Testim
Testim (testosterone) Gel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Structure Image
Uses
Testim® is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone levels and gonadotropins (FSH, LH) above the normal range.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): idiopathic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum levels but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range.
Testim® has not been clinically evaluated in males under 18 years of age.
Androgens are contraindicated in men with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate. Testim® is not indicated for use in women, has not been evaluated for use in women, and must not be used in women.
Pregnant and nursing women should avoid skin contact with Testim® application sites on men. Testosterone may cause fetal harm. Testosterone exposure during pregnancy has been reported to be associated with fetal abnormalities. In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which Testim® has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of a pregnant or nursing woman, the general area of contact on the woman should be immediately washed with soap and water.
Testim® should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients, including testosterone USP that is chemically synthesized from soy.
- Testim® should not be applied to the abdomen.
- Prolonged use of high doses of orally active 17-alpha-alkyl androgens (e.g., methyltestosterone) has been associated with serious hepatic adverse effects (peliosis hepatitis, hepatic neoplasms, cholestatic hepatitis, and jaundice). Peliosis hepatitis can be a life-threatening or fatal complication. Long-term therapy with testosterone enanthate, which elevates blood levels for prolonged periods has produced multiple hepatic adenomas. Transdermal testosterone is not known to produce these adverse effects.
- Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk for the development of prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma.
- Geriatric patients and other patients with clinical or demographic characteristics that are recognized to be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer should be evaluated for the presence of prostate cancer prior to initiation of testosterone replacement therapy. In men receiving testosterone replacement therapy, surveillance for prostate cancer should be consistent with current practices for eugonadal men (see PRECAUTIONS: Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility and Laboratory Tests).
- Edema, with or without congestive heart failure, may be a serious complication in patients with preexisting cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease. In addition to discontinuation of the drug, diuretic therapy may be required.
- Gynecomastia occasionally develops and occasionally persists in patients being treated for hypogonadism.
- The treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone may potentiate sleep apnea in some patients, especially those with risk factors such as obesity or chronic lung diseases.
Transfer of testosterone to another person can occur when vigorous skin-to-skin contact is made with the application site (See Clinical Studies).
The following precautions are recommended to minimize potential transfer of testosterone from Testim®-treated skin to another person:
- Patients should wash their hands thoroughly and immediately with soap and water after application of Testim®. Studies of hand-washing show that Testim® is effectively removed from the skin surface by thorough washing with soap and water.
- Patients should cover the application site(s) with clothing after the gel has dried (e.g. a shirt).
- Prior to any situation in which direct skin-to-skin contact is anticipated, patients should wash the application sites thoroughly with soap and water so as to remove drug residue.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which Testim® has been applied does come in direct contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed thoroughly with soap and water as soon as possible.
Changes in body hair distribution, significant increase in acne, or other signs of virilization of the female partner should be brought to the attention of a physician.
The physician should instruct patients to report any of the following:
- Too frequent or persistent erections of the penis.
- Any changes in skin color, ankle swelling or unexplained nausea and vomiting.
- Breathing disturbances, including those associated with sleep.
In a controlled clinical study, 304 patients were treated with Testim® 50 mg or 100 mg or placebo gel for up to 90 days. Two hundred-five (205) patients received Testim® 50 mg or 100 mg daily and 99 patients received placebo. Patients with adverse events that were possibly or probably related to study drug and reported by ≥1% of the Testim® patients and greater than placebo are listed in Table 3.
| Event | Testim®50 mg | Testim®100 mg | Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application Site Reactions | 2% | 4% | 3% |
| Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | 0% | 1% | 1% |
| Blood Pressure Diastolic Decreased | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Blood Pressure Increased | 1% | 1% | 0% |
| Gynecomastia | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Headache | 1% | 1% | 0% |
| Hematocrit/hemoglobin Increased | 1% | 2% | 0% |
| Hot Flushes | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Insomnia | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Lacrimation Increased | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Mood Swings | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Smell Disorder | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Spontaneous Penile Erection | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Taste Disorder | 1% | 1% | 0% |
The following adverse events possibly or probably related to Testim® occurred in fewer than 1% of patients but were greater in Testim® groups compared to the placebo group: activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged, blood creatinine increased, prothrombin time prolonged, appetite increased, sensitive nipples, and acne.
In this clinical trial of Testim®, six patients had adverse events that led to their discontinuation. These events included: vertigo, coronary artery disease, depression with suicidal ideation, urinary tract infection/pneumonia (none of which were considered related to Testim® administration), mood swings and hypertension. No Testim® patients discontinued due to skin reaction.
In one foreign Phase 3 trial, one subject discontinued due to a skin-related adverse event. In the pivotal U.S. and European Phase 3 trials combined, at the 50 mg dosage strength, the percentage of subjects reporting clinically notable increases in hematocrit or hemoglobin were similar to placebo. However, in the 100 mg dose group, 2.3% and 2.8% of patients had a clinically notable increase in hemoglobin (≥ 19 gm/dL) or hematocrit (≥ 58%), respectively.
In the combined ongoing U.S. and European open label extension studies, approximately 140 patients received Testim® for at least 6 months. The preliminary results from these studies are consistent with those reported for the U.S. controlled clinical trial.
Testim® contains testosterone, a Schedule III controlled substance as defined by the Anabolic Steroids Control Act. Oral ingestion of Testim® will not result in clinically significant serum testosterone concentrations due to extensive first-pass metabolism.
There were no reports of overdose in the Testim® clinical trials. There is one report of acute overdosage by injection of testosterone enanthate: testosterone levels of up to 11,400 ng/dL were implicated in a cerebrovascular accident.
The recommended starting dose of Testim® is 5 g of gel (one tube) containing 50 mg of testosterone applied once daily (preferably in the morning) to clean, dry intact skin of the shoulders and/or upper arms. Morning serum testosterone levels should then be measured approximately 14 days after initiation of therapy to ensure proper serum testosterone levels are achieved. If the serum testosterone concentration is below the normal range, or if the desired clinical response is not achieved, the daily Testim® dose may be increased from 5 g (one tube) to 10 g (two tubes) as instructed by the physician.
Upon opening the tube the entire contents should be squeezed into the palm of the hand and immediately applied to the shoulders and/or upper arms. Application sites should be allowed to dry for a few minutes prior to dressing. Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap and water after Testim® has been applied.
In order to prevent transfer to another person, clothing should be worn to cover the application sites. If direct skin-to-skin contact with another person is anticipated, the application sites must be washed thoroughly with soap and water.
In order to maintain serum testosterone levels in the normal range, the sites of application should not be washed for at least two hours after application of Testim®.
Do not apply Testim® to the genitals or to the abdomen.
Testim® contains testosterone, a Schedule III controlled substance as defined by the Anabolic Steroids Control Act. Testim® is supplied in unit-dose tubes in cartons of 30. Each tube contains 50 mg testosterone in 5 g of gel, and is supplied as follows:
| NDC Number | Strength | Package Size |
|---|---|---|
| 66887-001-05 | 1% (50 mg) | 30 tubes: 5 g per tube |
Storage
Store at room temperature 25°C (77°F); Excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Disposal
Used Testim® tubes should be discarded in household trash in a manner that prevents accidental application or ingestion by children or pets; contents flammable.
RX Only
Manufactured for:
Auxilium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Norristown, PA, 19401 USA
By: Contract Pharmaceuticals Limited
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L5N 6L6
Labeling Code: AA2500.09
Issued: January 2005
0105-001.a
127997
Advise patients to carefully read the information brochure that accompanies each carton of 30 Testim® single-use tubes.
Advise patients of the following:
- Testim® should not be applied to the scrotum, penis, or abdomen.
- Testim® should be applied once daily at approximately the same time each day to clean dry skin of the shoulders and/or upper arms.
- Washing or swimming may lessen testosterone levels; however, when washing occurs two or more hours post drug application, serum testosterone levels remain within the normal range.
- Testim® may be transferred to another person by vigorous contact with the application site. Potential for transfer may be reduced by washing hands thoroughly after application, by wearing clothing to cover the sites, and by washing the application sites thoroughly with soap and water prior to any direct skin-to-skin contact.
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels should be checked periodically (to detect polycythemia) in patients on long-term androgen therapy.
- Liver function, prostate specific antigen (PSA), cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) should be checked periodically.
- To ensure proper dosing, serum testosterone concentrations should be measured (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Oxyphenbutazone: Concurrent administration of oxyphenbutazone and androgens may result in elevated serum levels of oxyphenbutazone.
Insulin: In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may decrease blood glucose and, therefore, insulin requirements.
Propranolol: In a published pharmacokinetic study of an injectable testosterone product, administration of testosterone cypionate led to an increased clearance of propranolol in the majority of men tested. It is unknown if this would apply to Testim®.
Corticosteroids: The concurrent administration of testosterone with ACTH or corticosteroids may enhance edema formation; thus these drugs should be administered cautiously, particularly in patients with cardiac or hepatic disease.
Androgens may decrease levels of thyroxin-binding globulin, resulting in decreased total T4 serum levels and increased resin uptake of T3 and T4. Free thyroid hormone levels remain unchanged, however, and there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
Testosterone has been tested by subcutaneous injection and implantation in mice and rats. In mice, the implant induced cervical-uterine tumors, which metastasized in some cases. There is suggestive evidence that injection of testosterone into some strains of female mice increases their susceptibility to hepatoma. Testosterone is also known to increase the number of tumors and decrease the degree of differentiation of chemically induced carcinomas of the liver in rats.
There are rare reports of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients receiving long-term oral therapy with androgens in high doses. Withdrawal of the drugs did not lead to regression of the tumors in all cases.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk for the development of prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma. Geriatric patients and other patients with clinical or demographic characteristics that are recognized to be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer should be evaluated for the presence of prostate cancer prior to initiation of testosterone replacement therapy.
In men receiving testosterone replacement therapy, surveillance for prostate cancer should be consistent with current practices for eugonadal men.
Testim® is not indicated for women and must not be used in women. Testosterone may cause fetal harm.
Testim® is not indicated for women and must not be used in nursing mothers.
Safety and efficacy of Testim® in patients less than 18 years old has not been established.
Testim® 1% (testosterone gel) delivers physiologic amounts of testosterone, producing circulating testosterone levels that approximate normal levels (e.g., 300 - 1000 ng/dL) seen in healthy men.
Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), endogenous androgens, are responsible for normal growth and development of the male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects include the growth and maturation of the prostate, seminal vesicles, penis, and scrotum; the development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest, and axillary hair; laryngeal enlargement; vocal cord thickening; alterations in body musculature; and fat distribution.
Male hypogonadism results from insufficient secretion of testosterone and is characterized by low serum testosterone concentrations. Symptoms associated with male hypogonadism include decreased sexual desire with or without impotence, fatigue and loss of energy, mood depression, regression of secondary sexual characteristics, and osteoporosis. Hypogonadism is a risk factor for osteoporosis in men.
Drugs in the androgen class also promote retention of nitrogen, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, and decreased urinary excretion of calcium.
Androgens have been reported to increase protein anabolism and decrease protein catabolism. Nitrogen balance is improved only when there is sufficient intake of calories and protein. Androgens have been reported to stimulate the production of red blood cells by enhancing erythropoietin production.
Androgens are responsible for the growth spurt of adolescence and for the eventual termination of linear growth brought about by fusion of the epiphyseal growth centers. In children, exogenous androgens accelerate linear growth rates but may cause a disproportionate advancement in bone maturation. Use over long periods may result in fusion of the epiphyseal growth centers and termination of the growth process.
During exogenous administration of androgens, endogenous testosterone release may be inhibited through feedback inhibition of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH). At large doses of exogenous androgens, spermatogenesis may also be suppressed through feedback inhibition of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
There is a lack of substantial evidence that androgens are effective in accelerating fracture healing or in shortening post-surgical convalescence.
The pharmacokinetics of Testim® have been evaluated with administration of doses containing 50 mg and 100 mg of testosterone to adult males with morning testosterone levels ≤300 ng/dL.
Testim® is a topical formulation that dries quickly when applied to the skin surface. The skin serves as a reservoir for the sustained release of testosterone into the systemic circulation. Approximately 10% of the testosterone applied on the skin surface is absorbed into the systemic circulation during a 24-hour period.
In single dose studies, when either Testim® 50 mg or 100 mg was administered, absorption of testosterone into the blood continued for the entire 24 hour dosing period. Also, mean peak and average serum concentrations within the normal range were achieved within 24 hours.
With single daily applications of Testim® 50 mg and 100 mg, follow-up measurements at 30 and 90 days after starting treatment have confirmed that serum testosterone and DHT concentrations are generally maintained within the normal range.
Figure 1 summarizes the 24-hour pharmacokinetic profile of testosterone for patients maintained on Testim® 50 mg or Testim® 100 mg for 30 days.
Figure 1
Mean Steady-State Serum Testosterone (±SD) (ng/dL) Concentrations on Day 30 in Patients Applying Testim® Once Daily
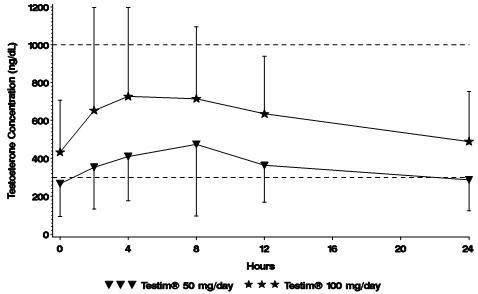
The average daily testosterone concentration produced by Testim® 100 mg at Day 30 was 612 (± 286) ng/dL and by Testim® 50 mg at Day 30 was 365 (± 187) ng/dL.
Figure 2 summarizes the 24-hour pharmacokinetic profile of DHT for patients maintained on Testim® 50 mg or Testim® 100 mg for 30 days.
Figure 2
Mean Steady-State Serum Dihydrotestosterone (±SD) (pg/mL) Concentrations on Day 30 in Patients Applying Testim® Once Daily
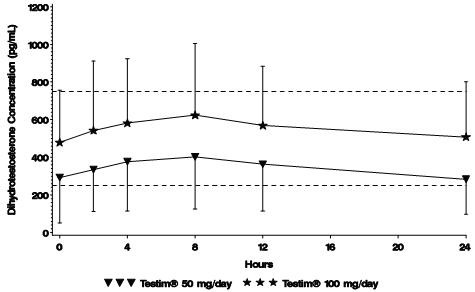
The average daily DHT concentration produced by Testim® 100 mg at Day 30 was 555 (± 293) pg/mL and by Testim® 50 mg at Day 30 was 346 (± 212) pg/mL.
The effect of showering (with mild soap) at 1, 2 and 6 hours post application of Testim® 100 mg was evaluated in a clinical trial in 12 men. The study demonstrated that the overall effect of washing was to lessen testosterone levels; however, when washing occurred two or more hours post drug application, serum testosterone levels remained within the normal range.
Circulating testosterone is chiefly bound in the serum to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. The albumin-bound fraction of testosterone easily dissociates from albumin and is presumed to be bioactive. The portion of testosterone bound to SHBG is not considered biologically active. Approximately 40% of testosterone in plasma is bound to SHBG, 2% remains unbound (free) and the rest is bound to albumin and other proteins. The amount of SHBG in the serum and the total testosterone level will determine the distribution of bioactive and nonbioactive androgen.
There is considerable variation in the half-life of testosterone as reported in the literature, ranging from ten to 100 minutes.
Testosterone is metabolized to various 17-keto steroids through two different pathways. The major active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and DHT. Testosterone is metabolized to DHT by steroid 5α-reductase located in the skin, liver, and the urogenital tract of the male. DHT binds with greater affinity to SHBG than does testosterone. In many tissues, the activity of testosterone depends on its reduction to DHT, which binds to cytosol receptor proteins. The steroid-receptor complex is transported to the nucleus where it initiates transcription and cellular changes related to androgen action. In reproductive tissues, DHT is further metabolized to 3α and 3β androstanediol. Inactivation of testosterone occurs primarily in the liver.
DHT concentrations increased in parallel with testosterone concentrations during Testim® treatment. After 90 days of treatment, mean DHT concentrations remained generally within the normal range for Testim®-treated subjects.
About 90% of a testosterone dose given intramuscularly is excreted in the urine as glucuronic and sulfuric acid conjugates of testosterone and metabolites; about 6% of a dose is excreted in the feces, mostly in the unconjugated form.
In patients treated with Testim® there are no observed differences in the average daily serum testosterone concentration at steady-state based on age or cause of hypogonadism. No formal studies were conducted in a pediatric age population or in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiencies.
Testim® was evaluated in a randomized multicenter, multi-dose, active and placebo controlled 90-day study in 406 adult males with morning testosterone levels ≤300 ng/dL. The study was double-blind for the doses of Testim® and placebo, but open label for the non-scrotal testosterone transdermal system. During the first 60 days, patients were evenly randomized to Testim® 50 mg, Testim® 100 mg, placebo gel, or testosterone transdermal system. At Day 60, patients receiving Testim® were maintained at the same dose, or were titrated up or down within their treatment group, based on 24-hour averaged serum testosterone concentration levels obtained on Day 30.
Of 192 hypogonadal men who were appropriately titrated with Testim® and who had sufficient data for analysis, 74% achieved an average serum testosterone level within the normal range on treatment Day 90.
Table 1 summarizes the mean testosterone concentrations on Day 30 for patients receiving Testim® 50 mg or 100 mg.
|
|
Testim® 50 mg n=94 |
Testim® 100 mg n=95 |
Placebo n=93 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cavg
(ng/dL) |
365 ± 187 | 612 ± 286 | 216 ± 79 |
|
Cmax
(ng/dL) |
538 ± 371 | 897 ± 565 | 271 ± 110 |
|
Cmin
(ng/dL) |
223 ± 126 | 394 ±189 | 164 ± 64 |
At Day 30, patients receiving Testim® 100 mg daily showed significant improvement from baseline in multiple sexual function parameters as measured by patient questionnaires when compared to placebo. These parameters included sexual motivation, sexual desire, sexual activity and spontaneous erections. For Testim® 100 mg, improvements in sexual motivation, spontaneous erections, and sexual desire were maintained through Day 90. Sexual enjoyment and satisfaction with erection duration were improved compared to baseline but these improvements were not significant compared to the placebo group.
In Testim®-treated patients, the number of days in which sexual activity was reported to occur increased by 123% from baseline at Day 30 and was still increased from baseline by 59% at Day 90. The number of days with spontaneous erections increased by 137% at Day 30 and was maintained at 78% at Day 90 for Testim®-treated patients compared to baseline.
Table 2 summarizes the changes in body composition at Day 90 for patients receiving Testim® 50 mg or 100 mg as measured by standardized whole body DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scanning.
| Days of Treatment |
Lean Body
Mass (Muscle) (kg) |
Total Fat Mass( kg) | % Body Fat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 61.6 | 29.4 | 30.9 |
| Day 90 | 63.3 | 28.6 | 29.8 |
| Change from Baseline | ↑1.6 | ↓0.8 | ↓1.1 |
At Day 90, mean increases from baseline in lean body mass and mean decreases from baseline in total fat mass and percent body fat in Testim®-treated patients were significant when compared to placebo-treated patients.
The potential for dermal testosterone transfer following Testim® use was evaluated in two clinical trials with males dosed with Testim® and their untreated female partners.
In the first trial (AUX-TG-206), 30 couples were evenly randomized to five groups. In the first four groups, 100 mg of Testim® was applied to the male abdomen and the couples were then asked to rub abdomen-to-abdomen for 15 minutes at 1 hour, 4 hours, 8 hours or 12 hours after dose application, respectively. In these couples, serum testosterone concentrations in female partners increased from baseline by at least 4 times and potential for transfer was seen at all timepoints.
When 6 males used a shirt to cover the abdomen at 15 minutes post-application and partners again rubbed abdomens for 15 minutes at the 1 hour timepoint, the potential for transfer was markedly reduced.
In the second trial (AUX-TG-209), 24 couples were evenly randomized to four groups. Testim® 100 mg was applied to the male arms and shoulders. In one group, 15 minutes of direct skin-to-skin rubbing began at 4 hours after application. In these six women, all of whom showered immediately after the rubbing activity, mean maximum serum testosterone concentrations increased from baseline by approximately 4 times. When males wore a long-sleeved T-shirt and rubbing was started at 1 and at 4 hours after application, the transfer of testosterone from male to female partners was prevented.
TESTIM GEL Package Label

TestimTESTOSTERONE GEL
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||