Therabenzaprine-60
Therabenzaprine-60
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
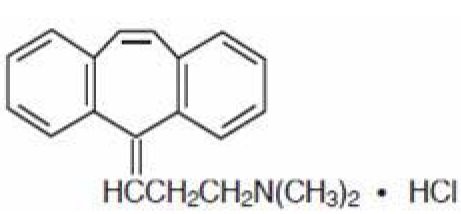
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is a white, crystalline tricyclic amine salt with the empirical formula C20H21N • HCl and a molecular weight of 311.9. It has a melting point of 217°C, and a pKa of 8.47 at 25°C. It is freely soluble in water and alcohol, sparingly soluble in isopropanol, and insoluble in hydrocarbon solvents. If aqueous solutions are made alkaline, the free base separates.
Cyclobenzaprine HCl is designated chemically as 3-(5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-N,N-dimethyl-1-propanamine hydrochloride, and has the following structural formula:
Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride Tablets, USP are supplied as 5 mg and 10 mg tablets for oral administration.
Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, FD C Yellow #6, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide; 5 mg tablets also contain FD C Red #40 and 10 mg tablets contain D C Yellow #10 and polysorbate.
Cyclobenzaprine HCl relieves skeletal muscle spasm of local origin without interfering with muscle function. It is ineffective in muscle spasm due to central nervous system disease.
Cyclobenzaprine reduced or abolished skeletal muscle hyperactivity in several animal models. Animal studies indicate that cyclobenzaprine does not act at the neuromuscular junction or directly on skeletal muscle. Such studies show that cyclobenzaprine acts primarily within the central nervous system at brain stem as opposed to spinal cord levels, although its action on the latter may contribute to its overall skeletal muscle relaxant activity. Evidence suggests that the net effect of cyclobenzaprine is a reduction of tonic somatic motor activity, influencing both gamma (γ) and alpha (α) motor systems.
Pharmacological studies in animals showed a similarity between the effects of cyclobenzaprine and the structurally related tricyclic antidepressants, including reserpine antagonism, norepinephrine potentiation, potent peripheral and central anticholinergic effects, and sedation. Cyclobenzaprine caused slight to moderate increase in heart rate in animals.
PharmacokineticsEstimates of mean oral bioavailability of cyclobenzaprine range from 33% to 55%. Cyclobenzaprine exhibits linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range 2.5 mg to 10 mg, and is subject to enterohepatic circulation. It is highly bound to plasma proteins. Drug accumulates when dosed three times a day, reaching steady state within 3-4 days at plasma concentrations about four-fold higher than after a single dose. At steady state in healthy subjects receiving 10 mg t.i.d. (n=18), peak plasma concentration was 25.9 ng/mL (range, 12.8-46.1 ng/mL), and area under the concentration-time (AUC) curve over an 8-hour dosing interval was 177 ng•hr/mL (range, 80-319 ng•hr/mL).
Cyclobenzaprine is extensively metabolized, and is excreted primarily as glucuronides via the kidney. Cytochromes P-450 3A4, 1A2, and, to a lesser extent, 2D6, mediate N-demethylation, one of the oxidative pathways for cyclobenzaprine. Cyclobenzaprine is eliminated quite slowly, with an effective half-life of 18 hours (range 8-37 hours; n=18); plasma clearance is 0.7 L/min.
The plasma concentration of cyclobenzaprine is generally higher in the elderly and in patients with hepatic impairment (see PRECAUTIONS, Use in the Elderly and PRECAUTIONS, Impaired Hepatic Function).
In a pharmacokinetic study in elderly individuals (≥65 yrs old), mean (n=10) steady state cyclobenzaprine AUC values were approximately 1.7-fold (171.0 ng•hr/mL, range 96.1-255.3) higher than those seen in a group of eighteen younger adults (101.4 ng•hr/mL, range 36.1-182.9) from another study. Elderly male subjects had the highest observed mean increase, approximately 2.4-fold (198.3 ng•hr/mL, range 155.6-255.3 versus 83.2 ng•hr/mL, range 41.1-142.5 for younger males) while levels in elderly females were increased to a much lesser extent, approximately 1.2-fold (143.8 ng•hr/mL, range 96.1-196.3 versus 115.9 ng•hr/mL, range 36.1-182.9 for younger females).
In light of these findings, therapy with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets in the elderly should be initiated with a 5 mg dose and titrated slowly upward.
In a pharmacokinetic study of sixteen subjects with hepatic impairment (15 mild, 1 moderate per Child-Pugh score), both AUC and Cmax were approximately double the values seen in the healthy control group. Based on the findings, cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in subjects with mild hepatic impairment starting with the 5 mg dose and titrating slowly upward. Due to the lack of data in subjects with more severe hepatic insufficiency, the use of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets in subjects with moderate to severe impairment is not recommended.
No significant effect on plasma levels or bioavailability of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets or aspirin was noted when single or multiple doses of the two drugs were administered concomitantly. Concomitant administration of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets and naproxen or diflunisal was well tolerated with no reported unexpected adverse effects. However combination therapy of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets with naproxen was associated with more side effects than therapy with naproxen alone, primarily in the form of drowsiness. No well-controlled studies have been performed to indicate that cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets enhance the clinical effect of aspirin or other analgesics, or whether analgesics enhance the clinical effect of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets in acute musculoskeletal conditions.
Eight double-blind controlled clinical studies were performed in 642 patients comparing cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride 10 mg, diazepam, and placebo. Muscle spasm, local pain and tenderness, limitation of motion, and restriction in activities of daily living were evaluated. In three of these studies there was a significantly greater improvement with cyclobenzaprine than with diazepam, while in the other studies the improvement following both treatments was comparable.
Although the frequency and severity of adverse reactions observed in patients treated with cyclobenzaprine were comparable to those observed in patients treated with diazepam, dry mouth was observed more frequently in patients treated with cyclobenzaprine and dizziness more frequently in those treated with diazepam. The incidence of drowsiness, the most frequent adverse reaction, was similar with both drugs.
The efficacy of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 mg was demonstrated in two seven-day, double-blind, controlled clinical trials enrolling 1405 patients. One study compared cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 and 10 mg t.i.d. to placebo; and a second study compared cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 and 2.5 mg t.i.d. to placebo. Primary endpoints for both trials were determined by patient-generated data and included global impression of change, medication helpfulness, and relief from starting backache. Each endpoint consisted of a score on a 5-point rating scale (from 0 or worst outcome to 4 or best outcome). Secondary endpoints included a physician's evaluation of the presence and extent of palpable muscle spasm.
Comparisons of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 mg and placebo groups in both trials established the statistically significant superiority of the 5 mg dose for all three primary endpoints at day 8 and, in the study comparing 5 and 10 mg, at day 3 or 4 as well. A similar effect was observed with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 10 mg (all endpoints). Physician-assessed secondary endpoints also showed that cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 mg was associated with a greater reduction in palpable muscle spasm than placebo.
Analysis of the data from controlled studies shows that cyclobenzaprine produces clinical improvement whether or not sedation occurs.
Surveillance ProgramA post-marketing surveillance program was carried out in 7607 patients with acute musculoskeletal disorders, and included 297 patients treated with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 10 mg for 30 days or longer. The overall effectiveness of cyclobenzaprine was similar to that observed in the double-blind controlled studies; the overall incidence of adverse effects was less (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Uses
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets are indicated as an adjunct to rest and physical therapy for relief of muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Improvement is manifested by relief of muscle spasm and its associated signs and symptoms, namely, pain, tenderness, limitation of motion, and restriction in activities of daily living.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets should be used only for short periods (up to two or three weeks) because adequate evidence of effectiveness for more prolonged use is not available and because muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions is generally of short duration and specific therapy for longer periods is seldom warranted.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets have not been found effective in the treatment of spasticity associated with cerebral or spinal cord disease, or in children with cerebral palsy.
Hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors or within 14 days after their discontinuation. Hyperpyretic crisis seizures, and deaths have occurred in patients receiving cyclobenzaprine (or structurally similar tricyclic antidepressants) concomitantly with MAO inhibitor drugs.
Acute recovery phase of myocardial infarction, and patients with arrhythmias, heart block or conduction disturbances, or congestive heart failure.
Hyperthyroidism.
Cyclobenzaprine is closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants, e.g., amitriptyline and imipramine. In short term studies for indications other than muscle spasm associated with acute musculoskeletal conditions, and usually at doses somewhat greater than those recommended for skeletal muscle spasm, some of the more serious central nervous system reactions noted with the tricyclic antidepressants have occurred (see WARNINGS, below, and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to produce arrhythmias, sinus tachycardia, prolongation of the conduction time leading to myocardial infarction and stroke.
Cyclobenzaprine may enhance the effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
GeneralBecause of its atropine-like action, cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride should be used with caution in patients with a history of urinary retention, angle-closure glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and in patients taking anticholinergic medication.
Impaired Hepatic FunctionThe plasma concentration of cyclobenzaprine is increased in patients with hepatic impairment (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Hepatic Impairment).
These patients are generally more susceptible to drugs with potentially sedating effects, including cyclobenzaprine. Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in subjects with mild hepatic impairment starting with a 5 mg dose and titrating slowly upward. Due to the lack of data in subjects with more severe hepatic insufficiency, the use of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets in subjects with moderate to severe impairment is not recommended.
Information for PatientsCyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets, especially when used with alcohol or other CNS depressants, may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle. In the elderly, the frequency and severity of adverse events associated with the use of cyclobenzaprine, with or without concomitant medications, is increased. In elderly patients, cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets should be initiated with a 5 mg dose and titrated slowly upward.
Cyclobenzaprine may have life-threatening interactions with MAO inhibitors (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Cyclobenzaprine may enhance the effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
Tricyclic antidepressants may block the antihypertensive action of guanethidine and similarly acting compounds.
Tricyclic antidepressants may enhance the seizure risk in patients taking tramadol.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityIn rats treated with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride for up to 67 weeks at doses of approximately 5 to 40 times the maximum recommended human dose, pale, sometimes enlarged, livers were noted and there was a dose-related hepatocyte vacuolation with lipidosis. In the higher dose groups this microscopic change was seen after 26 weeks and even earlier in rats which died prior to 26 weeks; at lower doses, the change was not seen until after 26 weeks.
Cyclobenzaprine did not affect the onset, incidence or distribution of neoplasia in an 81-week study in the mouse or in a 105-week study in the rat.
At oral doses of up to 10 times the human dose, cyclobenzaprine did not adversely affect the reproductive performance or fertility of male or female rats. Cyclobenzaprine did not demonstrate mutagenic activity in the male mouse at dose levels of up to 20 times the human dose.
PregnancyPregnancy Category B:Reproduction studies have been performed in rats, mice and rabbits at doses up to 20 times the human dose, and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cyclobenzaprine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing MothersIt is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because cyclobenzaprine is closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants, some of which are known to be excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride in pediatric patients below 15 years of age have not been established.
Use in the ElderlyThe plasma concentration of cyclobenzaprine is increased in the elderly (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Elderly ). The elderly may also be more at risk for CNS adverse events such as hallucinations and confusion, cardiac events resulting in falls or other sequelae, drug-drug and drug-disease interactions. For these reasons, in the elderly, cyclobenzaprine should be used only if clearly needed. In such patients cyclobenzaprine should be initiated with a 5 mg dose and titrated slowly upward.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Incidence of most common adverse reactions in the 2 double-blind, placebo-controlled 5 mg studies (incidence of greater than 3% on cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride 5 mg):
|
|
Cyclobenzaprine HCl 5 mg N=464 |
Cyclobenzaprine HCl 10 mg N=249 |
Placebo N=469 |
| Drowsiness |
29% |
38% |
10% |
| Dry Mouth |
21% |
32% |
7% |
| Fatigue |
6% |
6% |
3% |
| Headache |
5% |
5% |
8% |
Adverse reactions which were reported in 1% to 3% of the patients were: abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, nausea, irritability, mental acuity decreased, nervousness, upper respiratory infection, and pharyngitis.
The following list of adverse reactions is based on the experience in 473 patients treated with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 10 mg in additional controlled clinical studies, 7607 patients in the post-marketing surveillance program, and reports received since the drug was marketed. The overall incidence of adverse reactions among patients in the surveillance program was less than the incidence in the controlled clinical studies.
The adverse reactions reported most frequently with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride were drowsiness, dry mouth and dizziness. The incidence of these common adverse reactions was lower in the surveillance program than in the controlled clinical studies:
Note: Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 10 mg data are from one clinical trial. Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets 5 mg and placebo data are from two studies.
|
|
Clinical Studies With Cyclobenzaprine HCl 10 mg |
Surveillance Progam With Cyclobenzaprine HCl 10 mg |
| Drowsiness |
39% |
16% |
| Dry Mouth |
27% |
7% |
| Dizziness |
11% |
3% |
Among the less frequent adverse reactions, there was no appreciable difference in incidence in controlled clinical studies or in the surveillance program. Adverse reactions which were reported in 1% to 3% of the patients were: fatigue/tiredness, asthenia, nausea, constipation, dyspepsia, unpleasant taste, blurred vision, headache, nervousness, and confusion.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in post-marketing experience or with an incidence of less than 1% of patients in clinical trials with the 10 mg tablet:
Body as a Whole: Syncope; malaise.
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia; arrhythmia; vasodilatation;
palpitation; hypotension.
Digestive: Vomiting;
anorexia; diarrhea; gastrointestinal pain; gastritis; thirst; flatulence; edema
of the tongue; abnormal liver function and rare reports of hepatitis, jaundice
and cholestasis.
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylaxis;
angioedema; pruritus; facial edema; urticaria; rash.
Musculoskeletal: Local weakness.
Nervous System and Psychiatric: Seizures, ataxia; vertigo;
dysarthria; tremors; hypertonia; convulsions; muscle twitching; disorientation;
insomnia; depressed mood; abnormal sensations; anxiety; agitation; psychosis,
abnormal thinking and dreaming; hallucinations; excitement; paresthesia;
diplopia.
Skin: Sweating.
Special Senses: Ageusia; tinnitus.
Urogenital: Urinary frequency and/or retention.
Causal Relationship Unknown
Other reactions, reported rarely for cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride under circumstances where a causal relationship could not be established or reported for other tricyclic drugs, are listed to serve as alerting information to physicians:
Body as a Whole: Chest pain; edema.
Cardiovascular: Hypertension; myocardial infarction; heart
block; stroke.
Digestive: Paralytic ileus; tongue
discoloration; stomatitis; parotid swelling.
Endocrine: Inappropriate ADH syndrome.
Hematic and Lymphatic: Purpura; bone marrow depression;
leukopenia; eosinophilia; thrombocytopenia.
Metabolic,
Nutritional and Immune: Elevation and lowering of blood sugar levels;
weight gain or loss.
Musculoskeletal:
Myalgia.
Nervous System and Psychiatric:
Decreased or increased libido; abnormal gait; delusions; aggressive behavior;
paranoia; peripheral neuropathy; Bell's palsy; alteration in EEG patterns;
extrapyramidal symptoms.
Respiratory:
Dyspnea.
Skin: Photosensitization;
alopecia.
Urogenital: Impaired urination;
dilatation of urinary tract; impotence; testicular swelling; gynecomastia;
breast enlargement; galactorrhea.
Pharmacologic similarities among the tricyclic drugs require that certain withdrawal symptoms be considered when cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is administered, even though they have not been reported to occur with this drug. Abrupt cessation of treatment after prolonged administration rarely may produce nausea, headache, and malaise. These are not indicative of addiction.
For most patients, the recommended dose of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets is 5 mg three times a day. Based on individual patient response, the dose may be increased to 10 mg three times a day. Use of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets for periods longer than two or three weeks is not recommended (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE).
Less frequent dosing should be considered for hepatically impaired or elderly patients (see PRECAUTIONS, Impaired Hepatic Function , and Use in the Elderly ).
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
CCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Theramine acts by restoring and maintaining the balance of the neurotransmitters GABA, nitric oxide, serotonin, and acetylcholine that are associated with pain disorders and inflammatory conditions. Theramine stimulates the production ACTH to reduce inflammation.
Metabolism
The amino acids in Theramine are primarily absorbed by the stomach and small intestines. All cells metabolize the amino acids in Theramine. Circulating tryptophan, arginine and choline blood levels determine the production of serotonin, nitric oxide, and acetylcholine.
Excretion
Theramine is not an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4. These isoenzymes are principally responsible for 95% of all detoxification of drugs, with CYP3A4 being responsible for detoxification of roughly 50% of drugs. Amino acids do not appear to have an effect on drug metabolizing enzymes.
Uses
INDICATIONS FOR USE
Theramine is intended for the clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes of pain disorders and inflammatory conditions.
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
Administration of Theramine has demonstrated significant reduction in symptoms of pain and inflammation in patients with acute and chronic pain when used
for the dietary management of the metabolic processes associated with pain disorders and inflammatory conditions. Administration of Theramine results in
the induction and maintenance of pain relief in patients with pain disorders and inflammatory conditions.
PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
Theramine is contraindicated in an extremely small number of patients with hypersensitivity to any of the nutritional components of Theramine.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Ingestion of L-Tryptophan, L-Arginine, or Choline at high doses of up to 15 grams daily is generally well tolerated. The most common adverse reactions of higher
doses — from 15 to 30 grams daily — are nausea, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Theramine contains less than 1 gram per dose of amino acids however, some patients
may experience these symptoms at lower doses. The total combined amount of amino acids in each Theramine capsule does not exceed 300 mg.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Theramine does not directly influence the pharmacokinetics of prescription drugs. Clinical experience has shown that administration of Theramine may allow for lowering the dose of co-administered drugs under physician supervision.
OVERDOSE
There is a negligible risk of overdose with Theramine as the total amount of amino acids in a one month supply (90 capsules) is less than 30 grams. Overdose symptoms may include diarrhea, weakness, and nausea.
POST-MARKETING SURVEILLANCE
Post-marketing surveillance has shown no serious adverse reactions. Reported cases of mild rash and itching may have been associated with allergies to Theramine flavonoid ingredients, including Cinnamon, Cocoa, and Grape Seed. These reactions were temporary, transient in nature and subsided within 24-hours.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Administration
For the dietary management of the metabolic processes associated with pain disorders and inflammatory conditions. Take two (2) capsules every four hours or as directed by physician. As with most amino acid formulations Theramine should be taken without food to increase the absorption of key ingredients.
How Supplied
Theramine is supplied in purple and white, size 0 capsules in bottles of 60 and 90 capsules.
Physician Supervision
Theramine is a Medical Food product available by prescription only and may be used per FDA law, and product labeling only while the patient is under ongoing physician supervision.
U.S. patent pending
Manufactured by Arizona Nutritional Supplements, Inc. Chandler AZ 85225
Distributed exclusively by Physician Therapeutics LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Targeted Medical Pharma Inc. Los Angeles, CA
www.ptlcentral.com NDC: 68405-008-02 NDC: 68405-008-03
Storage
Store in a cool dry place 45-90ο F (8-32ο C) relative humidity below 50%. Theramine is supplied in a recyclable plastic bottle with a child-resistant cap.
68405-008-02 Directions for use: Must be administered under physician supervision. For adults only. As a Medical Food, take one (1) or two (2) capsules every four hours or as directed by physician. For the dietary management of Myalgia. Contains no added sugar, starch, wheat, yeast, preservatives, artificial flavor. Storage: Keep tightly closed in a cool dry place 8-32°C (45-90°F), relative humidity, below 50%. Warning: Keep this product out of the reach of children. NDC# 68405-008-02 LOT# 007007 PHYSICIAN THERAPEUTICS THERAMINE Medical Food Rx only 60 Capsules Ingredients: Each serving (per 2 capsules) contains: Proprietary Amino Acid Formulation Whey Protein Hydrolysate (milk sourced isolate), L-Arginine (as L-Arginine HCl), L-Histidine HCI, L-Glutamine, L-Serine Gamma Amino Butyric Acid Choline Bitartrate Griffonia Seed Extract (5-HTP) Cocoa Extract (6% Theobromine) Grape Seed Extract (85% Polyphenols) Cinnamon (bark) Other Ingredients: Gelatin, Tricalcium Phosphate, Silicon Dioxide, Magnesium Stearate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Titanium Dioxide, FDandC Red #3, FDandC Blue #1. Distributed exclusively by: Physicians Therapeutics A Division of Targeted Medical Pharma, Inc. Los Angeles, CA 90077 www.ptlcentral.com US Patent 7,582,315; 7,585,523; 7,595,067; 7,601,369. LOT 007007 EXP 08/13
A Convenience Packed Medical Food and Drug Therabenzaprine-60 PHYSICIAN THERAPEUTICS > Theramine 60 Capsules > Cyclobenzaprine 10 mg 60 Tablets No Refills Without Physician Authorization Rx Only NDC# 68405-580-26 of this co-pack


Therabenzaprine-60CYCLOBENZAPRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, .GAMMA.-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID KIT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||