VisionBlue
Dutch Ophthalmic Research Center International B.V.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- VisionBlue Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Precautions
- Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied
- Storage and Handling
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Description
VisionBlue™ (trypan blue ophthalmic solution) 0.06% is a sterile solution of trypan blue (an acid di-azo group dye). VisionBlue™ is a selective tissue staining agent for use as a medical aid in ophthalmic surgery.
Each mL of VisionBlue™ 0.06% contains: 0.6 mg trypan blue; 1.9 mg sodium mono-hydrogen orthophosphate (Na2HPO4.2H2O); 0.3 mg sodium di-hydrogen orthophosphate (NaH2PO4.2H2O); 8.2 mg sodium chloride (NaCl); and water for injection. The pH is 7.3 - 7.6. The osmolality is 257-314 mOsm/kg.
The drug substance trypan blue has the chemical name 3,3’-[(3,3’-dimethyl-4,4’-biphenylylene) bis (azo)] bis(5-amino-4-hydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic acid) tetra sodium salt, a molecular weight of 960.8, a molecular formula of C34H24N6Na4O14S4, and has the following chemical structure:
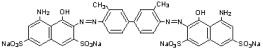
Clinical Pharmacology
VisionBlue™ selectively stains connective tissue structures in the human eye such as the anterior lens capsule of the human crystalline lens.
VisionBlue™ is intended to be applied directly on the anterior lens capsule, staining any portion of the capsule which comes in contact with the dye. Excess dye is washed out of the anterior chamber. The dye does not penetrate the capsule, permitting visualization of the anterior capsule in contrast to the non‑stained lens cortex and inner lens material.
VisionBlue Indications and Usage
Contraindications
VisionBlue™ is contraindicated when a non-hydrated (dry state), hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lens (IOL) is planned to be inserted into the eye because the dye may be absorbed by the IOL and stain the IOL.
Precautions
General
It is recommended that after injection all excess VisionBlue™ be immediately removed from the eye by thorough irrigation of the anterior chamber.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Trypan blue is carcinogenic in rats. Wister/Lewis rats developed lymphomas after receiving subcutaneous injections of 1% trypan blue dosed at 50 mg/kg every other week for 52 weeks (total dose approximately 1,250,000-fold the maximum recommended human dose of 0.06 mg per injection in a 60 kg person, assuming total absorption).
Trypan blue was mutagenic in the Ames test and caused DNA strand breaks in vitro.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C.
Trypan blue is teratogenic in rats, mice, rabbits, hamsters, dogs, guinea pigs, pigs, and chickens. The majority of teratogenicity studies performed involve intravenous, intraperitoneal, or subcutaneous administration in the rat. The teratogenic dose is 50 mg/kg as a single dose or 25 mg/kg/day during embryogenesis in the rat. These doses are approximately 50,000- and 25,000-fold the maximum recommended human dose of 0.06 mg per injection based in a 60 kg person, assuming that the whole dose is completely absorbed. Characteristic anomalies included neural tube, cardiovascular, vertebral, tail, and eye defects. Trypan blue also caused an increase in post-implantation mortality, and decreased fetal weight. In the monkey, trypan blue caused abortions with single or two daily doses of 50 mg/kg between 20th to 25th days of pregnancy, but no apparent increase in birth defects (approximately 50,000-fold maximum recommended human dose of 0.06 mg per injection, assuming total absorption). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Trypan blue should be given to a pregnant woman only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when trypan blue is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of trypan blue have been established in pediatric patients. Use of trypan blue is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study in pediatric patients.
Geriatric use
No overall differences in safety and effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Side Effects
Adverse reactions reported following use of VisionBlue™ include discoloration of high water content hydrogen intraocular lenses (see Contraindications) and inadvertent staining of the posterior lens capsule and vitreous face. Staining of the posterior lens capsule or staining of the vitreous face is generally self limited, lasting up to one week.
Dosage and Administration
Cataract surgery
VisionBlue™ is packaged in a 2.25 mL syringe to which a blunt cannula has to be attached.
After opening the eye, an air bubble is injected into the anterior chamber of the eye in order to minimize dilution of VisionBlue™ by the aqueous. VisionBlue™ is carefully applied onto the anterior lens capsule using a blunt cannula. Sufficient staining is achieved as soon as the dye has contacted the capsule. The anterior chamber is then irrigated with balanced salt solution to remove all excess dye. An anterior capsulotomy can then be performed.
How Supplied
VisionBlue™ 0.06% is supplied as follows:
0.5 mL of VisionBlue™ in a sterile single-use Luer Lok, 2.25 mL glass syringe, grey rubber plunger stopper and tip cap with polypropylene plunger rod in a peel pouch.
Storage and Handling
VisionBlue™ is stored at 15-25ºC (59-77ºF). Protect from direct sunlight.
VisionBlueTrypan Blue INJECTION, SOLUTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||