Vinorelbine
Teva Parenteral Medicines, Inc.
VINORELBINE Injection USP
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- VINORELBINE DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- VINORELBINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- VINORELBINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- VINORELBINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- VINORELBINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Single-Agent Vinorelbine Injection
- Vinorelbine Injection in Combination with Cisplatin
- Dose Modifications for Vinorelbine Injection
- Dose Modifications for Hematologic Toxicity
- Dose Modifications for Hepatic Insufficiency
- Dose Modifications for Concurrent Hematologic Toxicity and Hepatic Insufficiency
- Dose Modifications for Renal Insufficiency
- Dose Modifications for Neurotoxicity
- Administration Precautions
- Preparation for Administration
- Stability
- HOW SUPPLIED
- REFERENCES
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Rx ONLY
Vinorelbine injection should be administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. This product is for intravenous (IV) use only. Intrathecal administration of other vinca alkaloids has resulted in death. Syringes containing this product should be labeled "WARNING – FOR IV USE ONLY. FATAL if given intrathecally."
Severe granulocytopenia resulting in increased susceptibility to infection may occur. Granulocyte counts should be ≥1000 cells/mm3 prior to the administration of vinorelbine tartrate. The dosage should be adjusted according to complete blood counts with differentials obtained on the day of treatment.
Caution - It is extremely important that the intravenous needle or catheter be properly positioned before vinorelbine tartrate is injected. Administration of vinorelbine tartrate may result in extravasation causing local tissue necrosis and/or thrombophlebitis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Administration Precautions ).
VINORELBINE DESCRIPTION
Vinorelbine Injection USP is for intravenous administration. Each vial contains vinorelbine tartrate, USP equivalent to 10 mg (1-mL vial) or 50 mg (5-mL vial) vinorelbine in Water for Injection. No preservatives or other additives are present. The aqueous solution is sterile and nonpyrogenic.
Vinorelbine tartrate, USP is a semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid with antitumor activity. The chemical name is 3',4'-didehydro-4'-deoxy-C'-norvincaleukoblastine [R-(R*,R*)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:2)(salt)].
Vinorelbine tartrate, USP has the following structure:
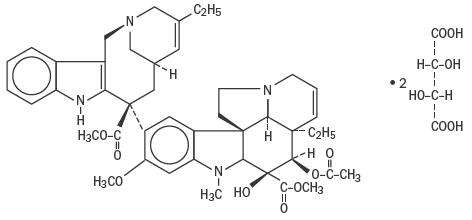
C45H54N4O8•2C4H6O6 M.W. 1079.12
Vinorelbine tartrate, USP is a white to yellow or light brown amorphous powder. The aqueous solubility is >1000 mg/mL in distilled water. The pH of Vinorelbine Injection USP is approximately 3.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Vinorelbine is a vinca alkaloid that interferes with microtubule assembly. The vinca alkaloids are structurally similar compounds comprised of 2 multiringed units, vindoline and catharanthine. Unlike other vinca alkaloids, the catharanthine unit is the site of structural modification for vinorelbine. The antitumor activity of vinorelbine is thought to be due primarily to inhibition of mitosis at metaphase through its interaction with tubulin. Like other vinca alkaloids, vinorelbine may also interfere with: 1) amino acid, cyclic AMP, and glutathione metabolism, 2) calmodulin-dependent Ca++-transport ATPase activity, 3) cellular respiration, and 4) nucleic acid and lipid biosynthesis. In intact tectal plates from mouse embryos, vinorelbine, vincristine, and vinblastine inhibited mitotic microtubule formation at the same concentration (2 µM), inducing a blockade of cells at metaphase. Vincristine produced depolymerization of axonal microtubules at 5 µM, but vinblastine and vinorelbine did not have this effect until concentrations of 30 µM and 40 µM, respectively. These data suggest relative selectivity of vinorelbine for mitotic microtubules.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine were studied in 49 patients who received doses of 30 mg/m2 in 4 clinical trials. Doses were administered by 15- to 20-minute constant-rate infusions. Following intravenous administration, vinorelbine concentration in plasma decays in a triphasic manner. The initial rapid decline primarily represents distribution of drug to peripheral compartments followed by metabolism and excretion of the drug during subsequent phases. The prolonged terminal phase is due to relatively slow efflux of vinorelbine from peripheral compartments. The terminal phase half-life averages 27.7 to 43.6 hours and the mean plasma clearance ranges from 0.97 to 1.26 L/h per kg. Steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) values range from 25.4 to 40.1 L/kg.
Vinorelbine demonstrated high binding to human platelets and lymphocytes. The free fraction was approximately 0.11 in pooled human plasma over a concentration range of 234 to 1169 ng/mL. The binding to plasma constituents in cancer patients ranged from 79.6% to 91.2%. Vinorelbine binding was not altered in the presence of cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, or doxorubicin.
Vinorelbine undergoes substantial hepatic elimination in humans, with large amounts recovered in feces after intravenous administration to humans. Two metabolites of vinorelbine have been identified in human blood, plasma, and urine; vinorelbine N-oxide and deacetylvinorelbine. Deacetylvinorelbine has been demonstrated to be the primary metabolite of vinorelbine in humans, and has been shown to possess antitumor activity similar to vinorelbine. Therapeutic doses of vinorelbine tartrate (30 mg/m2) yield very small, if any, quantifiable levels of either metabolite in blood or urine. The metabolism of vinca alkaloids has been shown to be mediated by hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in the CYP3A subfamily. This metabolic pathway may be impaired in patients with hepatic dysfunction or who are taking concomitant potent inhibitors of these isoenzymes (see PRECAUTIONS ). The effects of renal or hepatic dysfunction on the disposition of vinorelbine have not been assessed, but based on experience with other anticancer vinca alkaloids, dose adjustments are recommended for patients with impaired hepatic function (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
The disposition of radiolabeled vinorelbine given intravenously was studied in a limited number of patients. Approximately 18% and 46% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine and in the feces, respectively. Incomplete recovery in humans is consistent with results in animals where recovery is incomplete, even after prolonged sampling times. A separate study of the urinary excretion of vinorelbine using specific chromatographic analytical methodology showed that 10.9% ± 0.7% of a 30 mg/m2 intravenous dose was excreted unchanged in the urine.
The influence of age on the pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine was examined using data from 44 cancer patients (average age, 56.7 ± 7.8 years; range, 41 to 74 years; with 12 patients ≥60 years and 6 patients ≥65 years) in 3 studies. CL (the mean plasma clearance), t1/2 (the terminal phase half-life), and VZ (the volume of distribution during terminal phase) were independent of age. A separate pharmacokinetic study was conducted in 10 elderly patients with metastatic breast cancer (age range, 66 to 81 years; 3 patients >75 years; normal liver function tests) receiving vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 intravenously. CL, Vss, and t1/2 were similar to those reported for younger adult patients in previous studies. No relationship between age, systemic exposure (AUCo-∞), and hematological toxicity was observed.
The pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine are not influenced by the concurrent administration of cisplatin with vinorelbine tartrate (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions ).
Clinical Trials
Data from 1 randomized clinical study (211 evaluable patients) with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate and 2 randomized clinical trials (1044 patients) using vinorelbine tartrate combined with cisplatin support the use of vinorelbine tartrate in patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Single-Agent Vinorelbine Tartrate
Single-agent vinorelbine tartrate was studied in a North American, randomized clinical trial in which patients with Stage IV NSCLC, no prior chemotherapy, and Karnofsky Performance Status ≥70 were treated with vinorelbine tartrate (30 mg/m2) weekly or 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (425 mg/m2 IV bolus) plus leucovorin (LV) (20 mg/m2 IV bolus) daily for 5 days every 4 weeks. A total of 211 patients were randomized at a 2:1 ratio to vinorelbine tartrate (143) or 5-FU/LV (68). Vinorelbine tartrate showed improved survival time compared to 5-FU/LV. In an intent-to-treat analysis, the median survival time was 30 weeks versus 22 weeks for patients receiving vinorelbine tartrate versus 5-FU/LV, respectively (P = 0.06). The 1-year survival rates were 24% (±4% SE) for vinorelbine tartrate and 16% (±5% SE) for the 5-FU/LV group, using the Kaplan-Meier product-limit estimates. The median survival time with 5-FU/LV was similar to or slightly better than that usually observed in untreated patients with advanced NSCLC, suggesting that the difference was not related to some unknown detrimental effect of 5-FU/LV therapy. The response rates (all partial responses) for vinorelbine tartrate and 5-FU/LV were 12% and 3%, respectively.
Vinorelbine Tartrate in Combination with Cisplatin: Vinorelbine Tartrate plus Cisplatin versus Single-Agent Cisplatin
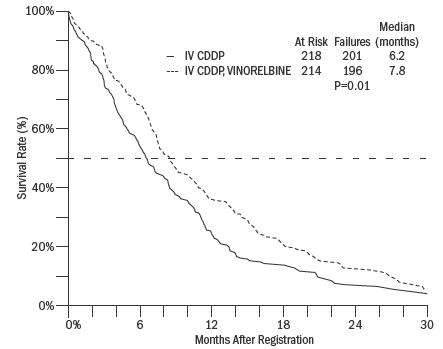
A Phase III open-label, randomized study was conducted which compared vinorelbine tartrate (25 mg/m2 per week) plus cisplatin (100 mg/m2 every 4 weeks) to single-agent cisplatin (100 mg/m2 every 4 weeks) in patients with Stage IV or Stage IIIb NSCLC patients with malignant pleural effusion or multiple lesions in more than one lobe who were not previously treated with chemotherapy. Patients included in the study had a performance status of 0 or 1, and 34% had received prior surgery and/or radiotherapy. Characteristics of the 432 randomized patients are provided in Table 1 . Two hundred and twelve patients received vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin and 210 received single-agent cisplatin. The primary objective of this trial was to compare survival between the 2 treatment groups. Survival ( Figure 1 ) for patients receiving vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin was significantly better compared to the patients who received single-agent cisplatin. The results of this trial are summarized in Table 1 .
Vinorelbine Tartrate plus Cisplatin versus Vindesine plus Cisplatin versus Single-Agent Vinorelbine Tartrate
In a large European clinical trial, 612 patients with Stage III or IV NSCLC, no prior chemotherapy, and WHO Performance Status of 0, 1, or 2 were randomized to treatment with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate (30 mg/m2 per week), vinorelbine tartrate (30 mg/m2 per week) plus cisplatin (120 mg/m2 days 1 and 29, then every 6 weeks), and vindesine (3 mg/m2 per week for 7 weeks, then every other week) plus cisplatin (120 mg/m2 days 1 and 29, then every 6 weeks). Patient characteristics are provided in Table 1 . Survival was longer in patients treated with vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin compared to those treated with vindesine plus cisplatin ( Figure 2 ). Study results are summarized in Table 1 .
Dose-Ranging Study
A dose-ranging study of vinorelbine tartrate (20, 25, or 30 mg/m2 per week) plus cisplatin (120 mg/m2 days 1 and 29, then every 6 weeks) in 32 patients with NSCLC demonstrated a median survival of 10.2 months. There were no responses at the lowest dose level; the response rate was 33% in the 21 patients treated at the 2 highest dose levels.
| Vinorelbine Tartrate/Cisplatin vs. Single-Agent Cisplatin | Vinorelbine Tartrate/Cisplatin vs. Vindesine/Cisplatin vs. Single-Agent Vinorelbine Tartrate | ||||
| Vinorelbine Tartrate/ Cisplatin |
Cisplatin | Vinorelbine Tartrate/ Cisplatin |
Vindesine/ Cisplatin |
Vinorelbine Tartrate | |
| Demographics | |||||
| Number of patients | 214 | 218 | 206 | 200 | 206 |
| Number of males | 146 | 141 | 182 | 179 | 188 |
| Number of females | 68 | 77 | 24 | 21 | 18 |
| Median age (years) | 63 | 64 | 59 | 59 | 60 |
| Range (years) | 33 to 84 | 37 to 81 | 32 to 75 | 31 to 75 | 30 to 74 |
| Stage of disease | |||||
| Stage IIIA | N/A | N/A | 11% | 11% | 10% |
| Stage IIIB | 8% | 8% | 28% | 25% | 32% |
| Stage IV | 92% | 92% | 50% | 55% | 47% |
| Local recurrence | N/A | N/A | 2% | 3% | 3% |
| Metastatic after surgery | N/A | N/A | 9% | 8% | 9% |
| Histology | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 54% | 52% | 32% | 40% | 28% |
| Squamous | 19% | 22% | 56% | 50% | 56% |
| Large cell | 14% | 14% | 13% | 11% | 16% |
| Unspecified | 13% | 13% | N/A | N/A | N/A |
|
Results
Median survival (months) |
7.8 | 6.2 | 9.2 |
7.4 | 7.2 |
| P value | P = 0.01 | ||||
| 12-Month survival rate | 38% | 22% | 35% | 27% | 30% |
| Overall response | 19% | 8% | 28% |
19% | 14% |
| P value | P < 0.001 | ||||
VINORELBINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Vinorelbine Injection USP is indicated as a single agent or in combination with cisplatin for the first-line treatment of ambulatory patients with unresectable, advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In patients with Stage IV NSCLC, Vinorelbine Injection USP is indicated as a single agent or in combination with cisplatin. In Stage III NSCLC, Vinorelbine Injection USP is indicated in combination with cisplatin.
VINORELBINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
Administration of vinorelbine tartrate injection is contraindicated in patients with pretreatment granulocyte counts <1000 cells/mm3 (see WARNINGS ).
WARNINGS
Vinorelbine tartrate should be administered in carefully adjusted doses by or under the supervision of a physician experienced in the use of cancer chemotherapeutic agents.
Patients treated with vinorelbine tartrate should be frequently monitored for myelosuppression both during and after therapy. Granulocytopenia is dose-limiting. Granulocyte nadirs occur between 7 and 10 days after dosing with granulocyte count recovery usually within the following 7 to 14 days. Complete blood counts with differentials should be performed and results reviewed prior to administering each dose of vinorelbine tartrate. Vinorelbine tartrate should not be administered to patients with granulocyte counts <1000 cells/mm3. Patients developing severe granulocytopenia should be monitored carefully for evidence of infection and/or fever. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for recommended dose adjustments for granulocytopenia.
Acute shortness of breath and severe bronchospasm have been reported infrequently, following the administration of vinorelbine tartrate and other vinca alkaloids, most commonly when the vinca alkaloid was used in combination with mitomycin. These adverse events may require treatment with supplemental oxygen, bronchodilators, and/or corticosteroids, particularly when there is pre-existing pulmonary dysfunction.
Reported cases of interstitial pulmonary changes and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), most of which were fatal, occurred in patients treated with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate. The mean time to onset of these symptoms after vinorelbine administration was 1 week (range 3 to 8 days). Patients with alterations in their baseline pulmonary symptoms or with new onset of dyspnea, cough, hypoxia, or other symptoms should be evaluated promptly.
Vinorelbine tartrate has been reported to cause severe constipation (e.g., Grade 3 to 4), paralytic ileus, intestinal obstruction, necrosis, and/or perforation. Some events have been fatal.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category D
Vinorelbine tartrate may cause fetal harm if administered to a pregnant woman. A single dose of vinorelbine has been shown to be embryo- and/or fetotoxic in mice and rabbits at doses of 9 mg/m2 and 5.5 mg/m2, respectively (one third and one sixth the human dose). At nonmaternotoxic doses, fetal weight was reduced and ossification was delayed. There are no studies in pregnant women. If vinorelbine tartrate is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant during therapy with vinorelbine tartrate.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Most drug-related adverse events of vinorelbine tartrate are reversible. If severe adverse events occur, vinorelbine tartrate should be reduced in dosage or discontinued and appropriate corrective measures taken. Reinstitution of therapy with vinorelbine tartrate should be carried out with caution and alertness as to possible recurrence of toxicity.
Vinorelbine tartrate should be used with extreme caution in patients whose bone marrow reserve may have been compromised by prior irradiation or chemotherapy, or whose marrow function is recovering from the effects of previous chemotherapy (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Administration of vinorelbine tartrate to patients with prior radiation therapy may result in radiation recall reactions (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and Drug Interactions ).
Patients with a prior history or pre-existing neuropathy, regardless of etiology, should be monitored for new or worsening signs and symptoms of neuropathy while receiving vinorelbine tartrate.
Care must be taken to avoid contamination of the eye with concentrations of vinorelbine tartrate used clinically. Severe irritation of the eye has been reported with accidental exposure to another vinca alkaloid. If exposure occurs, the eye should immediately be thoroughly flushed with water.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed that the major acute toxicities of vinorelbine tartrate are related to bone marrow toxicity, specifically granulocytopenia with increased susceptibility to infection. They should be advised to report fever or chills immediately. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant during treatment. Patients should be advised to contact their physician if they experience increased shortness of breath, cough, or other new pulmonary symptoms, or if they experience symptoms of abdominal pain or constipation.
Laboratory Tests
Since dose-limiting clinical toxicity is the result of depression of the white blood cell count, it is imperative that complete blood counts with differentials be obtained and reviewed on the day of treatment prior to each dose of vinorelbine tartrate (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, Hematologic ).
Hepatic
There is no evidence that the toxicity of vinorelbine tartrate is enhanced in patients with elevated liver enzymes. No data are available for patients with severe baseline cholestasis, but the liver plays an important role in the metabolism of vinorelbine tartrate. Because clinical experience in patients with severe liver disease is limited, caution should be exercised when administering vinorelbine tartrate to patients with severe hepatic injury or impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Drug Interactions
Acute pulmonary reactions have been reported with vinorelbine tartrate and other anticancer vinca alkaloids used in conjunction with mitomycin. Although the pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine are not influenced by the concurrent administration of cisplatin, the incidence of granulocytopenia with vinorelbine tartrate used in combination with cisplatin is significantly higher than with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate. Patients who receive vinorelbine tartrate and paclitaxel, either concomitantly or sequentially, should be monitored for signs and symptoms of neuropathy. Administration of vinorelbine tartrate to patients with prior or concomitant radiation therapy may result in radiosensitizing effects.
Caution should be exercised in patients concurrently taking drugs known to inhibit drug metabolism by hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in the CYP3A subfamily, or in patients with hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of vinorelbine tartrate with an inhibitor of this metabolic pathway may cause an earlier onset and/or an increased severity of side effects.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of vinorelbine tartrate has not been studied. Vinorelbine has been shown to affect chromosome number and possibly structure in vivo (polyploidy in bone marrow cells from Chinese hamsters and a positive micronucleus test in mice). It was not mutagenic in the Ames test and gave inconclusive results in the mouse lymphoma TK Locus assay. The significance of these or other short-term test results for human risk is unknown. Vinorelbine did not affect fertility to a statistically significant extent when administered to rats on either a once-weekly (9 mg/m2, approximately one third the human dose) or alternate-day schedule (4.2 mg/m2, approximately one seventh the human dose) prior to and during mating. However, biweekly administration for 13 or 26 weeks in the rat at 2.1 and 7.2 mg/m2 (approximately one fifteenth and one fourth the human dose) resulted in decreased spermatogenesis and prostate/seminal vesicle secretion.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category D
See WARNINGS section.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether the drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from vinorelbine tartrate, it is recommended that nursing be discontinued in women who are receiving therapy with vinorelbine tartrate.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of vinorelbine tartrate injection in pediatric patients have not been established. Data from a single arm study in 46 patients with recurrent solid malignant tumors, including rhabdomyosarcoma/undifferentiated sarcoma, neuroblastoma, and CNS tumors, at doses similar to those used in adults showed no meaningful clinical activity. Toxicities were similar to those reported in adult patients
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients in North American clinical studies of IV vinorelbine tartrate, approximately one third were 65 years of age or greater. No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between these patients and younger adult patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger adult patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
The pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine in elderly and younger adult patients are similar (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ).
VINORELBINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
The pattern of adverse reactions is similar whether vinorelbine tartrate is used as a single agent or in combination. Adverse reactions from studies with single-agent and combination use of vinorelbine tartrate are summarized in Tables 2 to 4.
Single-Agent Vinorelbine Tartrate
Data in the following table are based on the experience of 365 patients (143 patients with NSCLC; 222 patients with advanced breast cancer) treated with IV vinorelbine tartrate as a single agent in 3 clinical studies. The dosing schedule in each study was 30 mg/m2 vinorelbine tartrate on a weekly basis.
| Adverse Event | All Patients (n = 365) |
NSCLC (n = 143) |
||||
| Bone Marrow | ||||||
| Granulocytopenia | <2000 cells/mm3 | 90% | 80% | |||
| <500 cells/mm3 | 36% | 29% | ||||
| Leukopenia | <4000 cells/mm3 | 92% | 81% | |||
| <1000 cells/mm3 | 15% | 12% | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia | <100,000 cells/mm3 | 5% | 4% | |||
| <50,000 cells/mm3 | 1% | 1% | ||||
| Anemia | <11 g/dL | 83% | 77% | |||
| <8 g/dL | 9% | 1% | ||||
| Hospitalizations due to granulocytopenic complications | 9% | 8% | ||||
| Adverse Event | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |||
| All Patients | NSCLC | All Patients | NSCLC | All Patients | NSCLC | |
| Clinical Chemistry Elevations | ||||||
| Total Bilirubin (n = 351) | 13% | 9% | 4% | 3% | 3% | 2% |
| SGOT (n = 346) | 67% | 54% | 5% | 2% | 1% | 1% |
| General | ||||||
| Asthenia | 36% | 27% | 7% | 5% | 0% | 0% |
| Injection Site Reactions | 28% | 38% | 2% | 5% | 0% | 0% |
| Injection Site Pain | 16% | 13% | 2% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Phlebitis | 7% | 10% | <1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Digestive | ||||||
| Nausea | 44% | 34% | 2% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Vomiting | 20% | 15% | 2% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Constipation | 35% | 29% | 3% | 2% | 0% | 0% |
| Diarrhea | 17% | 13% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
Peripheral Neuropathy |
25% | 20% | 1% | 1% | <1% | 0% |
| Dyspnea | 7% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 1% | 0% |
| Alopecia | 12% | 12% | ≤1% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
Hematologic
Granulocytopenia is the major dose-limiting toxicity with vinorelbine tartrate. Dose adjustments are required for hematologic toxicity and hepatic insufficiency (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ). Granulocytopenia was generally reversible and not cumulative over time. Granulocyte nadirs occurred 7 to 10 days after the dose, with granulocyte recovery usually within the following 7 to 14 days. Granulocytopenia resulted in hospitalizations for fever and/or sepsis in 8% of patients. Septic deaths occurred in approximately 1% of patients. Prophylactic hematologic growth factors have not been routinely used with vinorelbine tartrate. If medically necessary, growth factors may be administered at recommended doses no earlier than 24 hours after the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Growth factors should not be administered in the period 24 hours before the administration of chemotherapy.
Whole blood and/or packed red blood cells were administered to 18% of patients who received vinorelbine tartrate.
Neurologic
Loss of deep tendon reflexes occurred in less than 5% of patients. The development of severe peripheral neuropathy was infrequent (1%) and generally reversible.
Skin
Like other anticancer vinca alkaloids, vinorelbine tartrate is a moderate vesicant. Injection site reactions, including erythema, pain at injection site, and vein discoloration, occurred in approximately one third of patients; 5% were severe. Chemical phlebitis along the vein proximal to the site of injection was reported in 10% of patients.
Gastrointestinal
Prophylactic administration of antiemetics was not routine in patients treated with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate. Due to the low incidence of severe nausea and vomiting with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate, the use of serotonin antagonists is generally not required.
Hepatic
Transient elevations of liver enzymes were reported without clinical symptoms.
Cardiovascular
Chest pain was reported in 5% of patients. Most reports of chest pain were in patients who had either a history of cardiovascular disease or tumor within the chest. There have been rare reports of myocardial infarction.
Pulmonary
Shortness of breath was reported in 3% of patients; it was severe in 2%. (See WARNINGS .) Interstitial pulmonary changes were documented.
Other
Fatigue occurred in 27% of patients. It was usually mild or moderate but tended to increase with cumulative dosing.
Other toxicities that have been reported in less than 5% of patients include jaw pain, myalgia, arthralgia, and rash. Hemorrhagic cystitis and the syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion were each reported in <1% of patients.
Combination Use
Adverse events for combination use are summarized in Tables 3 and 4 .
Vinorelbine Tartrate in Combination with Cisplatin
Vinorelbine Tartrate plus Cisplatin versus Single-Agent Cisplatin (Table 3)
Myelosuppression was the predominant toxicity in patients receiving combination therapy, Grade 3 and 4 granulocytopenia of 82% compared to 5% in the single-agent cisplatin arm. Fever and/or sepsis related to granulocytopenia occurred in 11% of patients on vinorelbine tartrate and cisplatin compared to 0% on the cisplatin arm.
Four patients on the combination died of granulocytopenia-related sepsis. During this study, the use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor ([G-CSF] filgrastim) was permitted, but not mandated, after the first course of treatment for patients who experienced Grade 3 or 4 granulocytopenia (≤1000 cells/mm3) or in those who developed neutropenic fever between cycles of chemotherapy. Beginning 24 hours after completion of chemotherapy, G-CSF was started at a dose of 5 mcg/kg per day and continued until the total granulocyte count was >1000 cells/mm3 on 2 successive determinations. G-CSF was not administered on the day of treatment.
Grade 3 and 4 anemia occurred more frequently in the combination arm compared to control, 24% vs. 8%, respectively. Thrombocytopenia occurred in 6% of patients treated with vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin compared to 2% of patients treated with cisplatin.
The incidence of severe non-hematologic toxicity was similar among the patients in both treatment groups. Patients receiving vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin compared to single-agent cisplatin experienced more Grade 3 and/or 4 peripheral numbness (2% vs. <1%), phlebitis/thrombosis/embolism (3% vs. <1%), and infection (6% vs. <1%). Grade 3 to 4-constipation and/or ileus occurred in 3% of patients treated with combination therapy and in 1% of patients treated with cisplatin.
Seven deaths were reported on the combination arm; 2 were related to cardiac ischemia, 1 massive cerebrovascular accident, 1 multisystem failure due to an overdose of vinorelbine tartrate, and 3 from febrile neutropenia. One death, secondary to respiratory infection unrelated to granulocytopenia, occurred with single-agent cisplatin.
Vinorelbine Tartrate plus Cisplatin versus Vindesine plus Cisplatin versus Single-Agent Vinorelbine Tartrate (Table 4)
Myelosuppression, specifically Grade 3 and 4 granulocytopenia, was significantly greater with the combination of vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin (79%) than with either single-agent vinorelbine tartrate (53%) or vindesine plus cisplatin (48%), P<0.0001. Hospitalization due to documented sepsis occurred in 4.4% of patients treated with vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin; 2% of patients treated with vindesine and cisplatin, and 4% of patients treated with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate. Grade 3 and 4 thrombocytopenia was infrequent in patients receiving combination chemotherapy and no events were reported with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate.
The incidence of Grade 3 and/or 4 nausea and vomiting, alopecia, and renal toxicity were reported more frequently in the cisplatin-containing combinations compared to single-agent vinorelbine tartrate. Severe local reactions occurred in 2% of patients treated with combinations containing vinorelbine tartrate; none were observed in the vindesine plus cisplatin arm. Grade 3 and 4 neurotoxicity was significantly more frequent in patients receiving vindesine plus cisplatin (17%) compared to vinorelbine tartrate plus cisplatin (7%) and single-agent vinorelbine tartrate (9%) (P< 0.005). Cisplatin did not appear to increase the incidence of neurotoxicity observed with single-agent vinorelbine tartrate.
| Vinorelbine Tartrate 25 mg/m2 plus Cisplatin 100 mg/m2
(n = 212) |
Cisplatin 100 mg/m2
(n = 210) |
|||||
| Adverse Event | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 |
| Bone Marrow | ||||||
| Granulocytopenia | 89% | 22% | 60% | 26% | 4% | 1% |
| Anemia | 88% | 21% | 3% | 72% | 7% | <1% |
| Leukopenia | 88% | 39% | 19% | 31% | <1% | 0% |
| Thrombocytopenia | 29% | 4% | 1% | 21% | 1% | <1% |
| Febrile neutropenia | N/A | N/A | 11% | N/A | N/A | 0% |
| Hepatic | ||||||
| Elevated transaminase | 1% | 0% | 0% | <1% | <1% | 0% |
| Renal | ||||||
| Elevated creatinine | 37% | 2% | 2% | 28% | 4% | <1% |
| Non-Laboratory | ||||||
| Malaise/fatigue/lethargy | 67% | 12% | 0% | 49% | 8% | 0% |
| Vomiting | 60% | 7% | 6% | 60% | 10% | 4% |
| Nausea | 58% | 14% | 0% | 57% | 12% | 0% |
| Anorexia | 46% | 0% | 0% | 37% | 0% | 0% |
| Constipation | 35% | 3% | 0% | 16% | 1% | 0% |
| Alopecia | 34% | 0% | 0% | 14% | 0% | 0% |
| Weight loss | 34% | 1% | 0% | 21% | <1% | 0% |
| Fever without infection | 20% | 2% | 0% | 4% | 0% | 0% |
| Hearing | 18% | 4% | 0% | 18% | 3% | <1% |
| Local (injection site reactions) | 17% | <1% | 0% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Diarrhea | 17% | 2% | <1% | 11% | 1% | <1% |
| Paresthesias | 17% | <1% | 0% | 10% | <1% | 0% |
| Taste alterations | 17% | 0% | 0% | 15% | 0% | 0% |
| Peripheral numbness | 11% | 2% | 0% | 7% | <1% | 0% |
| Myalgia/arthralgia | 12% | <1% | 0% | 3% | <1% | 0% |
| Phlebitis/thrombosis/embolism | 10% | 3% | 0% | <1% | 0% | <1% |
| Weakness | 12% | 2% | <1% | 7% | 2% | 0% |
| Dizziness/vertigo | 9% | <1% | 0% | 3% | <1% | 0% |
| Infection | 11% | 5% | <1% | <1% | <1% | 0% |
| Respiratory infection | 10% | 4% | <1% | 3% | 3% | 0% |
Vinorelbine Tartrate/Cisplatin |
Vindesine/Cisplatin |
Vinorelbine Tartrate  |
|||||||
| Adverse Event | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Grades | Grade 3 | Grade 4 |
| Bone Marrow | |||||||||
| Neutropenia | 95% | 20% | 58% | 79% | 26% | 22% | 85% | 25% | 28% |
| Leukopenia | 94% | 40% | 17% | 82% | 24% | 3% | 83% | 26% | 6% |
| Thrombocytopenia | 15% | 3% | 1% | 10% | 3% | 0.5% | 3% | 0% | 0% |
| Febrile neutropenia | N/A | N/A | 4% | N/A | N/A | 2% | N/A | N/A | 4% |
| Hepatic | |||||||||
Elevated bilirubin |
6% | N/A | N/A | 5% | N/A | N/A | 5% | N/A | N/A |
| Renal | |||||||||
Elevated creatinine |
46% | N/A | N/A | 37% | N/A | N/A | 13% | N/A | N/A |
| Non-Laboratory | |||||||||
| Nausea/vomiting | 74% | 27% | 3% | 72% | 24% | 1% | 31% | 1% | 1% |
| Alopecia | 51% | 7% | 0.5% | 56% | 14% | 0% | 30% | 2% | 0% |
| Ototoxicity | 10% | 1% | 1% | 14% | 1% | 0% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Local reactions | 17% | 2% | 0.5% | 7% | 0% | 0% | 22% | 2% | 0% |
| Diarrhea | 25% | 1.5% | 0% | 24% | 1% | 0% | 12% | 0% | 0.5% |
Neurotoxicity |
44% | 7% | 0% | 58% | 16% | 1% | 44% | 8% | 0.5% |
Observed During Clinical Practice
In addition to the adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been identified during post-approval use of vinorelbine tartrate. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to vinorelbine tartrate.
Body as a Whole: Systemic allergic reactions reported as anaphylaxis, pruritus, urticaria, and angioedema; flushing; and radiation recall events such as dermatitis and esophagitis (see PRECAUTIONS ) have been reported.
Hematologic: Thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolus and deep venous thrombosis, have been reported primarily in seriously ill and debilitated patients with known predisposing risk factors for these events.
Neurologic: Peripheral neurotoxicities such as, but not limited to, muscle weakness and disturbance of gait, have been observed in patients with and without prior symptoms. There may be increased potential for neurotoxicity in patients with pre-existing neuropathy, regardless of etiology, who receive vinorelbine tartrate. Vestibular and auditory deficits have been observed with vinorelbine tartrate, usually when used in combination with cisplatin.
Skin: Injection site reactions, including localized rash and urticaria, blister formation, and skin sloughing have been observed in clinical practice. Some of these reactions may be delayed in appearance.
Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia, mucositis, and pancreatitis have been reported.
Cardiovascular: Hypertension, hypotension, vasodilation, tachycardia, and pulmonary edema have been reported.
Pulmonary: Pneumonia has been reported.
Musculoskeletal: Headache has been reported, with and without other musculoskeletal aches and pains.
Other: Pain in tumor-containing tissue, back pain, and abdominal pain have been reported. Electrolyte abnormalities, including hyponatremia with or without the syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion, have been reported in seriously ill and debilitated patients.
Combination Use: Patients with prior exposure to paclitaxel and who have demonstrated neuropathy should be monitored closely for new or worsening neuropathy. Patients who have experienced neuropathy with previous drug regimens should be monitored for symptoms of neuropathy while receiving vinorelbine tartrate. Vinorelbine tartrate may result in radiosensitizing effects with prior or concomitant radiation therapy (see PRECAUTIONS ).
OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for overdoses of vinorelbine tartrate. Overdoses involving quantities up to 10 times the recommended dose (30 mg/m2) have been reported. The toxicities described were consistent with those listed in the ADVERSE REACTIONS section including paralytic ileus, stomatitis, and esophagitis. Bone marrow aplasia, sepsis, and paresis have also been reported. Fatalities have occurred following overdose of vinorelbine tartrate. If overdosage occurs, general supportive measures together with appropriate blood transfusions, growth factors, and antibiotics should be instituted as deemed necessary by the physician.
VINORELBINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Single-Agent Vinorelbine Injection
The usual initial dose of single-agent vinorelbine injection is 30 mg/m2 administered weekly. The recommended method of administration is an intravenous injection over 6 to 10 minutes. In controlled trials, single-agent vinorelbine injection was given weekly until progression or dose-limiting toxicity.
Vinorelbine Injection in Combination with Cisplatin
Vinorelbine injection may be administered weekly at a dose of 25 mg/m2 in combination with cisplatin given every 4 weeks at a dose of 100 mg/m2.
Blood counts should be checked weekly to determine whether dose reductions of vinorelbine injection and/or cisplatin are necessary. In the SWOG study, most patients required a 50% dose reduction of vinorelbine injection at day 15 of each cycle and a 50% dose reduction of cisplatin by cycle 3.
Vinorelbine injection may also be administered weekly at a dose of 30 mg/m2 in combination with cisplatin, given on days 1 and 29, then every 6 weeks at a dose of 120 mg/m2.
Dose Modifications for Vinorelbine Injection
The dosage should be adjusted according to hematologic toxicity or hepatic insufficiency, whichever results in the lower dose for the corresponding starting dose of vinorelbine injection (see Table 5 ).
Dose Modifications for Hematologic Toxicity
Granulocyte counts should be ≥1000 cells/mm3 prior to the administration of vinorelbine injection. Adjustments in the dosage of vinorelbine injection should be based on granulocyte counts obtained on the day of treatment according to Table 5 .
| Granulocytes on Day of Treatment (cells/mm3) | Percentage of Starting Dose of Vinorelbine Injection |
| ≥1500 | 100% |
| 1000 to 1499 | 50% |
| <1000 | Do not administer. Repeat granulocyte count in 1 week. If 3 consecutive weekly doses are held because granulocyte count is <1000 cells/mm3, discontinue vinorelbine injection. |
| Note: For patients who, during treatment with vinorelbine injection, experienced fever and/or sepsis while granulocytopenic or had 2 consecutive weekly doses held due to granulocytopenia, subsequent doses of vinorelbine injection should be: | |
| ≥1500 | 75% |
| 1000 to 1499 | 37.5% |
| <1000 | See above |
Dose Modifications for Hepatic Insufficiency
Vinorelbine injection should be administered with caution to patients with hepatic insufficiency. In patients who develop hyperbilirubinemia during treatment with vinorelbine injection, the dose should be adjusted for total bilirubin according to Table 6 .
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) |
Percentage of Starting Dose of Vinorelbine Injection |
| ≤2.0 | 100% |
| 2.1 to 3.0 | 50% |
| >3.0 | 25% |
Dose Modifications for Concurrent Hematologic Toxicity and Hepatic Insufficiency
In patients with both hematologic toxicity and hepatic insufficiency, the lower of the doses based on the corresponding starting dose of vinorelbine injection determined from Table 5 and Table 6 should be administered.
Dose Modifications for Renal Insufficiency
No dose adjustments for vinorelbine injection are required for renal insufficiency. Appropriate dose reductions for cisplatin should be made when vinorelbine injection is used in combination.
Dose Modifications for Neurotoxicity
If grade ≥2 neurotoxicity develops, vinorelbine injection should be discontinued.
Administration Precautions
Caution—vinorelbine injection must be administered intravenously. It is extremely important that the intravenous needle or catheter be properly positioned before any vinorelbine injection is injected. Leakage into surrounding tissue during intravenous administration of vinorelbine injection may cause considerable irritation, local tissue necrosis, and/or thrombophlebitis. If extravasation occurs, the injection should be discontinued immediately, and any remaining portion of the dose should then be introduced into another vein. Since there are no established guidelines for the treatment of extravasation injuries with vinorelbine injection, institutional guidelines may be used. The ONS Chemotherapy Guidelines provide additional recommendations for the prevention of extravasation injuries.1
As with other toxic compounds, caution should be exercised in handling and preparing the solution of vinorelbine injection. Skin reactions may occur with accidental exposure. The use of gloves is recommended. If the solution of vinorelbine injection contacts the skin or mucosa, immediately wash the skin or mucosa thoroughly with soap and water. Severe irritation of the eye has been reported with accidental contamination of the eye with another vinca alkaloid. If this happens with vinorelbine injection, the eye should be flushed with water immediately and thoroughly.
Procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be used. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.2–8 There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropriate.
Vinorelbine injection is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Parenteral drug products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. If particulate matter is seen, vinorelbine injection should not be administered.
Preparation for Administration
Vinorelbine injection must be diluted in either a syringe or IV bag using one of the recommended solutions. The diluted vinorelbine injection should be administered over 6 to 10 minutes into the side port of a free-flowing IV closest to the IV bag followed by flushing with at least 75 to 125 mL of one of the solutions. Diluted vinorelbine injection may be used for up to 24 hours under normal room light when stored in polypropylene syringes or polyvinyl chloride bags at 5° to 30°C (41° to 86°F)
Syringe
The calculated dose of vinorelbine injection should be diluted to a concentration between 1.5 and 3 mg/mL. The following solutions may be used for dilution:
5% Dextrose Injection, USP
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
IV Bag
The calculated dose of vinorelbine injection should be diluted to a concentration between 0.5 and 2 mg/mL. The following solutions may be used for dilution:
5% Dextrose Injection, USP
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
5% Dextrose and 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
Ringer's Injection, USP
Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP
Stability
Unopened vials of vinorelbine injection are stable until the date indicated on the package when stored under refrigeration at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) and protected from light in the carton. Unopened vials of vinorelbine injection are stable at temperatures up to 25°C (77°F) for up to 72 hours. This product should not be frozen.
HOW SUPPLIED
Vinorelbine Injection UPS is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution in water for injection, containing 10 mg vinorelbine tartrate, USP per mL. Vinorelbine Injection USP is available as follows:
| NDC Number | Total Contents | Package |
| 0703-4182-01 | 10 mg/1 mL | 1 Single-Use Vial per Carton |
| 0703-4183-01 | 50 mg/5 mL | 1 Single-Use Vial per Carton |
Store the vials under refrigeration at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) in the carton. Protect from light. DO NOT FREEZE.
REFERENCES
- ONS Clinical Practice Committee. Cancer Chemotherapy Guidelines: Recommendations for Practice. Pittsburgh, Pa: Oncology Nursing Society; 1999:32–41.
- Recommendations for the safe handling of parenteral antineoplastic drugs. Washington, DC: Division of Safety, National Institutes of Health; 1983. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service publication NIH 83-2621.
- AMA Council on Scientific Affairs. Guidelines for handling parenteral antineoplastics. JAMA. 1985;253:1590–1591.
- National Study Commission on Cytotoxic Exposure. Recommendations for handling cytotoxic agents. 1987. Available from Louis P. Jeffrey, Chairman, National Study Commission on Cytotoxic Exposure. Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Allied Health Sciences, 179 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115.
- Clinical Oncological Society of Australia. Guidelines and recommendations for safe handling of antineoplastic agents. Med J Australia. 1983;1:426–428.
- Jones RB, Frank R, Mass T. Safe handling of chemotherapeutic agents: a report from the Mount Sinai Medical Center. CA-A Cancer J for Clin. 1983;33:258–263.
- American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. ASHP technical assistance bulletin on handling cytotoxic and hazardous drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990;47:1033–1049
- Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs. (OSHA Work-Practice Guidelines.) Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 1996;53:1669–1685.
Rev. A 3/2013
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Vinorelbine Injection USP 10 mg/mL Single-Use Vial Carton Text
NDC 0703-4182-01 Rx only
VINORELBINE
Injection USP
equivalent to vinorelbine
tartrate, USP
10 mg/mL
1 mL Single-Use Vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE
ONLY
MUST BE DILUTED FOR
ADMINISTRATION
CAUTION: Cytotoxic Agent
TEVA
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Vinorelbine Injection USP 50 mg/5 mL Single-Use Vial Carton Text
NDC 0703-4183-01 Rx only
VINORELBINE
Injection USP
equivalent to vinorelbine
tartrate, USP
50 mg/5 mL
(10 mg/mL)
5 mL Single-Use Vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS USE
ONLY
MUST BE DILUTED FOR
ADMINISTRATION
CAUTION: Cytotoxic Agent
TEVA
VinorelbineVinorelbine INJECTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
VinorelbineVinorelbine INJECTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||