QUILLIVANT XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give QUILLIVANT XR to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them and it is against the law.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about QUILLIVANT XR. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about QUILLIVANT XR that was written for healthcare professionals. For more information, please contact NextWave Pharmaceuticals, Inc., at 1-800-206-8115 or visit the website at www.quillivantxr.com.
What are the ingredients in QUILLIVANT XR?
Active Ingredient: methylphenidate hydrochloride
Inactive Ingredients: sodium polystyrene sulfonate, povidone, triacetin, polyvinyl acetate, sucrose, anhydrous trisodium citrate, anhydrous citric acid, sodium benzoate, sucralose, poloxamer 188, corn starch, xanthan gum, talc, banana flavor, and silicon dioxide.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

LAB-0657-4.0
December 2013
Instructions for Use
QUILLIVANT™ XR (\kwil-ə-vant\)
(methylphenidate hydrochloride)
for extended-release oral suspension CII
Read the Instructions for Use before using QUILLIVANT XR and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with the doctor about your or your child's medical condition or treatment.
Step 1. Remove the QUILLIVANT XR bottle and oral dosing dispenser from the box (See Figure A ). If the oral dosing dispenser is missing or not provided, please contact your pharmacist for a replacement.
Figure A

Step 2. Check and make sure that the QUILLIVANT XR bottle contains liquid medicine (See Figure B ). If QUILLIVANT XR is still in powder form, do not use it. Return it to your pharmacist.
Figure B
Step 3. Shake the bottle well (up and down) for at least 10 seconds before each use (See Figure C ).
Figure C
Step 4. Uncap the bottle and check that the bottle adapter has been inserted into the bottle (See Figure D ).
Figure D
If bottle adapter (See Figure E ) has not been inserted into the bottle, insert adapter into the bottle as shown (See Figure F ).
Figure E
Figure F
Once the bottle adapter has been inserted into the bottle, it should not be removed. If the bottle adapter has not been inserted and is missing from the box, contact your pharmacist.
Step 5. Check the QUILLIVANT XR dose in milliliters (mL) as prescribed by your doctor. Locate this number on the oral dosing dispenser (See Figure G ).
Figure G
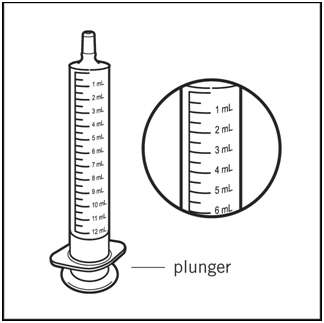
Step 6. Insert tip of the oral dosing dispenser into the upright bottle and push the plunger all the way down (See Figure H ).
Figure H

Step 7. With the oral dosing dispenser in place, turn the bottle upside down. Pull the plunger to the number of mL you need (the amount of liquid medicine in Step 5 – See Figure I ).
Figure I
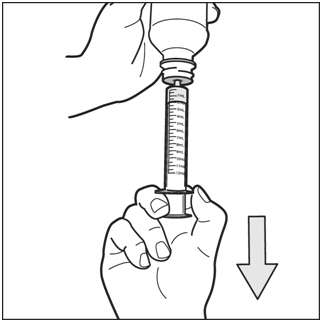
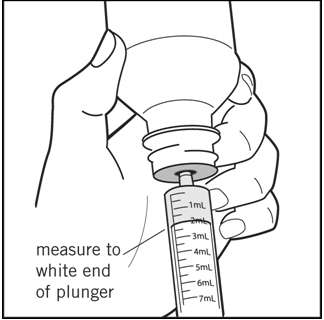
Measure the number of mL of medicine from the white end of the plunger (See Figure J ).
Figure J
Step 8. Remove the oral dosing dispenser from the bottle adapter.
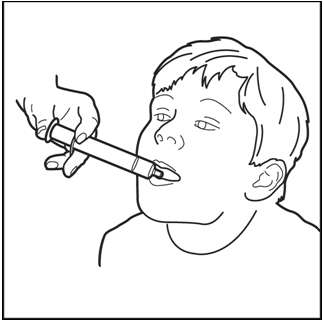
Step 9. Slowly squirt QUILLIVANT XR directly into your or your child's mouth (See Figure K ).
Figure K
Step 10. Cap the bottle tightly. Store the bottle upright at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C) (See Figure L ).
Figure L
Step 11. Clean the oral dosing dispenser after each use by placing in the dishwasher, or by rinsing with tap water (See Figure M ).
Figure M

These Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

LAB-0658-2.
August 2013
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg Bottle Label
Pfizer
NDC 24478-190-10
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
300 mg
(60 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
Liqui
XR™
TECHNOLOGY
Rx only
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg Bottle Carton
Pfizer
NDC 24478-190-10
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
300 mg
(60 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE
Rx only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 600 mg Bottle Label
Pfizer
NDC 24478-200-20
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
600 mg
(120 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
Liqui
XR™
TECHNOLOGY
Rx only
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 600 mg Bottle Carton
Pfizer
NDC 24478-200-20
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
600 mg
(120 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE
Rx only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 750 mg Bottle Label
Pfizer
NDC 24478-205-25
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
750 mg
(150 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
Liqui
XR™
TECHNOLOGY
Rx only
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 750 mg Bottle Carton
Pfizer
NDC 24478-205-25
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
750 mg
(150 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE
Rx only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 900 mg Bottle Label
Pfizer
NDC 24478-210-30
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
900 mg
(180 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
Liqui
XR™
TECHNOLOGY
Rx only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 900 mg Bottle Carton
Pfizer
NDC 24478-210-30
Pharmacist: Dispense the enclosed
Medication Guide to each patient.
Quillivant XR™
methylphenidate HCl
for extended-release oral suspension
900 mg
(180 mL when reconstituted)
25 mg/5 mL
(5 mg/mL) when reconstituted
CII
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE
Rx only

Quillivantmethylphenidate hydrochloride POWDER, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quillivantmethylphenidate hydrochloride POWDER, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quillivantmethylphenidate hydrochloride POWDER, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quillivantmethylphenidate hydrochloride POWDER, FOR SUSPENSION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||