Veterinary PLASMA LYTE 148
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Veterinary PLASMA LYTE 148 Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Side Effects
- Precautions
- Dosage and Administration
- OverDosage
- How Supplied
- Directions for use of plastic container
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
For Animal Use Only
Description
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic isotonic solution in a single dose container for intravenous administration. It contains no antimicrobial agents. Discard unused portion. The pH is adjusted with hydrochloric acid. Composition, osmolarity, pH, ionic concentration and caloric content are shown in Table 1.
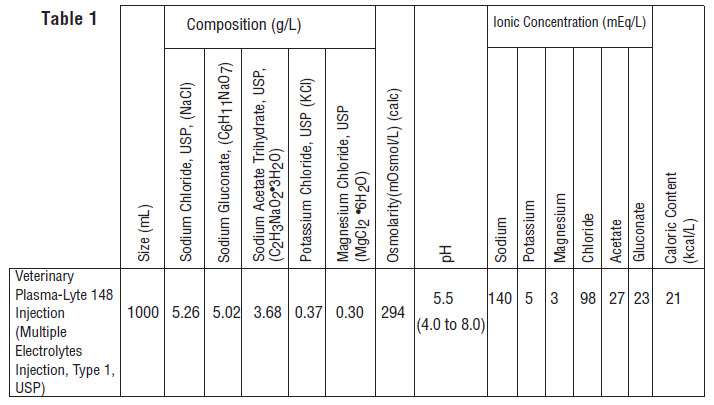
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) administered intravenously has value as a source of water, electrolytes, and calories. Normal physiologic osmolarity range is approximately 280 to 310 mOsmol/L. Administration of substantially hypertonic solutions may cause vein damage.
The plastic container is fabricated from a specially formulated polyvinyl chloride. The amount of water that can permeate from inside the container into the overwrap is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the plastic container can leach out certain of its chemical components in very small amounts within the expiration period, e.g., di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), up to 5 parts per million. However, the safety of the plastic has been confirmed in tests in animals according to USP biological tests for plastic containers as well as by tissue culture toxicity studies.
Clinical Pharmacology
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) has value as a source of water and electrolytes. It is capable of inducing diuresis depending on the clinical condition of the patient.
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) produces a metabolic alkalinizing effect. Acetate and gluconate ions are metabolized ultimately to carbon dioxide and water, which requires the consumption of hydrogen cations.
Veterinary PLASMA LYTE 148 Indications and Usage
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) is indicated as a source of water and electrolytes or as an alkalinizing agent.
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) is compatible with blood or blood components. It may be administered prior to or following the infusion of blood through the same administration set (i.e., as a priming solution), added to or infused concurrently with blood components, or used as a diluent in the transfusion of packed erythrocytes. PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP are equally compatible with blood or blood components.
Contraindications
None known
Warnings
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency, and in clinical states in which there exists edema with sodium retention.
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with hyperkalemia, severe renal failure, and in conditions in which potassium retention is present.
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) should be used with great care in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis. The administration of acetate or gluconate ions should be done with great care in those conditions in which there is an increased level or an impaired utilization of these ions, such as severe hepatic insufficiency.
The intravenous administration of PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states, or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injection. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the injection.
In patients with diminished renal function, administration of PLASMALYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) may result in sodium or potassium retention.
Side Effects
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, and hypervolemia. If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures, and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
Precautions
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation.
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) should be used with caution. Excess administration may result in metabolic alkalosis.
Caution must be exercised in the administration of PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin.
Do not administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact.
Dosage and Administration
As directed by a veterinarian. Dosage is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical condition of the patient as well as laboratory determinations.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
All injections in plastic containers are intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment.
Additives may be incompatible. Complete information is not available. Those additives known to be incompatible should not be used. Consult with pharmacist, if available. If, in the informed judgment of the veterinarian, it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. Do not store solutions containing additives.
OverDosage
In an event of overhydration or solute overload, re-evaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures. See Warnings , Precautions and Adverse Events .
How Supplied
PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) in plastic container is available as shown below:

Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized.
Avoid excessive heat. It is recommended the product be stored at room temperature (25°C/77°F); brief exposure up to 40°C/104°F does not adversely affect the product.
Directions for use of plastic container
To Open
Tear overwrap down side at slit and remove solution container. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Check for minute leaks by squeezing inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be impaired. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below.
Preparation for Administration
1. Suspend container from eyelet support.
2. Remove plastic protector from outlet port at bottom of container.
3. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
To Add Medication
WARNING: Additives may be incompatible.
To add medication before solution administration
1. Prepare medication site.
2. Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.
3. Mix solution and medication thoroughly. For high density medication such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
To add medication during solution administration
1. Close clamp on the set.
2. Prepare medication site.
3. Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.
4. Remove container from IV pole and/or turn to an upright position.
5. Evacuate both ports by squeezing them while container is in the upright position.
6. Mix solution and medication thoroughly.
7. Return container to in use position and continue administration.
CAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Manufactured for:
Abbott Laboratories
North Chicago, IL 60064
For customer service call (888) 299-7416
Printed in USA
07-19-69-401
Rev. August 2012

Principal Display Panel
04917-04-10
 Veterinary PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection
Veterinary PLASMA-LYTE 148 Injection
(Multiple Electrolytes Injection Type 1 USP)
1000 ml

Veterinary PLASMA LYTE 148sodium chloride, sodium gluconate, sodium acetate, potassium chloride and magnesium chloride INJECTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||