Zoledronic Acid
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use zoledronic acid injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for zoledronic acid injection. Zoledronic Acid Injection Concentrate for Intravenous InfusionInitial U.S. Approval: 2001 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES5.6INDICATIONS AND USAGEZoledronic acid injection is a bisphosphonate indicated for the treatment of: Hypercalcemia of malignancy (1.1) Patients with multiple myeloma and patients with documented bone metastases from solid tumors, in conjunction with standard antineoplastic therapy. Prostate cancer should have progressed after treatment with at least one hormonal therapy (1.2) 1.3DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONHypercalcemia of malignancy (2.1) 4 mg as a single-use intravenous infusion over no less than 15 minutes 4 mg as retreatment after a minimum of 7 days 2.2 4 mg as a single-use intravenous infusion over no less than 15 minutes every 3 to 4 weeks for patients with creatinine clearance of greater than 60 mL/min Reduce the dose for patients with renal impairment Coadminister oral calcium supplements of 500 mg and a multiple vitamin containing 400 IU of Vitamin D daily. 2.3DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS3CONTRAINDICATIONS4WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Patients being treated with zoledronic acid injection should not be treated with Reclast®* (5.1) Adequately rehydrate patients with hypercalcemia of malignancy prior to administration of zoledronic acid injection and monitor electrolytes during treatment (5.2) Renal toxicity may be greater in patients with renal impairment. Do not use doses greater than 4 mg. Treatment in patients with severe renal impairment is not recommended. Monitor serum creatinine before each dose (5.3) Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported. Preventive dental exams should be performed before starting zoledronic acid injection. Avoid invasive dental procedures (5.4) Severe incapacitating bone, joint, muscle pain may occur. Discontinue zoledronic acid injection if severe symptoms occur (5.5) Zoledronic acid injection can cause fetal harm. Women of childbearing potential should be advised of the potential hazard to the fetus and to avoid becoming pregnant (5.9, 8.1) Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures have been reported in patients receiving bisphosphonate therapy. These fractures may occur after minimal or no trauma. Evaluate patients with thigh or groin pain to rule out a femoral fracture. Consider drug discontinuation in patients suspected to have an atypical femur fracture. (5.6) Side Effects6.1To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact CARACO Pharmaceutical Laboratories Ltd. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS Aminoglycosides: May have an additive effect to lower serum calcium for prolonged periods (7.1) Loop diuretics: Concomitant use with zoledronic acid injection may increase risk of hypocalcemia (7.2) Nephrotoxic drugs: Use with caution (7.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether zoledronic acid is excreted in human milk (8.3) Pediatric Use: Not indicated for use in pediatric patients (8.4) Geriatric Use: Special care to monitor renal function (8.5)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- 1 ZOLEDRONIC ACID INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 ZOLEDRONIC ACID DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 ZOLEDRONIC ACID CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Drugs with Same Active Ingredient or in the Same Drug Class
- 5.2 Hydration and Electrolyte Monitoring
- 5.3 Renal Impairment
- 5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
- 5.5 Musculoskeletal Pain
- 5.6 Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures
- 5.7 Patients with Asthma
- 5.8 Hepatic Impairment
- 5.9 Use in Pregnancy
- 6 ZOLEDRONIC ACID ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
- 11 ZOLEDRONIC ACID DESCRIPTION
- 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
1.2 Multiple Myeloma and Bone Metastases of Solid Tumors
1.3 Important Limitation of Use
zoledronic acid injection
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
.
2.1 Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
no less than 15 minutes
see Warnings And Precautions (5.2)
see Warnings And Precautions (5.2)
2.2 Multiple Myeloma and Metastatic Bone Lesions of Solid Tumors
no less than 15 minutes
see Warnings And Precautions (5.2)
| Baseline Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Zoledronic Acid Injection Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| greater than 60 |
4 mg |
| 50 to 60 |
3.5 mg |
| 40 to 49 |
3.3 mg |
| 30 to 39 |
3 mg |
2.3 Preparation of Solution
4 mg/5 mL Single-Use Vial
| Remove and Use Zoledronic Acid Injection Volume (mL) | Dose (mg) |
|---|---|
| 4.4 |
3.5 |
| 4.1 |
3.3 |
| 3.8 |
3 |
The withdrawn concentrate must be diluted in 100 mL of sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
If not used immediately after dilution with infusion media, for microbiological integrity, the solution should be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). The refrigerated solution should then be equilibrated to room temperature prior to administration. The total time between dilution, storage in the refrigerator, and end of administration must not exceed 24 hours.
2.4 Method of Administration
see Warnings And Precautions (5.2)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Zoledronic Acid or Any Components of Zoledronic Acid Injection
see Adverse Reactions (6.2)
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drugs with Same Active Ingredient or in the Same Drug Class
®
5.2 Hydration and Electrolyte Monitoring
Patients with hypercalcemia of malignancy must be adequately rehydrated prior to administration of zoledronic acid injection. Loop diuretics should not be used until the patient is adequately rehydrated and should be used with caution in combination with zoledronic acid injection in order to avoid hypocalcemia. Zoledronic acid injection should be used with caution with other nephrotoxic drugs.
Standard hypercalcemia-related metabolic parameters, such as serum levels of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium, as well as serum creatinine, should be carefully monitored following initiation of therapy with zoledronic acid injection. If hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, or hypomagnesemia occur, short-term supplemental therapy may be necessary.
5.3 Renal Impairment
see Adverse Reactions (6.1) .
see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) .
5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
see Adverse Reactions (6.2) .
5.5 Musculoskeletal Pain
see Adverse Reactions (6.2)
5.6 Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures
Atypical5.7 Patients with Asthma
5.8 Hepatic Impairment
5.9 Use in Pregnancy
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
Renal Toxicity
see Warnings And Precautions (5) and Dosage And Administration (2)
| Patients Studied | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg n (%) |
Pamidronate 90 mg n (%) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. of Patients Studied |
86 |
(100) |
103 |
(100) |
| Total No. of Patients with any AE |
81 |
(94) |
95 |
(92) |
|
Body as a Whole
|
||||
| Fever |
38 |
(44) |
34 |
(33) |
| Progression of Cancer |
14 |
(16) |
21 |
(20) |
|
Cardiovascular
|
||||
| Hypotension |
9 |
(11) |
2 |
(2) |
|
Digestive
|
||||
| Nausea |
25 |
(29) |
28 |
(27) |
| Constipation |
23 |
(27) |
13 |
(13) |
| Diarrhea |
15 |
(17) |
17 |
(17) |
| Abdominal Pain |
14 |
(16) |
13 |
(13) |
| Vomiting |
12 |
(14) |
17 |
(17) |
| Anorexia |
8 |
(9) |
14 |
(14) |
|
Hemic and Lymphatic System
|
||||
| Anemia |
19 |
(22) |
18 |
(18) |
|
Infections
|
||||
| Moniliasis |
10 |
(12) |
4 |
(4) |
|
Laboratory Abnormalities
|
||||
| Hypophosphatemia |
11 |
(13) |
2 |
(2) |
| Hypokalemia |
10 |
(12) |
16 |
(16) |
| Hypomagnesemia |
9 |
(11) |
5 |
(5) |
|
Musculoskeletal
|
||||
| Skeletal Pain |
10 |
(12) |
10 |
(10) |
|
Nervous
|
||||
| Insomnia |
13 |
(15) |
10 |
(10) |
| Anxiety |
12 |
(14) |
8 |
(8) |
| Confusion |
11 |
(13) |
13 |
(13) |
| Agitation |
11 |
(13) |
8 |
(8) |
|
Respiratory
|
||||
| Dyspnea |
19 |
(22) |
20 |
(19) |
| Coughing |
10 |
(12) |
12 |
(12) |
|
Urogenital
|
||||
| Urinary Tract Infection
|
12 |
(14) |
15 |
(15) |
Acute Phase Reaction
Mineral and Electrolyte Abnormalities
| Grade 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter |
Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg |
||
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
|
Serum Creatinine |
2/86 |
(2%) |
3/100 |
(3%) |
Hypocalcemia |
1/86 |
(1%) |
2/100 |
(2%) |
Hypophosphatemia |
36/70 |
(51%) |
27/81 |
(33%) |
Hypomagnesemia |
0/71 |
— |
0/84 |
— |
| Grade 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg |
||
| n/N | (%) | n/N | (%) | |
Serum Creatinine |
0/86 |
— |
1/100 |
(1%) |
Hypocalcemia |
0/86 |
— |
0/100 |
— |
Hypophosphatemia |
1/70 |
(1%) |
4/81 |
(5%) |
Hypomagnesemia |
0/71 |
— |
1/84 |
(1%) |
Injection Site Reactions
Ocular Adverse Events
Adverse Reactions (6.2)
Multiple Myeloma and Bone Metastases of Solid Tumors
| Patients Studied | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg n (%) |
Pamidronate 90 mg n (%) |
Placebo n (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. of Patients |
1031 |
(100) |
556 |
(100) |
455 |
(100) |
| Total No. of Patients with any AE |
1015 |
(98) |
548 |
(99) |
445 |
(98) |
|
Blood and Lymphatic
|
||||||
| Anemia
|
344 |
(33) |
175 |
(32) |
128 |
(28) |
| Neutropenia |
124 |
(12) |
83 |
(15) |
35 |
(8) |
| Thrombocytopenia |
102 |
(10) |
53 |
(10) |
20 |
(4) |
|
Gastrointestinal
|
||||||
| Nausea |
476 |
(46) |
266 |
(48) |
171 |
(38) |
| Vomiting |
333 |
(32) |
183 |
(33) |
122 |
(27) |
| Constipation |
320 |
(31) |
162 |
(29) |
174 |
(38) |
| Diarrhea |
249 |
(24) |
162 |
(29) |
83 |
(18) |
| Abdominal Pain |
143 |
(14) |
81 |
(15) |
48 |
(11) |
| Dyspepsia |
105 |
(10) |
74 |
(13) |
31 |
(7) |
| Stomatitis |
86 |
(8) |
65 |
(12) |
14 |
(3) |
| Sore Throat |
82 |
(8) |
61 |
(11) |
17 |
(4) |
|
General Disorders and Administration Site
|
||||||
| Fatigue |
398 |
(39) |
240 |
(43) |
130 |
(29) |
| Pyrexia |
328 |
(32) |
172 |
(31) |
89 |
(20) |
| Weakness |
252 |
(24) |
108 |
(19) |
114 |
(25) |
| Edema Lower Limb |
215 |
(21) |
126 |
(23) |
84 |
(19) |
| Rigors |
112 |
(11) |
62 |
(11) |
28 |
(6) |
|
Infections
|
||||||
| Urinary Tract Infection |
124 |
(12) |
50 |
(9) |
41 |
(9) |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
101 |
(10) |
82 |
(15) |
30 |
(7) |
|
Metabolism
|
||||||
| Anorexia |
231 |
(22) |
81 |
(15) |
105 |
(23) |
| Weight Decreased |
164 |
(16) |
50 |
(9) |
61 |
(13) |
| Dehydration |
145 |
(14) |
60 |
(11) |
59 |
(13) |
| Appetite Decreased |
130 |
(13) |
48 |
(9) |
45 |
(10) |
|
Musculoskeletal
|
||||||
| Bone Pain |
569 |
(55) |
316 |
(57) |
284 |
(62) |
| Myalgia |
239 |
(23) |
143 |
(26) |
74 |
(16) |
| Arthralgia |
216 |
(21) |
131 |
(24) |
73 |
(16) |
| Back Pain |
156 |
(15) |
106 |
(19) |
40 |
(9) |
| Pain in Limb |
143 |
(14) |
84 |
(15) |
52 |
(11) |
|
Neoplasms
|
||||||
| Malignant Neoplasm Aggravated |
205 |
(20) |
97 |
(17) |
89 |
(20) |
|
Nervous
|
||||||
| Headache |
191 |
(19) |
149 |
(27) |
50 |
(11) |
| Dizziness (excluding vertigo) |
180 |
(18) |
91 |
(16) |
58 |
(13) |
| Insomnia |
166 |
(16) |
111 |
(20) |
73 |
(16) |
| Paresthesia |
149 |
(15) |
85 |
(15) |
35 |
(8) |
| Hypoesthesia |
127 |
(12) |
65 |
(12) |
43 |
(10) |
|
Psychiatric
|
||||||
| Depression |
146 |
(14) |
95 |
(17) |
49 |
(11) |
| Anxiety |
112 |
(11) |
73 |
(13) |
37 |
(8) |
| Confusion |
74 |
(7) |
39 |
(7) |
47 |
(10) |
|
Respiratory
|
||||||
| Dyspnea |
282 |
(27) |
155 |
(28) |
107 |
(24) |
| Cough |
224 |
(22) |
129 |
(23) |
65 |
(14) |
|
Skin
|
||||||
| Alopecia |
125 |
(12) |
80 |
(14) |
36 |
(8) |
| Dermatitis |
114 |
(11) |
74 |
(13) |
38 |
(8) |
| Grade 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg |
Placebo | |||
| n/N | (%) | n/N | (%) | n/N | (%) | |
Serum Creatinine  |
7/529 |
(1%) |
4/268 |
(2%) |
4/241 |
(2%) |
Hypocalcemia |
6/973 |
(<1%) |
4/536 |
(<1%) |
0/415 |
— |
Hypophosphatemia |
115/973 |
(12%) |
38/537 |
(7%) |
14/415 |
(3%) |
Hypermagnesemia |
19/971 |
(2%) |
2/535 |
(<1%) |
8/415 |
(2%) |
Hypomagnesemia |
1/971 |
(<1%) |
0/535 |
— |
1/415 |
(<1%) |
| Grade 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Parameter | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg |
Placebo | |||
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
|
Serum Creatinine  |
2/529
|
(<1%)
|
1/268
|
(<1%)
|
0/241
|
—
|
Hypocalcemia |
7/973 |
(<1%) |
3/536 |
(<1%) |
2/415 |
(<1%) |
Hypophosphatemia |
5/973 |
(<1%) |
0/537 |
— |
1/415 |
(<1%) |
Hypermagnesemia |
0/971 |
— |
0/535 |
— |
2/415 |
(<1%) |
Hypomagnesemia |
2/971 |
(<1%) |
1/535 |
(<1%) |
0/415 |
— |
Renal Toxicity
| Patient Population/Baseline Creatinine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Myeloma and Breast Cancer | Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg | ||
| n/N | (%) | n/N | (%) | |
| Normal |
27/246 |
(11%) |
23/246 |
(9%) |
| Abnormal |
2/26 |
(8%) |
2/22 |
(9%) |
| Total |
29/272 |
(11%) |
25/268 |
(9%) |
|
Solid Tumors
|
Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg
|
Placebo
|
||
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
|
| Normal |
17/154 |
(11%) |
10/143 |
(7%) |
| Abnormal |
1/11 |
(9%) |
1/20 |
(5%) |
| Total |
18/165 |
(11%) |
11/163 |
(7%) |
|
Prostate Cancer
|
Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg
|
Placebo
|
||
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
n/N
|
(%)
|
|
| Normal |
12/82 |
(15%) |
8/68 |
(12%) |
| Abnormal |
4/10 |
(40%) |
2/10 |
(20%) |
| Total |
16/92 |
(17%) |
10/78 |
(13%) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
see Warnings And Precautions (5)
Acute Phase Reaction-
Musculoskeletal Pain
see Warnings And Precautions (5 )
Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures
see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)
Ocular Adverse Events
Hypersensitivity Reactions
CNS : Special Senses : Gastrointestinal : Skin : Musculoskeletal : Cardiovascular : Respiratory: Renal : General Disorders and Administration Site : Laboratory Abnormalities :
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
In-vitro In-vitro In-vivo
7.1 Aminoglycosides
7.2 Loop Diuretics
7.3 Nephrotoxic Drugs
7.4 Thalidomide
No dose adjustment for zoledronic acid injection 4 mg is needed when coadministered with thalidomide. In a pharmacokinetic study of 24 patients with multiple myeloma, zoledronic acid injection 4 mg given as a 15 minute infusion was administered either alone or with thalidomide (100 mg once daily on days 1 to 14 and 200 mg once daily on days 15 to 28). Coadministration of thalidomide with zoledronic acid injection did not significantly change the pharmacokinetics of zoledronic acid or creatinine clearance.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D [see Warnings and Precaution (5.9)]
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of zoledronic acid injection in pregnant women. Zoledronic acid injection may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Bisphosphonates, such as zoledronic acid injection, are incorporated into the bone matrix and are gradually released over periods of weeks to years. The extent of bisphosphonate incorporation into adult bone, and hence, the amount available for release back into the systemic circulation, is directly related to the total dose and duration of bisphosphonate use. Although there are no data on fetal risk in humans, bisphosphonates do cause fetal harm in animals, and animal data suggest that uptake of bisphosphonates into fetal bone is greater than into maternal bone. Therefore, there is a theoretical risk of fetal harm (e.g., skeletal and other abnormalities) if a woman becomes pregnant after completing a course of bisphosphonate therapy. The impact of variables such as time between cessation of bisphosphonate therapy to conception, the particular bisphosphonate used, and the route of administration (intravenous versus oral) on this risk has not been established. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking or after taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
2
max(0-last)
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
see Dosage And Administration (2.4)
11 DESCRIPTION
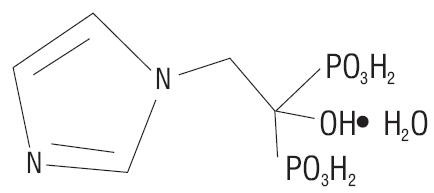
5102722
Inactive Ingredients:
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
In vitro
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
see Dosage And Administration (2) .
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
max1/2α1/2β1/2γ0-24h0-24h
In-vitro ex-vivo In vitro
Metabolism
in vitroin vivo14
Excretion
Special Populations
Pediatrics
see Pediatric Use (8.4)
Geriatrics
Race
Hepatic Insufficiency
Renal Insufficiency
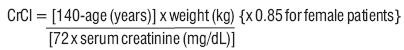
0.40-∞0-240-∞see Warnings And Precautions (5.2)
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
in-vivo
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Hypercalcemia of Malignancy
NOTEAdministration of zoledronic acid injection 4 mg given as a 5-minute intravenous infusion has been shown to result in an increased risk of renal toxicity, as measured by increases in serum creatinine, which can progress to renal failure. The incidence of renal toxicity and renal failure has been shown to be reduced when zoledronic acid injection 4 mg is given as a 15-minute intravenous infusion. Zoledronic acid injection should be administered by intravenous infusion over no less than 15 minutes [see Warnings And Precautions (5.1, 5.2) and Dosage And Administration (2.4) ].
In these studies, no additional benefit was seen for zoledronic acid injection 8 mg over zoledronic acid injection 4 mg; however, the risk of renal toxicity of zoledronic acid injection 8 mg was significantly greater than that seen with zoledronic acid injection 4 mg.
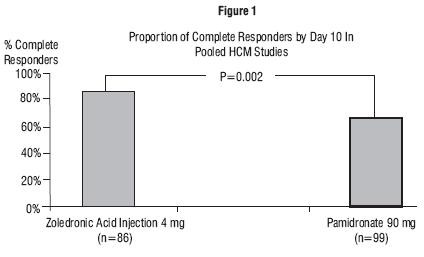
| Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg | Pamidronate 90 mg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete Response | N | Response Rate | N | Response Rate |
|
By Day 4
|
86 |
45.3% |
99 |
33.3% |
|
By Day 7
|
86 |
82.6% |
99 |
63.6% |
|
Duration of Response
|
N
|
Median Duration (Days)
|
N
|
Median Duration (Days)
|
|
Time to Relapse
|
86 |
30 |
99 |
17 |
|
Duration of Complete Response
|
76 |
32 |
69 |
18 |
14.2 Clinical Trials in Multiple Myeloma and Bone Metastases of Solid Tumors
| Patient Population | No. of Patients | Zoledronic Acid Injection Dose | Control | Median Duration (Planned Duration) Zoledronic Acid Injection 4 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple myeloma or metastatic breast cancer |
1,648 |
4 and 8 |
Pamidronate 90 mg Q3 to 4 weeks |
12 months (13 months) |
| Metastatic prostate cancer |
643 |
4 and 8 |
Placebo |
10.5 months (15 months) |
| Metastatic solid tumor other than breast or prostate cancer |
773 |
4 and 8 |
Placebo |
3.8 months (9 months) |
I. Analysis of Proportion of Patients with a SRE |
II. Analysis of Time to the First SRE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study |
Study Arm & Patient Number | Proportion | Difference |
P-value | Median (Days) | Hazard Ratio |
P-value |
|
Prostate Cancer
|
Zoledronic acid injection 4 mg (n=214) Placebo (n=208) |
33% 44% |
-11% (-20%, -1%) |
0.02 |
Not Reached 321 |
0.67 (0.49, 0.91) |
0.011 |
|
Solid
Tumors |
Zoledronic acid injection 4 mg (n=257) Placebo (n=250) |
38% 44% |
-7% (-15%, 2%) |
0.13 |
230 163 |
0.73 (0.55, 0.96) |
0.023 |
I. Analysis of Proportion of Patients with a SRE |
II. Analysis of Time to the First SRE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study |
Study Arm & Patient Number | Proportion | Difference |
P-value | Median (Days) | Hazard Ratio |
P-value |
|
Multiple Myeloma &
Breast Cancer |
Zoledronic acid injection 4 mg (n=561) Pamidronate (n=555) |
44% 46% |
-2% (-7.9%, 3.7%) |
0.46 |
373 363 |
0.92 (0.77, 1.09) |
0.32 |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patients should be instructed to tell their doctor if they have kidney problems before being given zoledronic acid injection.
- Patients should be informed of the importance of getting their blood tests (serum creatinine) during the course of their zoledronic acid injection therapy.
- Zoledronic acid injection should not be given if the patient is pregnant or plans to become pregnant, or if she is breast-feeding.
- Patients should be advised to have a dental examination prior to treatment with zoledronic acid injection and should avoid invasive dental procedures during treatment.
- Patients should be informed of the importance of good dental hygiene and routine dental care.
- Patients with multiple myeloma and bone metastasis of solid tumors should be advised to take an oral calcium supplement of 500 mg and a multiple vitamin containing 400 IU of Vitamin D daily.
- Patients should be advised to report any thigh, hip or groin pain. It is unknown whether the risk of atypical femur fracture continues after stopping therapy.
- Patients should be aware of the most common side effects including: anemia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, fatigue, fever, weakness, lower limb edema, anorexia, decreased weight, bone pain, myalgia, arthralgia, back pain, malignant neoplasm aggravated, headache, dizziness, insomnia, paresthesia, dyspnea, cough, and abdominal pain.
- There have been reports of bronchoconstriction in aspirin-sensitive patients receiving bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. Before being given zoledronic acid, patients should tell their doctor if they are aspirin-sensitive.
Caraco Pharmaceutical Laboratories, Ltd.
Sun Pharmaceutical Ind. Ltd.
PJPI0320
ISS. 12/2012
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - LABEL
NDC 47335-035-40
Zoledronic Acid Injection
4 mg/5mL (0.8 mg/mL)
Concentrate for Intravenous Infusion
Not for direct injection
Dose must be diluted.
Rx only
5 mL Sterile Single-Use Vial

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON
NDC 47335-035-40
Zoledronic Acid Injection
4 mg/5 mL (0.8 mg/mL)
Concentrate for Intravenous Infusion
Sterile Concentrate
Not for direct injection.
Dose must be diluted.
Do not mix with calcium-containing infusion solutions.
See package insert for Preparation of Solution.
Rx only
One 5 mL Single-Use Vial
SUN PHARMA
Zoledronic AcidZoledronic Acid INJECTION, SOLUTION, CONCENTRATE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||