Rizatriptan Benzoate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use rizatriptan benzoate safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for rizatriptan benzoate tablets. Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998 RECENT MAJOR CHANGESIndications and Usage Acute 1INDICATIONS AND USAGE1B/1D1 Limitations of Use: Use only after clear diagnosis of migraine has been established (1) Not indicated for the prophylactic therapy of migraine (1) Not indicated for the treatment of cluster headache (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adults: 5 or 10 mg single dose; separate repeat doses by at least two hours; maximum dose in a 24-hour period: 30 mg (2.1) Adjust dose if coadministered with propranolol (2.4) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Rizatriptan benzoate tablets: 5 and 10 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS History of ischemic heart disease or coronary artery vasospasm (4) History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (4) Peripheral vascular disease (4) Ischemic bowel disease (4) Uncontrolled hypertension (4) Recent (within 24 hours) use of another 5-HT1 agonist (e.g., another triptan), or of an ergotamine-containing medication (4) Hemiplegic or basilar migraine (4) MAO-A inhibitor used in the past 2 weeks (4) Hypersensitivity to rizatriptan benzoate tablets (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal's Angina: Perform cardiac evaluation in patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors (5.1) Arrhythmias: Discontinue dosing if occurs (5.2) Chest/throat/neck/jaw pain, tightness, pressure, or heaviness; Generally not associated with myocardial ischemia; Evaluate patients at high risk (5.3) Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke: Discontinue dosing if occurs (5.4) Gastrointestinal ischemic events, peripheral vasospastic reactions: Discontinue dosing if occurs (5.5) Medication Overuse Headache: Detoxification may be necessary (5.6) Serotonin Syndrome: Discontinue dosing if occurs (5.7) Side Effects6.1 To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CARACO Pharmaceutical Laboratories Ltd. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1) Information describing the use and dosing of rizatriptan benzoate in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old) is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled for pediatric use.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 RIZATRIPTAN BENZOATE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 RIZATRIPTAN BENZOATE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 RIZATRIPTAN BENZOATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 RIZATRIPTAN BENZOATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 RIZATRIPTAN BENZOATE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patient Information
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-5 mg label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-5 mg showbox
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-10 mg label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-10 mg showbox
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Rizatriptan
Information related to usage of rizatriptan benzoate in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old) is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric patient (6 to 17 years old) usage information.
Limitations of Use
- Rizatriptan benzoate tablets should only be used where a clear diagnosis of migraine has been established. If a patient has no response for the first migraine attack treated with rizatriptan benzoate tablets, the diagnosis of migraine should be reconsidered before rizatriptan benzoate tablets are administered to treat any subsequent attacks.
- Rizatriptan benzoate tablets are not indicated for use in the management of hemiplegic or basilar migraine [see Contraindications (4)].
- Rizatriptan benzoate tablets are not indicated for the prevention of migraine attacks.
- Safety and effectiveness of rizatriptan benzoate tablets have not been established for cluster headache.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information in Adults
[see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
Redosing in Adults
2.2 Dosing Information in Pediatric Patients (Age 6 to 17 Years)
Information related to dosage of rizatriptan benzoate in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old) is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that dosage information.
2.4 Dosage Adjustment for Patients on Propranolol
Adult Patients
[see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pediatric Patients
Dosage adjustment information of rizatriptan benzoate for pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old) taking propranolol is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that dosage adjustment information.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 5 mg tablets are pale pink-colored, capsule-shaped uncoated tablets debossed with “231” on one side and plain on other side.
- 10 mg tablets are pale pink-colored, capsule-shaped uncoated tablets debossed with “232” on one side and plain on other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Ischemic coronary artery disease (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction, or documented silent ischemia), or other significant underlying cardiovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Coronary artery vasospasm including Prinzmetal's angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Ischemic bowel disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Recent use (i.e., within 24 hours) of another 5-HT1 agonist, ergotamine-containing medication, or ergot-type medication (such as dihydroergotamine or methysergide) [see Drug Interactions (7.2 and 7.3)]
- Hemiplegic or basilar migraine.
- Concurrent administration or recent discontinuation (i.e., within 2 weeks) of a MAO-A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Hypersensitivity to rizatriptan benzoate tablets and rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets (angioedema and anaphylaxis seen) [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal's Angina
1
[see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Arrhythmias
1
5.3 Chest, Throat, Neck and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure
11
5.4 Cerebrovascular Events
11
[see Contraindications (4)]
5.5 Other Vasospasm Reactions
1 1
11
5.6 Medication Overuse Headache
5.7 Serotonin Syndrome
[see Drug Interactions (7.5)]. [see Drug Interactions (7.4) and Patient Counseling Information (17)]
5.8 Increase in Blood Pressure
1[see Contraindications (4)]
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal's Angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Chest and or Throat, Neck and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Cerebrovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Other Vasospasm Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Medication Overuse Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- Increase in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adults
Incidence in Controlled Clinical Trials
| Adverse Reactions | % of Patients | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets 5 mg (N=977) |
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets 10 mg (N=1167) |
Placebo (N=627) |
|
|
Atypical Sensations
|
4 |
5 |
4 |
| Paresthesia |
3 |
4 |
<2 |
|
Pain and other Pressure Sensations
|
6 |
9 |
3 |
| Chest Pain: tightness/pressure and/or heaviness |
<2 |
3 |
1 |
| Neck/throat/jaw: pain/tightness/pressure |
<2 |
2 |
1 |
| Regional Pain: tightness/pressure and/or heaviness |
<1 |
2 |
0 |
| Pain, location unspecified |
3 |
3 |
<2 |
|
Digestive
|
9 |
13 |
8 |
| Dry Mouth |
3 |
3 |
1 |
| Nausea |
4 |
6 |
4 |
|
Neurological
|
14 |
20 |
11 |
| Dizziness |
4 |
9 |
5 |
| Headache |
<2 |
2 |
<1 |
| Somnolence |
4 |
8 |
4 |
|
Other
|
|||
| Asthenia/fatigue |
4 |
7 |
2 |
Other Events Observed in Association with the Administration of Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets in Adults
General: Infrequent was facial edema. Rare were syncope and edema/swelling.
Atypical Sensations: Frequent were warm sensations.
Cardiovascular: Frequent was palpitation. Infrequent were tachycardia, cold extremities, and bradycardia.
Digestive: Frequent were diarrhea and vomiting. Infrequent were dyspepsia, tongue edema and abdominal distention.
Musculoskeletal: Infrequent were muscle weakness, stiffness, myalgia and muscle cramp/spasm.
Neurological/Psychiatric: Frequent were hypoesthesia, euphoria and tremor. Infrequent were vertigo, insomnia, confusion/disorientation, gait abnormality, memory impairment, and agitation.
Respiratory: Frequent was dyspnea. Infrequent was pharyngeal edema.
Special Senses: Infrequent were blurred vision and tinnitus. Rare was eye swelling.
Skin and Skin Appendage:
Pediatric Patients 6 to 17 Years of Age
Information relating to adverse reactions to rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets in a controlled clinical trial is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Orally Disintegrating Tablets in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old). However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Neurological/Psychiatric:
General: [see Contraindications (4)].
Special Senses:
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Propranolol
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.2 Ergot-Containing Drugs
[see Contraindications (4)]
7.3 Other 5-HT1 Agonists
1[see Contraindications (4)]
7.4 SSRIs/SNRIs and Serotonin Syndrome
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
7.5 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
[see Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 6 years of age have not been established.
Information related to the efficacy and safety of rizatriptan benzoate in the acute treatment of migraine in patients aged 6 to 17 years is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].8.5 Geriatric Use
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
10 OVERDOSAGE
No overdoses of rizatriptan were reported during clinical trials in adults.
Some adult patients who received 40 mg of rizatriptan either a single dose or as two doses with a 2-hour interdose interval had dizziness and somnolence.
In a clinical pharmacology study in which 12 adult subjects received rizatriptan, at total cumulative doses of 80 mg (given within four hours), two of the subjects experienced syncope, dizziness, bradycardia including third degree AV block, vomiting, and/or incontinence.
In addition, based on the pharmacology of rizatriptan, hypertension or myocardial ischemia could occur after overdosage. Gastrointestinal decontamination, (i.e., gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal) should be considered in patients suspected of an overdose with rizatriptan. Clinical and electrocardiographic monitoring should be continued for at least 12 hours, even if clinical symptoms are not observed.
The effects of hemo- or peritoneal dialysis on serum concentrations of rizatriptan are unknown.
11 DESCRIPTION
Rizatriptan benzoate tablets contain rizatriptan benzoate, a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine1B/1D (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist.
N,NHH-
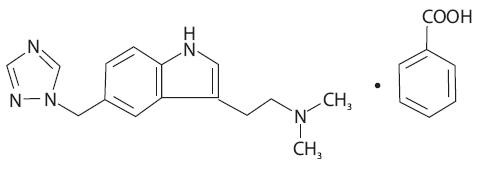
15195762
Rizatriptan benzoate tablets are available for oral administration in strengths of 5 and 10 mg (corresponding to 7.265 mg or 14.53 mg of the benzoate salt, respectively). Each compressed tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized maize starch, ferric oxide (red), and magnesium stearate.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Rizatriptan binds with high affinity to human cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Rizatriptan presumably exerts its therapeutic effects in the treatment of migraine headache by binding to 5-HT1B/1D receptors located on intracranial blood vessels and sensory nerves of the trigeminal system.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Rizatriptan is completely absorbed following oral administration. The mean oral absolute bioavailability of the rizatriptan benzoate tablet is about 45%, and mean peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) are reached in approximately 1 to 1.5 hours (Tmax). The presence of a migraine headache did not appear to affect the absorption or pharmacokinetics of rizatriptan. Food has no significant effect on the bioavailability of rizatriptan but delays the time to reach peak concentration by an hour. In clinical trials, rizatriptan was administered without regard to food.
The bioavailability and Cmax of rizatriptan were similar following administration of rizatriptan benzoate tablets and rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets, but the rate of absorption is somewhat slower with rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets, with Tmax delayed by up to 0.7 hour. AUC of rizatriptan is approximately 30% higher in females than in males. No accumulation occurred on multiple dosing.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution is approximately 140 liters in male subjects and 110 liters in female subjects. Rizatriptan is minimally bound (14%) to plasma proteins.
Metabolism
The primary route of rizatriptan metabolism is via oxidative deamination by monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A) to the indole acetic acid metabolite, which is not active at the 5-HT1B/1D receptor. N-monodesmethyl-rizatriptan, a metabolite with activity similar to that of parent compound at the 5‑HT1B/1D receptor, is formed to a minor degree. Plasma concentrations of N-monodesmethyl-rizatriptan are approximately 14% of those of parent compound, and it is eliminated at a similar rate. Other minor metabolites, the N-oxide, the 6-hydroxy compound, and the sulfate conjugate of the 6-hydroxy metabolite are not active at the 5-HT1B/1D receptor.
Elimination
The total radioactivity of the administered dose recovered over 120 hours in urine and feces was 82% and 12%, respectively, following a single 10 mg oral administration of 14C-rizatriptan. Following oral administration of 14C-rizatriptan, rizatriptan accounted for about 17% of circulating plasma radioactivity.
Approximately 14% of an oral dose is excreted in urine as unchanged rizatriptan while 51% is excreted as indole acetic acid metabolite, indicating substantial first pass metabolism.
The plasma half-life of rizatriptan in males and females averages 2 to 3 hours.
Cytochrome P450 Isoforms
Rizatriptan is not an inhibitor of the activities of human liver cytochrome P450 isoforms 3A4/5, 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, or 2E1; rizatriptan is a competitive inhibitor (Ki=1400 nM) of cytochrome P450 2D6, but only at high, clinically irrelevant concentrations.
Special Populations
Geriatric: Rizatriptan pharmacokinetics in healthy elderly non-migraineur volunteers (age 65 to 77 years) were similar to those in younger non-migraineur volunteers (age 18 to 45 years).
Pediatric: Information related to the pharmacokinetics of rizatriptan in pediatric migraineurs 6 to 17 years of age is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Gender: The mean AUC0-∞ and Cmax of rizatriptan (10 mg orally) were about 30% and 11% higher in females as compared to males, respectively, while Tmax occurred at approximately the same time.
Hepatic impairment: Following oral administration in patients with hepatic impairment caused by mild to moderate alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, plasma concentrations of rizatriptan were similar in patients with mild hepatic insufficiency compared to a control group of subjects with normal hepatic function; plasma concentrations of rizatriptan were approximately 30% greater in patients with moderate hepatic insufficiency.
Renal impairment: In patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 10 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), the AUC0-∞ of rizatriptan was not significantly different from that in subjects with normal renal function. In hemodialysis patients, (creatinine clearance <2 mL/min/1.73 m2), however, the AUC for rizatriptan was approximately 44% greater than that in patients with normal renal function.
Race: Pharmacokinetic data revealed no significant differences between African American and Caucasian subjects.
Drug Interactions
[See also Drug Interactions (7).]
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: Rizatriptan is principally metabolized via monoamine oxidase, ‘A’ subtype (MAO-A). Plasma concentrations of rizatriptan may be increased by drugs that are selective MAO-A inhibitors (e.g., moclobemide) or nonselective MAO inhibitors [type A and B] (e.g., isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and pargyline). In a drug interaction study, when rizatriptan 10 mg was administered to subjects (n=12) receiving concomitant therapy with the selective, reversible MAO-A inhibitor, moclobemide 150 mg t.i.d., there were mean increases in rizatriptan AUC and Cmax of 119% and 41% respectively; and the AUC of the active N-monodesmethyl metabolite of rizatriptan was increased more than 400%. The interaction would be expected to be greater with irreversible MAO inhibitors. No pharmacokinetic interaction is anticipated in patients receiving selective MAO-B inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.5)].
Propranolol: In a study of concurrent administration of propranolol 240 mg/day and a single dose of rizatriptan 10 mg in healthy adult subjects (n=11), mean plasma AUC for rizatriptan was increased by 70% during propranolol administration, and a four-fold increase was observed in one subject. The AUC of the active N-monodesmethyl metabolite of rizatriptan was not affected by propranolol [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Nadolol/Metoprolol: In a drug interactions study, effects of multiple doses of nadolol 80 mg or metoprolol 100 mg every 12 hours on the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of 10 mg rizatriptan were evaluated in healthy subjects (n=12). No pharmacokinetic interactions were observed.
Paroxetine: In a study of the interaction between the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) paroxetine 20 mg/day for two weeks and a single dose of rizatriptan 10 mg in healthy subjects (n=12), neither the plasma concentrations of rizatriptan nor its safety profile were affected by paroxetine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Drug Interactions (7.4), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Oral contraceptives:13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Oral carcinogenicity studies were conducted in mice (100 weeks) and rats (106 weeks) at doses of up to 125 mg/kg/day. Plasma exposures (AUC) at the highest dose tested were approximately 150 (mice) and 240 times (rats) that in humans at the maximum recommended daily dose (MRDD) of 30 mg/day. There was no evidence of an increase in tumor incidence related to rizatriptan in either species.
Mutagenesis: Rizatriptan was neither mutagenic nor clastogenic in a battery of in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicity studies, including: the microbial mutagenesis (Ames) assay, in vitro mammalian cell mutagenesis and chromosomal aberration assays, and the in vivo chromosomal aberration assay in mouse.
Impairment of Fertility: In a fertility study in rats, altered estrus cyclicity and delays in time to mating were observed in females treated orally with 100 mg/kg/day rizatriptan. The no-effect dose was 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 15 times the human exposure at the MRDD). There were no other fertility-related effects in the female rats. There was no impairment of fertility or reproductive performance in male rats treated with up to 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 550 times the human exposure at the MRDD).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adults
The efficacy of rizatriptan benzoate tablets was established in four multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Patients enrolled in these studies were primarily female (84%) and Caucasian (88%), with a mean age of 40 years (range of 18 to 71). Patients were instructed to treat a moderate to severe headache. Headache response, defined as a reduction of moderate or severe headache pain to no or mild headache pain, was assessed for up to 2 hours (Study 1) or up to 4 hours after dosing (Studies 2, 3 and 4). Associated symptoms of nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia and maintenance of response up to 24 hours post-dose were evaluated. A second dose of rizatriptan benzoate tablets was allowed 2 to 24 hours after dosing for treatment of recurrent headache in Studies 1 and 2. Additional analgesics and/or antiemetics were allowed 2 hours after initial treatment for rescue in all four studies.
| Study | Placebo | Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets 5 mg | Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets 10 mg |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
35% (n=304) |
62% |
71%  |
2 |
37% (n=82) |
— |
77% |
| 3 |
23% (n=80) |
63% |
— |
| 4 |
40% (n=159) |
60% |
67% |
Figure 1: Estimated Probability of Achieving an Initial Headache Response by 2 Hours in Pooled Studies 1, 2, 3, and 4 ††

††
For patients with migraine-associated photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea at baseline, there was a decreased incidence of these symptoms following administration of rizatriptan benzoate tablets compared to placebo.

†††
14.2 Pediatric Patients 6 to 17 Years of Age
Information contained in a clinical study relating to the efficacy of rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets in pediatric patients (6 to 17 years old) is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information).
Risk of Myocardial Ischemia and/or Infarction, Prinzmetal's Angina, Other Vasospasm-related Events, and Cerebrovascular Events
Inform patients that rizatriptan benzoate tablets may cause serious cardiovascular side effects such as myocardial infarction or stroke. Although serious cardiovascular events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.5)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of serotonin syndrome with the use of rizatriptan or other triptans, particularly during combined use with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Drug Interactions (7.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pregnancy
Inform patients that rizatriptan benzoate tablets should not be used during pregnancy unless the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Nursing Mothers
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Ability To Perform Complex Tasks
Since migraines or treatment with rizatriptan benzoate tablets may cause somnolence and dizziness, instruct patients to evaluate their ability to perform complex tasks during migraine attacks and after administration of rizatriptan benzoate tablets.
Medication Overuse Headache
Inform patients that use of acute migraine drugs for 10 or more days per month may lead to an exacerbation of headache, and encourage patients to record headache frequency and drug use (e.g., by keeping a headache diary) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Patient Information
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
Unless otherwise stated, the information in this Patient Information leaflet applies to both rizatriptan benzoate tablets and rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets.
What is rizatriptan benzoate tablet ?
Rizatriptan benzoate is a prescription medicine that belongs to a class of medicines called Triptans. Rizatriptan benzoate is available as a traditional tablet and as an orally disintegrating tablet.
Rizatriptan benzoate tablets are used to treat migraine attacks with or without aura in adults.
Rizatriptan benzoate is not to be used to prevent migraine attacks.
Rizatriptan benzoate is not for the treatment of hemiplegic or basilar migraines.
It is not known if rizatriptan benzoate is safe and effective for the treatment of cluster headaches.
It is not known if rizatriptan benzoate is safe and effective in children under 6 years of age.
Who should not take rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
Do not take rizatriptan benzoate tablets if you:
- have or have had heart problems
- have or have had a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- have or have had blood vessel problems including ischemic bowel disease
- have uncontrolled high blood pressure
- have taken other Triptan medicines in the last 24 hours
- have taken ergot-containing medicines in the last 24 hours
- have hemiplegic or basilar migraines
- take monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor or have taken a MAO inhibitor within the last 2 weeks
- are allergic to rizatriptan benzoate or any of the ingredients in rizatriptan benzoate tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in rizatriptan benzoate tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
Before you take rizatriptan benzoate tablets,
- have or have had heart problems, high blood pressure, chest pain, or shortness of breath
- have any risk factors for heart problems or blood vessel problems such as:
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- smoking
- obesity
- diabetes
- family history of heart problems
- you are post menopausal
- you are a male over 40
- have kidney or liver problems
- have any other medical condition
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if rizatriptan benzoate tablets will harm your unborn baby. If you become pregnant while taking rizatriptan benzoate tablets, talk to your healthcare provider.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if rizatriptan benzoate passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take rizatriptan benzoate tablets.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take,
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- propranolol containing medicines such as Inderal®*, Inderal®* LA, or Innopran®* XL
- medicines used to treat mood disorders, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
How should I take rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
- Take rizatriptan benzoate tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how much rizatriptan benzoate to take and when to take it.
- If your headache comes back after your first rizatriptan benzoate tablets dose:
- For adults: a second dose may be taken 2 hours after the first dose. Do not take more than 30 mg of rizatriptan benzoate tablets in a 24-hour period (for example, do not take more than three 10 mg tablets in a 24-hour period).
- If you take too much rizatriptan benzoate, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
What are the possible side effects of rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
Rizatriptan benzoate tablets may cause serious side effects.
-
heart attack. Symptoms of a heart attack may include:
- chest discomfort in the center of your chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back
- chest discomfort that feels like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain
- pain or discomfort in your arms, back, neck, jaw or stomach
- shortness of breath with or without chest discomfort
- breaking out in a cold sweat
- nausea or vomiting
- feeling lightheaded
-
stroke. Symptoms of a stroke may include the following sudden symptoms:
- numbness or weakness in your face, arm or leg, especially on one side of your body
- confusion, problems speaking or understanding
- problems seeing in one or both of your eyes
- problems walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- severe headache with no known cause
-
blood vessel problems. Symptoms of blood vessel problems may include:
-
stomach pain - bloody diarrhea
vision problems - coldness and numbness of hands and feet
-
-
serotonin syndrome. A condition called serotonin syndrome can happen when Triptan medicines such as rizatriptan benzoate tablets are taken with certain other medicines. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome may include:
-
agitation - hallucinations
- coma
- fast heartbeat
- fast changes in your blood pressure
- increased body temperature
- muscle spasm
- loss of coordination
- nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
-
- increased blood pressure
The most common side effects of rizatriptan benzoate tablets in adults include:
- feeling sleepy or tired
- pain or pressure in your chest or throat
- dizziness
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
- Store rizatriptan benzoate tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F).
- Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep rizatriptan benzoate tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of rizatriptan benzoate tablets.
What are the ingredients in rizatriptan benzoate tablets?
Active ingredient:
Inactive ingredients:
Information related to the usage of rizatriptan benzoate tablets and rizatriptan benzoate orally disintegrating tablets for pediatric patients aged 6 to 17 years is approved for Merck & Co., Inc.’s Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets. However, due to Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Caraco Pharmaceutical Laboratories, Ltd.
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-5 mg label
NDC 47335-231-88
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
5 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense with Patient Information Leaflet provided separately.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-5 mg showbox
NDC 47335-231-93
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
5 mg
Rx only
9 (3 x 3) Unit-of-Use Tablets
SUN PHARMA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-10 mg label
NDC 47335-232-88
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
10 mg
Rx only
100 TABLETS
SUN PHARMA
PHARMACIST: Dispense with Patient Information Leaflet provided separately.

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-10 mg showbox
NDC 47335-232-93
Rizatriptan Benzoate Tablets
10 mg
Rx only
9 (3 x 3) Unit-of-Use Tablets
SUN PHARMA

Rizatriptan BenzoateRizatriptan Benzoate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rizatriptan BenzoateRizatriptan Benzoate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||