Timolol GFS
Falcon Pharmaceuticals, Ltd.
Alcon Laboratories, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Timolol GFS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Timolol GFS.Timolol GFS (timolol maleate ophthalmic gel forming solution) 0.25% and 0.5%, Sterile topical ophthalmic dropsInitial U.S. Approval: 1978INDICATIONS AND USAGETimolol GFS is a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor indicated for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma ( 1 ).RECENT MAJOR CHANGESUse in Specific Populations, Pediatric Use (8.4). 6/2007DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION• Instill one drop in the affected eye(s) once daily ( 2 ).DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS• 5 mL size bottle filled with 2.5 mL or 5 mL of 0.25% or 0.5% sterile ophthalmic gel forming solution ( 3 ).CONTRAINDICATIONS• Bronchial asthma (or history of) ( 4 )• Severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( 4 )• Sinus bradycardia ( 4 )• Second or third degree atrioventricular block ( 4 )• Overt cardiac failure ( 4 )• Cardiogenic shock ( 4 )• Hypersensitivity to any component of this product ( 4 )WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS• Same adverse reactions found with systemic administration of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may occur with topical ophthalmic administration ( 5.1 ).• Beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may mask signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and should be administered with caution in diabetic patients subject to hypoglycemia ( 5.5 ).• Beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may mask certain clinical signs (e.g. tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism ( 5.6 ).Side EffectsMost common adverse reactions occur upon instillation and include transient blurred vision, burning, and stinging ( 6.1 ). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alcon Laboratories, Inc. at 1-800-757-9195 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS• Oral beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may have additive effects ( 7.1 )• Digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects ( 7.2 )• Catecholamine-depleting drugs may have additive effects ( 7.3 )• Quinidine may have additive effects ( 7.4 )
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 TIMOLOL GFS INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 TIMOLOL GFS DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 TIMOLOL GFS CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 General
- 5.2 Cardiac Failure
- 5.3 Bronchospasm and Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 5.4 Surgical Anesthesia
- 5.5 Diabetes Mellitus
- 5.6 Thyrotoxicosis
- 5.7 Cerebrovascular Insufficiency
- 5.8 Bacterial Keratitis
- 5.9 Choroidal Detachment
- 5.10 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- 5.11 Atopy/Anaphylaxis
- 5.12 Muscle Weakness
- 6 TIMOLOL GFS ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 TIMOLOL GFS DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Timolol GFS 0.25% and 0.5% are indicated for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop of Timolol GFS (either 0.25% or 0.5%) in the affected eye(s) once daily. It may be used alone or in combination with other intraocular pressure lowering medications.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
5 mL size bottle filled with 2.5 mL or 5 mL of 0.25% or 0.5% sterile ophthalmic gel forming solution
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Timolol GFS is contraindicated in patients with:
• bronchial asthma
• history of bronchial asthma
• severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
• sinus bradycardia
• second or third degree atrioventricular block
• overt cardiac failure
• cardiogenic shock
• hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 General
As with many topically applied ophthalmic drugs, this drug is absorbed systemically.
The same adverse reactions found with systemic administration of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may occur with topical ophthalmic administration. For example, severe respiratory reactions and cardiac reactions, including death due to bronchospasm in patients with asthma, and death due to cardiac failure, have been reported following systemic or ophthalmic administration of timolol maleate [see Contraindications (4) ].
5.2 Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be essential for support of the circulation in individuals with diminished myocardial contractility, and its inhibition by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may precipitate more severe failure.
In patients without a history of cardiac failure, continued depression of the myocardium with beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of cardiac failure, Timolol GFS should be discontinued.
5.3 Bronchospasm and Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Bronchospasm may occur. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., chronic bronchitis, emphysema) of mild or moderate severity, bronchospastic disease, or a history of bronchospastic disease (other than bronchial asthma or a history of bronchial asthma, in which Timolol GFS is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ]) should, in general, not receive beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors, including Timolol GFS.
5.4 Surgical Anesthesia
The necessity or desirability of withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors prior to major surgery is controversial. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade impairs the ability of the heart to respond to beta-adrenergically mediated reflex stimuli. This may augment the risk of general anesthesia in surgical procedures. Some patients receiving beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors have experienced protracted, severe hypotension during anesthesia. Difficulty in restarting and maintaining the heartbeat has also been reported. In patients undergoing elective surgery, consider gradual withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors. If necessary during surgery, the effects of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may be reversed by sufficient doses of adrenergic agonists.
5.5 Diabetes Mellitus
Beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors should be administered with caution in diabetic patients subject to hypoglycemia who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
5.6 Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may mask certain clinical signs (e.g. tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors that might precipitate a thyroid storm.
5.7 Cerebrovascular Insufficiency
Because of potential effects of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors on blood pressure and pulse, these agents should be used with caution in patients with cerebrovascular insufficiency. If signs or symptoms suggesting reduced cerebral blood flow develop following initiation of therapy with Timolol GFS, alternative therapy should be considered.
5.8 Bacterial Keratitis
Bacterial keratitis may occur with use of multiple dose containers of topical ophthalmic products when these containers are inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface. Instruct patients on appropriate instillation techniques [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ].
5.9 Choroidal Detachment
Choroidal detachment after filtration procedures has been reported with the administration of aqueous suppressant (e.g., timolol) therapy.
5.10 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
In patients with angle-closure glaucoma, the immediate objective of treatment is to reopen the angle. This may require constricting the pupil. Timolol GFS has little or no effect on the pupil and should not be used alone in the treatment of angle-closure glaucoma.
5.11 Atopy/Anaphylaxis
While taking beta receptor inhibitors, patients with a history of atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic challenge with such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
5.12 Muscle Weakness
Beta-adrenergic blockade has been reported to potentiate muscle weakness consistent with certain myasthenic symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and generalized weakness). Timolol has been reported to increase muscle weakness in some patients with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical trials with Timolol GFS, transient blurred vision upon instillation of the drop was reported in approximately one in three patients. The frequency of patients reporting burning and stinging upon instillation was approximately one in eight patients which was comparable to that observed for TIMOPTIC*.
Adverse reactions reported in 1-5% of patients were:
Ocular: Blepharitis, conjunctivitis, crusting, discomfort, foreign body sensation, hyperemia, pruritus and tearing;
Systemic: Headache, hypertension, and upper respiratory infections.
In a 3-month, double-masked, active-controlled, multicenter study in pediatric patients, the adverse reactions profile of Timolol GFS 0.25% and 0.5% was comparable to that seen in adult patients.
6.2 Additional Potential Side Effects Associated with Timolol Maleate
The following additional adverse experiences have been reported with the ocular administration of this or other timolol maleate formulations:
BODY AS A WHOLE
Asthenia/fatigue and chest pain.
CARDIOVASCULAR
Bradycardia, arrhythmia, hypotension, hypertension, syncope, heart block, cerebral vascular accident, cerebral ischemia, cardiac failure, worsening of angina pectoris, palpitation, cardiac arrest, pulmonary edema, dizziness, edema, claudication, Raynaud's phenomenon, and cold hands and feet.
DIGESTIVE
Nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, anorexia, and dry mouth.
IMMUNOLOGIC
Systemic lupus erythematosus.
NERVOUS SYSTEM/PSYCHIATRIC
Increase in signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis, paresthesia, somnolence, insomnia, nightmares, behavioral changes and psychic disturbances including confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, depression, disorientation, nervousness, and memory loss.
SKIN
Alopecia and psoriasiform rash or exacerbation of psoriasis.
HYPERSENSITIVITY
Signs and symptoms of systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria and localized and generalized rash.
RESPIRATORY
Bronchospasm (predominantly in patients with pre-existing bronchospastic disease), respiratory failure, dyspnea, nasal congestion, and cough.
ENDOCRINE
Masked symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
SPECIAL SENSES
Signs and symptoms of ocular irritation including blepharitis, keratitis, and dry eyes; ptosis; decreased corneal sensitivity; cystoid macular edema; visual disturbances including refractive changes and diplopia; pseudopemphigoid; choroidal detachment following filtration surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 )]; and tinnitus.
UROGENITAL
Retroperitoneal fibrosis, decreased libido, impotence and Peyronie's disease.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Oral Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Inhibitors
Patients who are receiving a beta-adrenergic receptor inhibiting agent orally and Timolol GFS should be observed for potential additive effects of beta-blockade, both systemic and on intraocular pressure. Patients should not usually receive two topical ophthalmic beta-adrenergic receptor inhibiting agents concurrently.
7.2 Digitalis and Calcium Antagonists
The concomitant use of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibiting agents with digitalis and calcium antagonists may have additive effects in prolonging atrioventricular conduction time.
Caution should be used in the co-administration of beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors, such as Timolol GFS, and oral or intravenous calcium antagonists because of possible atrioventricular conduction disturbances, left ventricular failure, or hypotension. In patients with impaired cardiac function, co-administration should be avoided.
7.3 Catecholamine-Depleting Drugs
Close observation of the patient is recommended when a beta receptor inhibitor is administered to patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs such as reserpine, because of possible additive effects and the production of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia, which may result in vertigo, syncope, or postural hypotension.
7.4 Quinidine
Potentiated systemic beta-blockade (e.g., decreased heart rate) has been reported during combined treatment with quinidine and timolol, possibly because quinidine inhibits the metabolism of timolol via the P-450 enzyme, CYP2D6.
7.5 Clonidine
Oral beta-adrenergic receptor inhibiting agents may exacerbate the rebound hypertension which can follow the withdrawal of clonidine. There have been no reports of exacerbation of rebound hypertension with ophthalmic timolol maleate.
7.6 Injectable Epinephrine
[See Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects
Pregnancy Category C: Teratogenicity studies with timolol in mice, rats, and rabbits at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day (7,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose) demonstrated no evidence of fetal malformations. Although delayed fetal ossification was observed at this dose in rats, there were no adverse effects on postnatal development of offspring. Doses of 1,000 mg/kg/day (142,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose) were maternotoxic in mice and resulted in an increased number of fetal resorptions. Increased fetal resorptions were also seen in rabbits at doses of 14,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose, in this case without apparent maternotoxicity.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Timolol GFS should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Timolol maleate has been detected in human milk following oral and ophthalmic drug administration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Timolol GFS, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and IOP-lowering effect of Timolol GFS 0.25% and 0.5% has been demonstrated in pediatric patients in a 3-month, multicenter, double-masked, active-controlled trial.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
10 OVERDOSAGE
No data are available with regard to human overdose with, or accidental oral ingestion of Timolol GFS. There have been reports of inadvertent overdose with Timolol maleate ophthalmic solution resulting in systemic effects similar to those seen with systemic beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors such as dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, bradycardia, bronchospasm, and cardiac arrest [see also Adverse Reactions (6) ].
Overdosage has been reported with timolol maleate tablets. A 30-year old female ingested 650 mg of timolol maleate tablets (maximum recommended oral daily dose is 60 mg) and experienced second and third degree heart block. She recovered without treatment but approximately two months later developed irregular heartbeat, hypertension, dizziness, tinnitus, faintness, increased pulse rate, and borderline first degree heart block.
An in vitro hemodialysis study, using 14C timolol added to human plasma or whole blood, showed that timolol was readily dialyzed from these fluids; however, a study of patients with renal failure showed that timolol did not dialyze readily.
11 DESCRIPTION
Timolol GFS (timolol maleate ophthalmic gel forming solution) is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitor. Its chemical name is (-)-1-(tert-butylamino)-3-[(4-morpholino-1,2,5-thia diazol-3-yl)oxy]-2-propanol maleate (1:1) (salt).
Timolol maleate possesses an asymmetric carbon atom in its structure and is provided at the levo-isomer. The nominal optical rotation of timolol maleate is:
[α] 25° in 0.1N HCl (C=5%) = -12.2°
405 nm
Its molecular formula is C13H24N4O3S·C4H4O4 and its structural formula is:

Timolol maleate has a molecular weight of 432.50. It is a white, odorless, crystalline powder which is soluble in water, methanol, and alcohol. Timolol GFS is a colorless to nearly colorless, slightly opalescent, and slightly viscous, is supplied as a sterile, isotonic, buffered, aqueous topical ophthalmic solution of timolol maleate in two dosage strengths. Timolol GFS has a pH of approximately 6.9 and an osmolality of approximately 290 mOsmol/kg. Each mL of Timolol GFS 0.25% contains 2.5 mg of timolol (3.4 mg of timolol maleate). Each mL of Timolol GFS 0.5% contains 5.0 mg of timolol (6.8 mg of timolol maleate). Inactive ingredients: xanthan gum, tromethamine, boric acid, mannitol, polysorbate-80, and purified water. Preservative: benzododecinium bromide 0.012%.
Xanthan gum is a purified high molecular weight polysaccharide gum produced from the fermentation by bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. An aqueous solution of xanthan gum, in the presence of tear protein (lysozyme), forms a gel. Upon contact with the precorneal tear film, Timolol GFS forms a gel that is subsequently removed by the flow of tears.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Timolol maleate is a beta1 and beta2 (non-selective) adrenergic receptor inhibitor that does not have significant intrinsic sympathomimetic, direct myocardial depressant, or local anesthetic (membrane-stabilizing) activity. Timolol GFS, when applied topically to the eye, has the action of reducing elevated, as well as normal, intraocular pressure, whether or not accompanied by glaucoma. Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of glaucomatous visual field loss and optic nerve damage. The precise mechanism of the ocular hypotensive action of Timolol GFS is not clearly established at this time. Tonography and fluorophotometry studies of Timolol GFS in man suggest that its predominant action may be related to reduced aqueous formation. However, in some studies, a slight increase in outflow facility was also observed. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade reduces cardiac output in both healthy subjects and patients with heart disease. In patients with severe impairment of myocardial function beta-adrenergic receptor inhibitors may inhibit the stimulatory effect of the sympathetic nervous system necessary to maintain adequate cardiac function. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade in the bronchi and bronchioles results in increased airway resistance from unopposed parasympathetic activities. Such an effect in patients with asthma or other bronchospastic conditions is potentially dangerous.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Because in some patients the intraocular pressure-lowering response to Timolol GFS may require a few weeks to stabilize, evaluation should include a determination of intraocular pressure after approximately 4 weeks of treatment with Timolol GFS. If the patient's intraocular pressure is still not at a satisfactory level on this regimen, concomitant therapy can be considered.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following topical ocular administration of timolol to humans, low concentrations of drug are found in plasma. After bilateral administration of a 0.5% timolol maleate solution to healthy volunteers, maximum plasma concentrations were generally below 5 ng/mL. Dosages higher than one drop of 0.5% Timolol GFS once daily have not been studied.
Pharmacokinetic studies in humans using this gel forming solution formulation were not performed. However, systemic uptake from a gel matrix is expected to be slower than from a non-gel forming solution based on studies using other gel forming solutions. The maximum plasma timolol concentration from the gel forming drop is not expected to exceed those of the 0.5% timolol maleate solution.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a two-year study of timolol maleate administered orally to rats, there was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of adrenal pheochromocytomas in male rats administered 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 42,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose). Similar differences were not observed in rats administered oral doses equivalent to approximately 14,000 times the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose. In a lifetime oral study in mice, there were statistically significant increases in the incidence of benign and malignant pulmonary tumors, benign uterine polyps, and mammary adenocarcinomas in female mice at 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 71,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose), but not at 5 or 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 700 or 7,000, respectively, times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose). In a subsequent study in female mice, in which postmortem examinations were limited to the uterus and the lungs, a statistically significant increase in the incidence of pulmonary tumors was again observed at 500 mg/kg/day. The increased occurrence of mammary adenocarcinomas was associated with elevations in serum prolactin, which occurred in female mice administered oral timolol at 500 mg/kg/day, but not at oral doses of 5 or 50 mg/kg/day. An increased incidence of mammary adenocarcinomas in rodents has been associated with administration of several other therapeutic agents that elevate serum prolactin, but no correlation between serum prolactin levels and mammary tumors has been established in humans. Furthermore, in adult human female subjects who received oral dosages of up to 60 mg of timolol maleate (the maximum recommended human oral dosage), there were no clinically meaningful changes in serum prolactin.
Timolol maleate was devoid of mutagenic potential when tested in vivo (mouse) in the micronucleus test and cytogenetic assay (doses up to 800 mg) and in vitro in a neoplastic cell transformation assay (up to 100 mcg/mL). In Ames tests, the highest concentrations of timolol employed, 5,000 or 10,000 mcg/plate, were associated with statistically significant elevations of revertants observed with tester strain TA 100 (in seven replicate assays), but not in the remaining three strains. In the assays with tester strain TA 100, no consistent dose-response relationship was observed, and the ratio of test to control revertants did not reach 2. A ratio of 2 is usually considered the criterion for a positive Ames test.
Reproduction and fertility studies in rats demonstrated no adverse effect on male or female fertility at doses up to 21,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In controlled, double-masked, multicenter clinical studies, Timolol GFS administered once daily was compared to equivalent concentrations of TIMOPTIC* (timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) [Merck and Co., Inc.] administered twice daily. Timolol GFS once daily was shown to be equally effective in lowering intraocular pressure as the equivalent concentration of TIMOPTIC administered twice daily.
The effect of timolol in lowering intraocular pressure was evident for 24 hours with a single dose of Timolol GFS. Repeated observations over a three-month study period indicate that the intraocular pressure-lowering effect of Timolol GFS was consistent. The results from the clinical trials are shown in the following figures.

Timolol GFS administered once daily had a safety profile similar to that of an equivalent concentration of TIMOPTIC administered twice daily. Due to the physical characteristics of the formulation, transient blurred vision was reported more frequently in patients administered Timolol GFS [see Adverse Reactions (6) ]. Timolol GFS has not been studied in patients wearing contact lenses.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Timolol GFS, 0.25% timolol equivalent and 0.5% timolol equivalent, are both supplied as either a 2.5 mL or 5 mL solution in a 5 mL white polyethylene bottle with a natural polyethylene dropper tip and a yellow polypropylene overcap. Tamper evidence is provided with a shrink band around the closure and neck area of the DROP-TAINER®** package.
• 0.25% 2.5 mL fill NDC 61314-224-25
5 mL fill NDC 61314-224-05
• 0.5% 2.5 mL fill NDC 61314-225-25
5 mL fill NDC 61314-225-05
Storage and Handling
Store at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F).
Protect from light.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
How to Use the DROP-TAINER® Bottle
The DROP-TAINER® bottle is designed to assure the delivery of a precise dose of medication. Before using your DROP-TAINER® bottle, read the complete instructions carefully.
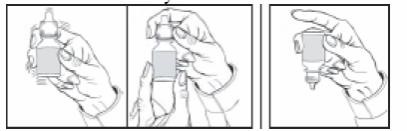
1. If you use other topically applied ophthalmic medications, they should be administered at least 10 minutes before Timolol GFS.
2. Wash hands before each use.
3. Before using the medication for the first time, be sure the Safety Seal on the bottle is unbroken.
4. Tear off the Safety Seal to break the seal.
5. Before each use, shake once and remove the screw cap.
6. Invert the bottle and hold the bottle between your thumb and middle finger, with the tips of the fingers pointing towards you.

7. Tilt your head back and position the bottle above the affected eye. DO NOT TOUCH THE EYE WITH THE TIP OF THE DROPPER.
8. With the opposite hand, place a finger under the eye. Gently pull down until a "V" pocket is made between your eye and lower lid.
9. With the hand holding the bottle, place your index finger on the bottom of the bottle. Push the bottom of the bottle to dispense one drop of medication. DO NOT SQUEEZE THE SIDES OF THE BOTTLE.
10. Repeat 6, 7, 8, and 9 with other eye if instructed to do so.
11. Replace screw cap by turning until firmly touching the bottle.
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye(s) or surrounding structures. Patients should also be instructed that ocular solutions, if handled improperly, could become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye(s) and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Patients should be advised that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
Patients should be instructed to invert the closed container and shake once before each use. It is not necessary to shake the container more than once.
Patients requiring concomitant topical ophthalmic medications should be instructed to administer these at least 10 minutes before instilling Timolol GFS.
Patients with bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, or cardiac failure should be advised not to take this product [see Contraindications (4) ].
Patients should be advised that transient blurred vision or visual disturbance, generally lasting from 30 seconds to 5 minutes, following instillation may impair the ability to perform hazardous tasks such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle.
*TIMOPTIC is a Registered trademark of Merck & Co., Inc.
**DROP-TAINER® is a registered trademark of Alcon Research, Ltd.
Distributed by:
FALCON Pharmaceuticals, Ltd.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134
Manufactured by:
ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134
9005450-0310
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 61314-224-05
Rx Only
FALCON® PHARMACEUTICALS
Timolol GFS
Timolol maleate ophthalmic gel forming solution
0.25%
5 mL STERILE
AFFILIATE OF ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
QUALITY RX

Timolol GFStimolol maleate SOLUTION, GEL FORMING, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Timolol GFStimolol maleate SOLUTION, GEL FORMING, EXTENDED RELEASE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||