Topiramate
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- TOPIRAMATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- TOPIRAMATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- LABOR & DELIVERY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- TOPIRAMATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
TOPIRAMATE DESCRIPTION

CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of ActionPharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Metabolism and Excretion
Pharmacokinetic Interactions
Drug Interactions
Special Populations
Renal Impairment
PRECAUTIONS: Adjustment of Dose in Renal FailureDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hemodialysis
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hepatic Impairment
Age, Gender, and Race
Special Populations: Renal ImpairmentPRECAUTIONS: Adjustment of Dose in Renal FailureDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Pediatric Pharmacokinetics
CLINICAL STUDIES
Epilepsy
Monotherapy Controlled Trial
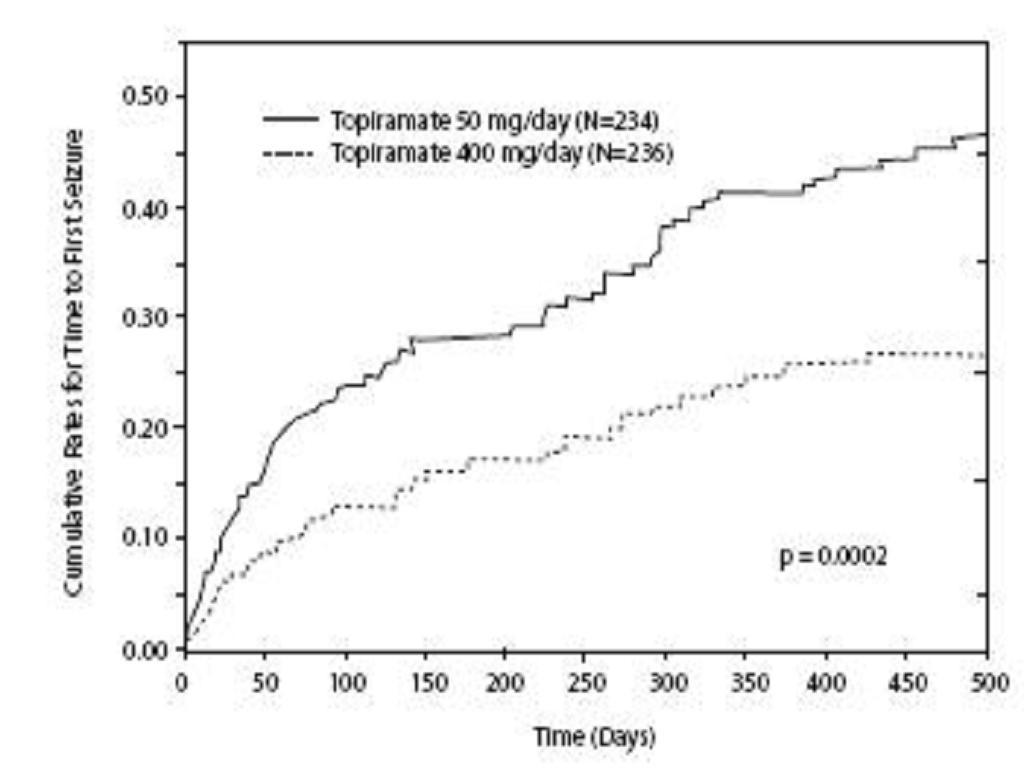
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trials in Adult Patients With Partial Onset Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Pediatric Patients Ages 2 to 16 Years With Partial Onset Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
Target Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)ProtocolStabilization DosePlaceboa2004006008001,000
Protocol Efficacy ResultsPlacebo2004006008001,000mg/kg/day*
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Monotherapy EpilepsyAdjunctive Therapy Epilepsy
TOPIRAMATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Metabolic AcidosisAcute Myopia and Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma
Oligohidrosis and Hyperthermia
Withdrawal of AEDs
Cognitive/Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events
ADVERSE REACTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Valproic Acid UseKidney Stones
Paresthesia
Adjustment of Dose in Renal Failure
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Decreased Hepatic Function
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
PRECAUTIONS: Kidney Stones
LABORATORY TESTS
WARNINGSDRUG INTERACTIONS
AED Co-administeredAED ConcentrationTopiramate ConcentrationPRECAUTIONS, Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Valproic Acid Use
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
LABOR & DELIVERY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
WARNINGSGERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONRace and Gender Effects
TOPIRAMATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Monotherapy Epilepsy
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Body System/ Adverse Event50400(N=160)(N=159)
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)bBody System/ Adverse Event50400(N=57)(N=57)
Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy
Incidence in Epilepsy Controlled Clinical Trials Adjunctive TherapyPartial Onset Seizures, Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures, and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
Other Adverse Events Observed During Double-Blind Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy Trials
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Body System/ Adverse EventcPlacebo (N=291)200-400 ( N=183)600-1,000 (N=414)
Incidence in Study 119Add-On TherapyAdults with Partial Onset Seizures
Body System/Adverse EventcTopiramate Dosage (mg/day)Placebo (N=92)200 (N=171)
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Adverse EventPlacebo (N=216)200 (N=45)400 (N=68)600-1,000 (N=414)
Body System/Adverse EventPlacebo (N=101)Topiramate (N=98)
Other Adverse Events Observed During All Epilepsy Clinical Trials
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
WARNINGS
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
EpilepsyMonotherapy Use
Adjunctive Therapy Use
Adults (17 Years of Age and Over) - Partial Seizures, Primary Generalized Tonic- Clonic Seizures, or Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
CLINICAL STUDIES, Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trials in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
CLINICAL STUDIES, Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Patients with Renal Impairment
Geriatric Patients (Ages 65 Years and Over)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Patients with Renal ImpairmentCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations: Age, Gender, and Race
Patients with Hepatic Disease
HOW SUPPLIED
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
-
● alone to treat seizures in patients 10 years and older
-
● with other medicines to treat seizures in adults and children over age 2
-
● have kidney problems, especially kidney stones, or are getting kidney dialysis
-
● have a history of metabolic acidosis (blood and body fluid abnormality)
-
● have liver problems
-
● have osteoporosis (weak or brittle bones) and/or soft bones (osteomalacia) or decreased bone density (osteopenia)
-
● have lung or breathing problems
-
● have eye problems, especially glaucoma
-
● have diarrhea
-
● have a growth problem
-
● are on a diet high in fat called a ketogenic diet
-
● are having surgery
-
● are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if TOPIRAMATE can harm your unborn baby.
-
● are breastfeeding. TOPIRAMATE may pass into your milk. Talk to your healthcare professional about the best way to feed your baby while taking TOPIRAMATE.
-
● suffer from depression, mood problems or suicidal thoughts or behavior
-
● other medicines that impair or decrease your thinking, concentration, or muscle coordination (e.g. central nervous system depressant medicines).
-
● birth control pills. TOPIRAMATE may make your birth control pills less effective. Tell your healthcare professional if your menstrual bleeding changes while you are taking birth control pills and TOPIRAMATE.
-
● Take TOPIRAMATE exactly as prescribed. Your healthcare professional will usually start you on a low dose of TOPIRAMATE and slowly increase your dose until the best dose is found for you.
-
● TOPIRAMATE Tablets should be swallowed whole. Avoid, chewing the tablets as they may leave a bitter taste.
-
● Never store any medicine and food mixture for use at a later time.
-
● TOPIRAMATE can be taken before, during, or after a meal. Drink plenty of fluids during the day to prevent kidney stones while taking TOPIRAMATE.
-
● If you take too much TOPIRAMATE, call your healthcare professional or poison control center right away or go to an emergency room.
-
● If you miss a single dose of TOPIRAMATE, take it as soon as you can. However, if you are within 6 hours of taking your next scheduled dose, wait until then to take your usual dose of TOPIRAMATE, and skip the missed dose. Do not double your dose. If you have missed more than one dose, you should call your healthcare professional for advice.
-
● Do not stop taking TOPIRAMATE unless a healthcare professional tells you to stop taking TOPIRAMATE. Your healthcare professional will tell you how to slowly stop taking TOPIRAMATE.
-
● If you are taking Topiramate or other antiepileptic drugs for epilepsy or seizures, you may need to avoid activities where loss of consciousness (passing out) could result in serious danger to yourself or those around you (including swimming, driving a car, climbing in high places, etc.). Talk to your doctor before engaging in such activities.
-
● Unless prescribed by your healthcare professional, you should avoid other medicines that also impair or decrease your thinking, concentration, or muscle coordination (e.g. central nervous system depressant medicines).
-
● You should avoid drinking alcohol while taking TOPIRAMATE. Alcohol with TOPIRAMATE can make side effects such as sleepiness and dizziness worse.
-
● Do not drive a car or operate heavy machinery until you know how TOPIRAMATE affects you. TOPIRAMATE can impair your thinking, motor skills, and/or vision.
-
● metabolic acidosis. Metabolic acidosis is a condition that happens when there is too much acid in your blood. Metabolic acidosis can cause symptoms such as tiredness, loss of appetite, irregular heartbeat, and impaired consciousness. Call your healthcare professional right away if you get these symptoms with TOPIRAMATE. Your healthcare professional should do a blood test (measurement of serum bicarbonate) to monitor your bicarbonate level while you are taking TOPIRAMATE.
-
● eye problems. Serious eye problems include:
-
● a sudden decrease in vision (acute myopia) with or without eye pain and
-
● a blockage of fluid in the eye causing increased pressure in the eye (secondary angle closure glaucoma).
-
● decreased sweating (oligohidrosis) and increased body temperature (fever).Patients, especially children, should be watched closely for signs of decreased sweating and fever (increased body temperature), especially in hot temperatures. Some patients may need hospital treatment for this condition.
-
● effects on thinking and alertness. TOPIRAMATE may affect thinking skills and cause confusion, problems with concentration, attention, memory, and/or speech. TOPIRAMATE may cause depression or mood problems, tiredness, and sleepiness. Call your healthcare professional right away if you experience any of these side effects.
-
● dizziness or loss of muscle coordination in patients who take TOPIRAMATE alone or with other seizure medicines.
-
● high blood ammonia levels and effects on mental activities. High ammonia in the blood can affect your mental activities and decrease alertness, can make you feel tired or fatigued, or can cause vomiting. This has happened when TOPIRAMATE has been used with a medicine called valproic acid.
-
● kidney stones. Drink plenty of fluids when taking TOPIRAMATE to decrease your chances of getting kidney stones.
-
● tingling of the arms and legs (paresthesia) is a common side effect of TOPIRAMATE.
-
● Store at 20to 25(6877
-
● Keep TOPIRAMATE and all medicines out of the reach of children.
-
● Tablets - lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, pre-gelatinized starch, lactose monohydrate, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, opadry white (titanium dioxide, hypromellose 3cp, hypromellose 6cp, PEG 400, polysorbate 80) for 25 mg tablets, opadry yellow (titanium dioxide, hypromellose 3cp, hypromellose 6cp, PEG 400, polysorbate 80, iron oxide yellow) for 50 mg tablets, opadry yellow, hypromellose 6cp titanium dioxide, PEG 400, iron oxide yellow, polysorbate 80, iron oxide red) for 100 mg tablets and), opadry pink (titanium dioxide, hypromellose 6cp, PEG 400, iron oxide red) for 200 mg tablets.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

TopiramateTopiramate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!