Topiramate
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- TOPIRAMATE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- CLINICAL STUDIES
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- TOPIRAMATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- LABORATORY TESTS
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- LABOR & DELIVERY
- NURSING MOTHERS
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- TOPIRAMATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
TOPIRAMATE DESCRIPTION
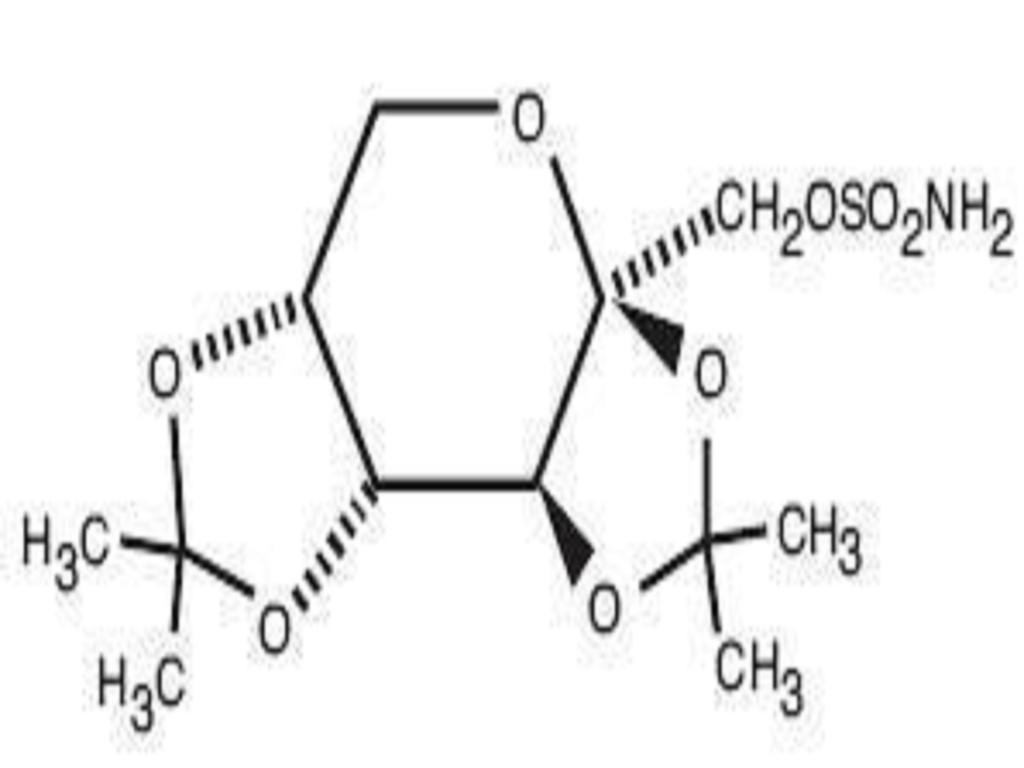
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of ActionPharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
Metabolism and Excretion
Pharmacokinetic Interactions
Drug Interactions
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Renal ImpairmentPRECAUTIONS: Adjustment of Dose in Renal FailureDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hemodialysis
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hepatic Impairment
Age, Gender, and Race
Special Populations: Renal ImpairmentPRECAUTIONS: Adjustment of Dose in Renal FailureDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Pediatric Pharmacokinetics
CLINICAL STUDIES
Epilepsy
Monotherapy Controlled Trial
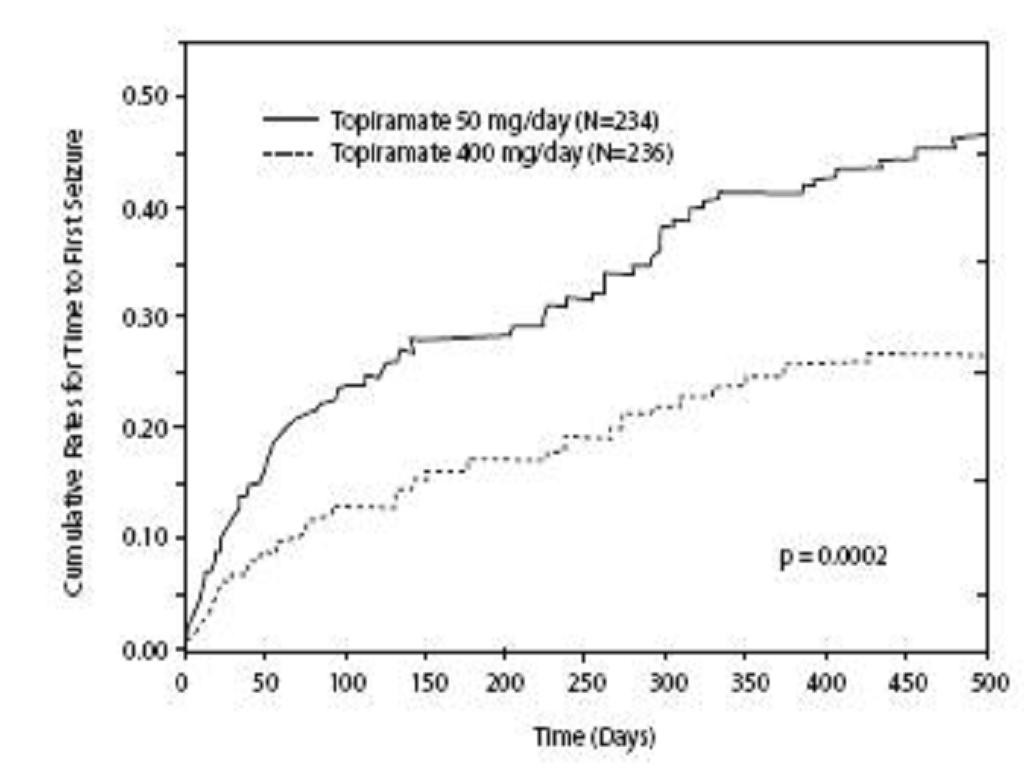
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trials in Adult Patients With Partial Onset Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Pediatric Patients Ages 2 to 16 Years With Partial Onset Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
Target Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)ProtocolStabilization DosePlaceboa2004006008001,000
Protocol Efficacy ResultsPlacebo2004006008001,000mg/kg/day*
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Monotherapy EpilepsyAdjunctive Therapy Epilepsy
TOPIRAMATE CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS
Metabolic AcidosisAcute Myopia and Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma
Oligohidrosis and Hyperthermia
Withdrawal of AEDs
Cognitive/Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events
Adults
Cognitive-Related Dysfunction
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Psychiatric/Behavioral Disturbances
Somnolence/Fatigue
Pediatric Patients
Sudden Unexplained Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP)
PRECAUTIONS
Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Valproic Acid UseKidney Stones
Paresthesia
Adjustment of Dose in Renal Failure
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Decreased Hepatic Function
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
PRECAUTIONS: Kidney Stones
LABORATORY TESTS
WARNINGSDRUG INTERACTIONS
Antiepileptic Drugs
AED Co-administeredAED ConcentrationTopiramate ConcentrationPRECAUTIONS, Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Valproic Acid Use
Other Drug Interactions
Digoxin:
CNS Depressants:
Oral Contraceptives:
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ):
Pioglitazone:
Lithium:
Haloperidol:
Amitriptyline:
Sumatriptan:
Risperidone:
Propranolol:
Dihydroergotamine:
Others:
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
PREGNANCY
Pregnancy Category C.LABOR & DELIVERY
NURSING MOTHERS
PEDIATRIC USE
WARNINGSGERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONRace and Gender Effects
TOPIRAMATE ADVERSE REACTIONS
Monotherapy Epilepsy
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Body System/ Adverse Event50400(N=160)(N=159)
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)bBody System/ Adverse Event50400(N=57)(N=57)
Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy
Incidence in Epilepsy Controlled Clinical Trials Adjunctive TherapyPartial Onset Seizures, Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures, and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
Other Adverse Events Observed During Double-Blind Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy Trials
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Body System/ Adverse EventcPlacebo (N=291)200-400 ( N=183)600-1,000 (N=414)
Incidence in Study 119Add-On TherapyAdults with Partial Onset Seizures
Body System/Adverse EventcTopiramate Dosage (mg/day)Placebo (N=92)200 (N=171)
Topiramate Dosage (mg/day)Adverse EventPlacebo (N=216)200 (N=45)400 (N=68)600-1,000 (N=414)
Body System/Adverse EventPlacebo (N=101)Topiramate (N=98)
Other Adverse Events Observed During All Epilepsy Clinical Trials
Autonomic Nervous System Disorders:
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular Disorders, General:
Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders:
Gastrointestinal System Disorders:
Heart Rate and Rhythm Disorders:
Liver and Biliary System Disorders:
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders:
Musculoskeletal System Disorders:
Neoplasms:
Platelet, Bleeding, and Clotting Disorders:
Psychiatric Disorders:
Red Blood Cell Disorders:
Reproductive Disorders, Male:
Skin and Appendages Disorders:
Special Senses Other, Disorders:
Urinary System Disorders:
Vascular (Extracardiac) Disorders:
Vision Disorders:
White Cell and Reticuloendothelial System Disorders:
Postmarketing and Other Experience
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
WARNINGS
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
EpilepsyMonotherapy Use
Adjunctive Therapy Use
Adults (17 Years of Age and Over) - Partial Seizures, Primary Generalized Tonic- Clonic Seizures, or Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
CLINICAL STUDIES, Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trials in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
CLINICAL STUDIES, Adjunctive Therapy Controlled Trial in Patients With Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Patients with Renal Impairment
Geriatric Patients (Ages 65 Years and Over)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Patients with Renal ImpairmentCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations: Age, Gender, and Race
Patients with Hepatic Disease
HOW SUPPLIED
STORAGE AND HANDLING
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
FDA approved Medication GuideEye Disorders
5.1
Oligohydrosis and Hyperthermia
5.2
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Metabolic Acidosis
5.4
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
5.5
Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy
5.8
Kidney Stones
5.9
Fetal Toxicity
8.18.9
7.3
8.1
SPL MEDGUIDE
-
● any sudden decrease in vision with or without eye pain and redness,
-
● a blockage of fluid in the eye causing increased pressure in the eye (secondary angle closure glaucoma).
-
● These eye problems can lead to permanent loss of vision if not treated. You should call your healthcare provider right away if you have any new eye symptoms.
-
● thoughts about suicide or dying
-
● attempts to commit suicide
-
● new or worse depression
-
● new or worse anxiety
-
● feeling agitated or restless
-
● panic attacks
-
● trouble sleeping (insomnia)
-
● new or worse irritability
-
● acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
-
● acting on dangerous impulses
-
● an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
-
● other unusual changes in behavior or mood
-
● Stopping topiramate tablets suddenly can cause serious problems.
-
● Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
-
● Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
-
● Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
-
● Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
-
● If you take topiramate tablets during pregnancy, your baby has a higher risk for birth defects called cleft lip and cleft palate. These defects can begin early in pregnancy, even before you know you are pregnant.
-
● Cleft lip and cleft palate may happen even in children born to women who are not taking any medicines and do not have other risk factors.
-
● There may be other medicines to treat your condition that have a lower chance of birth defects.
-
● All women of childbearing age should talk to their healthcare providers about using other possible treatments instead of topiramate tablets. If the decision is made to use topiramate tablets, you should use effective birth control (contraception) unless you are planning to become pregnant. You should talk to your doctor about the best kind of birth control to use while you are taking topiramate tablets.
-
● Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking topiramate tablets. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will continue to take topiramate tablets while you are pregnant.
-
● Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking topiramate tablets, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy.
-
● to treat certain types of seizures (partial onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures) in people 10 years and older,
-
● with other medicines to treat certain types of seizures (partial onset seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome) in adults and children 2 years and older.
-
● have or have had depression, mood problems or suicidal thoughts or behavior
-
● have kidney problems, kidney stones or are getting kidney dialysis
-
● have a history of metabolic acidosis (too much acid in the blood)
-
● have liver problems
-
● have osteoporosis, soft bones, or decreased bone density
-
● have lung or breathing problems
-
● have eye problems, especially glaucoma
-
● have diarrhea
-
● have a growth problem
-
● are on a diet high in fat and low in carbohydrates, which is called a ketogenic diet
-
● are having surgery
-
● are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
-
● are breastfeeding. Topiramate passes into breast milk. It is not known if the topiramate that passes into breast milk can harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take topiramate tablets.
-
● Valproic acid
-
● any medicines that impair or decrease your thinking, concentration, or muscle coordination.
-
● birth control pills. Topiramate tablets may make your birth control pills less effective. Tell your healthcare provider if your menstrual bleeding changes while you are taking birth control pills and topiramate tablets.
-
● Take topiramate tablets exactly as prescribed.
-
● Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose without talking to your healthcare provider.
-
● Topiramate tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not chew the tablets. They may leave a bitter taste.
-
● Do not store any medicine and food mixture for later use.
-
● Topiramate tablets can be taken before, during, or after a meal. Drink plenty of fluids during the day. This may help prevent kidney stones while taking topiramate tablets.
-
● If you take too much topiramate tablets, call your healthcare provider or poison control center right away or go to the nearest emergency room.
-
● If you miss a single dose of topiramate tablets, take it as soon as you can. However, if you are within 6 hours of taking your next scheduled dose, wait until then to take your usual dose of topiramate tablets, and skip the missed dose. Do not double your dose. If you have missed more than one dose, you should call your healthcare professional for advice.
-
● Do not stop taking topiramate tablets without talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping topiramate tablets suddenly may cause serious problems. If you have epilepsy and you stop taking topiramate tablets suddenly, you may have seizures that do not stop. Your healthcare provider will tell you how to stop taking topiramate tablets slowly.
-
● Your healthcare provider may do blood tests while you take topiramate tablets.
-
● Do not drink alcohol while taking topiramate tablets. Topiramate tablets and alcohol can affect each other causing side effects such as sleepiness and dizziness.
-
● Do not drive a car or operate heavy machinery until you know how topiramate tablet affects you. Topiramate tablets can slow your thinking and motor skills, and may affect vision.
-
● tiredness
-
● loss of appetite
-
● irregular heartbeat
-
● impaired consciousness
-
● tingling of the arms and legs (paresthesia)
-
● not feeling hungry
-
● nausea
-
● a change in the way foods taste
-
● diarrhea
-
● weight loss
-
● nervousness
-
● upper respiratory tract infection
-
● Store topiramate tablets at 20- 25(68- 77- 30(59- 86[see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. PROTECT FROM MOISTURE.
-
● Keep topiramate tablets in a tightly closed container.
-
● Keep topiramate tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

TopiramateTopiramate TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!