RANITIDINE
PRODUCT INFORMATION Rx Only
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- RANITIDINE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- RANITIDINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- RANITIDINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- PRECAUTIONS
- RANITIDINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- RANITIDINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
RANITIDINE DESCRIPTION
2132243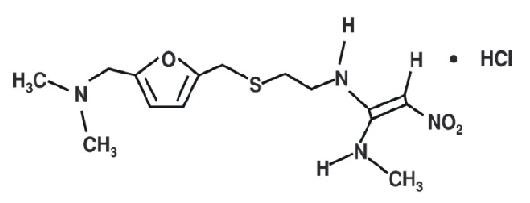
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
2Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption:Distribution:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Geriatrics:
Pediatrics: 1/2max max
| Table 1. Ranitidine Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Patients Following Oral Dosing | ||||
| Population (age) | n | Dosage Form (dose) |
Cmax
(ng/mL) |
Tmax
(hours) |
| Gastric or duodenal ulcer (3.5 to 16 years) |
12 | Tablets (1 to 2 mg/kg) |
54 to 492 | 2.0 |
| Otherwise healthy requiring Ranitidine (0.7 to 14 years, Single dose) |
10 | Syrup (2 mg/kg) |
244 | 1.61 |
| Otherwise healthy requiring Ranitidine (0.7 to 14 years, Multiple dose) |
10 | Syrup (2 mg/kg) |
320 | 1.66 |
Pharmacodynamics:
Antisecretory Activity: 1. Effects on Acid Seretion:
| Table 2. Effect of Oral Ranitidine on Gastric Acid Secretion | |||||
| Time After Dose, hours |
% Inhibition of Gastric Acid Output by Dose, mg | ||||
| 75-80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | ||
| Basal | Up to 4 | 99 | 95 | ||
| Nocturnal | Up to 13 | 95 | 96 | 92 | |
| Betazole | Up to 3 | 97 | 99 | ||
| Pentagastin | Up to 5 | 58 | 72 | 72 | 80 |
| Meal | Up to 3 | 73 | 79 | 95 | |
2. Effects on Other Gastrointestinal Secretions:
Pepsin:
Intrinsic Factor:
Serum Gastrin:
Other Pharmacologic Actions :
- Gastric bacterial flora - increase in nitrate-reducing organisms, significance not known.
- Prolactin levels - no effect in recommended oral or Intravenous (IV) dosage, but small, transient, dose-related increases in serum prolactin have been reported after IV bolus injections of 100 mg or more.
- Other pituitary hormones - no effect on serum gonadotropins, TSH, or GH. Possible impairment of vasopressin release.
- No change in cortisol, aldosterone, androgen, or estrogen levels.
- No antiandrogenic action.
- No effect on count, motility, or morphology of sperm.
Clinical Trials: Active Duodenal Ulcer:
| Table 3. Duodenal Ulcer Patient Healing Rates | ||||
| Ranitidine* | Placebo* | |||
| Number Entered |
Healed / Evaluable |
Number Entered |
Healed / Evaluable |
|
| Outpatients | 195 |
69/182 (38%) † |
188 |
31/164 (19%) |
| Week 2 | ||||
| Week 4 | 137/187 (73%) † |
76/168 (45%) |
||
†p
| Table 4. Mean Daily Doses of Antacid | ||
| Ulcer Healed | Ulcer Not Healed | |
| Ranitidine | 0.06 | 0.71 |
| Placebo | 0.71 | 1.43 |
Maintenance Therapy in Duodenal Uicer:
| Table 5. Duodenal Ulcer Prevalence | |||||
| Double-Blind, Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Trials | |||||
| Multicenter Trial |
Drug | Duodenal Ulcer Prevalence | No. Of Patients | ||
| 0-4 Months |
0-8 Months |
0-12 Months |
|||
| USA | RAN | 20%* | 24%* | 35%* | 138 |
| PLC | 44% | 54% | 59% | 139 | |
| Foreign | RAN | 12%* | 21%* | 28%* | 174 |
| PLC | 56% | 64% | 68% | 165 | |
p
2
Gastric Ulcer:
| Table 6. Gastric Ulcer Patient Healing Rates | ||||
| Ranitidine* | Placebo* | |||
| Number Entered |
Healed / Evaluable |
Number Entered |
Healed / Evaluable |
|
| Outpatients | 92 |
16/83 (19%) |
94 |
10/83 (12%) |
| Week 2 | ||||
| Week 6 | 50/73 (68%) † |
35/69 (51%) |
||
†p
Maintenance of Helaing of Gastric Ulcers:
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome):
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
Erosive Esophagitis:
| Table 7. Erosive Esophagitis Patient Healing Rates | ||
| Healed / Evaluable | ||
| Placebo* n=229 |
Ranitidine HCl 150 mg 4 times daily* n=215 |
|
| Week 4 | 43/198 (22%) | 96/206 (47%) † |
| Week 8 | 63/176 (36%) | 142/200 (71%) † |
| Week 12 | 92/159 (58%) | 162/192 (84%) † |
†p
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis:
RANITIDINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer. Most patients heal within 4 weeks. Studies available to date have not assessed the safety of ranitidine in uncomplicated duodenal ulcer for periods of more than 8 weeks.
- Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of acute ulcers. No placebo-controlled comparative studies have been carried out for periods of longer than 1 year.
- The treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and systemic mastocytosis).
- Short-term treatment of active, benign gastric ulcer. Most patients heal within 6 weeks and the usefulness of further treatment has not been demonstrated. Studies available to date have not assessed the safety of ranitidine in uncomplicated, benign gastric ulcer for periods of more than 6 weeks.
- Maintenance therapy for gastric ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of acute ulcers. Placebo-controlled studies have been carried out for 1 year.
- Treatment of GERD. Symptomatic relief commonly occurs within 24 hours after starting therapy with ranitidine 150 mg twice daily.
- Treatment of endoscopically diagnosed erosive esophagitis. Symptomatic relief of heartburn commonly occurs within 24 hours of therapy initiation with Ranitidine 150 mg 4 times daily.
- Maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis. Placebo-controlled trials have been carried out for 48 weeks.
RANITIDINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS
General:
- Symptomatic response to therapy with ranitidine does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.
- Since ranitidine is excreted primarily by the kidney, dosage should be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Caution should be observed in patients with hepatic dysfunction since ranitidine is metabolized in the liver.
- Rare reports suggest that ranitidine may precipitate acute porphyric attacks in patients with acute porphyria. Ranitidine should therefore be avoided in patients with a history of acute Porphyria.
Drug Interactions:
Procainamide:
Warfarin:
Atazanavir:
Delavirdine:
Gefitinib:
Glipizide:
Ketoconazole:
Midazolam:
Triazolam:
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Escherichia coli
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects:
Nursing Mothers:
Pediatric Use:
Geriatric Use:
RANITIDINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Central Nervous System:
Cardiovascular: 2
Gastrointestinal:
Hepatic:
Musculoskeletal:
Hematologic:
Endocrine:
Integumentary:
Respiratory:222
Other:
OVERDOSAGE
RANITIDINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Active Duodenal Ulcer:Active Duodenal UlcerMaintenance of Healing of Duodenal Ulcers:
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome):
Benign Gastric Ulcer:
Maintenance of Healing of Gastric Ulcers:
GERD:
Erosive Esophagitis:
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis:
Pediatric Use:
Treatment of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers:
Maintenance of Healing of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers:
Treatment of GERD and Erosive Esophagitis:
Dosage Adjustment for Patients With Impaired Renal Function:
HOW SUPPLIED
| Bottles of 30 |
NDC 54868-4048-2 |
| Bottles of 60 |
NDC 54868-4048-0 |
| Bottles of 90 |
NDC 54868-4048-3 |
| Bottles of 100 |
NDC 54868-4048-1 |
| Bottles of 180 |
NDC 54868-4048-4 |
| Bottles of 30 |
NDC 54868-4350-0 |
| Bottles of 100 |
NDC 54868-4350-1 |
Manufactured by:
Distributed by:
Relabeling and Repackaging by:
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL


RANITIDINERANITIDINE TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RANITIDINERANITIDINE TABLET
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!