TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
H.J. Harkins Company, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use tamsulosin hydrochloride safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for tamsulosin hydrochloride. Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Capsules USP*, 0.4 mg Initial U.S. Approval: 1997RECENT MAJOR CHANGESDosage and Administration (2) 4/2009 Contraindications (4) 12/2009 Warnings and Precautions Drug Interactions (5.2) 12/2009 Screening for Prostate Cancer (5.4) 12/2009INDICATIONS AND USAGE Tamsulosin hydrochloride is an alpha1 adrenoceptor antagonist indicated for treatment of the signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (1) Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules are not indicated for the treatment of hypertension (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 0.4 mg once daily taken approximately one-half hour following the same meal each day (2) Can be increased to 0.8 mg once daily for patients who fail to respond to the 0.4 mg dose after 2 to 4 weeks of dosing (2) If discontinued or interrupted for several days, therapy should start again with the 0.4 mg once-daily dose (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Capsules: 0.4 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to tamsulosin hydrochloride or any component of tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules (4, 6.2) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Advise patients about the possibility of symptoms related to postural hypotension and to avoid situations where injury could result should syncope occur (5.1) Should not be used in combination with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (5.2, 7.1). Use with caution in combination with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4, with strong or moderate inhibitors of CYP2D6, in patients known to be CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, or in combination with other cytochrome P450 inhibitors. (5.2, 7.1, 12.3) Should not be used in combination with other alpha adrenergic blocking agents (5.2, 7.2, 12.3) Exercise caution with concomitant administration of warfarin (5.2, 7.4, 12.3) Advise patients about the possibility and seriousness of priapism (5.3) Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome has been observed during cataract surgery in some patients. Advise patients considering cataract surgery to tell their ophthalmologist that they have taken tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules. (5.5) Advise patients to be screened for the presence of prostate cancer prior to treatment and at regular intervals afterwards (5.4) Side Effects The most common adverse events (≥2% of patients and at a higher incidence than placebo) with the 0.4 mg dose or 0.8 mg dose were headache, dizziness, rhinitis, infection, abnormal ejaculation, asthenia, back pain, diarrhea, pharyngitis, chest pain, cough increased, somnolence, nausea, sinusitis, insomnia, libido decreased, tooth disorder, and blurred vision (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Wockhardt USA LLC., at 1-800-346-6854 or FDA at1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 0.4 mg should not be used with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole). Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules should be used with caution in combination with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., erythomycin), in combination with strong (e.g.,paroxetine) or moderate (e.g.,terbinafine) inhibitors of CYP2D6, or in patients known to be CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, particularly at a dose higher than 0.4 mg (e.g., 0.8 mg) (5.2, 7.1, 12.3) Concomitant use of PDE5 inhibitors with tamsulosin can potentially cause symptomatic hypotension (5.2, 7.3, 12.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pediatric Use: Not indicated for use in pediatric populations (8.4, 12.3) Geriatric Use: No overall differences in efficacy or safety vs. younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older adults cannot be ruled out (8.5, 12.3) Renal Impairment: Has not been studied in patients with end stage renal disease (8.6, 12.3) Hepatic Impairment: Has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (8.7, 12.3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 6 TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
see Clinical Studies (14)2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
see Adverse Reactions (6.2)5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Orthostasis
see Adverse Reactions (6.1)see Patient Counseling Information (17.1)5.2 Drug Interactions
see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
See Drug Interactions (7.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
5.3 Priapism
1see Patient Counseling Information (17.2)5.4 Screening for Prostate Cancer
see Patient Counseling Information (17.3)5.5 Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome
1see Adverse Reactions (6.2)111115.6 Sulfa Allergy
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Table 1 Treatment-Emergent1 Adverse Events Occurring in ≥2% of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Capsules or Placebo Patients in Two U.S. Short-Term Placebo-Controlled Clinical Studies
|
BODY SYSTEM/ ADVERSE EVENT |
TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES GROUPS 0.4 mg 0.8 mg n=502 n=492 |
PLACEBO n=493 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| BODY AS WHOLE |
|
|
|
| Headache |
97 (19.3%) |
104 (21.1%) |
99 (20.1%) |
| Infection2
|
45 (9.0%) |
53 (10.8%) |
37 (7.5%) |
| Asthenia |
39 (7.8%) | 42 (8.5%) | 27 (5.5)% |
| Back Pain |
35 (7.0%) |
41 (8.3%) | 27 (5.5%) |
| Chest Pain |
20 (4.0%) | 20 (4.1%) | 18 (3.7%) |
| NERVOUS SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Dizziness |
75 (14.9%) | 84 (17.1%) | 50 (10.1%) |
| Somnolence |
15 (3.0%) | 21 (4.3%) | 8 (1.6%) |
| Insomnia |
12 (2.4%) |
7 (1.4%) | 3 (0.6%) |
| Libido Decreased |
5 (1.0%) |
10 (2.0%) |
6 (1.2%) |
| RESPIRATORY SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Rhinitis3
|
66 (13.1%) |
88 (17.9%) | 41 (8.3%) |
| Pharyngitis |
29 (5.8%) | 25 (5.1%) | 23 (4.7%) |
| Cough Increased |
17 (3.4%) |
22 (4.5%) |
12 (2.4%) |
| Sinusitis |
11 (2.2%) |
18 (3.7%) |
8 (1.6%) |
| DIGESTIVE SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Diarrhea |
31 (6.2%) |
21 (4.3%) | 22 (4.5%) |
| Nausea |
13 (2.6%) |
19 (3.9%) | 16 (3.2%) |
| Tooth Disorder |
6 (1.2%) |
10 (2.0%) | 7 (1.4%) |
| UROGENITAL SYSTEM |
|
|
|
| Abnormal Ejaculation |
42 (8.4%) |
89 (18.1%) | 1 (0.2%) |
| SPECIAL SENSES |
|
|
|
| Blurred vision |
1 (0.2%) |
10 (2.0%) | 2 (0.4%) |
- The adverse event occurred for the first time after initial dosing with double-blind study medication.
- The adverse event was present prior to or at the time of initial dosing with double-blind study medication and subsequently increased in severity during double-blind treatment; or
- The adverse event was present prior to or at the time of initial dosing with double-blind study medication, disappeared completely, and then reappeared during double-blind treatment.
3
Signs and Symptoms of Orthostasis
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)
Abnormal Ejaculation
Laboratory Tests
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
1see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cytochrome P450 Inhibition
Strong and Moderate Inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2D6maxsee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
maxsee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
Cimetidine
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)
7.2 Other Alpha Adrenergic Blocking Agents
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)7.3 PDE5 Inhibitors
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)7.4 Warfarin
in vitroin vivosee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)7.5 Nifedipine, Atenolol, Enalapril
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)7.6 Digoxin and Theophylline
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)7.7 Furosemide
maxsee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects,Pregnancy Category B.8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
®
8.5 Geriatric Use
see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)8.6 Renal Impairment
cr2see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)8.7 Hepatic Impairment
see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)10 OVERDOSAGE
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)11 DESCRIPTION
1ARo
202825
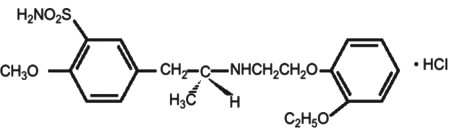
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
11111A1B1D11A
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14)].12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Effect of Food
maxmax
Figure 1 Mean Plasma Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Concentrations Following Single-Dose Administration of Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Capsules 0.4 mg Under Fasted and Fed Conditions (n=8)
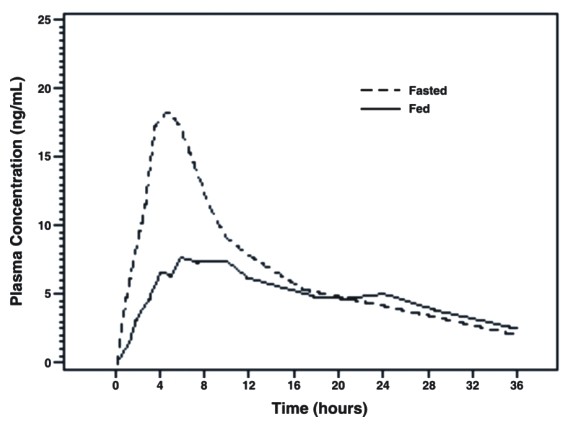
Table 2 Mean (± S.D.) Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Capsules 0.4 mg Once Daily or 0.8 mg Once Daily with a Light Breakfast, High-Fat Breakfast or Fasted
| Pharmacokinetic 0.4 mg QD to healthy volunteers; m=23 0.8 mg QD to healthy volunteers; n=22 Parameter (age range 18 to 32 years) (age range 18 to 32 years) Light Breakfast Fasted Light Breakfast High-Fast Breakfast Fasted |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmin (ng/mL) |
4.0 ± 2.6 |
3.8 ± 2.5 |
12.3 ± 6.7 |
13.5 ± 7.6 |
13.3 ± 13.3 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) |
10.1 ± 4.8 |
17.1 ± 17.1 |
29.8 ± 10.3 |
29.1 ± 11.0 |
41.6 ± 15.6 |
| Cmax/Cmin Ratio |
3.1 ± 1.0 |
5.3 ± 2.2 |
2.7 ± 0.7 |
2.5 ± 0.8 |
3.6 ± 1.1 |
| Tmax (hours) |
6.0 |
4.0 |
7.0 |
6.6 |
5.0 |
| T1/2 (hours) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
14.9 ± 3.9 |
| AUCτ (ng•hr/mL) |
151 ± 81.5 |
199 ± 94.1 |
440 ± 195 |
449 ± 217 |
557 ± 257 |
max
max
1/2
τ
Distribution
1in vitro
Metabolism
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
Excretion
Special Populations
Pediatric Use
see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)
Geriatric (Age) Use
see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)
Renal Impairment
cr 2cr2cr2cr2see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)
Hepatic Impairment
see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450 Inhibition
Strong and Moderate Inhibitors of CYP3A4 or CYP2D6
maxsee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
maxsee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
Cimetidine
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)
Other Alpha Adrenergic Blocking Agents
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.2)
PDE5 Inhibitors
see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3)
Warfarin
in vitroin vivosee Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.4)
Nifedipine, Atenolol, Enalapril
see Drug Interactions (7.5)
Digoxin and Theophylline
see Drug Interactions (7.6)
Furosemide
maxsee Drug Interactions (7.7)
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
in vitroin vivo
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
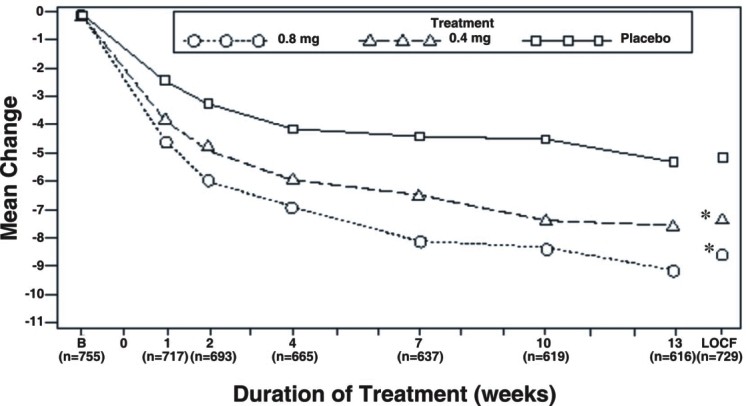
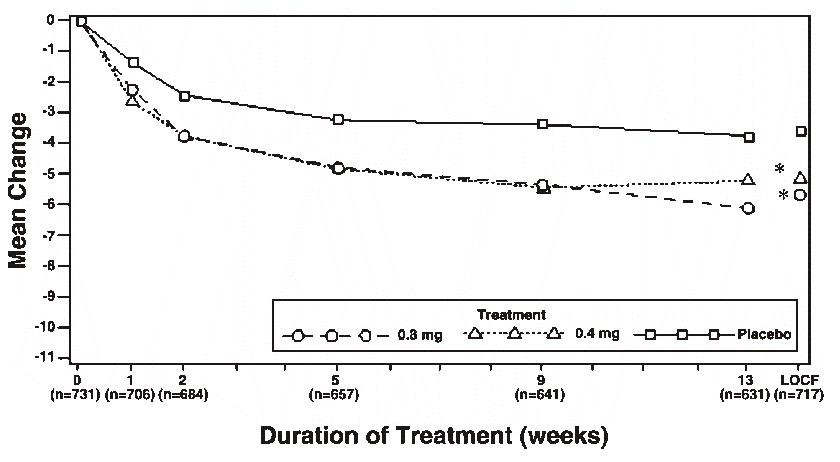
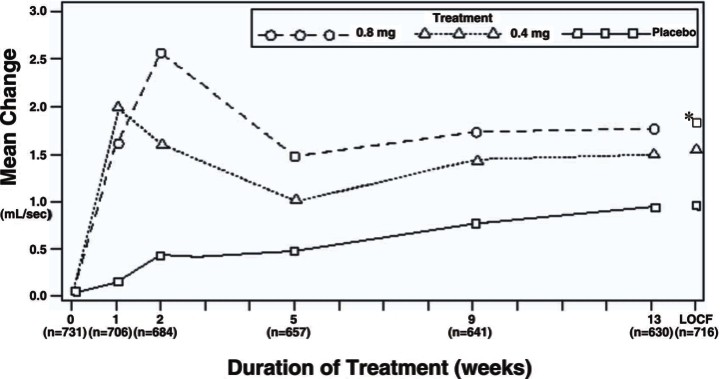
Table 3 Mean (±S.D.) Changes from Baseline to Week 13 in Total AUA Symptom Score** and Peak Urine Flow Rate (mL/sec)
|
|
Total AUA Symptom Score
Mean Baseline Value |
Mean Change |
Peak Urine Flow Rate Mean Baseline Value |
Mean Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 † |
|
|
|
|
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 0.8 mg once daily |
19.9 ± 4.9 n=247 |
-9.6* ± 6.7 n=237 |
9.57 ± 2.51 n=247 |
1.78* ± 3.35 n=247 |
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 0.4 mg once daily |
19.8 ± 5.0 n=254 |
-8.3* ± 6.5 n=246 |
9.46 ± 2.49 n=254 |
1.75* ± 3.57 n=254 |
| Placebo | 19.6 ± 4.9 n=254 |
-5.5 ± 6.6 n=246 |
9.75 ± 2.54 n=254 |
0.52 ± 3.39 n=253 |
| Study 2 ‡ |
|
|
|
|
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 0.8 mg once daily |
18.2 ± 5.6 n=244 |
-5.8* ± 6.4 n=238 |
9.96 ± 3.16 n=244 |
1.79* ± 3.36 n=237 |
| Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 0.4 mg once daily |
17.9 ± 5.8 n=248 |
-5.1* ± 6.4 n=244 |
9.94 ± 3.14 n=248 |
1.52 ± 3.64 n=244 |
| Placebo | 19.2 ± 6.0 n=239 |
-3.6 ± 5.7 n=235 |
9.95 ± 3.12 n=239 |
0.93 ± 3.28 n=235 |
**
†
‡
Figure 2A Mean Change from Baseline in Total AUA Symptom Score (0-35) Study 1
*
Figure 2B Mean Change from Baseline in Total AUA Symptom Score (0-35) Study 2
*
Figure 3A Mean Increase in Peak Urine Flow Rate (mL/sec) Study 1
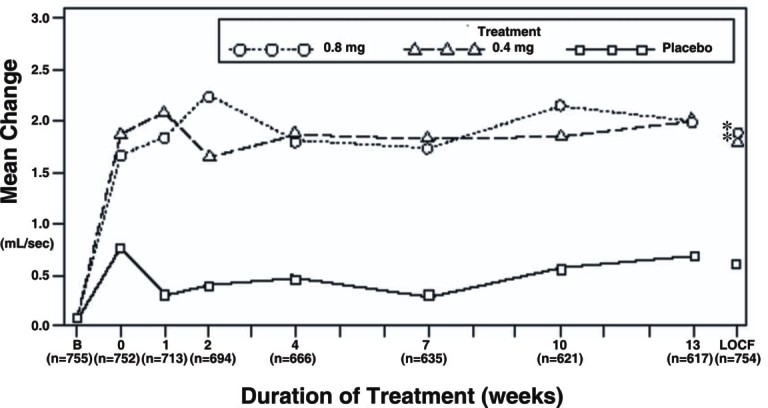
*
Figure 3B Mean Increase in Peak Urine Flow Rate (mL/sec) Study 2
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Store at 20° to 25°C (68°C to 77°F)
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (17.6).17.1 Hypotension
see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)17.2 Priapism
see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)17.3 Screening for Prostate Cancer
see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)17.4 Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome
see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)17.5 Administration
17.6 FDA-approved Patient Labeling
®
Manufactured by:
Distributed by:
- Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules are not for women.
- Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules are not for children.
- any kidney or liver problems.
- any history of low blood pressure.
- any allergies to sulfa or any other medicines.
- if you are planning to have cataract surgery.
- any prescription medicines, including blood pressure medicines.
- any non-prescription medicines, including vitamins and herbal supplements.
- Take tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do not crush, chew, or open tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules.
- Take tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules one time each day, about 30 minutes after the same meal each day. For example, you may take tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules 30 minutes after dinner each day.
- If you miss a dose of tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules, take it as soon as you remember. If you miss your dose for the whole day, continue with your next dose on your regular schedule. Do not take two doses at the same time.
- If you stop or forget to take tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules for several days, talk with your doctor before starting again.
- If you take more tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules than prescribed, call your doctor right away.
- Decreased blood pressure when changing positions. Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules may cause a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing, especially after the first dose or when changing doses.
- fainting
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- Allergic reactions. Make your doctor aware of any allergic reactions you may experience while taking tamsulosin hydrochloride.
- rash
- itching
- hives
- swelling of face, tongue, or throat
- difficulty breathing
- A painful erection that will not go away.Tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules can cause a painful erection (priapism), which cannot be relieved by having sex. If this happens, get medical help right away. If priapism is not treated, you may not be able to get an erection in the future.
- Eye problems during cataract surgery. During cataract surgery, a condition called intraoperative floppy iris syndrome (IFIS) can happen if you take or have taken tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules. If you need to have cataract surgery, be sure to tell your surgeon if you take or have taken tamsulosin hydrochloride capsules.
- runny nose
- dizziness
- decreased semen
- Active Ingredient: tamsulosin hydrochloride
- Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, talc, triethyl citrate, FD and C blue # 1, FD and C red # 40, FD and C yellow # 10, titanium dioxide, gelatin, shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, strong ammonia solution, black iron oxide and potassium hydroxide
*USP dissolution test is pending.
TAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDETAMSULOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!