Taclonex
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Taclonex Ointment safely and effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for Taclonex Ointment. Taclonex (calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate) Ointment, 0.005%/0.064% for topical useInitial U.S. Approval: 2006.INDICATIONS AND USAGETaclonex® Ointment is a vitamin D analogue and corticosteroid combination product indicated for the topical treatment of psoriasis vulgaris in adults 18 years of age and older (1.1).Limitations of Use:• Do not use on face, axillae or groin (1.2)• Do not use if skin atrophy is present at the treatment site (1.2)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Apply Taclonex®Ointment to affected area(s) once daily for up to 4 weeks. The maximum weekly dose should not exceed 100g. Treatment of more than 30% body surface area is not recommended (2). Taclonex® Ointment is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSOintment, 0.005%/0.064%Each gram of Taclonex® Ointment contains 52.18 mcg of calcipotriene hydrate (equivalent to 50 mcg of calcipotriene) and 0.643 mg of betamethasone dipropionate (equivalent to 0.5 mg of betamethasone)(3).CONTRAINDICATIONSNone (4). WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria have been reported. If it occurs, discontinue treatment until parameters of calcium metabolism normalize (5.1) Topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome and unmask latent diabetes (5.2) Systemic absorption may require evaluation for HPA axis suppression (5.2) Modify use should HPA axis suppression develop (5.2) Potent corticosteroids, use on large areas, prolonged use or occlusive use may increase systemic absorption (5.3) Local adverse reactions with topical steroids may include atrophy, striae, irritation, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation and allergic contact dermatitis and may be more likely with occlusive use or more potent corticosteroids (5.3, 6.1) Children may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity when treated with topical corticosteroids (5.2, 8.4) Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are pruritus and scaly rash. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact LEO Pharma Inc. at 1-877-494-4536 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/ medwatch.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 TACLONEX INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 TACLONEX DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 TACLONEX CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Effects on Calcium Metabolism
- 5.2 Effects on Endocrine System
- 5.3 Local Adverse Reactions with Topical Corticosteroids
- 5.4 Allergic Contact Dermatitis with Topical Corticosteroids
- 5.5 Allergic Contact Dermatitis with Topical Calcipotriene
- 5.6 Concomitant Skin Infections
- 5.7 Skin Irritation
- 5.8 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
- 6 TACLONEX ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 TACLONEX DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON LABEL 100 G
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Indication
Taclonex® (calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate) Ointment is indicated for the topical treatment of psoriasis vulgaris in adults 18 years of age and older.
1.2 Limitations of Use
- Taclonex® Ointment should not be applied to the face, axillae or groin.
- Taclonex® Ointment should not be used if there is skin atrophy at the treatment site.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply an adequate layer of Taclonex® Ointment to the affected area(s) once daily for up to 4 weeks. The maximum weekly dose should not exceed 100 g. Treatment of more than 30% body surface area is not recommended. Taclonex® Ointment should be rubbed in gently and completely. Patients should wash their hands after applying Taclonex® Ointment.
Taclonex® Ointment is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ointment, 0.005%/0.064%
Each gram of Taclonex® Ointment contains 52.18 mcg of calcipotriene hydrate (equivalent to 50 mcg of calcipotriene) and 0.643 mg of betamethasone dipropionate (equivalent to 0.5 mg of betamethasone) in off-white to yellow paraffin ointment base.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Calcium Metabolism
Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria have been reported with use of Taclonex®. If hypercalcemia or hypercalciuria develop, treatment should be discontinued until parameters of calcium metabolism have normalized. In the trials that included assessment of the effects of Taclonex® Ointment on calcium metabolism, such testing was done after 4 weeks of treatment. The effects of Taclonex® Ointment on calcium metabolism following treatment durations of longer than 4 weeks have not been evaluated.
5.2 Effects on Endocrine System
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for clinical glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. This may occur during treatment or upon withdrawal of the topical corticosteroid.
HPA axis suppression has been observed with Taclonex® Ointment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ]. The effects of Taclonex® Ointment on the HPA axis following treatment durations of longer than 4 weeks have not been adequately studied.
In a trial of 32 subjects concomitantly treated with Taclonex® Scalp Topical Suspension on the scalp and Taclonex® Ointment on the body, adrenal suppression was identified in 5 of 32 subjects (15.6%) after 4 weeks of treatment [see Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics (12.2) ].
Because of the potential for systemic absorption, use of topical corticosteroids may require that patients be periodically evaluated for HPA axis suppression. Factors that predispose a patient using a topical corticosteroid to HPA axis suppression include the use of more potent steroids, use over large surface areas, use over prolonged periods, use under occlusion, use on an altered skin barrier, and use in patients with liver failure.
An ACTH stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA axis suppression. If HPA axis suppression is documented, an attempt should be made to gradually withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent steroid. Manifestations of adrenal insufficiency may require supplemental systemic corticosteroids. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids.
Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and unmasking of latent diabetes mellitus can also result from systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids.
Use of more than one corticosteroid-containing product at the same time may increase the total systemic corticosteroid exposure.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from use of topical corticosteroids [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ].
5.3 Local Side Effects with Topical Corticosteroids
Local adverse reactions may be more likely to occur with occlusive use, prolonged use or use of higher potency corticosteroids. Reactions may include atrophy, striae, telangiectasias, burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, and miliaria. Some local adverse reactions may be irreversible.
5.4 Allergic Contact Dermatitis with Topical Corticosteroids
Allergic contact dermatitis to any component of topical corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by a failure to heal rather than a clinical exacerbation. Clinical diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis can be confirmed by patch testing.
5.5 Allergic Contact Dermatitis with Topical Calcipotriene
Allergic contact dermatitis has been observed with use of topical calcipotriene. Clinical diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis can be confirmed by patch testing.
5.6 Concomitant Skin Infections
Concomitant skin infections should be treated with an appropriate antimicrobial agent. If the infection persists, Taclonex® Ointment should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately treated.
5.7 Skin Irritation
If irritation develops, treatment with Taclonex® Ointment should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
5.8 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
Patients who apply Taclonex® Ointment to exposed skin should avoid excessive exposure to either natural or artificial sunlight, including tanning booths, sun lamps, etc. Physicians may wish to limit or avoid use of phototherapy in patients who use Taclonex® Ointment.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
The data described below reflect exposure to Taclonex® Ointment in 2448 subjects, including 1992 exposed for 4 weeks, and 289 exposed for 8 weeks. Taclonex® Ointment was studied primarily in placebo- and active-controlled trials (N = 1176, and N = 1272, respectively). The population was 15-97 years old, 61% males and 39% females, mostly white (97%) and had a baseline disease severity ranging from mild to very severe. Most subjects received once daily application, and the median weekly dose was 24.5 g.
The percentage of subjects reporting at least one adverse event was 27.1% in the Taclonex® Ointment group, 33.0% in the calcipotriene group, 28.3% in the betamethasone group, and 33.4% in the vehicle group.
Table 1
Adverse Events Reported by ≥1% of Subjects by Preferred Term
| Taclonex® Ointment N = 2448 |
Calcipotriene N = 3197 |
Betamethasone dipropionate N = 1164 |
Vehicle N = 470 |
|
| Any Adverse Event | 663 (27.1) | 1055 (33.0) | 329 (28.3) | 157 (33.4) |
| Preferred Term | # of subjects (%) | |||
| Pruritis | 75 (3.1) | 183 (5.7) | 38 (3.3) | 43 (9.1) |
| Headache | 69 (2.8) | 75 (2.3) | 44 (3.8) | 12 (2.6) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 56 (2.3) | 77 (2.4) | 34 (2.9) | 9 (1.9) |
| Psoriasis | 30 (1.2) | 47 (1.5) | 14 (1.2) | 5 (1.1) |
| Rash scaly | 30 (1.2) | 40 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.2) |
| Influenza | 23 (0.9) | 34 (1.1) | 14 (1.2) | 6 (1.3) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 20 (0.8) | 19 (0.6) | 12 (1.0) | 3 (0.6) |
| Erythema | 15 (0.6) | 54 (1.7) | 3 (0.3) | 5 (1.1) |
| Application site pruritus | 13 (0.5) | 24 (0.8) | 10 (0.9) | 6 (1.3) |
| Skin irritation | 11 (0.4) | 60 (1.9) | 8 (0.7) | 5 (1.1) |
| Pain | 7 (0.3) | 12 (0.4) | 3 (0.3) | 5 (1.1) |
| Burning sensation | 6 (0.2) | 30 (0.9) | 3 (0.3) | 6 (1.3) |
A lesional/perilesional adverse event was generally defined as an adverse event located ≤ 2 cm from the lesional border.
Table 2
Lesional/Perilesional Adverse Events Reported by ≥1% of Subjects
| Taclonex® Ointment N = 2448 |
Calcipotriene N = 3197 |
Betamethasone dipropionate N = 1164 |
Vehicle N = 470 |
|
| Any Adverse Event | 213 (8.7) | 419 (13.1) | 85 (7.3) | 76 (16.2) |
| Preferred Term | # of subjects (%) | |||
| Pruritis | 69 (2.8) | 170 (5.3) | 31 (2.7) | 41 (8.7) |
| Rash scaly | 29 (1.2) | 38 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Application site pruritus | 12 (0.5) | 24 (0.8) | 10 (0.9) | 6 (1.3) |
| Erythema | 9 (0.4) | 36 (1.1) | 2 (0.2) | 4 (0.9) |
| Skin irritation | 9 (0.4) | 51 (1.6) | 8 (0.7) | 5 (1.1) |
| Burning sensation | 6 (0.2) | 25 (0.8) | 3 (0.3) | 5 (1.1) |
For subjects who reported lesional/perilesional adverse events, the median time to onset was 7 days for Taclonex® Ointment, 7 days for calcipotriene, 5 days for betamethasone dipropionate, and 3 days for vehicle.
Other less common reactions (less than 1% but more than 0.1%) were, in decreasing order of incidence, folliculitis, rash papular, rash pustular, and skin hypopigmentation. Skin atrophy, telangiectasia and skin hyperpigmentation were reported infrequently (0.1%).
In a separate trial, subjects (N = 207) with at least moderate disease severity were given Taclonex® Ointment intermittently on an "as needed" basis for up to 52 weeks. The median use was 15.4 g per week. The effects of Taclonex® Ointment on calcium metabolism were not studied and the effects on the HPA axis were not adequately studied. The following adverse reactions were reported by 1% or more of the subjects: pruritus (7.2%), psoriasis (3.4%), skin atrophy (1.9%), folliculitis (1.4%), burning sensation (1.4%), skin depigmentation (1.4%), ecchymosis (1.0%), erythema (1.0%) and hand dermatitis (1.0%). One case of serious flare-up of psoriasis was reported.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Taclonex® Ointment have been identified post-approval: pustular psoriasis and rebound effect.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Pregnant women were excluded from the clinical studies conducted with Taclonex® Ointment. Taclonex® Ointment should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Taclonex® Ointment. Taclonex® Ointment contains calcipotriene that has been shown to be fetotoxic and betamethasone dipropionate that has been shown to be teratogenic in animals when given systemically.
Teratogenicity studies with calcipotriene were performed by the oral route in rats and rabbits. In rabbits, increased maternal and fetal toxicity were noted at a dosage of 12 mcg/kg/day (144 mcg/m2/day); a dosage of 36 mcg/kg/day (432 mcg/m2/day) resulted in a significant increase in the incidence of incomplete ossification of the pubic bones and forelimb phalanges of fetuses. In a rat study, a dosage of 54 mcg/kg/day (324 mcg/m2/day) resulted in a significantly increased incidence of skeletal abnormalities (enlarged fontanelles and extra ribs). The enlarged fontanelles are most likely due to the effect of calcipotriene upon calcium metabolism. The estimated maternal and fetal no-adverse effect levels (NOAEL) in the rat (108 mcg/m2/day) and rabbit (48 mcg/m2/day) derived from oral studies are lower than the estimated maximum topical dose of calcipotriene in man (460 mcg/m2/day).
Corticosteroids are generally teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels.
Betamethasone dipropionate has been shown to be teratogenic in mice and rabbits when given by the subcutaneous route at dosages of 156 mcg/kg/day (468 mcg/m2/day) and 2.5 mcg/kg/day (30 mcg/m2/day), respectively. Those dose levels are lower than the estimated maximum topical dose in man (about 5950 mcg/m2/day). The abnormalities observed included umbilical hernia, exencephaly and cleft palate.
Two oral peri- and post-natal development studies were conducted with rats:
Pregnant Wistar rats were dosed daily with calcipotriene at exposures of 0, 6, 18 or 54 mcg/kg/day from gestation day 15 through day 20 postpartum. No remarkable effects were observed on any parameter, including survival, behavior, body weight, litter parameters, or the ability to nurse or rear pups.
Betamethasone dipropionate was evaluated for effects when orally administered to pregnant rats from gestation day 6 through day 20 postpartum at dosages of 0, 100, 300, and 1000 mcg/kg/day. Mean maternal body weight was significantly reduced on gestation day 20 in animals dosed at 300 and 1000 mcg/kg/day. The mean duration of gestation was slightly, but statistically significantly, increased at 100, 300, and 1000 mcg/kg/day. The mean percentage of pups that survived to day 4 was reduced in relation to dosage. On lactation day 5, the percentage of pups with a reflex to right themselves when placed on their back was significantly reduced at 1000 mcg/kg/day. No effects on the ability of pups to learn were observed, and the ability of the offspring of treated rats to reproduce was not affected.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects.
It is not known whether topically administered calcipotriene or corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk.
Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Taclonex® Ointment is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of the use of Taclonex® Ointment in pediatric patients have not been studied. Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, children under the age of 12 years may be at particular risk of systemic adverse effects when they are treated with topical medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
HPA axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in the clinical studies of Taclonex® Ointment, approximately 14% were 65 years and older and approximately 3% were 75 years and over.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of Taclonex® Ointment were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. All other reported clinical experience has not identified any differences in response between elderly and younger patients.
8.6 Unevaluated Uses
The safety and efficacy of Taclonex® Ointment in patients with known or suspected disorders of calcium metabolism have not been evaluated.
The safety and efficacy of Taclonex® Ointment in patients with erythrodermic, exfoliative, or pustular psoriasis have not been evaluated.
The safety and efficacy of Taclonex® Ointment in patients with severe renal insufficiency or severe hepatic disorders have not been evaluated.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Topically applied Taclonex® Ointment can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects [
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)
].
11 DESCRIPTION
Taclonex® (calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate) Ointment, 0.005%/0.064% contains calcipotriene hydrate and betamethasone propionate. It is intended for topical use only.
Calcipotriene hydrate is a synthetic vitamin D3 analogue.
Chemically, calcipotriene hydrate is (5Z,7E,22E,24S)-24-cyclopropyl-9,10-secochola-5,7,10(19),22-tetraene-1(alpha),3(beta),24-triol,hydrate, with the empirical formula C27H40O3H2O, a molecular weight of 430.6, and the following structural formula:

Calcipotriene hydrate is a white to almost white crystalline compound.
Betamethasone dipropionate is a synthetic corticosteroid.
Betamethasone dipropionate has the chemical name 9-fluoro-11(beta),17,21-trihydroxy-16(beta)-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione17,21-dipropionate, with the empirical formula C28H37FO7, a molecular weight of 504.6, and the following structural formula:
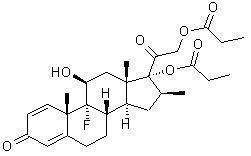
Betamethasone dipropionate is a white to almost white odorless powder.
Each gram of Taclonex® Ointment contains 52.18 mcg of calcipotriene hydrate (equivalent to 50 mcg of calcipotriene) and 0.643 mg of betamethasone dipropionate (equivalent to 0.5 mg of betamethasone) in off-white to yellow paraffin ointment base of mineral oil, PPG-11 stearyl ether, all-rac-alpha-tocopherol, butylhydroxytoluene, and white petrolatum.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Taclonex® Ointment combines the pharmacological effects of calcipotriene hydrate as a synthetic vitamin D3 analogue and betamethasone dipropionate as a synthetic corticosteroid. However, while their pharmacologic and clinical effects are known, the exact mechanisms of their actions in psoriasis vulgaris are unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Vasoconstriction:
In a vasoconstrictor study, the skin blanching response of Taclonex® Ointment was consistent with that of a potent corticosteroid.
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis Suppression:
Taclonex® Ointment was applied once daily for 4 weeks to adult subjects (N = 12) with psoriasis vulgaris to study its effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Of eleven subjects tested, none demonstrated adrenal suppression as indicated by a 30-minute post-stimulation cortisol level ≤ 18 mcg/dL.
However in another clinical study of Taclonex® Ointment, one subject (N = 19) demonstrated adrenal suppression.
HPA axis suppression was evaluated in adult subjects (N=32) with extensive psoriasis involving at least 30% of the scalp and, in total, 15-30% of the body surface area. Treatment consited of once daily application of Talconex Scalp® Topical Suspension on the scalp in combination with Taclonex® Ointment on the body. Adrenal suppression as indicated by a 30-minutes post-stimulation cortisol level less than or equal to 18 mcg/dL was observed in 5 of 32 subjects (15.6%) after 4 weeks of treatment as per the recommended duration of use (see Dosage and Administration (2.1) .
Effects on Calcium Metabolism
In the combination use study described above, the effects of once daily application of Taclonex® Ointment on the body in combination with Taclonex Scalp® Topical Suspension on the scalp on calcium metabolism were also examined. Elevated urinary calcium levels outside the normal range were observed in 1 of 35 subjects (2.9%) after 4 weeks of treatment.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The systemic effect of Taclonex® Ointment in extensive psoriasis was investigated in the trial described above. In this study, the serum levels of calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate and their major metabolites were measured after 4 weeks (maximum recommended duration of treatment) and also after 8 weeks of once daily application of Taclonex® Ointment on the body in combination with Taclonex Scalp® Topical Suspension on the scalp. Both calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate were below the lower limit of quantification in all serum samples of the 34 subjects evaluated. However, one major metabolite of calcipotriene (MC1080) was quantifiable in 10 of 34 (29.4%) subjects at week 4 and in five of 12 (41.7%) subjects at week 8. The major metabolite of betamethasone dipropionate, betamethasone 17-propionate (B17P) was also quantifiable in 19 of 34 (55.9%) subjects at week 4 and seven of 12 (58.3%) subjects at week 8. The serum concentrations for MC1080 ranged from 20-75 pg/mL. The clinical significance of this finding is unknown.
Metabolism
Calcipotriene:
Calcipotriene metabolism following systemic uptake is rapid and occurs in the liver. The primary metabolites of calcipotriene are less potent than the parent compound.
Calcipotriene is metabolized to MC1046 (the alpha,beta-unsaturated ketone analogue of calcipotriene), which is metabolized further to MC1080 (a saturated ketone analogue). MC1080 is the major metabolite in plasma. MC1080 is slowly metabolized to calcitroic acid.
Betamethasone dipropionate:
Betamethasone dipropionate is metabolized to betamethasone 17-propionate and betamethasone, including the 6beta-hydroxy derivatives of those compounds by hydrolysis. Betamethasone 17-propionate (B17P) is the primary metabolite.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
When calcipotriene was applied topically to mice for up to 24 months at dosages of 3, 10 and 30 mcg/kg/day (corresponding to 9, 30 and 90 mcg/m2/day), no significant changes in tumor incidence were observed when compared to control.
In a study in which albino hairless mice were exposed to both ultra-violet radiation (UVR) and topically applied calcipotriene, a reduction in the time required for UVR to induce the formation of skin tumors was observed (statistically significant in males only), suggesting that calcipotriene may enhance the effect of UVR to induce skin tumors.
When betamethasone dipropionate was applied topically to CD-1 mice for up to 24 months at dosages approximating 1.3, 4.2 and 8.5 mcg/kg/day in females, and 1.3, 4.2, and 12.9 mcg/kg/day in males (corresponding to dosages of up to approximately 26 mcg/m2/day and 39 mcg/m2/day, in females and males, respectively), no significant changes in tumor incidence were observed when compared to control.
When betamethasone dipropionate was administered via oral gavage to male and female Sprague Dawley rats for up to 24 months at dosages of 20, 60, and 200 mcg/kg/day (corresponding to dosages of approximately 3, 10, and 30 mcg/m2/day), no significant changes in tumor incidence were observed when compared to control.
Calcipotriene did not elicit any genotoxic effects in the Ames mutagenicity assay, the mouse lymphoma TK locus assay, the human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test, or the mouse micronucleus test. Betamethasone dipropionate did not elicit any genotoxic effects in the Ames mutagenicity assay, the mouse lymphoma TK locus assay, or in the rat micronucleus test.
Studies in rats with oral doses of up to 54 mcg/kg/day (324 mcg/m2/day) of calcipotriene indicated no impairment of fertility or general reproductive performance. Studies in male rats at oral doses of up to 200 mcg/kg/day (1200 mcg/m2/day), and in female rats at oral doses of up to 1000 mcg/kg/day (6000 mcg/m2/day), of betamethasone dipropionate indicated no impairment of fertility.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In an international, multi-center, double-blind, vehicle- and active-controlled, parallel-group trial, 1603 subjects with mild to very severe psoriasis vulgaris on trunk and limbs were treated once daily for 4 weeks. Subjects were randomized to one of four treatment arms: Taclonex® Ointment, calcipotriene hydrate 50 mcg/g in the same vehicle, betamethasone dipropionate 0.64 mg/g in the same vehicle, and vehicle alone. The mean age of the subjects was 48.4 years and 60.5% were male. Most subjects had disease of moderate severity at baseline.
Efficacy was assessed as the proportion of subjects with absent or very mild disease according to the Investigator's Global Assessment of Disease Severity at end of treatment (4 weeks). "Absent" disease was defined as no evidence of redness, thickness, or scaling. "Very mild disease" was defined as controlled disease, but not entirely cleared: lesions with some discoloration with absolutely minimal thickness, i.e. the edges to the lesions(s) could just be felt. Table 3 contains the response rates for this trial.
Table 3
Percentage of Subjects with Absent or Very Mild Disease According to the Investigator's Global Assessment of Disease Severity at End of Treatment (4 weeks).*
| Taclonex® Ointment N = 490 |
Calcipotriene N = 480 |
Betamethasone dipropionate N = 476 |
Vehicle N = 157 |
|
| Absent or very mild disease | 48.0% | 16.5% | 26.3% | 7.6% |
*Subjects with mild disease at baseline were required to have "Absent" disease to be considered a success.
In addition to the pivotal trial (N = 490), four randomized, double-blind, vehicle- or active-controlled, parallel-group trials were conducted and provided supportive evidence of efficacy. These studies included a total of 1058 subjects treated with Taclonex® Ointment once daily for up to 4 weeks.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Taclonex® Ointment is off-white to yellow in color, available in collapsible tubes of:
60 gram (NDC 50222-227-04)
100 gram (NDC 50222-227-81)
16.2 Storage
Store Taclonex®Ointment between 20 - 25° C (68 - 77° F); excursions permitted between 15 - 30° C (59 - 86° F).
[See USP controlled room temperature.]
16.3 Handling
Keep out reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Inform patients of the following:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician.
- It is for external use only.
- Avoid contact with the face or eyes. If this medicine gets on face or in eyes, wash area right away.
- Wash hands after application.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it has been prescribed.
- The treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered as to be occlusive, unless directed by the physician. Patients should report any signs of adverse reactions to their physician.
- Other products containing calcipotriene or a corticosteroid should not be used with Taclonex® Ointment without first talking to the physician.
- Instruct patients who use Taclonex® Ointment to avoid excessive exposure to either natural or artificial sunlight (including tanning booths, sun lamps, etc.). Physicians may wish to limit or avoid use of phototherapy in patients who use Taclonex® Ointment.
Patient Information
Taclonex
®
Ointment (pronounced TAK-lo-NEKS)
(calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate) Ointment, 0.005%/0.064%
Read the Patient Information that comes with Taclonex® Ointment before you start using it and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition or treatment.
Important information: Taclonex® Ointment is for use on the skin only (topical use only). Do not use Taclonex® Ointment on the face, under arms or on groin area. Do not swallow Taclonex® Ointment. Another product, Taclonex® Topical Suspension contains the same medicine that is in Taclonex® Ointment and is used to treat psoriasis vulgaris on the scalp. If you use both medicines to treat your psoriasis vulgaris, be sure to follow your doctor’s directions carefully so that you do not use too much of one or both of these medications.
What is Taclonex
®
Ointment?
Taclonex® Ointment is a prescription medicine that is for use on the skin only (a topical medicine). Taclonex® Ointment is used to treat psoriasis vulgaris in adults 18 years of age and older.
Taclonex® Ointment is not recommended for use in children. Taclonex® Ointment has not been studied in patients under the age of 18.
Who should not use Taclonex
®
Ointment?
Do not use Taclonex
®
Ointment if you:
- have a calcium metabolism disorder
- have one of the following types of psoriasis:
• erythrodermic psoriasis
• exfoliative psoriasis
• pustular psoriasis - have severe kidney or liver disease
- have thin skin (atrophy) at the site to be treated
- are allergic to anything in Taclonex® Ointment.
See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients.
What should I tell my doctor before using Taclonex
®
Ointment?
Tell your doctor about all of your health conditions, including if you:
• have a skin infection. Your skin infection should be treated before starting Taclonex® Ointment.
• are getting phototherapy treatments (light therapy) for your psoriasis.
• are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Taclonex® Ointment can harm your unborn baby. You and your doctor will have to decide if Taclonex® Ointment is right for you while pregnant.
• are breastfeeding. It is not known if Taclonex® Ointment passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription, and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Taclonex® Ointment and some other medicines can interact with each other. Especially tell your doctor if you use:
• other corticosteroid medicines
• other medicines for your psoriasis
How should I use Taclonex
®
Ointment?
• Use Taclonex® Ointment exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
• Do not use more than the maximum recommended weekly amount of 100 grams of Taclonex® Ointment.
• Apply Taclonex® Ointment once a day to the areas of your skin affected by psoriasis. Gently rub Taclonex® Ointment into your affected skin areas.
• Only use Taclonex® Ointment as directed by your doctor. Taclonex® Ointment is recommended for up to 4 weeks of treatment. Do not use Taclonex® Ointment for more than 4 weeks unless prescribed by your doctor.
• Do not use Taclonex® Ointment on the face, under arms or on groin area. If you accidentally get Taclonex® Ointment on the face or in the eyes wash the area with water right away.
• If you forget to use Taclonex® Ointment, use it as soon as you remember. Then go on as before.
• Wash your hands well after applying Taclonex® Ointment.
Using Taclonex
®
Ointment:
Do not bandage or tightly cover the treated skin area.
Remove the cap and check that the aluminum seal covers the tube before the first use. To break the seal, turn the cap over and punch through the seal.
What should I avoid while using Taclonex
®
Ointment?
Avoid spending a long time in the sunlight. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Use sunscreen if you have to be in the sunlight. Talk to your doctor if you get a sunburn.
What are the possible side effects of Taclonex
®
Ointment?
The most common side effects are:
• itching
• rash
Other less common side effects with Taclonex® Ointment include:
• redness of the skin
• skin irritation
• skin burning
• inflamed hair pores (folliculitis)
• change of skin color (at the site of application)
• rash with pus-filled papules
• thinning of the skin (atrophy)
• swollen fine blood vessels (this makes your skin appear red at the site of application)
Taclonex
®
Ointment may cause serious side effects. Serious side effects are more likely to happen if you use too much Taclonex® Ointment, use it for too long, or use it with other topical medicines that contain corticosteroids, calcipotriene, or certain other ingredients. Check with your doctor before using other topical medicines. Taclonex® Ointment can pass through your skin. Serious side effects may include:
• too much calcium in your blood or urine
• adrenal gland problems
Your doctor may do special blood and urine tests to check your calcium levels and adrenal gland function while you are using Taclonex® Ointment.
Call your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the side effects with Taclonex® Ointment. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I store Taclonex
®
Ointment?
• Store Taclonex® Ointment at room temperature, 68 - 77° F (20 - 25° C); Make sure the cap on the tube is tightly closed.
• Taclonex® Ointment has an expiration date (exp.) marked on the tube. Do not use the ointment after this date.
• Keep Taclonex® Ointment and all medicines out of the reach of children and pets.
General information about Taclonex
®
Ointment
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use Taclonex® Ointment for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Taclonex® Ointment to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Taclonex® Ointment. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Taclonex® Ointment that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Taclonex® Ointment?
Active ingredients: calcipotriene hydrate, betamethasone dipropionate.
Inactive ingredients: mineral oil, PPG-11 stearyl ether, all-rac-alpha-tocopherol, butylhydroxytoluene, and white petrolatum.


Manufactured by:
LEO Laboratories Ltd. (LEO Pharma)
Dublin, Ireland
Distributed by:
LEO Pharma Inc.
1 Sylvan Way, Parsippany, NJ 07054 USA
1-877-494-4536
U.S. Patent Nos.: RE39,706 E and 6,753,013.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON LABEL 100 G

NDC 50222-227-81
TACLONEX® (calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate) Ointment, 0.005%/0.064%
Rx Only
For Topical Use Only
Net Wt. 100 g
Each gram contains 52.18 mcg of calcipotriene hydrate (equivalent to 50 mcg of calcipotriene) and 0.643 mg of betamethasone dipropionate (equivalent to 0.5 mcg of betamethasone) in an ointment base of mineral oil, PPG-11 stearyl ether, all-rac-alpha-tocopherol, butylhydroxytoluene, and white petrolatum.
Store Taclonex Ointment between 20 - 25° C (68 - 77° F); excursions permitted between 15 - 30° C (59 - 86° F).
Keep out of reach of children.
Usual Dosage: Apply once daily, or as directed by physician. See Insert for complete information.
Distributed by LEO Pharma Inc.
Taclonexcalcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate OINTMENT
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||