Xenazine
Lundbeck Inc.
Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use XENAZINE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XENAZINE Xenazine (tetrabenazine) Tablet, for Oral Use Initial U.S. Approval: 2008BOXED WARNING WARNING: DEPRESSION AND SUICIDALITY See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning . Increases the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington's disease. (5.3) Balance risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for control of choreiform movements when considering the use of XENAZINE. (5.1) Monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. (5.3) Inform patients, caregivers and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. (5.3) Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. (5.3) XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients who are actively suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression. (4, 5.3) INDICATIONS AND USAGEXENAZINE is a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease. (1)DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Individualization of dose with careful weekly titration is required. The 1st week's starting dose is 12.5 mg daily; 2nd week, 25 mg (12.5 mg twice daily); then slowly titrate at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg to a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. (2.1, 2.2) Doses of 37.5 mg and up to 50 mg per day should be administered in three divided doses per day with the maximum recommended single dose not to exceed 25 mg. (2.2) Patients requiring doses above 50 mg per day should be genotyped for the drug metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6 to determine if the patient is a poor metabolizer (PM) or an extensive metabolizer (EM). (2.2, 5.4) The maximum daily dose in PMs is 50 mg with a maximum single dose of 25 mg. (2.2) The maximum daily dose in EMs and intermediate metabolizers (IMs) 100 mg with a maximum single dose of 37.5 mg. (2.2) If serious adverse events occur, titration should be stopped and the dose of XENAZINE should be reduced. If the adverse event(s) do not resolve, consider withdrawal of XENAZINE. (2.2, 5.2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 12.5 mg and 25 mg XENAZINE tablets for oral use (12.5 mg non-scored, 25 mg scored). (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients who are actively suicidal, or who have depression which is untreated or undertreated. (4, 5.3) XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with impaired hepatic function. (2.4, 4, 8.6, 12.3) XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs or reserpine. (4, 7.3, 7.4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Periodically reevaluate the benefit of XENAZINE and potential for adverse effects such as worsening mood, cognition, rigidity and functional capacity. (5.1) Do not exceed 50 mg/day and the maximum single dose should not exceed 25 mg if administered in conjunction with a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine). (5.3, 7.1) Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS). (5.5, 7.6) Discontinue XENAZINE if this occurs. (5.5, 7.6) Restlessness, agitation, akathisia and parkinsonism. Reduce dose or discontinue XENAZINE if this occurs. (5.6, 5.7) Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia. Monitor for dysphagia. (5.8) Sedation/somnolence. May impair the patient's ability to drive or operate complex machinery. (5.9) Alcohol or other sedating drugs can worsen sedation and somnolence. (5.10, 7.4) QTc prolongation. Do not prescribe in combination with other drugs that prolong QTc. (5.11, 7.5, 7.6, 12.2) Exaggerates extrapyramidal disorders when used with drugs that reduce or antagonize dopamine. Discontinue XENAZINE if this occurs. (5.15) Side EffectsThe most common adverse reactions are (>10% and at least 5% greater than placebo): Sedation/somnolence, fatigue, insomnia, depression, akathisia, anxiety, nausea. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact XENAZINE Information Center at 1-888-882-6013 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch . USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Based on animal data, tetrabenazine may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 XENAZINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 XENAZINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 XENAZINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Clinical Worsening and Adverse Effects
- 5.2 Dosing of XENAZINE
- 5.3 Risk of Depression and Suicidality
- 5.4 Laboratory Tests
- 5.5 Risk of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
- 5.6 Risk of Akathisia, Restlessness, and Agitation
- 5.7 Risk of Parkinsonism
- 5.8 Risk of Dysphagia
- 5.9 Risk of Sedation and Somnolence
- 5.10 Interaction with Alcohol
- 5.11 Risk of QTc Prolongation
- 5.12 Concomitant Use of Neuroleptic Drugs, Reserpine and MAOIs
- 5.13 Risk of Hypotension and Orthostatic Hypotension
- 5.14 Risk of Hyperprolactinemia
- 5.15 Risk of Tardive Dyskinesia (TD)
- 5.16 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illnesses
- 5.17 Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues
- 6 XENAZINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 8.1 Pregnancy
- 8.2 Labor and Delivery
- 8.3 Nursing Mothers
- 8.4 Pediatric Use
- 8.5 Geriatric Use
- 8.6 Use in Patients with Hepatic Disease
- 8.7 Use in Patients with Depression and Suicidality
- 8.8 Use in Poor or Extensive CYP2D6 Metabolizers
- 8.9 Use in Patients at Risk from QTc Prolongation
- 8.10 Use in Patients with Renal Disease
- 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 XENAZINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- MEDICATION GUIDE
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Xenazine® (tetrabenazine) Tablets
XENAZINE can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington's disease. Anyone considering the use of XENAZINE must balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for control of choreiform movements. Close observation of patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior should accompany therapy. Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the risk of depression and suicidality and should be instructed to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician.
Particular caution should be exercised in treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation, which are increased in frequency in Huntington's disease. XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients who are actively suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XENAZINE is indicated for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Considerations
The chronic daily dose of XENAZINE used to treat chorea associated with Huntington's disease (HD) is determined individually for each patient. When first prescribed, XENAZINE therapy should be titrated slowly over several weeks to identify a dose of XENAXINE that reduces chorea and is tolerated. XENAZINE can be administered without regard to food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Individualization of Dose
The dose of XENAZINE should be individualized.
Dosing Recommendations Up to 50 mg per day
The starting dose should be 12.5 mg per day given once in the morning. After one week, the dose should be increased to 25 mg per day given as 12.5 mg twice a day. XENAZINE should be titrated up slowly at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg daily, to allow the identification of a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. If a dose of 37.5 to 50 mg per day is needed, it should be given in a three times a day regimen. The maximum recommended single dose is 25 mg. If adverse events such as akathisia, restlessness, parkinsonism, depression, insomnia, anxiety or sedation occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse event does not resolve, consideration should be given to withdrawing XENAZINE treatment or initiating other specific treatment (e.g., antidepressants) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Dosing Recommendations Above 50 mg per day
Patients who require doses of XENAZINE greater than 50 mg per day should be first tested and genotyped to determine if they are poor metabolizers (PMs) or extensive metabolizers (EMs) by their ability to express the drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6. The dose of XENAZINE should then be individualized accordingly to their status as PMs or EMs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Extensive and Intermediate CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Genotyped patients who are identified as extensive (EMs) or intermediate metabolizers (IMs) of CYP2D6, who need doses of XENAZINE above 50 mg per day, should be titrated up slowly at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg daily, to allow the identification of a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. Doses above 50 mg per day should be given in a three times a day regimen. The maximum recommended daily dose is 100 mg and the maximum recommended single dose is 37.5 mg. If adverse events such as akathisia, parkinsonism, depression, insomnia, anxiety or sedation occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse event does not resolve, consideration should be given to withdrawing XENAZINE treatment or initiating other specific treatment (e.g., antidepressants) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers
In PMs, the initial dose and titration is similar to EMs except that the recommended maximum single dose is 25 mg, and the recommended daily dose should not exceed a maximum of 50 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Medications that are strong CYP2D6 inhibitors such as quinidine or antidepressants (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine) significantly increase the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ, therefore, the total dose of XENAZINE should not exceed a maximum of 50 mg and the maximum single dose should not exceed 25 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Because the safety and efficacy of the increased exposure to XENAZINE and other circulating metabolites are unknown, it is not possible to adjust the dosage of XENAZINE in hepatic impairment to ensure safe use. Therefore, XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.16), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Discontinuation of Treatment
Treatment with XENAZINE can be discontinued without tapering. Re-emergence of chorea may occur within 12 to 18 hours after the last dose of XENAZINE [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)].
2.6 Resumption of Treatment
Following treatment interruption of greater than five (5) days, XENAZINE therapy should be re-titrated when resumed. For short-term treatment interruption of less than five (5) days, treatment can be resumed at the previous maintenance dose without titration.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
XENAZINE tablets are available in the following strengths and packages:
The 12.5 mg XENAZINE tablets are white, cylindrical biplanar tablets with beveled edges, non-scored, embossed on one side with "CL" and "12.5."
The 25 mg XENAZINE tablets are yellowish-buff, cylindrical biplanar tablets with beveled edges, scored, embossed on one side with "CL" and "25."
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients who are actively suicidal, or in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with impaired hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.16), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). XENAZINE should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within a minimum of 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
- XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking reserpine. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting XENAZINE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Clinical Worsening and Adverse Effects
Huntington's disease is a progressive disorder characterized by changes in mood, cognition, chorea, rigidity, and functional capacity over time. In a 12-week controlled trial, XENAZINE was also shown to cause slight worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Whether these effects persist, resolve, or worsen with continued treatment is unknown. Therefore, proper use of the drug requires attention to all facets of the underlying disease process over time.
Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for XENAZINE in their patients by assessing the beneficial effect on chorea and possible adverse effects, including depression, cognitive decline, parkinsonism, dysphagia, sedation/somnolence, akathisia, restlessness and disability. It may be difficult to distinguish between drug-induced side-effects and progression of the underlying disease; decreasing the dose or stopping the drug may help the clinician distinguish between the two possibilities. In some patients, underlying chorea itself may improve over time, decreasing the need for XENAZINE.
5.2 Dosing of XENAZINE
Proper dosing of XENAZINE involves titration of therapy to determine an individualized dose for each patient. When first prescribed, XENAZINE therapy should be titrated slowly over several weeks to allow the identification of a dose that both reduces chorea and is tolerated [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Some adverse effects such as depression, fatigue, insomnia, sedation/somnolence, parkinsonism and akathisia may be dose-dependent and may resolve or lessen with dosage adjustment or specific treatment. If the adverse effect does not resolve or decrease, consider discontinuing XENAZINE.
Doses above 50 mg should not be given without CYP2D6 genotyping patients to determine if they are poor metabolizers [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
5.3 Risk of Depression and Suicidality
Patients with Huntington's disease are at increased risk for depression, suicidal ideation or behaviors (suicidality). XENAZINE increases the risk for suicidality in patients with HD. All patients treated with XENAZINE should be observed for new or worsening depression or suicidality. If depression or suicidality does not resolve, consider discontinuing treatment with XENAZINE.
In a 12-week, double-blind placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with Huntington's disease, 10 of 54 patients (19%) treated with XENAZINE were reported to have an adverse event of depression or worsening depression compared to none of the 30 placebo-treated patients. In two open-label studies (in one study, 29 patients received XENAZINE for up to 48 weeks; in the second study, 75 patients received XENAZINE for up to 80 weeks), the rate of depression/worsening depression was 35%.
In all of the HD chorea studies of XENAZINE (n=187), one patient committed suicide, one attempted suicide, and six had suicidal ideation.
Clinicians should be alert to the heightened risk of suicide in patients with Huntington's disease regardless of depression indices. Reported rates of completed suicide among individuals with Huntington's disease range from 3-13% and over 25% of patients attempt suicide at some point in their illness.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed of the risks of depression, worsening depression, and suicidality associated with XENAZINE and should be instructed to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Patients with HD who express suicidal ideation should be evaluated immediately.
5.4 Laboratory Tests
Before prescribing a daily dose of XENAZINE that is greater than 50 mg per day, patients should be genotyped to determine if they express the drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6. CYP2D6 testing is necessary to determine whether patients are poor metabolizers (PMs), extensive (EMs) or intermediate metabolizers (IMs) of XENAZINE.
Patients who are PMs of XENAZINE will have substantially higher levels of the primary drug metabolites (about 3-fold for α-HTBZ and 9-fold for β-HTBZ) than patients who are EMs. The dosage should be adjusted according to a patient's CYP2D6 metabolizer status. In patients who are identified as CYP2D6 PMs, the maximum recommended total daily dose is 50 mg and the maximum recommended single dose is 25 mg [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use In Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Risk of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with XENAZINE and other drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.6)]. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatinine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria, rhabdomyolysis, and acute renal failure. The diagnosis of NMS can be complicated; other serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection), and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal disorders can present with similar signs and symptoms. Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever, and primary central nervous system pathology.
The management of NMS should include (1) immediate discontinuation of XENAZINE and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy; (2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and (3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for NMS.
Recurrence of NMS has been reported. If treatment with XENAZINE is needed after recovery from NMS, patients should be monitored for signs of recurrence.
5.6 Risk of Akathisia, Restlessness, and Agitation
In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with HD, akathisia was observed in 10 (19%) of XENAZINE-treated patients and 0% of placebo-treated patients. In an 80-week open-label study, akathisia was observed in 20% of XENAZINE-treated patients. Akathisia was not observed in a 48-week open-label study. Patients receiving XENAZINE should be monitored for the presence of akathisia. Patients receiving XENAZINE should also be monitored for signs and symptoms of restlessness and agitation, as these may be indicators of developing akathisia. If a patient develops akathisia, the XENAZINE dose should be reduced; however, some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
5.7 Risk of Parkinsonism
XENAZINE can cause parkinsonism. In a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with HD, symptoms suggestive of parkinsonism (i.e., bradykinesia, hypertonia and rigidity) were observed in 15% of XENAZINE-treated patients compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients. In 48-week and 80-week open-label studies, symptoms suggestive of parkinsonism were observed in 10% and 3% of XENAZINE-treated patients, respectively. Because rigidity can develop as part of the underlying disease process in Huntington's disease, it may be difficult to distinguish between this drug-induced side-effect and progression of the underlying disease process. Drug-induced parkinsonism has the potential to cause more functional disability than untreated chorea for some patients with Huntington's disease. If a patient develops parkinsonism during treatment with XENAZINE, dose reduction should be considered; in some patients, discontinuation of therapy may be necessary.
5.8 Risk of Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a component of HD. However, drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission have been associated with esophageal dysmotility and dysphagia. Dysphagia may be associated with aspiration pneumonia. In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with HD, dysphagia was observed in 4% of XENAZINE-treated patients and 3% of placebo-treated patients. In 48-week and 80-week open-label studies, dysphagia was observed in 10% and 8% of XENAZINE-treated patients, respectively. Some of the cases of dysphagia were associated with aspiration pneumonia. Whether these events were related to treatment is unknown.
5.9 Risk of Sedation and Somnolence
Sedation is the most common dose-limiting adverse effect of XENAZINE. In a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with chorea associated with HD, sedation/somnolence was observed in 17/54 (31%) XENAZINE-treated patients and in 1 (3%) placebo-treated patient. Sedation was the reason upward titration of XENAZINE was stopped and/or the dose of XENAZINE was decreased in 15/54 (28%) patients. In all but one case, decreasing the dose of XENAZINE resulted in decreased sedation. In 48-week and 80-week open-label studies, sedation/somnolence was observed in 17% and 57% of XENAZINE-treated patients, respectively. In some patients, sedation occurred at doses that were lower than recommended doses.
Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness to maintain the safety of themselves or others, such as operating a motor vehicle or operating hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of XENAZINE and know how the drug affects them.
5.10 Interaction with Alcohol
Patients should be advised that the concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Drug Interactions (7.4)].
5.11 Risk of QTc Prolongation
XENAZINE causes a small increase (about 8 msec) in the corrected QT (QTc) interval. QT prolongation can lead to development of torsade de pointes-type ventricular tachycardia with the risk increasing as the degree of prolongation increases [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The use of XENAZINE should be avoided in combination with other drugs that are known to prolong QTc, including antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, thioridazine, ziprasidone), antibiotics (e.g., moxifloxacin), Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide), and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications or any other medications known to prolong the QTc interval [see Drug Interactions (7.5, 7.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
XENAZINE should also be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias. Certain circumstances may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including (1) bradycardia; (2) hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; (3) concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; and (4) presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval [see Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
5.12 Concomitant Use of Neuroleptic Drugs, Reserpine and MAOIs
Neuroleptic Drugs
Patients taking neuroleptic (antipsychotic) drugs (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, olanzapine, risperidone, thioridazine, ziprasidone) were excluded from clinical studies during the XENAZINE development program. Adverse reactions associated with XENAZINE, such as QTc prolongation, NMS, and extrapyramidal disorders, may be exaggerated by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.11) , Drug Interactions (7.5, 7.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
Reserpine
Reserpine binds irreversibly to VMAT2, and the duration of its effect is several days. The physician should wait for chorea to reemerge before administering XENAZINE to avoid overdosage and major depletion of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting XENAZINE. XENAZINE and reserpine should not be used concomitantly [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs. XENAZINE should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within a minimum of 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
5.13 Risk of Hypotension and Orthostatic Hypotension
XENAZINE induced postural dizziness in healthy volunteers receiving single doses of 25 or 50 mg. One subject had syncope and one subject with postural dizziness had documented orthostasis. Dizziness occurred in 4% of XENAZINE-treated patients (vs. none on placebo) in the 12-week controlled trial; however, blood pressure was not measured during these events. Monitoring of vital signs on standing should be considered in patients who are vulnerable to hypotension.
5.14 Risk of Hyperprolactinemia
XENAZINE elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. Following administration of 25 mg to healthy volunteers, peak plasma prolactin levels increased 4- to 5-fold. Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one third of human breast cancers are prolactin-dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if XENAZINE is being considered for a patient with previously detected breast cancer. Although amenorrhea, galactorrhea, gynecomastia and impotence can be caused by elevated serum prolactin concentrations, the clinical significance of elevated serum prolactin concentrations for most patients is unknown. Chronic increase in serum prolactin levels (although not evaluated in the XENAZINE development program) has been associated with low levels of estrogen and increased risk of osteoporosis. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of XENAZINE.
5.15 Risk of Tardive Dyskinesia (TD)
A potentially irreversible syndrome of involuntary, dyskinetic movements may develop in patients treated with neuroleptic drugs. In an animal model of orofacial dyskinesias, acute administration of reserpine, a monoamine depletor, has been shown to produce vacuous chewing in rats. Although the pathophysiology of tardive dyskinesia remains incompletely understood, the most commonly accepted hypothesis of the mechanism is that prolonged post-synaptic dopamine receptor blockade leads to supersensitivity to dopamine. Neither reserpine nor XENAZINE, which are dopamine depletors, have been reported to cause clear tardive dyskinesia in humans, but as pre-synaptic dopamine depletion could theoretically lead to supersensitivity to dopamine, and XENAZINE can cause the extrapyramidal symptoms also known to be associated with neuroleptics (e.g., parkinsonism and akathisia), physicians should be aware of the possible risk of tardive dyskinesia. If signs and symptoms of TD appear in a patient treated with XENAZINE, drug discontinuation should be considered.
5.16 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illnesses
Clinical experience with XENAZINE in patients with systemic illnesses is limited.
Depression and Suicidality
XENAZINE may increase the risk for depression or suicidality in patients with a history of depression or suicidal behavior or in patients with diseases, conditions, or treatments that cause depression or suicidality. XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression or who are actively suicidal [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Disease
XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Heart Disease
XENAZINE has not been evaluated in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease. Patients with these diagnoses were excluded from premarketing clinical trials.
5.17 Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues
Since XENAZINE or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues, it could accumulate in these tissues over time. This raises the possibility that XENAZINE may cause toxicity in these tissues after extended use. Neither ophthalmologic nor microscopic examination of the eye was conducted in the chronic toxicity study in dogs. Ophthalmologic monitoring in humans was inadequate to exclude the possibility of injury occurring after long-term exposure.
The clinical relevance of XENAZINE's binding to melanin-containing tissues is unknown. Although there are no specific recommendations for periodic ophthalmologic monitoring, prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following risks are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Depression and suicidality [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Akathisia, restlessness and agitation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Parkinsonism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Commonly Observed Side Effects in Controlled Clinical Trials
The most common adverse reactions from Table 1 occurring in over 10% of XENAZINE-treated patients, and at least 5% greater than placebo, were sedation/somnolence (31%), fatigue (22%), insomnia (22%), depression (19%), akathisia (19%), and nausea (13%).
6.2 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
During its development, XENAZINE was administered to 773 unique subjects and patients. The conditions and duration of exposure to XENAZINE varied greatly, and included single and multiple dose clinical pharmacology studies in healthy volunteers (n=259) and open-label (n=529) and double-blind studies (n=84) in patients.
In a randomized, 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trial of HD subjects, adverse reactions (ARs) were more common in the XENAZINE group than in the placebo group. Forty-nine of 54 (91%) patients who received XENAZINE experienced one or more ARs at any time during the study. The ARs most commonly reported (over 10%, and at least 5% greater than placebo) were sedation/somnolence (31% vs. 3% on placebo), fatigue (22% vs. 13% on placebo), insomnia (22% vs. 0% on placebo), depression (19% vs. 0% on placebo), akathisia (19% vs. 0% on placebo), and nausea (13% vs. 7% on placebo).
Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥4% Patients
The number and percentage of the most commonly reported AEs that occurred at any time during the study in ≥4% of XENAZINE-treated patients, and with a greater frequency than in placebo-treated patients, are presented in Table 1 in decreasing order of frequency within body systems for the XENAZINE group.
| Body System | AE Term | XENAZINE n = 54 n (%) |
Placebo n = 30 n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS | Sedation/somnolence | 17 (31%) | 1 (3%) |
| Insomnia | 12 (22%) | - | |
| Depression | 10 (19%) | - | |
| Anxiety/anxiety aggravated | 8 (15%) | 1 (3%) | |
| Irritability | 5 (9%) | 1 (3%) | |
| Appetite decreased | 2 (4%) | - | |
| Obsessive reaction | 2 (4%) | - | |
| CENTRAL & PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM | Akathisia | 10 (19%) | - |
| Balance difficulty | 5 (9%) | - | |
| Parkinsonism/bradykinesia | 5 (9%) | - | |
| Dizziness | 2 (4%) | - | |
| Dysarthria | 2 (4%) | - | |
| Gait unsteady | 2 (4%) | - | |
| Headache | 2 (4%) | 1 (3%) | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM DISORDERS | Nausea | 7 (13%) | 2 (7%) |
| Vomiting | 3 (6%) | 1 (3%) | |
|
BODY AS A WHOLE – GENERAL |
Fatigue | 12 (22%) | 4 (13%) |
| Fall | 8 (15%) | 4 (13%) | |
| Laceration (head) | 3 (6%) | - | |
| Ecchymosis | 3 (6%) | - | |
| RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS | Upper respiratory tract infection | 6 (11%) | 2 (7%) |
| Shortness of breath | 2 (4%) | - | |
| Bronchitis | 2 (4%) | - | |
| URINARY SYSTEM DISORDERS | Dysuria | 2 (4%) | - |
Dose escalation was discontinued or dosage of study drug was reduced because of one or more ARs in 28 of 54 (52%) patients randomized to XENAZINE. These ARs consisted of sedation (15), akathisia (7), parkinsonism (4), depression (3), anxiety (2), fatigue (1) and diarrhea (1). Some patients had more than one AR and are, therefore, counted more than once.
Adverse Reactions Due to Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
The following table describes the incidence of events considered to be extrapyramidal adverse reactions.
| Event | Patients (%) reporting event | |
|---|---|---|
| XENAZINE n = 54 |
Placebo n = 30 |
|
| Akathisia |
10 (19%) | 0 |
| Extrapyramidal event |
8 (15%) | 0 |
| Any extrapyramidal event | 18 (33%) | 0 |
Patients may have had events in more than one category.
6.3 Laboratory Tests
No clinically significant changes in laboratory parameters were reported in clinical trials with XENAZINE. In controlled clinical trials, XENAZINE caused a small mean increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), laboratory values as compared to placebo.
6.4 Vital Signs
In controlled clinical trials, XENAZINE did not affect blood pressure, pulse, and body weight. Orthostatic blood pressure was not consistently measured in the XENAZINE clinical trials.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors
In vitro studies indicate that α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are substrates for CYP2D6. Strong CYPD6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine) markedly increase exposure to these metabolites. A reduction in XENAZINE dose may be necessary when adding a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine, quinidine) in patients maintained on a stable dose of XENAZINE. The daily dose of XENAZINE should not exceed 50 mg per day and the maximum single dose of XENAZINE should not exceed 25 mg in patients taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.9), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Reserpine
Reserpine binds irreversibly to VMAT2 and the duration of its effect is several days. Prescribers should wait for chorea to reemerge before administering XENAZINE to avoid overdosage and major depletion of serotonin and norepinephrine in the CNS. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting XENAZINE. XENAZINE and reserpine should not be used concomitantly [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs. XENAZINE should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within a minimum of 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 Alcohol
Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
7.5 Drugs that Cause QTc Prolongation
Since XENAZINE causes a small increase in QTc prolongation (about 8 msec), the concomitant use with other drugs that are known to cause QTc prolongation should be avoided including antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, thioridazine, ziprasidone), antibiotics (e.g., moxifloxacin), Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide), and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications or any other medications known to prolong the QTc interval. XENAZINE should also be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias. Certain circumstances may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including (1) bradycardia; (2) hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; (3) concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; and (4) presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11, 5.12), Drug Interactions (7.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
7.6 Neuroleptic Drugs
Adverse reactions associated with XENAZINE, such as QTc prolongation, NMS, and extrapyramidal disorders, may be exaggerated by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists, including antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, olanzapine, risperidone, thioridazine, ziprasidone) [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.9, 5.11, 5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.5)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. XENAZINE should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Tetrabenazine had no clear effects on embryo-fetal development when administered to pregnant rats throughout the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (or 3 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 100 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis). Tetrabenazine had no effects on embryo-fetal development when administered to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (or 12 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). Because neither rat nor rabbit dosed with tetrabenazine produce 9-desmethyl-beta-DHTBZ, a major human metabolite, these studies may not have adequately addressed the potential effects of tetrabenazine on embryo-fetal development in humans.
When tetrabenazine was administered to female rats (doses of 5, 15, and 30 mg/kg/day) from the beginning of organogenesis through the lactation period, an increase in stillbirths and offspring postnatal mortality was observed at 15 and 30 mg/kg/day and delayed pup maturation was observed at all doses. The no-effect dose for stillbirths and postnatal mortality was 0.5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Because rats dosed with tetrabenazine do not produce 9-desmethyl-beta-DHTBZ, a major human metabolite, this study may not have adequately assessed the potential effects of tetrabenazine on the offspring of women exposed in utero and via lactation.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effect of XENAZINE on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether XENAZINE or its metabolites are excreted in human milk.
Since many drugs are excreted into human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from XENAZINE, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue XENAZINE, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of XENAZINE in children have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites have not been formally studied in geriatric subjects.
8.6 Use in Patients with Hepatic Disease
The use of XENAZINE in patients with liver disease is contraindicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.16), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Use in Patients with Depression and Suicidality
Patients with HD are at increased risk for depression, suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality), and XENAZINE increases these risks. XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression or who are actively suicidal. XENAZINE may increase the risk for depression or suicidality in patients with a history of depression or suicidal behavior or in patients with diseases, conditions, or treatments that cause depression or suicidality [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Depression
Symptoms of sadness, worsening of depression, withdrawal, insomnia, irritability, hostility (aggressiveness), akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), anxiety, agitation, or panic attacks may increase with XENAZINE. Depression/worsening depression was noted in 35% of XENAZINE-treated patients during studies with XENAZINE.
Suicidality
The rate of completed suicide among individuals with Huntington's disease ranges from 3-13% and over 25% of patients with HD attempt suicide at some point in their illness.
8.8 Use in Poor or Extensive CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Patients who require doses of XENAZINE greater than 50 mg per day, should be first tested and genotyped to determine if they are poor (PMs) or extensive metabolizers (EMs) by their ability to express the drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6. The dose of XENAZINE should then be individualized accordingly to their status as either poor (PMs) or extensive metabolizers (EMs) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Poor Metabolizers
Poor CYP2D6 metabolizers (PMs) will have substantially higher levels of exposure to the primary metabolites (about 3-fold for α-HTBZ and 9-fold for β-HTBZ) compared to EMs. The dosage should, therefore, be adjusted according to a patient's CYP2D6 metabolizer status by limiting a single dose to a maximum of 25 mg and the recommended daily dose to not exceed a maximum of 50 mg/day in patients who are CYP2D6 PMs [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Extensive/Intermediate Metabolizers
In extensive (EMs) or intermediate metabolizers (IMs), the dosage of XENAZINE can be titrated to a maximum single dose of 37.5 mg and a recommended maximum daily dose of 100 mg [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Drug Interaction (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.9 Use in Patients at Risk from QTc Prolongation
XENAZINE causes a small increase in QTc interval (8 msec). It should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, or a history of hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, or cardiac arrhythmias (e.g., bradycardia), or in combination with other drugs that are known to prolong QTc, including antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, haloperidol, thioridazine, ziprasidone), antibiotics (e.g., moxifloxacin), Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide), and Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol), antiarrhythmic medications or any other medications known to prolong the QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.11, 5.12), Drug Interactions (7.5, 7.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
8.10 Use in Patients with Renal Disease
The effects of renal insufficiency in the pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites have not been formally studied.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance Class
XENAZINE is not a controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Clinical trials did not reveal any tendency for drug seeking behavior, though these observations were not systematic. Abuse has not been reported from the postmarketing experience in countries where XENAZINE has been marketed.
As with any CNS-active drug, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of XENAZINE misuse or abuse (such as development of tolerance, increasing dose requirements, drug-seeking behavior).
Abrupt discontinuation of XENAZINE from patients did not produce symptoms of withdrawal or a discontinuation syndrome; only symptoms of the original disease were observed to re-emerge [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Human Experience
Three episodes of overdose occurred in the open-label trials performed in support of registration. Eight cases of overdose with XENAZINE have been reported in the literature. The dose of XENAZINE in these patients ranged from 100 mg to 1 g. Adverse reactions associated with XENAZINE overdose included acute dystonia, oculogyric crisis, nausea and vomiting, sweating, sedation, hypotension, confusion, diarrhea, hallucinations, rubor, and tremor.
10.2 Management of Overdose
Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any CNS-active drug. General supportive and symptomatic measures are recommended. Cardiac rhythm and vital signs should be monitored. In managing overdosage, the possibility of multiple drug involvement should always be considered. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians' Desk Reference® (PDR®).
11 DESCRIPTION
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) is a monoamine depletor for oral administration. The molecular weight of tetrabenazine is 317.43; the pKa is 6.51. Tetrabenazine is a hexahydro-dimethoxy-benzoquinolizine derivative and has the following chemical name: cis rac –1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-9,10-dimethoxy-3-(2-methylpropyl)-2H-benzo[a]quinolizin-2-one.
The empirical formula C19H27NO3 is represented by the following structural formula:
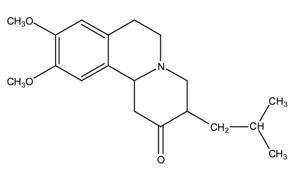
Tetrabenazine is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol.
Each XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) Tablet contains either 12.5 or 25 mg of tetrabenazine as the active ingredient.
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) Tablets contain tetrabenazine as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: lactose, magnesium stearate, maize starch, and talc. The 25 mg strength tablet also contains yellow iron oxide as an inactive ingredient.
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) is supplied as a yellowish-buff scored tablet containing 25 mg of XENAZINE or as a white non-scored tablet containing 12.5 mg of XENAZINE.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism by which XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) exerts its anti-chorea effects is unknown but is believed to be related to its effect as a reversible depletor of monoamines (such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine) from nerve terminals. Tetrabenazine reversibly inhibits the human vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT2) (Ki ≈ 100 nM), resulting in decreased uptake of monoamines into synaptic vesicles and depletion of monoamine stores. Human VMAT2 is also inhibited by dihydrotetrabenazine (HTBZ), a mixture of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ. α- and β-HTBZ, major circulating metabolites in humans, exhibit high in vitro binding affinity to bovine VMAT2. Tetrabenazine exhibits weak in vitro binding affinity at the dopamine D2 receptor (Ki = 2100 nM).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
QTc Prolongation
The effect of a single 25 or 50 mg dose of XENAZINE on the QT interval was studied in a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled crossover study in healthy male and female subjects with moxifloxacin as a positive control. At 50 mg, XENAZINE caused an approximately 8 msec mean increase in QTc (90% CI: 5.0, 10.4 msec). Additional data suggest that inhibition of CYP2D6 in healthy subjects given a single 50 mg dose of XENAZINE does not further increase the effect on the QTc interval. Effects at higher exposures to either XENAZINE or its metabolites have not been evaluated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11, 5.12), Drug Interactions (7.5, 7.6), and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
Melanin Binding
Tetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues (i.e., eye, skin, fur) in pigmented rats. After a single oral dose of radiolabeled tetrabenazine, radioactivity was still detected in eye and fur at 21 days post dosing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of tetrabenazine, the extent of absorption is at least 75%. After single oral doses ranging from 12.5 to 50 mg, plasma concentrations of tetrabenazine are generally below the limit of detection because of the rapid and extensive hepatic metabolism of tetrabenazine by carbonyl reductase to the active metabolites α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ. α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are metabolized principally by CYP2D6. Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are reached within 1 to 1½ hours post-dosing. α-HTBZ is subsequently metabolized to a minor metabolite, 9-desmethyl-α-DHTBZ. β-HTBZ is subsequently, metabolized to another major circulating metabolite, 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ, for which Cmax is reached approximately 2 hours post-dosing.
Food Effects
The effects of food on the bioavailability of XENAZINE were studied in subjects administered a single dose with and without food. Food had no effect on mean plasma concentrations, Cmax, or the area under the concentration time course (AUC) of α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ. XENAZINE can, therefore, be administered without regard to meals.
Distribution
Results of PET-scan studies in humans show that radioactivity is rapidly distributed to the brain following intravenous injection of 11C-labeled tetrabenazine or α-HTBZ, with the highest binding in the striatum and lowest binding in the cortex.
The in vitro protein binding of tetrabenazine, α-HTBZ, and β-HTBZ was examined in human plasma for concentrations ranging from 50 to 200 ng/mL. Tetrabenazine binding ranged from 82% to 85%, α-HTBZ binding ranged from 60% to 68%, and β-HTBZ binding ranged from 59% to 63%.
Metabolism
After oral administration in humans, at least 19 metabolites of tetrabenazine have been identified. α-HTBZ, β-HTBZ and 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ, are the major circulating metabolites, and they are, subsequently, metabolized to sulfate or glucuronide conjugates. α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are formed by carbonyl reductase that occurs mainly in the liver. α-HTBZ is O-dealkylated by CYP450 enzymes, principally CYP2D6, with some contribution of CYP1A2 to form 9-desmethyl-α-DHTBZ, a minor metabolite. β-HTBZ is O-dealkylated principally by CYP2D6 to form 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ.
The results of in vitro studies do not suggest that tetrabenazine, α-HTBZ, or β-HTBZ are likely to result in clinically significant inhibition of CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, or CYP3A. In vitro studies suggest that neither tetrabenazine nor its α- or β-HTBZ metabolites are likely to result in clinically significant induction of CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, or CYP2C19.
Neither tetrabenazine nor its α- or β-HTBZ metabolites is likely to be a substrate or inhibitor of P-glycoprotein at clinically relevant concentrations in vivo.
No in vitro metabolism studies have been conducted to evaluate the potential of the 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ metabolite to interact with other drugs. The activity of this metabolite relative to the parent drug is unknown.
Elimination
After oral administration, tetrabenazine is extensively hepatically metabolized, and the metabolites are primarily renally eliminated. α-HTBZ, β-HTBZ and 9-desmethyl-β-DHTBZ have half-lives of 7 hours, 5 hours and 12 hours respectively. In a mass balance study in 6 healthy volunteers, approximately 75% of the dose was excreted in the urine and fecal recovery accounted for approximately 7-16% of the dose. Unchanged tetrabenazine has not been found in human urine. Urinary excretion of α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ accounted for less than 10% of the administered dose. Circulating metabolites, including sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of HTBZ metabolites as well as products of oxidative metabolism, account for the majority of metabolites in the urine.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patient
The pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites have not been studied in pediatric subjects [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Geriatric Patient
The pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites have not been formally studied in geriatric subjects [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Gender
There is no apparent effect of gender on the pharmacokinetics of α-HTBZ or β-HTBZ.
Race
Racial differences in the pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites have not been formally studied.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The effect of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its primary metabolites has not been studied.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The disposition of tetrabenazine was compared in 12 patients with mild to moderate chronic liver impairment (Child-Pugh scores of 5-9) and 12 age- and gender-matched subjects with normal hepatic function who received a single 25 mg dose of tetrabenazine. In patients with hepatic impairment, tetrabenazine plasma concentrations were similar to or higher than concentrations of α-HTBZ, reflecting the markedly decreased metabolism of tetrabenazine to α-HTBZ. The mean tetrabenazine Cmax in hepatically impaired subjects was approximately 7- to 190-fold higher than the detectable peak concentrations in healthy subjects. The elimination half-life of tetrabenazine in subjects with hepatic impairment was approximately 17.5 hours. The time to peak concentrations (tmax) of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ was slightly delayed in subjects with hepatic impairment compared to age-matched controls (1.75 hrs vs. 1.0 hrs), and the elimination half lives of the α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ were prolonged to approximately 10 and 8 hours, respectively. The exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ was approximately 30-39% greater in patients with liver impairment than in age-matched controls. The safety and efficacy of this increased exposure to tetrabenazine and other circulating metabolites are unknown so that it is not possible to adjust the dosage of tetrabenazine in hepatic impairment to ensure safe use. Therefore, tetrabenazine is contraindicated in patients with hepatic impairment. [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.16), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients Who Are Poor or Extensive CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Patients should be genotyped for drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6, prior to treatment with daily doses of XENAZINE over 50 mg [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Poor Metabolizers
Although the pharmacokinetics of XENAZINE and its metabolites in subjects who do not express the drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6, poor metabolizers, (PMs), have not been systematically evaluated, it is likely that the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ would be increased similar to that observed in patients taking strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (3- and 9-fold, respectively). Patients who are PMs should not be given doses greater than 50 mg per day and the maximum recommended single dose is 25 mg [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4), and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Extensive or Intermediate CYP2D6 Metabolizers
In patients who express the enzyme, CYP2D6, (extensive [EMs] or intermediate [IMs] metabolizers), the maximum recommended daily dose is 100 mg per day, with a maximum recommended single dose of 37.5 mg [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Drug Interactions
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
In vitro studies indicate that α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ are substrates for CYP2D6. The effect of CYP2D6 inhibition on the pharmacokinetics of tetrabenazine and its metabolites was studied in 25 healthy subjects following a single 50 mg dose of tetrabenazine given after 10 days of administration of the strong CYP2D6 inhibitor paroxetine 20 mg daily. There was an approximately 30% increase in Cmax and an approximately 3-fold increase in AUC for α-HTBZ in subjects given paroxetine prior to tetrabenazine compared to tetrabenazine given alone. For β-HTBZ, the Cmax and AUC were increased 2.4- and 9-fold, respectively, in subjects given paroxetine prior to tetrabenazine given alone. The elimination half-life of α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ was approximately 14 hours when tetrabenazine was given with paroxetine.
Strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine) markedly increase exposure to these metabolites. The effect of moderate or weak CYP2D6 inhibitors such as duloxetine, terbinafine, amiodarone, or sertraline on the exposure to XENAZINE and its metabolites has not been evaluated [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)].
Digoxin
Digoxin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein. A study in healthy volunteers showed that XENAZINE (25 mg twice daily for 3 days) did not affect the bioavailability of digoxin, suggesting that at this dose, XENAZINE does not affect P-glycoprotein in the intestinal tract. In vitro studies also do not suggest that XENAZINE or its metabolites are P-glycoprotein inhibitors.
Reserpine
XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking reserpine. At least 20 days should elapse after stopping reserpine before starting XENAZINE [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
XENAZINE is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs. XENAZINE should not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within a minimum of 14 days of discontinuing therapy with an MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No increase in tumors was observed in p53+/- transgenic mice treated orally with tetrabenazine at doses of 0, 5, 15 and 30 mg/kg/day for 26 weeks. When compared to humans receiving a 50 mg dose of XENAZINE, mice dosed with a 30 mg/kg dose of tetrabenazine produce about one sixth the levels of 9-desmethyl-beta-DHTBZ, a major human metabolite. Therefore, this study may not have adequately characterized the potential of tetrabenazine to be carcinogenic in people.
Mutagenesis
Tetrabenazine and metabolites α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ were negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay. Tetrabenazine was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells in the presence of metabolic activation. α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ were clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. In vivo micronucleus tests were conducted in male and female rats and male mice. Tetrabenazine was negative in male mice and rats but produced an equivocal response in female rats.
Because the bioactivation system used in the in vitro studies was hepatic S9 fraction prepared from rat, a species that, when dosed with tetrabenazine, does not produce 9-desmethyl-beta-DHTBZ, a major human metabolite, these studies may not have adequately assessed the potential of XENAZINE to be mutagenic in humans. Furthermore, since the mouse produces very low levels of this metabolite when dosed with tetrabenazine, the in vivo study may not have adequately assessed the potential of XENAZINE to be mutagenic in humans.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of tetrabenazine (doses of 5, 15, or 30 mg/kg/day) to female rats prior to and throughout mating, and continuing through day 7 of gestation resulted in disrupted estrous cyclicity at doses greater than 5 mg/kg/day (less than the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis).
No effects on mating and fertility indices or sperm parameters (motility, count, density) were observed when males were treated orally with tetrabenazine (doses of 5, 15 or 30 mg/kg/day; up to 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) prior to and throughout mating with untreated females.
Because rats dosed with tetrabenazine do not produce 9-desmethyl-beta-DHTBZ, a major human metabolite, these studies may not have adequately assessed the potential of XENAZINE to impair fertility in humans.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1
The efficacy of XENAZINE as a treatment for the chorea of Huntington's disease was established primarily in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multi-center trial (Study 1) conducted in ambulatory patients with a diagnosis of HD. The diagnosis of HD was based on family history, neurological exam, and genetic testing. Treatment duration was 12 weeks, including a 7-week dose titration period and a 5-week maintenance period followed by a 1-week washout. The dose of XENAZINE was started at 12.5 mg per day and titrated upward at weekly intervals in 12.5 mg increments until satisfactory control of chorea was achieved, until intolerable side effects occurred, or until a maximal dose of 100 mg per day was reached.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the Total Chorea Score, an item of the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS). On this scale, chorea is rated from 0 to 4 (with 0 representing no chorea) for 7 different parts of the body. The total score ranges from 0 to 28.
As shown in Figure 1, Total Chorea Scores for subjects in the drug group declined by an estimated 5.0 units during maintenance therapy (average of Week 9 and Week 12 scores versus baseline), compared to an estimated 1.5 units in the placebo group. The treatment effect of 3.5 units was statistically significant. At the Week 13 follow-up in Study 1 (1 week after discontinuation of the study medication), the Total Chorea Scores of subjects receiving XENAZINE returned to baseline.
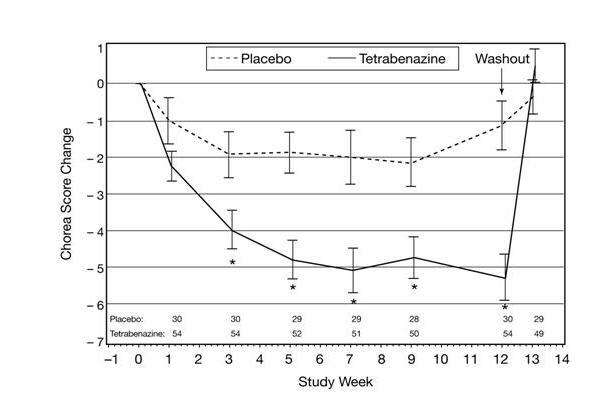
|
(error bars are ± s.e.m.) *p<0.05 |
Figure 1. Mean ± s.e.m. Changes from Baseline in Total Chorea Score in 84 HD Subjects Treated with XENAZINE (n=54) or Placebo (n=30)
Figure 2 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from the XENAZINE and placebo treatment groups who achieved the level of reduction in the Total Chorea Score shown on the X axis. The left-ward shift of the curve (toward greater improvement) for XENAZINE-treated patients indicates that these patients were more likely to have any given degree of improvement in chorea score. Thus, for example, about 7% of placebo patients had a 6-point or greater improvement compared to 50% of XENAZINE-treated patients. The percentage of patients achieving reductions of at least 10, 6, and 3-points from baseline to Week 12 are shown in the inset table.
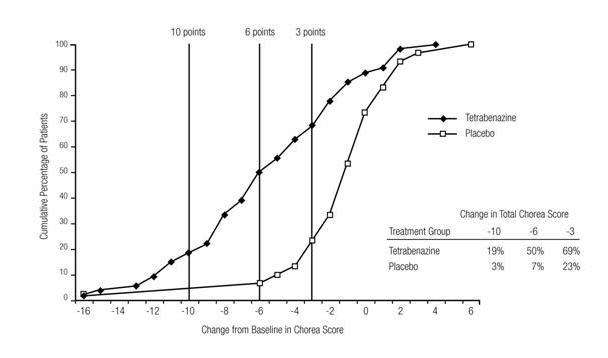
Figure 2. Cumulative Percentage of Patients with Specified Changes from Baseline in Total Chorea Score. The Percentages of Randomized Patients within each treatment group who completed Study 1 were: Placebo 97%, Tetrabenazine 91%.
A Physician-rated Clinical Global Impression (CGI) favored XENAZINE statistically. In general, measures of functional capacity and cognition showed no difference between XENAZINE and placebo. However, one functional measure (Part 4 of the UHDRS), a 25-item scale assessing the capacity for patients to perform certain activities of daily living, showed a decrement for patients treated with XENAZINE compared to placebo, a difference that was nominally statistically significant. A 3-item cognitive battery specifically developed to assess cognitive function in patients with HD (Part 2 of the UHDRS) also showed a decrement for patients treated with XENAZINE compared to placebo, but the difference was not statistically significant.
Study 2
A second controlled study was performed in patients who had been treated with open-label XENAZINE for at least 2 months (mean duration of treatment was 2 years). They were randomized to continuation of XENAZINE at the same dose (n=12) or to placebo (n=6) for three days, at which time their chorea scores were compared. Although the comparison did not reach statistical significance (p=0.1), the estimate of the treatment effect was similar to that seen in Study 1 (about 3.5 units).
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
XENAZINE (tetrabenazine) tablets are available in the following strengths and packages:
The 12.5 mg XENAZINE tablets are white, cylindrical biplanar tablets with beveled edges, non-scored, embossed on one side with "CL" and "12.5".
Bottles of 112: NDC 67386-421-01
The 25 mg XENAZINE tablets are yellowish-buff, cylindrical biplanar tablets with beveled edges, scored, embossed on one side with "CL" and "25".
Bottles of 112: NDC 67386-422-01
16.2 Storage
Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved Medication Guide
Physicians are advised to discuss the following issues with patients and their families:
17.1 Risk of Suicidality
Patients and their families should be told that XENAZINE may increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behaviors. Patients and their families should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of suicidal ideation and should report it immediately to the patient's physician [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
17.2 Risk of Depression
Patients and their families should be told that XENAZINE may cause depression or may worsen pre-existing depression. They should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of sadness, worsening of depression, withdrawal, insomnia, irritability, hostility (aggressiveness), akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), anxiety, agitation, or panic attacks and should report such symptoms promptly to the patient's physician [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
17.3 Dosing of XENAZINE
Patients and their families should be told that the dose of XENAZINE will be titrated up slowly to the dose that is best for each patient. Sedation, akathisia, parkinsonism, depression, and difficulty swallowing may occur. Such symptoms should be promptly reported to the physician and the XENAZINE dose may need to be reduced or discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), and Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.6, 5.7, 5.9)].
17.4 Risk of Sedation and Somnolence
Patients should be told that XENAZINE may induce sedation and somnolence and may impair the ability to perform tasks that require complex motor and mental skills. Patients should be advised that until they learn how they respond to XENAZINE, they should be careful doing activities that require them to be alert, such as driving a car or operating machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
17.5 Interaction with Alcohol
Patients and their families should be advised that alcohol may potentiate the sedation induced by XENAZINE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
17.6 Usage in Pregnancy
Patients and their families should be advised to notify the physician if the patient becomes pregnant or intends to become pregnant during XENAZINE therapy, or is breast-feeding or intending to breast-feed an infant during therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
17.7 General Advice
Patients and their families should be advised to notify the physician of all medications the patient is taking and to consult with the physician before starting any new medications.
Manufactured by:
Recipharm Fontaine SAS
Rue des Prés Potets
21121 Fontaine-les-Dijon
France
For:
Lundbeck
Deerfield, IL 60015, U.S.A.
Xenazine® is a registered trademark of Valeant International Bermuda
Revised: September 2012
606430D
MEDICATION GUIDE
Xenazine® (ZEN-uh-zeen)
(tetrabenazine) Tablets
Read the Medication Guide that comes with XENAZINE before you start taking it and each time you refill the prescription. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. You should share this information with your family members and caregivers.
What is the most important information I should know about XENAZINE?
-
XENAZINE can cause serious side effects, including:
- depression
- suicidal thoughts
- suicidal actions
- You should not start taking XENAZINE if you are depressed (have untreated depression or depression that is not well controlled by medicine) or have suicidal thoughts.
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts or feelings. This is especially important when XENAZINE is started and when the dose is changed.
Call the doctor right away if you become depressed or have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- feel sad or have crying spells
- loose interest in seeing your friends or doing things you used to enjoy
- sleep a lot more or a lot less than usual
- feel unimportant
- feel guilty
- feel hopeless or helpless
- feel more irritable, angry or aggressive than usual
- feel more or less hungry than usual or notice a big change in your body weight
- have trouble paying attention
- feel tired or sleepy all the time
- have thoughts about hurting yourself or ending your life
What is XENAZINE?
XENAZINE is a medicine that is used to treat the involuntary movements (chorea) of Huntington's disease. XENAZINE does not cure the cause of the involuntary movements, and it does not treat other symptoms of Huntington's disease, such as problems with thinking or emotions.
It is not known whether XENAZINE is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take XENAZINE?
Do not take XENAZINE if you:
- are depressed or have thoughts of suicide. See "What is the most important information I should know about XENAZINE?"
- have liver problems.
- are taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medicine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- are taking reserpine. Do not take medicines that contain reserpine (such as Serpalan® and Renese®-R) with XENAZINE. If your doctor plans to switch you from taking reserpine to XENAZINE, you must wait at least 20 days after your last dose of reserpine before you start taking XENAZINE.
What should I tell my doctor before taking XENAZINE?
Tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have emotional or mental problems (for example, depression, nervousness, anxiety, anger, agitation, psychosis, previous suicidal thoughts or suicide attempts)
- have liver disease
- have any allergies. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of the ingredients in XENAZINE.
- have breast cancer or a history of breast cancer
- have heart disease that is not stable, have heart failure or recently had a heart attack
- have an irregular heart beat (cardiac arrhythmia)
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if XENAZINE can harm your unborn baby.
- are breast-feeding. It is not known if XENAZINE passes into breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription medicines and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal products. Using XENAZINE with certain other medicines may cause serious side effects. Do not start any new medicines while taking XENAZINE without talking to your doctor first.
How should I take XENAZINE?
- XENAZINE is a tablet that you take by mouth.
- Take XENAZINE exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- You may take XENAZINE with or without food.
- Your doctor will increase your dose of XENAZINE each week for several weeks, until you and your doctor find the best dose for you.
- If you stop taking XENAZINE or miss a dose, your involuntary movements may return or worsen in 12 to 18 hours after the last dose.
- Before starting XENAZINE, you should talk to your healthcare provider about what to do if you miss a dose. If you miss a dose and it is time for your next dose, do not double the dose.
- Tell your doctor if you stop taking XENAZINE for more than 5 days. Do not take another dose until you talk to your doctor.
- If your doctor thinks you need to take more than 50 mg of XENAZINE each day, you will need to have a blood test to see if it is safe for you.
What should I avoid while taking XENAZINE?
Sleepiness (sedation) is a common side effect of XENAZINE. While taking XENAZINE, do not drive a car or operate dangerous machinery until you know how XENAZINE affects you. Drinking alcohol and taking other drugs that may also cause sleepiness while you are taking XENAZINE may increase any sleepiness caused by XENAZINE.
What are the possible side effects of XENAZINE?
XENAZINE can cause serious side effects, including:
- Depression, suicidal thoughts, or actions. See "What is the most important information I should know about XENAZINE?"
-
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS). Call your doctor right away and go to the nearest emergency room if you develop these signs and symptoms that do not have another obvious cause:
-
- high fever -
- stiff muscles -
- problems thinking -
- very fast or uneven heartbeat -
- increased sweating
-
- Parkinsonism. Symptoms of Parkinsonism include: slight shaking, body stiffness, trouble moving or keeping your balance.
- Restlessness. You may get a condition where you feel a strong urge to move. This is called akathisia.
- Trouble swallowing. XENAZINE may increase the chance that you will have trouble swallowing. Increased coughing may be the first sign that you are having trouble swallowing. Trouble swallowing increases your risk of pneumonia.
- Irregular heartbeat. XENAZINE increases your chance of having certain changes in the electrical activity in your heart which can be seen on an electrocardiogram (EKG). These changes can lead to a dangerous abnormal heartbeat. Taking XENAZINE with certain medicines may increase this chance.
- Dizziness due to blood pressure changes when you change position (orthostatic hypotension). Change positions slowly from lying down to sitting up and from sitting up to standing when taking XENAZINE. Tell your doctor right away if you get dizzy or faint while taking XENAZINE. Your doctor may need to watch your blood pressure closely.
- Tardive dyskinesia (TD). TD is a condition where there is repeated facial grimacing that cannot be controlled, sticking out of the tongue, smacking of the lips, puckering and pursing of the lips, and rapid eye blinking. XENAZINE works like other drugs that can cause TD. If you get TD with XENAZINE, it is possible that the TD will not go away.
Common side effects with XENAZINE include:
- sleepiness (sedation)
- trouble sleeping
- depression
- tiredness (fatigue)
- anxiety
- restlessness
- agitation
- nausea
Tell your doctor if you have any side effects. Do not stop taking XENAZINE without talking to your doctor first.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about XENAZINE
XENAZINE contains the active ingredient tetrabenazine. It also contains these inactive ingredients: lactose, maize starch, talc, and magnesium stearate. The 25 mg tablet, which is pale yellow, also contains yellow iron oxide.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use XENAZINE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give XENAZINE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. Keep XENAZINE out of the reach of children.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about XENAZINE. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about XENAZINE that is written for healthcare professionals. You can also call the XENAZINE Information Center at 1-888-882-6013 (option 1) or visit www.xenazineusa.com.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Recipharm Fontaine SAS
Rue des Prés Potets
21121 Fontaine-les-Dijon
France
For:
Lundbeck
Deerfield, IL 60015, U.S.A.
Xenazine® is a registered trademark of Valeant International Bermuda
Revised: September 2012
606430D
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 12.5 mg Bottle Label
NDC 67386-421-01
112 Tablets
Rx only
Xenazine®
(tetrabenazine) Tablets
12.5 mg
MEDICATION GUIDE TO BE DISPENSED
WITH EACH PRESCRIPTION.
GO TO www.xenazineusa.com

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Bottle Label
NDC 67386-422-01
112 Tablets
Rx only
Xenazine®
(tetrabenazine) Tablets
25 mg
MEDICATION GUIDE TO BE DISPENSED
WITH EACH PRESCRIPTION.
GO TO www.xenazineusa.com
Xenazinetetrabenazine TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Xenazinetetrabenazine TABLET
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||