General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc
Sensorcaine 0.5% (Bupivacaine HCl) 5mg/mL 50mL multi dose vial
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
SENSORCAINE DESCRIPTION
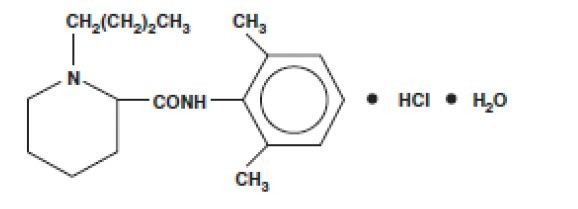
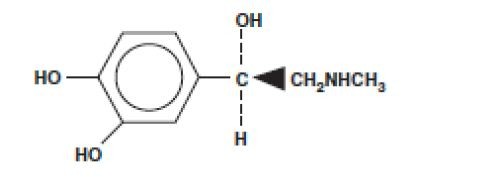
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
INDICATIONS & USAGE
SENSORCAINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRECAUTIONS
SENSORCAINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
OVERDOSAGE
Acute emergencies from local anesthetics are generally related to high plasma levels encountered during therapeutic use of local
anesthetics or to unintended subarachnoid injection of local anesthetic solution (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, WARNINGS, and
PRECAUTIONS).
Management of Local Anesthetic Emergencies
The first consideration is prevention, best accomplished by careful and constant monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory vital
signs and the patient’s state of consciousness after each local anesthetic injection. At the first sign of change, oxygen should be
administered.
The first step in the management of systemic toxic reactions, as well as underventilation or apnea due to unintentional subarachnoid
injection of drug solution, consists of immediate attention to the establishment and maintenance of a patent airway and effective
assisted or controlled ventilation with 100% oxygen with a delivery system capable of permitting immediate positive airway pressure
by mask.This may prevent convulsions if they have not already occurred.
If necessary, use drugs to control the convulsions. A 50 to 100 mg bolus I.V. injection of succinylcholine will paralyze the patient
without depressing the central nervous or cardiovascular systems and facilitate ventilation. A bolus I.V. dose of 5 to 10 mg of
diazepam or 50 to 100 mg of thiopental will permit ventilation and counteract central nervous system stimulation, but these drugs also
depress the central nervous system, respiratory and cardiac function, add to postictal depression, and may result in apnea. Intravenous
barbiturates, anticonvulsant agents, or muscle relaxants should only be administered by those familiar with their use. Immediately
after the institution of these ventilatory measures, the adequacy of the circulation should be evaluated. Supportive treatment of
circulatory depression may require administration of intravenous fluids, and, when appropriate, a vasopressor dictated by the clinical
situation (such as ephedrine or epinephrine to enhance myocardial contractile force).
Endotracheal intubation, employing drugs and techniques familiar to the clinician, may be indicated after initial administration of
oxygen by mask, if difficulty is encountered in the maintenance of a patent airway or if prolonged ventilatory support (assisted or
controlled) is indicated.
Recent clinical data from patients experiencing local anesthetic-induced convulsions demonstrated rapid development of hypoxia,
hypercarbia, and acidosis with bupivacaine within a minute of the onset of convulsions. These observations suggest that oxygen
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
The dose of any local anesthetic administered varies with the anesthetic procedure, the area to be anesthetized, the vascularity of the
tissues, the number of neuronal segments to be blocked, the depth of anesthesia and degree of muscle relaxation required, the duration
of anesthesia desired, individual tolerance, and the physical condition of the patient. The smallest dose and concentration required to
produce the desired result should be administered. Dosages of Sensorcaine should be reduced for young, elderly and/or debilitated
patients and patients with cardiac and/or liver disease. The rapid injection of a large volume of local anesthetic solution should be
avoided and fractional (incremental) doses should be used when feasible.
For specific techniques and procedures, refer to standard textbooks.
There have been adverse event reports of chondrolysis in patients receiving intra-articular infusions of local anesthetics following
arthroscopic and other surgical procedures. Sensorcaine is not approved for this use (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND
ADMINISTRATION).).
In recommended doses, Sensorcaine (bupivacaine HCl) produces complete sensory block, but the effect on motor function differs
among the three concentrations.
0.25%—when used for caudal, epidural, or peripheral nerve block, produces incomplete motor block. Should be used for operations
in which muscle relaxation is not important, or when another means of providing muscle relaxation is used concurrently. Onset of
action may be slower than with the 0.5% or 0.75% solutions.
0.5%—provides motor blockade for caudal, epidural, or nerve block, but muscle relaxation may be inadequate for operations in which
complete muscle relaxation is essential.
0.75%—produces complete motor block. Most useful for epidural block in abdominal operations requiring complete muscle
relaxation, and for retrobulbar anesthesia. Not for obstetrical anesthesia.
The duration of anesthesia with Sensorcaine is such that for most indications, a single dose is sufficient.
Maximum dosage limit must be individualized in each case after evaluating the size and physical status of the patient, as well as the
usual rate of systemic absorption from a particular injection site. Most experience to date is with single doses of Sensorcaine up to
225 mg with epinephrine 1:200,000 and 175 mg without epinephrine; more or less drug may be used depending on individualization
of each case.
These doses may be repeated up to once every three hours. In clinical studies to date, total daily doses up to 400 mg have been
reported. Until further experience is gained, this dose should not be exceeded in 24 hours. The duration of anesthetic effect may be
prolonged by the addition of epinephrine.
The dosages in Table 1 have generally proved satisfactory and are recommended as a guide for use in the average adult. These
dosages should be reduced for elderly or debilitated patients. Until further experience is gained Sensorcaine is not recommended for
pediatric patients younger than 12 years. Sensorcaine is contraindicated for obstetrical paracervical blocks, and is not recommended
for intravenous regional anesthesia (Bier Block).
Use in Epidural Anesthesia
During epidural administration of Sensorcaine, 0.5% and 0.75% solutions should be administered in incremental doses of 3 mL to
5 mL with sufficient time between doses to detect toxic manifestations of unintentional intravascular or intrathecal injection. In
obstetrics, only the 0.5% and 0.25% concentrations should be used; incremental doses of 3 mL to 5 mL of the 0.5% solution not
exceeding 50 mg to 100 mg at any dosing interval are recommended. Repeat doses should be preceded by a test dose containing
epinephrine if not contraindicated. Use only the single dose ampules and single dose vials for caudal or epidural anesthesia; the
multiple dose vials contain a preservative and therefore should not be used for these procedures.
Test Dose for Caudal and Lumbar Epidural Blocks
See PRECAUTIONS.
Unused portions of solutions in single dose containers should be discarded, since this product form contains no preservatives.
TABLE 1. DOSAGE RECOMMENDATIONS —
SENSORCAINE (bupivacaine HCl) INJECTIONS
|
|
Each Dose
|
Each Dose
|
|
Type of Block
|
Conc.
|
(mL)
|
(mg)
|
Motor Block (1)
|
Local Infiltration
|
0.25% (4)
|
up to max.
|
up to max.
|
|
Epidural
|
0.75% (2,4)
|
10 to 20
|
75 to 150
|
complete
|
|
0.5% (4)
|
10 to 20
|
50 to 100
|
moderate to complete
|
|
0.25% (4)
|
10 to 20
|
25 to 50
|
partial to moderate
|
Caudal
|
0.5% (4)
|
15 to 30
|
75 to 150
|
moderate to complete
|
|
0.25% (4)
|
15 to 30
|
37.5 to 75
|
moderate
|
Peripheral Nerves
|
0.5% (4)
|
5 to max.
|
25 to max.
|
moderate to complete
|
|
0.25% (4)
|
5 to max.
|
12.5 to max.
|
moderate to complete
|
Retrobulbar (3)
|
0.75% (4)
|
2 to 4
|
15 to 30
|
complete
|
Sympathetic
|
0.25%
|
20 to 50
|
50 to 125
|
|
Epidural (3)
|
0.5%
|
2 to 3
|
10 to 15
|
|
Test Dose
|
w/epi
|
|
10 to 15 mcg epinephrine (see PRECAUTIONS)
|
10 to 15 mcg epinephrine (see PRECAUTIONS) |
HOW SUPPLIED
HOW SUPPLIED
SOLUTIONS OF SENSORCAINE (BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE) SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR THE PRODUCTION
OF SPINAL ANESTHESIA (SUBARACHNOID BLOCK) BECAUSE OF INSUFFICIENT DATA TO SUPPORT SUCH USE.
Sensorcaine-MPF (methylparaben free) is available in the following forms:
With Epinephrine:
Product No.
|
NDC No.
|
Strength
|
Size
|
460837
|
63323-468-37
|
0.25%
|
30 mL Single dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460817
|
63323-468-17
|
0.25%
|
10 mL Single dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460217
|
63323-462-17
|
0.5%
|
10 mL Single dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460237
|
63323-462-37
|
0.5%
|
30 mL Single dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460231
|
63323-462-31
|
0.5%
|
30 mL Single dose Vials packaged in 5.
|
461037
|
63323-406-37
|
0.75%
|
30 mL Single dose Vials packaged in 25.
|
Product No.
|
NDC No.
|
Strength
|
Size
|
460417
|
63323-464-17
|
0.25%
|
10 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460433*
|
63323-464-33
|
0.25%
|
30 mL ampules packaged in 5.
|
460437
|
63323-464-37
|
0.25%
|
30 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460431
|
63323-464-31
|
0.25%
|
30 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in 5.
|
460617
|
63323-466-17
|
0.5%
|
10 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460637
|
63323-466-37
|
0.5%
|
30 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460631
|
63323-466-31
|
0.5%
|
30 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in 5.
|
460633*
|
63323-466-33
|
0.5%
|
30 mL ampules packaged in 5.
|
470217
|
63323-472-17
|
0.75%
|
10 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
470237
|
63323-472-37
|
0.75%
|
30 mL Single Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
470233*
|
63323-472-33
|
0.75%
|
30 mL ampules packaged in 5.
|
Product No.
|
NDC No.
|
Strength
|
Size
|
460157
|
63323-461-57
|
0.25%
|
50 mL Multiple Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460357
|
63323-463-57
|
0.5%
|
50 mL Multiple Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
Product No.
|
NDC No.
|
Strength
|
Size
|
460557
|
63323-465-57
|
0.25%
|
50 mL Multiple Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
460757
|
63323-467-57
|
0.5%
|
50 mL Multiple Dose Vials packaged in trays of 25.
|
PACKAGE LABEL

Sensorcaine
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride INJECTION, SOLUTION
Product Information
|
|
Product Type
|
Human prescription drug label |
Item Code (Source)
|
NDC:52584-467(NDC:63323-467) |
|
Route of Administration
|
PERINEURAL |
DEA Schedule
|
|
Packaging
|
|
#
|
Item Code
|
Package Description
|
Marketing Start Date
|
Marketing End Date
|
|
1 |
|
50 in 1 VIAL |
|
|
|
2 |
NDC:52584-467-57 |
1 in 1 BAG |
|
|
Marketing Information
|
|
Marketing Category
|
Application Number or Monograph Citation
|
Marketing Start Date
|
Marketing End Date
|
|
ANDA |
ANDA018304 |
2011-10-18 |
|
|


