Warfarin Sodium
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- BOXED WARNING
- WARFARIN SODIUM DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
- WARFARIN SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- PRECAUTIONS
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
- PREGNANCY
- PEDIATRIC USE
- GERIATRIC USE
- WARFARIN SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
- SPL MEDGUIDE
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARFARIN SODIUM DESCRIPTION
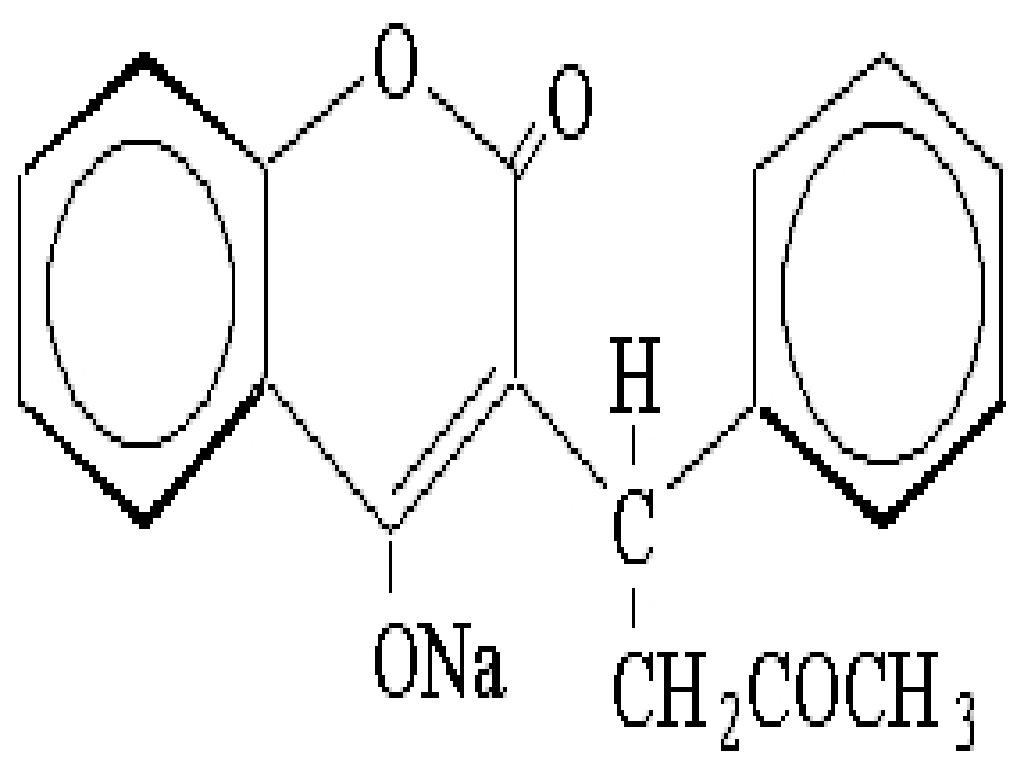
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Distribution
WARNINGS
Metabolism
**
Excretion
Pharmacogenomics
Elderly
Asians
Renal Dysfunction
Hepatic Dysfunction
CLINICAL TRIALS
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Myocardial Infarction
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
*****
Mechanical and Bioprosthetic Heart Valves
INDICATIONS & USAGE
WARFARIN SODIUM CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
Hemorrhagic tendencies or blood dyscrasias.
Recent or contemplated surgery of:
Bleeding tendencies associated with active ulceration or overt bleeding of:
Threatened abortion,
Inadequate laboratory facilities
Unsupervised patients with senility,
Spinal puncture
Miscellaneous
WARNINGS
Lactation
Severe to moderate hepatic or renal insufficiency.
Infectious diseases or disturbances of intestinal flora:
Trauma
Surgery or trauma
Indwelling catheters.
Severe to moderate hypertension.
Known or suspected deficiency in protein C mediated anticoagulant response
Miscellaneous
PRECAUTIONS
Periodic determination of PT/INR is essential.Laboratory Control.PharmacogenomicsDrug-Drug and Drug-Disease Interactions
It is generally good practice to monitor the patient
Drugs may interact with warfarin sodium through pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic mechanisms. Pharmacodynamic mechanisms for drug interactions with warfarin sodium are synergism (impaired hemostasis, reduced clotting factor synthesis), competitive antagonism (vitamin K), and altered physiologic control loop for vitamin K metabolism (hereditary resistance). Pharmacokinetic mechanisms for drug interactions with warfarin sodium are mainly enzyme induction, enzyme inhibition, and reduced plasma protein binding. It is important to note that some drugs may interact by more than one mechanism.
The following factors, alone or in combination, may be responsible for INCREASED PT/INR response:
Endogenous Factors:
Exogenous Factors:
The following factors, alone or in combination, may be responsible for DECREASED PT/INR response:
Endogenous Factors:
Exogenous Factors:
Classes of Drugs
Specific Drugs Reported
Botanical (Herbal) Medicines
-
● Bromelains, danshen, dong quai (Angelica sinensis), garlic, Ginkgo biloba, ginseng, and cranberry products are associated most often with an INCREASE in the effects of warfarin sodium.
-
● Coenzyme Q10 (ubidecarenone) and St. John's wort are associated most often with a DECREASE in the effects of warfarin sodium.
Botanicals that contain coumarins with potential anticoagulant effects:
Miscellaneous botanicals with anticoagulant properties:
Botanicals that contain salicylate and/or have antiplatelet properties:
Botanicals with fibrinolytic properties:
Botanicals with coagulant properties:
Effect on Other Drugs
Considerations for Increased Bleeding Risk
PharmacokineticsDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
CONTRAINDICATIONSPatients should be informed that all warfarin sodium, USP, products represent the same medication, and should not be taken concomitantly, as overdosage may result.CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
CONTRAINDICATIONSPREGNANCY
CONTRAINDICATIONSPEDIATRIC USE
GERIATRIC USE
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONWARFARIN SODIUM ADVERSE REACTIONS
-
● Treatment.)
-
● Bleeding which occurs when the PT/INR is within the therapeutic range warrants diagnostic investigation since it may unmask a previously unsuspected lesion, e.g., tumor, ulcer, etc.
-
● Necrosis of skin and other tissues. (SeeWARNINGS.)
-
● Adverse reactions reported infrequently include: hypersensitivity/allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions, systemic cholesterol microembolization, purple toes syndrome, hepatitis, cholestatic hepatic injury, jaundice, elevated liver enzymes, hypotension, vasculitis, edema, anemia, pallor, fever, rash, dermatitis, including bullous eruptions, urticaria, angina syndrome, chest pain, abdominal pain including cramping, flatulence/bloating, fatigue, lethargy, malaise, asthenia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pain, headache, dizziness, loss of consciousness, syncope, coma, taste perversion, pruritus, alopecia, cold intolerance, and paresthesia including feeling cold and chills.
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and SymptomsTreatment
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
The best available information supports the following recommendations for dosing of warfarin sodium.Venous Thromboembolism (including deep venous thrombosis [DVT] and pulmonary embolism [PE])
Atrial Fibrillation
Post-Myocardial Infarction
Mechanical and Bioprosthetic Heart Valves
Recurrent Systemic Embolism and Other Indications
An INR of greater than 4 appears to provide no additional therapeutic benefit in most patients and is associated with a higher risk of bleeding.
Initial Dosage
-
● Clinical factors including age, race, body weight, sex, concomitant medications, and comorbidities and
-
● Genetic factors (CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes).
Maintenance
PRECAUTIONS
Duration of Therapy
Missed Dose
Laboratory Control
The PT should be determined daily after the administration of the initial dose until PT/INR results stabilize in the therapeutic range. Intervals between subsequent PT/INR determinations should be based upon the physician's judgment of the patient's reliability and response to warfarin sodium in order to maintain the individual within the therapeutic range.To ensure adequate control, it is recommended that additional PT tests be done when other warfarin products are interchanged with warfarin sodium tablets, USP, as well as whenever other medications are initiated, discontinued, or taken irregularlyPRECAUTIONS
Treatment During Dentistry and Surgery
Conversion From Heparin Therapy
-
● 5 hours after the last IV bolus dose of heparin, or
-
● 4 hours after cessation of a continuous IV infusion of heparin, or
-
● 24 hours after the last subcutaneous heparin injection.
HOW SUPPLIED
Bottles of 100Bottles of 1000Bottles of 5000Cartons of 100 10blister packs
STORAGE AND HANDLING
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)Advise patients to:
-
● Tell their physician if they fall often as this may increase their risk for complications.
-
● Strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage schedule. Do not take or discontinue any other drug, including salicylates (e.g., aspirin and topical analgesics), other over-the-counter drugs, and botanical (herbal) products except on advice of your physician.
-
● Notify their physician immediately if any unusual bleeding or symptoms occur. Signs and symptoms of bleeding include: pain, swelling or discomfort, prolonged bleeding from cuts, increased menstrual flow or vaginal bleeding, nosebleeds, bleeding of gums from brushing, unusual bleeding or bruising, red or dark brown urine, red or tar black stools, headache, dizziness, or weakness.
-
● Contact their doctor
-
● Avoid any activity or sport that may result in traumatic injury.
-
● Obtain prothrombin time tests and make regular visits to their physician or clinic to monitor therapy.
-
● Carry identification stating that they are taking warfarin sodium.
-
● If the prescribed dose of warfarin sodium is missed, take the dose as soon as possible on the same day but do not take a double dose of warfarin sodium the next day to make up for missed doses.
-
● Eat a normal, balanced diet to maintain a consistent intake of vitamin K. Avoid drastic changes in dietary habits, such as eating large amounts of leafy, green vegetables.
-
● Contact their physician to report any serious illness, such as severe diarrhea, infection, or fever.
-
● Be aware that if therapy with warfarin sodium is discontinued, the anticoagulant effects of warfarin sodium may persist for about 2 to 5 days.
SPL MEDGUIDE
Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USPWhat is the most important information I should know about warfarin sodium?
-
● You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you take warfarin sodium and:
-
● are 65 years of age or older
-
● have a history of stomach or intestinal bleeding
-
● have high blood pressure (hypertension)
-
● have a history of stroke, or "mini-stroke" (transient ischemic attack or TIA)
-
● have serious heart disease
-
● have a low blood count or cancer
-
● have had trauma, such as an accident or surgery
-
● have kidney problems
-
● take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding, including:
-
● a medicine that contains heparin
-
● other medicines to prevent or treat blood clots
-
● nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
● take warfarin sodium for a long time. Warfarin sodium is the active ingredient in Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP.
Do not take other medicines that contain warfarin sodium while taking Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP.
-
● Get your regular blood test to check for your response to warfarin sodium. This blood test is called an INR test. The INR test checks to see how fast your blood clots. Your healthcare provider will decide what INR numbers are best for you. Your dose of warfarin sodium will be adjusted to keep your INR in a target range for you.
-
● Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of bleeding problems:
-
● pain, swelling, or discomfort
-
● headaches, dizziness, or weakness
-
● unusual bruising (bruises that develop without known cause or grow in size)
-
● nosebleeds
-
● bleeding gums
-
● bleeding from cuts takes a long time to stop
-
● menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
-
● pink or brown urine
-
● red or black stools
-
● coughing up blood
-
● vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
-
● Some foods and beverages can interact with warfarin sodium and affect your treatment and dose.
-
● Eat a normal, balanced diet. Talk to your healthcare provider before you make any diet changes. Do not eat large amounts of leafy, green vegetables. Leafy, green vegetables contain vitamin K. Certain vegetable oils also contain large amounts of vitamin K. Too much vitamin K can lower the effect of warfarin sodium.
-
● Always tell all of your healthcare providers that you take warfarin sodium.
-
● Wear or carry information that you take warfarin sodium.
What is warfarin sodium?
Who should not take warfarin sodium?
Do not take warfarin sodium if:
-
● your chance of having bleeding problems is higher than the possible benefit of treatment. Your healthcare provider will decide if warfarin sodium is right for you. Talk to your healthcare provider about all of your health conditions.
-
● you are pregnant unless you have a mechanical heart valve.Warfarin sodium may cause birth defects, miscarriage, or death of your unborn baby.
-
● you are allergic to warfarin or any of the other ingredients in Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP.
-
● have bleeding problems
-
● fall often
-
● have liver or kidney problems
-
● have high blood pressure
-
● have a heart problem called congestive heart failure
-
● have diabetes
-
● plan to have any surgery or a dental procedure
-
● have any other medical conditions
-
● are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. See "Who should not take warfarin sodium?"
-
● are breast-feeding. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take warfarin sodium and breast-feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,What is the most important information I should know about warfarin sodium?
How should I take warfarin sodium?
-
● Take warfarin sodium exactly as prescribed.Your healthcare provider will adjust your dose from time to time depending on your response to warfarin sodium.
-
● You must have regular blood tests and visits with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition.
-
● If you miss a dose of warfarin sodium, call your healthcare provider.Take the dose as soon as possible on the same day.Do nottake a double dose of warfarin sodium the next day to make up for a missed dose.
-
● Call your healthcare provider right away if you:
-
● take too much warfarin sodium
-
● are sick with diarrhea, an infection, or have a fever
-
● fall or injure yourself, especially if you hit your head. Your healthcare provider may need to check you
-
● Do not do any activity or sport that may cause a serious injury.
Warfarin sodium may cause serious side effects including:
-
● See "What is the most important information I should know about warfarin sodium?"
-
● Death of skin tissue (skin necrosis or gangrene).This can happen soon after starting warfarin sodium. It happens because blood clots form and block blood flow to an area of your body. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain, color, or temperature change to any area of your body. You may need medical care right away to prevent death or loss (amputation) of your affected body part.
-
● "Purple toes syndrome."Call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain in your toes and they look purple in color or dark in color.
How should I store Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP?
-
● Store warfarin sodium at 68to 77(20to 25
-
● Keep warfarin sodium in a tightly closed container, and keep warfarin sodium out of the light.
General information about warfarin sodium.
What are the ingredients in Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP?
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION

Warfarin SodiumWarfarin Sodium TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PLEASE, BE CAREFUL!
Be sure to consult your doctor before taking any medication!