Zidovudine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use zidovudine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for zidovudine capsules, USP.Zidovudine Capsules, USPInitial U.S. Approval: 1987 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES(5.6)BOXED WARNINGWARNING: RISK OF HEMATOLOGICAL TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. Hematologic toxicity including neutropenia and severe anemia have been associated with the use of zidovudine. (5.1) Symptomatic myopathy associated with prolonged use of zidovudine. (5.2) Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues including zidovudine. Suspend treatment if clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity occur. (5.3) INDICATIONS AND USAGE Treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) infection in combination with other antiretroviral agents. (1.1) Prevention of maternal-fetal HIV-1 transmission. (1.2) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Treatment of HIV-1 infection:Adults: 600 mg/day in divided doses with other antiretroviral agents. Pediatric patients (aged 4 weeks to
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- WARNING: RISK OF HEMATOLOGICAL TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS
- 1 ZIDOVUDINE INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 ZIDOVUDINE DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 ZIDOVUDINE CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Hematologic Toxicity/Bone Marrow Suppression
- 5.2 Myopathy
- 5.3 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly With Steatosis
- 5.4 Use With Interferon- and Ribavirin-Based Regimens in HIV-1/HCV Co-Infected Patients
- 5.5 Use With Other Zidovudine-Containing Products
- 5.6 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
- 5.7 Fat Redistribution
- 6 ZIDOVUDINE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 ZIDOVUDINE DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg (100 Capsule Bottle)
- PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK OF HEMATOLOGICAL TOXICITY, MYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS
Hematologic Toxicity: Zidovudine capsules have been associated with hematologic toxicity including neutropenia and severe anemia, particularly in patients with advanced HIV-1 disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myopathy: Prolonged use of zidovudine has been associated with symptomatic myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly: Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues alone or in combination, including zidovudine and other antiretrovirals. Suspend treatment if clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of HIV-1
1.2 Prevention of Maternal-Fetal HIV-1 Transmission
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- antepartum therapy of HIV-1 infected mothers
- intrapartum therapy of HIV-1 infected mothers
- post-partum therapy of HIV-1 exposed neonate.
- In most cases, zidovudine capsules, USP for prevention of maternal-fetal HIV-1 transmission should be given in combination with other antiretroviral drugs.
- Prevention of HIV-1 transmission in women who have received zidovudine capsules, USP for a prolonged period before pregnancy has not been evaluated.
- Because the fetus is most susceptible to the potential teratogenic effects of drugs during the first 10 weeks of gestation and the risks of therapy with zidovudine capsules, USP during that period are not fully known, women in the first trimester of pregnancy who do not require immediate initiation of antiretroviral therapy for their own health may consider delaying use; this indication is based on use after 14 weeks gestation.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Treatment of HIV-1 Infection
Adults:
Pediatric Patients (Aged 4 Weeks to <18 Years):
| Body Weight (kg) |
Total Daily Dose |
Dosage Regimen and Dose |
|
| Twice Daily |
Three Times Daily |
||
| 4 to <9 |
24 mg/kg/day |
12 mg/kg |
8 mg/kg |
| ≥9 to <30 |
18 mg/kg/day |
9 mg/kg |
6 mg/kg |
| ≥30 |
600 mg/day |
300 mg |
200 mg |
222
2.2 Prevention of Maternal-Fetal HIV-1 Transmission
Maternal Dosing:[see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
Neonatal Dosing:
| Route |
Total Daily Dose |
Dose and Dosage Regimen |
| Oral |
8 mg/kg/day |
2 mg/kg every 6 hours |
| IV |
6 mg/kg/day |
1.5 mg/kg infused over 30 minutes, every 6 hours |
2.3 Patients With Severe Anemia and/or Neutropenia
3[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
2.4 Patients With Renal Impairment
End-Stage Renal Disease:[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]
2.5 Patients With Hepatic Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hematologic Toxicity/Bone Marrow Suppression
3
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
5.2 Myopathy
5.3 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly With Steatosis
5.4 Use With Interferon- and Ribavirin-Based Regimens in HIV-1/HCV Co-Infected Patients
In vitro [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]
5.5 Use With Other Zidovudine-Containing Products
Zidovudine should not be administered with combination products that contain zidovudine as one of their components (e.g., COMBIVIR® [lamivudine and zidovudine] tablets or TRIZIVIR® [abacavir sulfate, lamivudine, and zidovudine] tablets).
5.6 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Mycobacterium aviumPneumocystis jiroveciialso
5.7 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance,” have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Hematologic toxicity, including neutropenia and anemia [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
- Symptomatic myopathy [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
- Hepatic decompensation in patients co-infected with HIV-1 and hepatitis C [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adults:
| Adverse Reaction | Zidovudine 500 mg/day (n = 453) |
Placebo (n = 428) |
|---|---|---|
|
*Reported in ≥5% of study population. †Not statistically significant versus placebo. |
||
|
Body as a whole
|
|
|
| Asthenia |
9%†
|
6% |
| Headache |
63% |
53% |
| Malaise |
53% |
45% |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
|
|
| Anorexia |
20% |
11% |
| Constipation |
6%†
|
4% |
| Nausea |
51% |
30% |
| Vomiting |
17% |
10% |
| Test (Abnormal Level) |
Zidovudine 500 mg/day (n = 453) |
Placebo (n = 428) |
|---|---|---|
| ULN = Upper limit of normal. |
||
| Anemia (Hgb<8 g/dL) |
1% |
<1% |
| Granulocytopenia (<750 cells/mm3) |
2% |
2% |
| Thrombocytopenia (platelets<50,000/mm3) |
0% |
<1% |
| ALT (>5 x ULN) |
3% |
3% |
| AST (>5 x ULN) |
1% |
2% |
Study ACTG 300: ® 2
| Adverse Reaction | EPIVIR plus Zidovudine (n = 236) |
Didanosine (n = 235) |
|---|---|---|
|
*Includes pain, discharge, erythema, or swelling of an ear. |
||
|
Body as a whole
|
|
|
| Fever |
25% |
32% |
|
Digestive
|
|
|
| Hepatomegaly |
11% |
11% |
| Nausea & vomiting |
8% |
7% |
| Diarrhea |
8% |
6% |
| Stomatitis |
6% |
12% |
| Splenomegaly |
5% |
8% |
|
Respiratory
|
|
|
| Cough |
15% |
18% |
| Abnormal breath sounds/wheezing |
7% |
9% |
|
Ear, Nose, and Throat
|
|
|
| Signs or symptoms of ears*
|
7% |
6% |
| Nasal discharge or congestion |
8% |
11% |
|
Other
|
|
|
| Skin rashes |
12% |
14% |
| Lymphadenopathy |
9% |
11% |
| ULN = Upper limit of normal. ANC = Absolute neutrophil count. |
||
|
Test (Abnormal Level)
|
EPIVIR plus Zidovudine
|
Didanosine
|
| Neutropenia (ANC<400 cells/mm3) |
8% |
3% |
| Anemia (Hgb<7 g/dL) |
4% |
2% |
| Thrombocytopenia (platelets<50,000/mm3) |
1% |
3% |
| ALT (>10 x ULN) |
1% |
3% |
| AST (>10 x ULN) |
2% |
4% |
| Lipase (>2.5 x ULN) |
3% |
3% |
| Total amylase (>2.5 x ULN) |
3% |
3% |
2
Use for the Prevention of Maternal-Fetal Transmission of HIV-1:3in utero
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Body as a Whole:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Cardiovascular:,
Endocrine:
Eye:
Gastrointestinal:
General:
Hemic and Lymphatic:
Hepatobiliary Tract and Pancreas:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous:
Respiratory:
Skin:
Special Senses:
Urogenital:
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antiretroviral Agents
Stavudine:in vitro
Nucleoside Analogues Affecting DNA Replication:in vitro
7.2 Doxorubicin
in vitro
7.3 Hematologic/Bone Marrow Suppressive/Cytotoxic Agents
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C.
[see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
[see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry:
8.3 Nursing Mothers
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
8.4 Pediatric Use
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14.2), (14.3)]
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
[see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
OD
11 DESCRIPTION
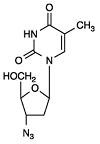
101354
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Bioavailability:
| Parameter | Mean ± SD (except where noted) |
|---|---|
|
*Median [range]. †Approximate range. |
|
| Oral bioavailability (%) |
64 ± 10 (n = 5) |
| Apparent volume of distribution (L/kg) |
1.6 ± 0.6 (n = 8) |
| Plasma protein binding (%) |
<38 |
| CSF:plasma ratio*
|
0.6 [0.04 to 2.62] (n = 39) |
| Systemic clearance (L/hr/kg) |
1.6 ± 0.6 (n = 6) |
| Renal clearance (L/hr/kg) |
0.34 ± 0.05 (n = 9) |
| Elimination half-life (hr)†
|
0.5 to 3 (n = 19) |
Metabolism and Elimination:
Effect of Food on Absorption:
Special Populations:Renal Impairment:
| Parameter | Control Subjects (Normal Renal Function) (n = 6) |
Patients With Renal Impairment (n = 14) |
|---|---|---|
|
*Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. |
||
| CrCl (mL/min) |
120 ± 8 |
18 ± 2 |
| Zidovudine AUC (ng•hr/mL) |
1,400 ± 200 |
3,100 ± 300 |
| Zidovudine half-life (hr) |
1 ± 0.2 |
1.4 ± 0.1 |
Hepatic Impairment: [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Pediatric Patients:
Patients Aged 3 Months to 12 Years: 2[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
Patients Aged Less Than 3 Months: in utero[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
| Parameter | Birth to 14 Days | Aged 14 Days to 3 Months | Aged 3 Months to 12 Years |
|---|---|---|---|
|
*Data presented as mean ± standard deviation except where noted. †Median [range]. |
|||
| Oral bioavailability (%) |
89 ± 19 (n = 15) |
61 ± 19 (n = 17) |
65 ± 24 (n = 18) |
| CSF:plasma ratio |
no data |
no data |
0.68 [0.03 to 3.25] †
(n = 38) |
| CL (L/hr/kg) |
0.65 ± 0.29 (n = 18) |
1.14 ± 0.24 (n = 16) |
1.85 ± 0.47 (n = 20) |
| Elimination half-life (hr) |
3.1 ± 1.2 (n = 21) |
1.9 ± 0.7 (n = 18) |
1.5 ± 0.7 (n = 21) |
Nursing Mothers: [see Use In Specific Populations (8.3) ]
Geriatric Patients
Gender:
Drug Interactions:[See Drug Interactions (7)]
| Note: ROUTINE DOSE MODIFICATION OF ZIDOVUDINE IS NOT WARRANTED WITH COADMINISTRATION OF THE FOLLOWING DRUGS. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug and Dose |
Zidovudine Dose |
n | Zidovudine Concentrations |
Concentration of Coadministered Drug |
|
| AUC | Variability | ||||
| ↑ = Increase; ↓= Decrease; ↔ = no significant change; AUC = area under the concentration versus time curve; CI = confidence interval. * This table is not all inclusive. † Estimated range of percent difference. |
|||||
| Atovaquone 750 mg q 12 hr with food |
200 mg q 8 hr |
14 |
↑AUC 31% |
Range 23% to 78%† |
↔ |
| Clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily |
100 mg q 4 hr x 7 days |
4 |
↓AUC 12% |
Range ↓34% to ↑14% |
Not Reported |
| Fluconazole 400 mg daily |
200 mg q 8 hr |
12 |
↑AUC 74% |
95% CI: 54% to 98% |
Not Reported |
| Lamivudine 300 mg q 12 hr |
single 200 mg |
12 |
↑AUC 13% |
90% CI: 2% to 27% |
↔ |
| Methadone 30 to 90 mg daily |
200 mg q 4 hr |
9 |
↑AUC 43% |
Range 16% to 64%† |
↔ |
| Nelfinavir 750 mg q 8 hr x 7 to 10 days |
single 200 mg |
11 |
↓AUC 35% |
Range 28% to 41% |
↔ |
| Probenecid 500 mg q 6 hr x 2 days |
2 mg/kg q 8 hr x 3 days |
3 |
↑AUC 106% |
Range 100% to 170%† |
Not Assessed |
| Rifampin 600 mg daily x 14 days |
200 mg q 8 hr x 14 days |
8 |
↓AUC 47% |
90% CI: 41% to 53% |
Not Assessed |
| Ritonavir 300 mg q 6 hr x 4 days |
200 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
9 |
↓AUC 25% |
95% CI: 15% to 34% |
↔ |
| Valproic acid 250 mg or 500 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
100 mg q 8 hr x 4 days |
6 |
↑AUC 80% |
Range 64% to 130%† |
Not Assessed |
Ribavirin: In vitro[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action:
Antiviral Activity:50905050
Resistance:
Cross-Resistance:
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
+/-in vitro
13.2 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology Studies
in vitro
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adults
Combination Therapy:
Monotherapy:3
14.2 Pediatric Patients
310
| Endpoint | EPIVIR plus Zidovudine (n = 236) |
Didanosine (n = 235) |
|---|---|---|
| HIV disease progression or death (total) |
15 (6.4%) |
37 (15.7%) |
| Physical growth failure |
7 (3%) |
6 (2.6%) |
| Central nervous system deterioration |
4 (1.7%) |
12 (5.1%) |
| CDC Clinical Category C |
2 (0.8%) |
8 (3.4%) |
| Death |
2 (0.8%) |
11 (4.7%) |
14.3 Prevention of Maternal-Fetal HIV-1 Transmission
33
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Zidovudine Capsules USP, 100 mg are white/white size ‘3’ hard gelatin capsules imprinted with ‘D’ on white cap and ‘01’ on white body with black edible ink.
Bottles of 100 NDC 65862-107-01
10 x 10 Unit-dose Capsules NDC 65862-107-10
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Advice for the Patient
Neutropenia and Anemia:[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Myopathy[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Lactic Acidosis/Hepatomegaly[see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
HIV-1/HCV Co-Infection[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Use With Other Zidovudine-Containing Products: [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Redistribution/Accumulation of Body Fat:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Common Adverse Reactions:[see Adverse Reactions (6)]
Drug Interactions: [see Drug Interactions (7)]
Pregnancy:in utero [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Information About HIV-1 Infection:
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safe sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier method to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- Do not breastfeed. Zidovudine is excreted in human breast milk. Mothers with HIV-1 should not breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in the breast milk.
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
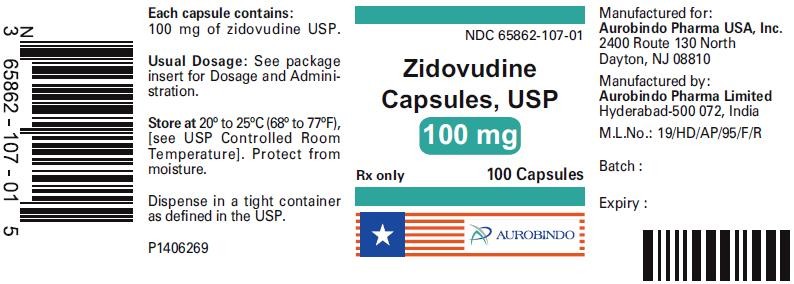
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg (100 Capsule Bottle)
NDC 65862-107-01
Zidovudine Capsules, USP
100 mg
Rx only 100 Capsules
AUROBINDO
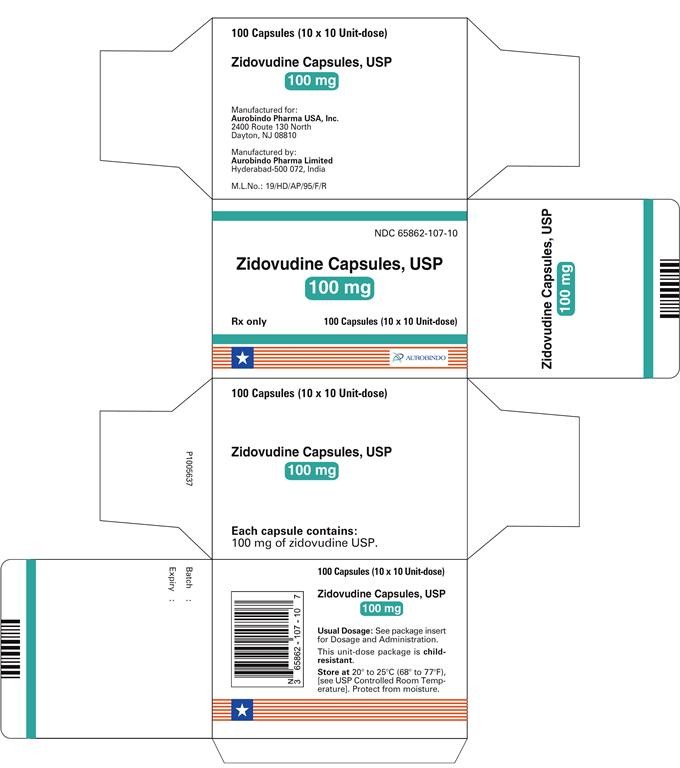
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Blister Carton (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
NDC 65862-107-10
Zidovudine Capsules, USP
100 mg
Rx only 100 Capsules (10 x 10 Unit-dose)
AUROBINDO
ZidovudineZidovudine CAPSULE
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||